If you are reading the article, then you are interested in the stages of making a bridge. People have been doing dental prosthetics for decades. Today, revolutionary changes are taking place in this area. New discoveries help find solutions for patients with complex diagnoses.
For those who have no idea what a bridge is and what it is needed for, let us bring some clarity. A dental bridge is a non-removable structure that consists of artificial teeth. The main use of bridges is to restore multiple missing teeth. The support is provided by healthy teeth or implants.
Let's look at the advantages of the design:
- Completes the natural appearance from an aesthetic point of view, gives confidence;
- Preserve chewing function (a person may not deny himself when choosing foods and preparing his favorite dishes);
- Speech and diction are preserved;
- Average price tag;
- From a hygiene point of view, they are easy to care for.
Grinding healthy teeth to secure the structure is the only drawback. Because of this, there may be a risk of destruction of the natural teeth that serve as support. A team consisting of two people works with the patient: a dental technician and an orthopedic dentist.
What are bridges?
If several teeth in a row are severely damaged or missing, a bridge can be used to restore them.
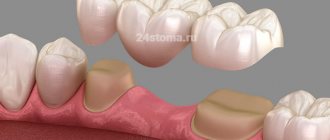
This is a non-removable orthopedic structure, which consists of several artificial teeth connected in a row. It is fixed on supporting teeth located on both sides of the destroyed ones, or on specially installed implants. A bridge is a permanent structure consisting of dental crowns connected into a single unit, which is used to replace missing teeth. Fixation of this prosthesis can be done both on teeth rotated under crowns (located on the sides of the dentition defect) and supported by dental implants. As for the length of bridges, they can range from 3 to 14 units (the number of crowns in the prosthesis).
Manufacturing and installation features
Replacing teeth with bridges is a complex, multi-step process during which the patient repeatedly visits the doctor. From the moment of the first request until the final installation, the following stages lie ahead:
- Initial consultation with determination of prosthetic tactics.
- Assessment of the general condition of the oral cavity with a thorough examination of the supporting teeth. In this case, an orthopantomography or CT scan of the jaw may be required. When inflammatory diseases of the mouth are detected, they are treated. If necessary, the patient undergoes professional teeth cleaning (plaque and tartar are removed).
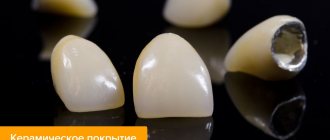
- The choice of material for prosthetics - much depends on the financial viability of the patient. In dentistry, the Dent Academy produces all types of bridges - from relatively cheap metal ones to quite expensive ceramic ones made of zirconium dioxide.
- When choosing a bridge prosthesis on implants, preliminary installation of implants is carried out (the process of their engraftment takes up to 6 months).
- To install dentures on inlays, crowns or half-crowns, the crowns are pre-treated with a drill. To install the pins, tooth depulpation is performed.
- An impression is then taken of the prepared jaw and sent to a dental laboratory.
- In the laboratory, based on the cast, a plaster model of the dentition is made, on which a frame is formed.
- The next step is to make the prosthesis itself, which is then installed on the model, where it is modified. When using CAD/CAM technology, virtually no modification is required.
- Fitting stage - at the patient’s next visit to the dentist, the resulting product is installed
Important! Any discomfort that occurs during fitting should be reported to a specialist - his task is to make the final adjustment of the prosthesis so that it does not cause any inconvenience to the person in the future.
- Final fixation - the prosthesis is finally fixed on the supporting teeth. The service life of a high-quality product can be calculated for many years!
For several days after installing the “new thing,” it is recommended to follow simple rules that will facilitate the process of adaptation to the presence of an artificial structure in the mouth:
- avoid hot and excessively cold foods;
- increase the chewing load on the denture gradually - this will allow the jaws to better “remember” the forgotten function of chewing;
- If there is pain in the gums, swelling, or severe discomfort, immediately consult a specialist;
- In the absence of any complications, a preventive examination by a specialist is recommended after a month.
