Mechanisms of appearance
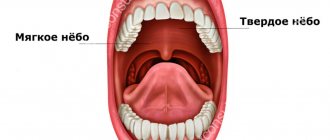
The appearance of redness in the oral cavity, namely on the palate, is provoked by several factors. Experts highlight the main ones of all existing ones.
Fungal
Oral candidiasis (thrush)
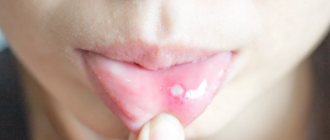
Among fungal infections, the leader is thrush , which develops against the background of disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, namely changes in the microflora. The oral mucosa becomes covered with a rash - small but densely spaced red spots.
Provoking factors are: antibiotics, decreased protective functions of the body. In this option, antibacterial agents are prescribed to improve the functioning of the digestive system.
The characteristic red spots (in children there is a whitish coating) become brown during treatment, after which they completely disappear.
Bacterial
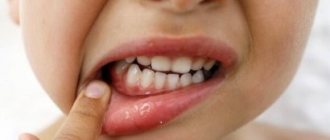
The presence of red spots in the mouth may indicate a bacterial infection, most often caused by streptococci. The development of bacteria is accompanied by changes in the soft tissue of the oral mucosa and skin. The lesions can be pinpoint or in the form of spots that merge with each other and form a single inflamed area.
Scarlet fever
The most common diseases of a bacterial nature are the following: tonsillitis, acute tonsillitis, scarlet fever, pharyngitis, etc. To eliminate the red rash, it is recommended to supplement drug treatment with topical antiseptic drugs.
Viral
One of the reasons for the formation of a red spot on the upper palate is a respiratory disease, which is characterized by the location of the infection in the oral cavity. In this case, not only the mucous membrane of the mouth is affected, but also the nose (rhinitis). A viral infection is recognized by the following signs:
- sore throat, dryness;
- discomfort when swallowing food;
- dry cough, worse in the morning or at night;
- muscle and headache.
Sometimes there is a sensation of a foreign body in the larynx. If the red spots do not have any plaque, then most likely the body has been infected by a simple virus. A whitish or other shade indicates the accumulation of pus. To make a diagnosis, you must make an appointment with a doctor.
The treatment process for a viral infection of the body does not require separate treatment of the rash; therapy is prescribed according to the standard regimen.
Allergic
Red spots on the palate can also be found due to allergies. Characteristic features:
- the location of the rash in the oral cavity is symmetrical;
- tiny dots (small pimples) in different places can merge, forming a larger spot;
- no burning, itching;
- red spots are also found on the skin;
- There are no other symptoms that worsen the person’s physical condition.
The first priority in dealing with stains is to identify the irritant and eliminate it.
Traumatic
Burns
This mechanism for the appearance of red spots on the mucous membrane is due to the influence of mechanical and physical factors. Mechanical impacts are those that irritate the soft tissues of the oral cavity over a long period of time or occur instantly.
In the first case, these may be dentures, sharp edges of teeth, or braces. The second option usually happens unexpectedly, for example, when the mucous membrane is bitten or damaged by a dental instrument. Physical effects include burns, electric shocks, and radiation exposure. Red spots are eliminated with special treatment, which is aimed at eliminating the consequences of injury, healing the wound and restoring the structure of the mucosa.
Vascular pathology
Spots or dots of red color due to pathological processes occurring in the vessels appear and disappear spontaneously and repeatedly .
In this case, only a comprehensive examination will help diagnose the problem.
What causes the appearance of rashes
- viruses that cause diseases of the upper respiratory tract;
- influenza virus;
- Epstein-Barr virus (causative agent of mononucleosis);
- adenovirus;
- enterovirus HSV - 1 (virus that causes herpetic sore throat).
If infected with any of these viruses, the ciliated epithelium lining the upper respiratory tract is affected.
Of the bacterial microorganisms that can cause the symptom of “red throat,” the most common is streptococcus A (GAS). This is practically the only bacterium that can infect the throat. This is what causes streptococcal sore throat.
- Encyclopedia of rashes - 2
If there are red spots on the sky - this is stomatitis
With stomatitis, the spots that appear on the palate are located separately from each other or merge to form islands. Their color can range from pale pink to bright red.