Construction of bridges
The main parts of a bridge are artificial teeth (sometimes simulating part of the gum) and attachments in the form of dental crowns, inlays or clasps. In appearance, all this resembles a bridge, hence the name of the prosthesis. Bridges are used to replace 1 to 4 consecutive missing teeth, depending on their type. At the same time, there must be healthy teeth to the right and left of the dentition defect, which can become a support for the prosthesis and withstand additional chewing pressure, which can reach several tens of kilograms.
The intermediate part of the bridge may have different principles of connection with the mucous membrane:
- Flushing. When there is space between the mucous membrane and the bridge. The washable bridge allows food to pass freely under the structure, facilitating hygienic care.
- Tangent. When the denture body touches the mucous membrane on one side, this is important for the anterior part of the teeth, where it is important from a functional, linguistic and esthetic point of view. A bridge of this design is usually installed on the front teeth.
- Saddle-shaped. When the bridge is completely connected to the mucosa, the joint is connected to the joint. This is not the best option in terms of functionality and reliability, but there are cases when you cannot do without it, for example, in the area of the front teeth.
Content
- What is a dental bridge and metal ceramics?
- Flaws
- Advantages
- How does the installation work?
- Caring for metal-ceramic bridges
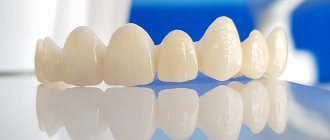
Bridges help solve the problem of missing one or more teeth in a row. The structures are made from different materials, have different strength and aesthetics and, accordingly, prices. A metal-ceramic bridge is the most common and inexpensive option, which is popular among patients.
Materials for the manufacture of bridges
Dental bridges are usually made from the following materials:
- Metal is a classic durable option and has been the only option for many years. It lasts a long time, easily adapts to different chewing loads, but it is too unsightly, so it is mainly placed only on the back teeth. It's the cheapest;
- Sintered metal is a more expensive option with better aesthetics. It is a metal frame with a ceramic coating that makes the structure white and similar to natural teeth. Still quite durable, although inferior in aesthetics to other options;
- All-ceramic dentures are very aesthetic prostheses, but they are expensive and fragile. Due to their lack of structure, they can create natural color and translucency of teeth, but cannot withstand heavy chewing loads. Recommended to be placed in the front of the jaw;
- Zirconium dioxide is a modern material, but at the same time extremely durable and aesthetic. Unfortunately, it is very expensive, but it lasts a long time and, as a result, is quite inexpensive.
- Combined designs: combine metal and metal-ceramics. They are placed if part of the teeth falls into the smile area, then they are covered with ceramics for better aesthetics, leaving metal teeth invisible to save money;
- Metal-plastic is an inexpensive option in which the metal is covered with white plastic to match the color of the teeth. It does not provide sufficient aesthetics and deteriorates quickly, so it is rarely used;
- Plastic is a material for temporary bridges that are installed before making permanent ones. Not suitable for regular wear due to its fragility and tendency to accumulate harmful bacteria.
The material is usually selected in accordance with the wishes and financial capabilities of the patient, as well as depending on the area of prosthetics.
Complications
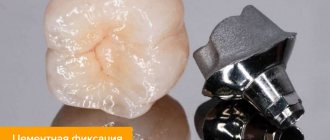
Due to temporary fixation, the following complications are possible:
- de-cementing;
- damage to the supporting structure;
- breakage of the orthopedic structure during removal;
- development of gingivitis or peri-implantitis due to insufficient removal of temporary cement from the gingival sulcus.
The most severe complication is peri-implantitis, in the event of which it is necessary to remove the structure as quickly as possible, remove excess cement and carry out anti-inflammatory measures.
Breakage of the prosthesis or supporting structures is possible due to too much retention force of the temporary cement. Most often, temporary crowns made of plastic or composite materials break. Correcting the situation is quite simple - the damage is glued together with plastic or composite right in the office.