Experts distinguish several types of the disease:
- viral;
- herpetic;
- candida;
- aphthous;
- bacterial;
- traumatic.
In addition to redness, the disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- swelling of soft tissues;
- nervousness due to pain in the mouth;
- refusal to eat;
- in some cases, an increase in temperature.
Drug treatment involves the use of topical and oral drugs:
- Famciclovir – taken orally, daily dose – 1500 mg;
- Valacyclovir - take the drug 2 times a day, 2000 mg;
- Miramistin - used for rinsing the mouth 4 times a day, the duration of one treatment is at least 1 minute;
- Amiksin is a means to strengthen the immune system, prevents relapses, and is taken according to the schedule.
To enhance the effect of drug treatment, it is allowed to use rinsing compositions prepared according to traditional recipes:
- decoctions based on chamomile, calendula and other plants that have antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects;
- carrot juice diluted half with warm water;
- horseradish root juice mixed with an equal amount of water;
- white cabbage juice, diluted with a small amount of water;
- linden infusion (200 ml), mixed with soda (1/2 tsp).
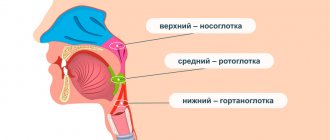
If it's a sore throat
The source of the disease is a virus, transmitted by airborne droplets. The spots in the mouth grow instantly, forming one continuous redness.
Symptoms:
- abdominal pain;
- a sharp increase in temperature, maintaining high levels for several days;
- redness of the oral mucosa;
- copious amounts of saliva;
- increase in lymph node parameters;
- muscle weakness;
- pain when swallowing;
- red spots on the palate turn into bubbles with cloudy liquid;
- Erosion remains at the site of the opening of the blisters.
The patient is prescribed 4-6 times of gargling with antiseptics, anti-inflammatory drugs, antipyretics and painkillers. Children under one year old, as well as patients with complications, are sent to the hospital.
During the treatment period, it is necessary to exclude aggressive foods and foods with a hard structure from the diet, so as not to provoke injury to the inflamed mucosa.
Traditional therapy can be supplemented with folk remedies:
- drinking teas based on rosehip, lemon, raspberry;
- gargling with decoctions (sage, chamomile, linden, onion peel);
- resorption of honey;
- rinsing the mouth with beet juice, saline solution, garlic infusion.
If it's tonsillitis
The disease occurs in an acute form, affects the palatine tonsils, and the causative agent is streptococcus. During the development of the disease, a large number of toxins and antigens are released, which destabilizes the functioning of the joints, heart muscle, and kidneys.
Characteristic symptoms:
- pain in the larynx, radiating to the neck and ears;
- increase in body temperature (slight);
- headache, brittle bones;
- tonsils become covered with plaque, the surface becomes loose;
- lymph nodes enlarge.
For drug treatment, antibiotics of the penicillin group (Augmentin, Amoxiclav) or macrolides (Sumamed, Azithromycin) are recommended. Local agents are also prescribed (Lugol's solution, antiseptics, antibacterial spray).
To increase the effectiveness of treatment, namely to eliminate red spots, traditional medicine recipes are also used:
- gargling solution made from warm water (200 ml), soda (tsp), salt (tsp), iodine (5 drops);
- decoctions and infusions of plants (calendula, raspberry leaves, peppermint, oak bark, wormwood, plantain leaves, etc.);
- teas from black currant, honey, linden blossom, rose hips, marshmallow, etc.;
- chewing propolis;
- warm compresses on the neck.
What other diseases can cause the appearance of red spots on the palate in children and adults?
If red spots appear on the palate of yourself or your child, be sure to consult a doctor.
A person can encounter the problem of redness of the palate only once during his life or periodically, which is due to the nature of the disease that has these symptoms. Relapses include herpes, thrush, and enterovirus infections.
Once the body has been affected, it is impossible to get rid of them. When conditions are favorable for viruses and bacteria, the disease worsens, so it is important to take preventive measures to suppress the pathogen.
The characteristic red rash in the mouth is one of the symptoms of other diseases.
- of tuberculosis is flat red spots on the oral mucosa. Over time, the reddish or red-yellow inclusions merge to form plaques. The surface of the formations is heterogeneous, the color becomes red-bloody.
- ARVI is recognized in particular by red spots on the soft palate and tongue. Associated symptoms are characteristic of acute respiratory diseases.
- Oncology, among a large number of signs, has one more, which is related to the oral mucosa. A small ulcer forms on the palate, increasing in size over time. However, at first it does not cause discomfort, there are no painful sensations. Reaching large volumes, the ulcer begins to interfere, and difficulty is experienced when swallowing.
- Vitamin deficiency is characterized by a deficiency of vitamins and minerals important for all body systems. Their deficiency weakens protective functions and increases vulnerability to bacteria, fungi, viruses and infections. Red spots with vitamin deficiency are located locally on the skin and mucous membranes, without spreading intensively to neighboring areas.
- Herpes is a viral infection that once it enters the body, does not disappear. The disease worsens against the background of weakened immunity. A characteristic sign: small red spots on the mucous membrane, increasing in size, transforming into small bubbles with liquid inside.
- Chickenpox is diagnosed mainly in children under 14 years of age, but this does not exclude the risk of infection in adults. Not only the skin, but also the mucous membranes are covered with spots. In the mouth you can first find small red dots, which turn into bubbles and very soon burst. This results in gray or yellow ulcers with redness around the circumference.
- Measles is characterized by a rash on the skin and mucous membranes, high fever, general physical weakness, and lack of appetite. The affected area even extends to the mucous membrane of the eyes. Initially, white spots form in the mouth behind the cheeks, and as it moves to other areas, the rash acquires a bright red tint.
- Infectious mononucleosis is recognized by its extensive affected area; spots cover not only the palate, but the entire oral mucosa. There is a soreness in the larynx, and the tonsils increase in size. Breathing becomes difficult due to nasal congestion. Characteristics of the spots: the color is bright, the parameters are impressive, they appear more often along the palate, and quickly spread to other areas.
- Scarlet fever is recognized by red spots that are localized on the soft palate. Other signs of the disease: headache, fever, nausea, pain when swallowing. The tongue becomes crimson in color, the mucous membrane is inflamed, and the rash on the skin is very itchy.
A similar mechanism for the appearance of spots in each individual case still has characteristic features and accompanying signs by which the diagnosis is made. But sometimes even the experience and colossal knowledge of a specialist do not make it possible to diagnose the problem without laboratory tests. Therefore, you should not postpone going to the clinic so that the situation does not get out of control.
Allergic spots
If the cause is an allergy, the doctor will prescribe antihistamines.
Red spots on the palate, which are not accompanied by symptoms of intoxication and a sharp drop in body temperature, may indicate an allergic reaction of the body. Among the main irritants that provoke changes in the color of the tissues of the oral mucosa are the following:
- taking medications;
- installation of a filling made of composite materials or a crown made of polymers;
- products;
- dental pins, prosthetic structures;
- products used for oral hygiene.
You should also not exclude typical allergens: animal hair, flowering plants, detergents based on chemical compounds used for household needs.
You can neutralize the effect of irritants with the help of antihistamines. They are selected individually, taking into account the type of allergen and the state of the immune system. Pharmacological agents that have an antihistamine effect are systemic and local. The success of treatment depends on the speed of elimination of the pathogen.
Red spots in the mouth during poisoning appear as a result of capillary paresis. The classic variant is a meningitis rash. It is recognized by the following sign: when pressed, the spots turn sharply pale, the color gains intensity as the impact weakens.
Allergic reaction as a cause of rash without fever
The pathological reaction of the immune system is the result of exposure to external factors. The causes of an allergic reaction may be:
- rinses, toothpastes of bright color, with a pungent odor and taste;
- low-quality filling material or dental structures - braces, veneers;
- certain foods: citrus fruits, honey, nuts;
- low quality plastic toys that a small child puts in his mouth.
The allergic reaction occurs without fever. Rashes are observed not only on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, but also on the skin. A typical symptom is severe itching of the skin.
Treatment includes antiallergic drugs; local dosage forms are prescribed only in severe cases. These can be hormonal ointments that reduce itching and reduce redness on the skin. The main task is to eliminate contact with the allergen and prevent its re-entry.