When permanent structures are removed, the ceramic veneer often chips, which requires the manufacture of a new denture. Therefore, it is undesirable to fix ceramic or metal-ceramic prostheses with temporary cement. The least common cases in orthopedic dentistry are cases of breakage or fracture of the crown of a tooth and other damage to supporting structures. Also considered quite rare is the case of excessive load on the implant with the development of peri-implantitis.
Indications and contraindications for the installation of bridges
Direct indications for the installation of bridges are the absence of a chewing tooth or one to four front teeth with supporting teeth on either side of them that can withstand heavy loads. Dentures with a bridge have a number of relative and absolute contraindications. This includes:
- no more than 4 incisors, 2 premolars, 1 molar in a row;
- bruxism (involuntary grinding of teeth, the damage of which can be neutralized by wearing special mouthguards);
- bite pathology (in this case, orthodontic treatment will have to be carried out before prosthetics);
- periodontitis and severe periodontal disease;
- pathological abrasion of hard dental tissues;
- diseases of the bone tissue of the upper jaw (for example, osteoporosis, osteomyelitis);
- acute inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity;
- poor oral hygiene.
This may also include general contraindications to surgery itself: for example, problems with blood clotting, allergies to painkillers, acute chronic diseases, taking anticoagulants, mental illness and much more.
Recommendations for caring for dental bridges
In addition to the general rules of daily hygiene (cleaning with paste and brush at least twice a day - morning and evening, as well as every time after eating), additional requirements must be observed. So how do you clean dental bridges? In addition to the usual brushing with a soft toothbrush (each tooth separately, sweeping movements from the gum to the cutting edge), you must also use an irrigator, and if you don’t have one at hand, thoroughly rinse your mouth with water. The presence of a flushing hole between the central part of the dental bridge and the gum greatly facilitates the daily care of the denture. In addition, during professional oral hygiene, which, by the way, must be carried out at least twice a year, the hygienist should pay special attention to the bridge prosthesis - check for food debris and plaque accumulation at the junction of the prosthesis and gums, and also carefully polish artificial teeth and crowns on supporting teeth.
Stages of installing a dental bridge
- Examination and diagnosis.
This stage is very important. This allows you to eliminate any restrictions and determine the type of bridge the patient needs. The doctor will examine the entire mouth. He will direct you to a targeted x-ray if it is a specific tooth, or rather a CT scan (images that are more precise and less radial) to see the teeth in all projections. You may also need a panoramic x-ray to see the entire situation. These technologies are available at the Implantmaster clinic. Our specialists have the ability to model a new smile in 3D. This way, the patient will see the results that can be achieved. Additional tests may be prescribed. Based on the data obtained, a further treatment plan is formed.
- Preparing the oral cavity for prosthetics.
The design will last a long time if the patient does not have untreated teeth, gum inflammation, tartar and soft plaque. Preliminary treatment of caries and cleaning of the oral cavity is carried out, during which all dental deposits are qualitatively removed.
- Prepare your teeth before placing a bridge.
The selected teeth are ground under the holder and, if necessary, wiped down. Depulpation is a procedure for removing the neurovascular bundle from a tooth. Why is this necessary before installing a bridge? During tooth rotation, overheating of the pulp is possible, causing the development of pulpitis. In this regard, the pulp is sometimes pre-squeezed.
- Receiving a fingerprint (scanning).
In our clinic, ground down teeth are scanned instead of taking impressions. The 3Shape trios scanner scans everything in the mouth, individual teeth and bridge spaces. The workflow becomes more efficient and comfortable for patients. It makes it easy to take full-color 3D impressions for subsequent creation of prosthetics. When the bridge is ready, the patient is asked to try it on.
- Fitting
If during fitting no manufacturing inaccuracies are found: it fits tightly, fits well over the bite and the patient likes the appearance of the prosthesis, the bridge in the oral cavity is installed with special dental cement. After this, the doctor conducts a detailed consultation and gives recommendations on how to properly care for the oral cavity and the product.
What to do if the bridge falls out or a tooth hurts under the bridge
From time to time, crowns and bridges can fall out for one reason or another. Although in most cases people do not experience discomfort, when this occurs, a significant amount of
restorations can have a significant impact on the well-being and functioning of the mouth. The reasons why these abutments may fall out are usually due to new decay under or around the crown or bridge.
Even though crowns cover most of the tooth above the gum line, there is still some exposed surface around the edge of the crown. This means that food, bacteria, acids and cavity-causing microorganisms can become attached to the tooth. If it is not cleaned properly every day, new cavities are bound to form. These small cavities expand deeper, causing it to deteriorate to the point where there is nothing for the crown to attach to.
When a crown or bridge falls out, it is important to preserve the restoration.
You should take your crown or bridge with you in case it can be reattached in place.
The dentist will check the structure of the abutment tooth to see if the sound is sufficient to continue to support the restoration. If possible, the dentist will simply fix the crown or bridge in place (fixation of the bridge). If the supporting teeth are not stable enough, your dentist will likely recommend re-treating the area with a new restoration or suggesting a different type of tooth replacement. The doctor's consultation
Caring for bridges
When replacing teeth with bridges, dentists recommend the following measures:
- Daily hygiene morning and evening. You need to use a brush and paste. After each meal, rinse your mouth with clean water or mouthwash and use dental floss (floss).
- Hard-to-reach places and interdental spaces are cleaned with wide movements, without pressing on the crowns.
- It is important to exclude hard nuts, seeds and other foods that can cause chips and cracks.
- For the first time after installation, you should not drink coffee and tea, red wine, or freshly squeezed juice.
- At least once every six months, visit the dental clinic for preventive examinations and undergo professional cleaning.
- All structures have a certain duration. It depends on the material used and manufacturing technology. This period ranges from 5 to 15 years. Sooner or later the product will need to be replaced, otherwise it may simply break and fall off.
Ceramic dentures
Ceramic bridges can be classified as cast, as they are produced by casting ceramic mass into molds with further milling (turning). Zirconium dioxide prostheses are considered one of the most modern - they are maximally biocompatible and have excellent aesthetic properties. These advantages are overshadowed only by the high requirements for their manufacturing technology, but this problem is solved through the active use of computer technology. The color of the material is also selected on the computer.
The high accuracy of fitting of permanent ceramic bridges, including those made of zirconium dioxide, is due to the use of CAD/CAM technology - specialized computer software with a programmable manufacturing process. This technology is actively used in our clinic and has already proven itself to be very positive.
The advantage of ceramic bridges is that they can be used to replace defects that cannot be replaced by other prostheses. For example, 4 missing incisors or 2 small molars can be replaced with ceramic dentures. A relative disadvantage is their slightly lower strength compared to metal-ceramics.
This is interesting! Ceramic dentures are very resistant to all types of loads - static and dynamic, but they can crack from a strong point blow, so you should not click your teeth while trying to crack a nut or open a beer bottle.
Combined dentures
This group includes metal-plastic (metal with plastic lining) and metal-ceramic structures. For many years, the combination of plastic as a facing material and a metal frame has made it possible to carry out effective, visually beautiful prosthetics, especially for anterior teeth. However, with the advent of ceramics, the popularity of metal-plastic structures for dental prosthetics is waning.
The basis for a metal-ceramic bridge is a metal frame onto which ceramics are applied. The frame provides maximum rigidity and strength, and with the help of special processing of the ceramic part, the dentures are given an excellent appearance. At AcademyDent, preference is given to metal-ceramic bridges; the clinic’s specialists have all the necessary skills for their manufacture and installation.
What material to choose a bridge from?
Metal-ceramic bridges
The next stage of construction is metal-ceramic bridges. This type of “bridge” has made it possible to significantly expand the scope of application of bridges in solid castings by covering them with ceramics. The statement “cover them with ceramics” is not entirely true, since this design of the prosthesis implies not only an all-metal coating, but also a modification of the design, due to which the metal-ceramic bridge consists of a metal frame and a ceramic coating. This led to its advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages:
- Significant improvement in aesthetic performance compared to permanent bridges
- Expanding the scope of application, which implies the possibility of using such a design when restoring defects in the anterior group of teeth
- The almost complete correspondence of this type of prosthesis to the natural appearance of the teeth allows the patient to quickly psychologically adapt to them, which largely restores the level of quality of life.
Flaws:
- The absence of a chemical bond between the metal structure and the ceramic veneer suggests the possibility of the ceramic cracking
- The presence of metal in the oral cavity can cause allergic reactions, galvanic effects and negative effects of metal on dental tissue and staining.
The aesthetics of metal-ceramic prostheses is relative. Compared to solid bridges, the design of the prosthesis is much wider, however, the passage of metal through ceramic masses and designs with a “garland” do not allow comparing the aesthetic qualities of such a prosthesis with an all-ceramic one.
However, it is important to note that replacing the cobalt-chromium alloy more commonly used in metal frames with noble high-gold alloys provides superior aesthetics.
The natural color of gold, which shines through the ceramic masses, allows you to recreate the natural color of your teeth. Together with the advantages of metal-ceramic prostheses and the absence of the disadvantages of all-ceramic bridges, this design occupies a leading position in terms of aesthetics and functionality.
All-ceramic bridges
All-ceramic bridges have firmly established themselves as one of the most aesthetically pleasing and functional designs. This explains that manufacturing companies often improve methods for making just such prostheses. Computer modeling and milling are increasingly being introduced into everyday dental practice. The development of these technologies makes it possible to increasingly reduce the time required to build bridges, right down to visiting the dentist.
Methods of layering ceramic masses with restoration of the smallest dental structures make it possible to create prostheses that are as close as possible to natural teeth. Thanks to the strength characteristics of modern ceramic materials, metal-free bridges have excellent functional characteristics, but this also has a downside.
While metal-ceramic implants have a certain degree of flexibility, all-ceramic implants have a much lower elastic modulus. For this reason, loads that lead to chipping of ceramics in metal-ceramic structures can lead to rupture of metal-free “bridges” with the need for their complete replacement, and ceramic fragments can be repaired in a clinical setting.
And yet, despite this drawback, all-ceramic bridge designs are the most progressive and will be the vector for the development of materials and production technologies.
Adhesive bridges
An alternative to the work of a prosthodontist is increasingly offering adhesive bridges, which can also be made by appointment with a dentist, if he has sufficient skills. Adhesive bridges are made of composite materials using fiberglass tape, similar to the construction of a bridge, or using conventional orthodontic wire.
This combination allows dentures to be made directly in the patient’s mouth in one visit with minimal preparation of the supporting teeth, which significantly reduces the financial component of the problem.
However, the functional qualities of such prostheses are not always satisfactory, and the aesthetic qualities of composite materials often cannot compete with ceramic materials due to the impeccable polishing and natural shine of the latter. But with the correct choice of such a treatment method for the restoration of short-length defects in the dentition in the lateral areas extending beyond the aesthetic zone, in areas with less functional load, this design of bridge prostheses turns out to be extremely logical and convenient: the dentures have a long service life, providing patients with a beautiful appearance view.
General overview
Divergence and convergence of supporting elements are factors limiting the possibility of installing classic bridge-type prostheses. The problem is caused by the differentiated position of the units - it is impossible to eliminate the discrepancy through conventional preparation, since the volume of tissue requiring removal is too large and can lead to opening of the pulp chamber. Composite bridges are a model that includes a special joint, thanks to which the system can be placed even on units located at an angle to each other.
Metal is used as a material for the manufacture of such structures. The structure includes several elements:
- An intermediate occlusal pad located above the edentulous area;
- Fixation devices placed on support units;
- A connecting mechanism that combines structural elements into a system.