Rare diseases
Sometimes, behind red spots in the oral cavity lies the symptoms of rare, but quite dangerous diseases. The success of their treatment directly depends on early diagnosis and timely drug treatment, which minimizes the development of serious complications.
| Rare diseases | |
| Name | Description |
| Pyogenic granuloma | Dome-shaped erythematous nodular fragments form on the oral mucosa. Red spots often open and bleed, the process is accompanied by burning and pain. |
| Petechiae | An erythematous rash appears in the oral cavity, which occurs against the background of infectious mononucleosis. |
| Kaposi's sarcoma | It is characterized by the appearance of a non-inflammatory rash on the oral mucosa, provoked by the development of oncology. Later, the affected area spreads to the skin and lymph nodes. |
Often, red spots on the roof of the mouth signal simple problems; rare diseases are diagnosed in only 5% of cases. However, this is not a reason to postpone going to the clinic, because the insidiousness of such diseases lies in the intensive progression and development of complications, ending in suffocation against the background of swelling of the larynx.
Types and nature of rashes
There are many diseases that are accompanied by the appearance of a rash in the mouth. Important diagnostic factors are the structure, structure, appearance and location of the rash.
The following types of rashes may appear in the oral cavity:
- Bubbles are small structures in the cavity of which there is serous content of a liquid consistency. The most common cause of rashes of this nature is herpes.
- Pustules are structures that are filled with cloudy contents. As a result of the pathological process, purulent exudate accumulates inside them. Rashes of this nature can be both superficial and deep.
- Blisters are a type of rash that persists on the mucous membrane for several minutes or hours. Such lesions can be diagnosed in patients against the background of an allergic reaction.
- Nodules are structures that form under the superficial layers of the dermis and do not have a cavity. Due to the formation and growth of nodules, the tissue acquires a lumpy structure.
- The scales are a consequence of the process of keratinization of tissues located on the surface.
- Ulcerative rashes most often appear after damage to boils and pustules.
In some cases, a rash may appear in the form of red spots.
With a viral infection, the rashes are small in size, not associated together and are scattered along the back of the throat. With a bacterial infection, the rash looks like large red dots concentrated into small spots. In addition to them, a white coating and slight swelling may form on the tonsils and the back wall of the pharynx.
Allergic rashes are small, pink in color and scattered over the entire surface. In addition, the patient has severe swelling of the tongue.
Diagnostics
The success of any treatment process directly depends on the accuracy of diagnosing the problem. If you notice red spots on the roof of your mouth, you should consult a physician. You will also need to undergo an examination by a dentist and otolaryngologist. If there is a suspicion of an infectious disease, the specialist will refer you for a scraping to identify the pathogen.
Drug treatment involves taking antibiotics and antiviral drugs. Among other things, local treatment of the throat and oral mucosa is prescribed through regular rinsing procedures. Regardless of the disease, it would be appropriate to use a vitamin complex to strengthen the body’s protective properties.
The main aids in making a diagnosis are laboratory tests of blood and urine. Characteristic symptoms and test results indicate a particular problem.
Diagnostic methods
Rashes may indicate the presence of a pathology such as ordinary stomatitis or candidiasis. However, often such a symptom indicates dangerous diseases occurring in the human body. It is for this reason that when a rash appears on the palate, it is imperative to undergo a thorough diagnosis and not self-medicate.
The patient examination includes the following activities:
- General examination of the areas of the rash and examination of the medical history. In addition, the presence of any additional symptoms must be clarified.
- Laboratory research. Based on the results of a general blood test, you can find out the cause of the rash and make an accurate diagnosis. An increase in the number of leukocytes or erythrocyte sedimentation rate indicates an inflammatory process or an infectious disease. Against the background of an allergic reaction, an increase in the number of eosinophils is noted.
- Analysis of images of the contents of the rashes themselves. In fungal pathology, micelles of pathogenic fungi can be seen when examined under a microscope. Signs of cancer are the presence of atypical cells in the samples.
Based on the results of the studies, the doctor may prescribe additional tests for HIV infection or syphilis, as well as a thorough dermatological examination.
We recommend watching the video: