Causes How to fix?
How to increase the service life of a prosthesis Poor environment, poor nutrition, and polluted water lead to more and more people suffering from diseases of the teeth and oral cavity. In some cases, teeth cannot be saved. But the possibilities of modern prosthetics make it possible to restore your smile and self-confidence. Provided that the denture does not fly off. And this, unfortunately, happens.
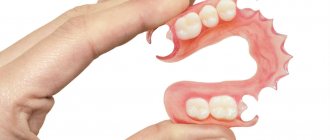
Depending on whether some teeth are preserved or completely lost, complete and partial removable dentures are installed. Complete dentures are supported by:
- Cohesion of wet surfaces - adhesion
- Relief of the oral cavity: tubercles, protruding parts and depressions (retention)
- Valve fixation. Due to the difference in pressure, a vacuum forms under the restoration, holding it in place.
What needs to be done to ensure that the dentures fit well and can be worn comfortably
Article navigation
- Why is it comfortable or uncomfortable to wear?
- - due to atrophy
- - due to poor quality manufacturing
- - due to breakdown
- If the bridge or crown becomes uncomfortable
- Solutions to the problem
- Preparation and diagnostics
- Correct manufacturing
- Fitting
- addictive
- Adjustment
- Fixation means
- When to repair and when to completely replace
- Alternative
Question for a specialist
Many clinics promise to supply comfortable removable dentures. But wearing them, as a rule, results in discomfort for patients. New artificial teeth can be uncomfortable initially – immediately after prosthetics. And they may become like this after some time. Fixed tooth replacement structures are very rarely uncomfortable. There are many reasons for discomfort, as well as ways to solve the problem. Today we will tell you how to get comfortable dentures and what you need to do to achieve this.
Solutions to the problem
There are many ways to restore lost stability, differing in the scale of intervention in the structure and tissues of the oral cavity, effectiveness and financial costs.
The choice of a specific method is determined taking into account the clinical situation, the patient’s preferences, and his availability of funds. It could be:
- adjustment or replacement of fixing elements;
- relocation;
- use of fixing creams;
- implantation;
- making a new prosthesis;
- other methods.
Sometimes, although rarely, it is possible to do without adjusting the prosthesis at all, limiting ourselves to teaching the patient how to use it correctly.
There are methods for properly biting and chewing food and controlling your masticatory muscles. By teaching them to the patient, you can solve the problem of fixation without resorting to relining or another method of correction.
Use of fixing agents
The use of fixation creams is considered by dentists as a temporary measure that allows them to use the device with relative comfort until it is repaired or replaced with a new one. A properly manufactured prosthesis should be securely fixed without gluing.
Fixing pastes have different adhesive strengths. Curing of adhesives occurs after their contact with oral fluid. The usual duration of fixing creams is 8-10 hours. That is, you need to apply the cream every day.
The standard technology for its use includes:
- applying the paste in a continuous or intermittent strip to the supporting surface of the base;
- placing the product in place and squeezing it with your teeth for a few seconds (according to the instructions);
- Remove the device in the evening, clean it and the gums from any remaining cream.
The advantages of fixing creams include the ability to temporarily stabilize almost any structure. The main disadvantage is the hassle of use and the need to clean the denture and gums of the cream every day.
Moreover, usually some part of the cream is swallowed, which leaves an unpleasant sensation. In addition, when eating hot food, some creams lose their adhesive strength and require reapplication.
Relocation
Relining is the operation of applying a layer of hardening polymer to the supporting surface of the prosthesis, which exactly repeats the configuration of the alveolar process. This ensures reliable fixation and proper distribution of the chewing load.
One of the objectives pursued by relining is the creation of a circular valve around the supporting surface of the base, ensuring “suction” of the structure to the mucous membrane.
Relocation is carried out in the following sequence.
- Removing a 1 mm thick layer from the supporting surface of the prosthesis, covering the artificial teeth with Vaseline to prevent self-polymerizing plastic from sticking to them.
- Mixing the polymer paste and applying it to the prepared base surface.
- Installing the product in place and closing the teeth. At the same time, the applied plastic copies the shape of the alveolar process, and its excess is squeezed out into the vestibular and oral area.
- After a pause necessary for the initial hardening of the material, the denture is removed from the mouth and placed in a polymerizer to gain final hardness.
- Removal of excess material, grinding.
After this, the product is ready for use. Its supporting surface exactly matches the configuration of the alveolar process.
The technology of clinical relining was described above. A laboratory technique is also used, in which a supporting layer of polymer is applied in the laboratory based on a previously taken impression.
Advantages of relocation:
- obtaining a supporting surface of the base that ideally matches the shape of the alveolar process;
- simplicity and manufacturability of the method.
Flaws:
- the need to get used to the prosthesis again;
- relative high cost (with laboratory relocation, the cost of the operation is comparable to the manufacture of a new product);
- the appearance of the structure may deteriorate due to differences in color and texture of the old and restored parts.
Types of fast-hardening plastics in dentistry and their areas of application.
In this publication, we will consider the designs of removable dentures for the upper jaw.
Here https://www.vash-dentist.ru/protezirovanie/semnyie-p/pochemu-voznikaet-stomatit.html read about the symptoms of denture stomatitis and methods of its treatment.
other methods
In addition to relining and using fixing creams, the following fixation methods are also used.
- Adjusting or replacing the locking mechanism. The simplest operation is tightening the clasps.
In some cases, it is possible to replace them with attachments of various designs, for example, a matrix-matrix system or telescopic crowns.Replacing a mechanism sometimes requires serious adjustments to the product and turning of the supporting tooth to install telescopic bushings.
- Installation of implants of various designs (regular intraosseous, taking on the function of additional supporting teeth, mini-implants, intramucosal structures).
- Magnetic fixation and some others.
The main disadvantage of the above methods is the relatively high cost of operations (with the exception of clasp correction). It makes sense to resort to them only if the product has not lasted long.
If its service life exceeds 3-5 years, it is more advisable to manufacture a new product.
Watch the video to see how the fixation of a denture is improved.
Why are orthopedic structures comfortable or uncomfortable to wear?
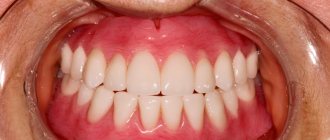
In order for fixed and removable dentures to be comfortable to wear, these structures must meet the following characteristics:
- fit tightly to the gums and teeth (if they are preserved in the row) - do not move or fall out,
- securely fixed on the gums and teeth (as well as on implants, if this type of prosthetics is used),
- did not disturb the bite and occlusion: i.e. so that all teeth fit together correctly when a person chews or talks, or even just remains silent,
- did not provoke allergies,
- did not have sharp edges or elements that would injure tissue in the mouth.
Why discomfort develops will be discussed below.
Due to bone atrophy
- When discomfort appears: months or years after prosthetics.
One of the most important factors influencing the comfort of wearing is the exact repetition of the anatomical features of the gums (prosthetic bed) and supporting teeth by the prosthesis. But even the initial tight fit of dentures, mostly removable ones, will be lost over time. Because in places where there are no tooth roots, there is no longer the usual chewing load on the bone. The bone tissue, and along with it the gums, decreases in size and sags (this is called “atrophy”). That is, the anatomical features change.
But the prosthesis remains what it was. Therefore, a gap appears between it and the gum, and the seal weakens. Accordingly, fixation is lost. The orthopedic structure begins to shift, rub when chewing and talking, and fall out of the mouth. But dentistry can offer patients help and modify the prosthesis to suit the changed “relief”.
Due to poor quality workmanship
- When discomfort appears: immediately after prosthetics or a short time after it.
Poor quality impressions taken before prosthetics or the production of irrational orthopedic structures lead to many problems. The denture base does not fit well, high or low crowns do not allow you to chew food normally, and the jaw joints begin to hurt or click. But at first after prosthetics, the patient and even the doctor can attribute everything to addiction. Indeed, it takes a long time to get used to massive dentures (up to 2 months), and chewing with them is unusual at first.
However, constant and very strong rubbing of the gums, poor jaw closure, constant or increasing pain, a feeling that the denture is “dangling” on the jaw or is squeezing it too much should alert you. In such a situation, you need to insist on a thorough diagnosis and identification of the causes of the problem.
Due to breakdown, poor maintenance or end of life
- When discomfort occurs: immediately after a breakdown or 2-5-10 years after prosthetics (when the life of the prosthesis has expired). Poor care reduces service life, discomfort due to this can occur at any time.
A crack or chip in an orthopedic structure, severe stretching of the base (as a rule, appears in nylon products), abrasion of the material in any area of the prosthesis. All these signs indicate that either the structure was incorrectly used by the patient or a breakdown occurred. Or, the prosthesis has already lost all its qualities and good fit due to poor care or too long wearing - longer than the declared service life.
Negative factors
Lack of stability even at the initial stage of wearing a prosthetic structure is usually a consequence of poor-quality adjustment of the base to the relief of the alveolar process. Achieving a complete match is quite difficult - the process requires long-term joint participation of the dentist and the patient. In addition to manual adjustments, the gingival structure also adapts to the foreign body, gradually rearranging itself to the shape of the base of the replacement system. As adaptation progresses, the connection density increases, which ultimately allows the patient not to pay attention to the installed prosthesis, and eliminates problems with diction or eating.
The body's habituation can be accelerated by constantly wearing the device in the first days after receiving it, including use at night, and despite any discomfort that may arise - with the exception of severe pain. The average duration of adaptation varies in the range of three to four weeks, after which the effect of the presence of a foreign element completely disappears. However, a successful outcome is by no means guaranteed - in some situations the body may continue to reject the product, or it may lose its tightness after several months of wearing.
Negative factors causing loss of stability of a removable denture include:
- Poor fit of the base to the alveolar surface, which is more common when restoring the mandibular region;
- Insufficient number of supporting elements of the dentition, which does not allow achieving tight fixation;
- Features of the anatomical structure of the jaw region associated with the location of the masticatory muscles, lips and hyoid frenulum;
- Incorrect choice of fastening method - clasps, attachments, pelots, screw and magnetic elements, as well as telescopic crowns covering support units can be used for fixation;
- Atrophic changes leading to a decrease in the volume of the alveolar process are one of the key problems associated with the features of removable prosthetics, which do not provide sufficient load on the bone tissue. Gradual resorption leads to deformation of the ridge, which necessitates a change in the configuration of the replacement structure;
- Excessive mobility of supporting elements caused by both pathological processes and prolonged wearing of the prosthesis;
- Dysfunction of the muscular structure of the oral cavity.
It is worth noting that in some cases, problems with fixation can also arise with installed bridge structures - usually due to the destruction of the cement structure that secures the artificial crown to the surface of the tooth - however, adjusting their position takes much less time.
What to do if a bridge or crown becomes uncomfortable
It is worth immediately noting that fixed orthopedic structures - crowns and bridges - cannot be modified. If they do not fit well, then either they were made incorrectly, or the bonding cement has broken down - there is still a chance to “save” the prosthesis, but not always. Another option is that the tooth under the crown has begun to decay. In all these cases, the crown or bridge wobbles and falls off. And the patient is prescribed new prosthetics.
Read on the topic: what to do if the dental bridge begins to loosen - useful recommendations for maintaining the beauty and health of your smile.
Next, we will talk about removable orthopedic structures - how to increase the fit and comfort of wearing.
Solutions to help get rid of the problem
The following methods will help you make comfortable dentures and achieve a tight fit to the gums:
- rational approach to diagnosis and preparation for prosthetics,
- correct production,
- teaching the patient how to handle new teeth,
- the patient follows all the dentist’s recommendations,
- regular visits to the doctor for relocation of the structure,
- the use of special adhesives,
- repair or new prosthetics,
- dental implantation.
All this is brief, but now let’s look at each point in more detail.
Reviews
Unfortunately, many removable devices, especially complete ones, have insufficient fixation, which causes great discomfort.
Some people deal with this by adapting to the situation - using fixing creams or even changing their lifestyle. Others, without delay, go to the doctor.
If you have had to adjust your dentures due to loss of stability, please share your experience with us. Leave a comment at the bottom of this page.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags dentures removable dentures
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
Review of the most popular Korean dental implants
Next article
What is the danger of blood oozing from under the crown of a tooth?
Preparation and full diagnostics before prosthetics
It is impossible to make comfortable dentures without a responsible approach to diagnostics before prosthetics and to the preparation of the oral cavity. In order for dentures - acrylic, nylon, clasp and others - to be comfortable, you need to undergo several studies. All of them will be useful for identifying contraindications, as well as for accurately modeling the prosthetic structure.
The first thing in diagnosis is an x-ray, panoramic image (OPTG) or CT (computed tomography) of the jaw. The second is taking impressions or impressions of the teeth. By the way, today you can make not ordinary impressions, but digital ones - using an intraoral scanner. The third is functional diagnostics, where bite parameters are assessed in dynamics, i.e. how the patient chews. This is one of the most important factors for making a prosthetic product comfortable. Otherwise, it can only be worn for beauty. Such diagnostics consists of assessing the work of the masticatory muscles, the movements of the jaw joints, and the closure of the jaws during movement.
Read on the topic: digital diagnostics before prosthetics - how modern devices help make comfortable dentures.
As part of the preparation, it is necessary to cure all identified dental diseases - eliminate caries, pulpitis, properly fill and strengthen the root canals. So that later the supports under the prosthesis do not fail, and it does not wobble, it fits tightly.
Complex on 4 OSSTEM implants with delayed loading - from RUB 170,000.
Complex implantation Osstem (South Korea) with delayed loading after 4-6 months.
Guarantee for the doctor’s work - unlimited Call now or order a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
Possible consequences
Long-term use of unstable prostheses is not without negative consequences for its owner - both mild and minor, and serious, threatening health:
- Physical and psychological discomfort due to the device falling out and moving when talking and chewing food.
- Rubbing of gums, injury (biting) of cheeks. Despite the seeming harmlessness of minor injuries to the oral mucosa, if there are permanent injuries, the matter can end in cancer.
- Slurred speech.
- Changes in facial expression when proportions are disturbed.
- Constant entry of food under the structure , poor chewing, leading to disruption of the digestive process and gastrointestinal diseases.
- Breakage of the structure due to accidental jumping out of place.
- The need to constantly monitor the position of the prosthesis and correct it, which is especially inconvenient in the presence of strangers.
What factors are taken into account when choosing abutment teeth and their number.
Come here to find out what requirements apply to denture bases.
At this address https://www.vash-dentist.ru/protezirovanie/semnyie-p/vospalenie-desnyi-pod.html we will discuss the tactics of treating gum inflammation under a denture.
Proper production of dentures
During the manufacturing process[1], it is important to follow all the nuances of the technological process (it is different for each material). If a mistake is made at any stage, then a defect may appear in the product, and the fit will not be tight. Chewing with such “teeth” is not only inconvenient, it is impossible.
Therefore, choose experienced orthopedic doctors. Also, priority should be given to clinics that either have their own dental laboratories or have entered into an agreement with a large modern laboratory.
How to manage without dentures?
Alas, you cannot do without prosthetics. The loss of even one tooth disrupts the harmony in the oral cavity. In place of a lost tooth, the skin becomes less elastic, the correct oval of the face is lost over time, and signs of aging appear. The load on the remaining teeth increases. The jaw bone becomes thinner and the gum structure changes.
After tooth extraction, less blood flows into this area of tissue, and the number of blood vessels in the area where the tooth is missing decreases. As a result, the structure of the jaw bone is disrupted. All these processes then lead to displacement of the dentition, to an incorrect bite. And this, in turn, affects the quality of chewing food and disrupts the digestion process.
Even a person’s speech is impaired. Due to the absence of individual teeth, it is impossible to pronounce some sounds correctly. Especially if the problem affects the front teeth. Moreover, the absence of the front row of teeth leads to changes in the nasolabial fold. It lengthens, the corners of the mouth droop, and the person begins to look older than his age.
Fitting, installation and training in use
How long does it take to install dentures? This depends on the type of orthopedic structure. On average, production takes 1-2 weeks if the clinic has its own laboratory. Third-party manufacturing will take the same amount of time, but add another 1-2 weeks for transporting the structure to the clinic for fitting. Do not skip fittings and tell the doctor about any inconveniences - this will ensure a tighter fit of the base to the prosthetic bed. Installing a finished prosthesis on a patient will take about 1 hour (this may include training on how to clean and wear it).
Precautionary measures
The service life of removable dentures depends on their type, operating conditions, and quality of manufacture. The service life of conventional acrylic devices is usually up to 5 years. Higher-quality clasp systems can last 10 years or more with proper operation, control and timely correction.
The durability of structures is also affected by the condition of the supporting teeth. It is necessary to monitor their stability. If they start to wobble, you need to see a dentist.
After completing all work with the prosthesis, the doctor gives written or oral recommendations on how to care for it.
It is recommended to store rubber products in water at night to prevent deformation. Designs made from modern materials (acrylic, nylon) do not need to be placed in a container with water overnight. You don't have to take them off at all while you sleep.
But, if a person wants to give his gums a rest, the denture is cleaned and placed in a case to prevent dust or accidental mechanical damage from getting on it.
If the removable structure is not used for a long time, it is recommended to place it in a container with a special antiseptic solution or boiled water.
Even if a product is in satisfactory condition after long-term use, there comes a time when it needs to be replaced with a new one. This requirement is associated, first of all, with a change in the shape of the prosthetic bed due to bone atrophy.
For the first time, adaptation of the base to the changed jaw can be done using relining. However, this is often not recommended, since multiple adjustments can lead to malocclusion, changes in the nature of movement of the lips, jaws and tongue, and facial expression.
In addition, over time, the properties of the polymer from which the base is made deteriorate. The material ages, microcracks appear on it, in which bacteria accumulate. Therefore, if the device has served its service life, it is advisable to replace it with a new one.
The frequency of visiting a doctor to monitor the condition of a removable denture should be at least once every 2 years. Fixed bridge structures require more frequent inspection - 2 times a year.
Habituation and home care
A properly completed adaptation period and regular care are the key to making wearing an artificial “jaw” more comfortable (although getting used to it is difficult). Let's figure out what's what. In the first days (a week or two), you need to sleep with the denture in your mouth - this way adaptation will happen faster. Normally, the feeling that it is in the way, pressing, or trying to fall out should gradually disappear.
Caring for the “removers” involves removing them after every meal or any snack in order to clean and rinse the structure. In the morning and evening, thorough cleaning is carried out using a brush and paste. Once or twice a week it should be soaked in an ultrasonic bath or in a container with a disinfectant solution. And every 6 months you should visit the dentist for professional cleaning of the structure and examination of the oral cavity. A set of care procedures will help protect the denture base from tartar buildup and preserve the properties of the material - for a tight fit of the structure to the gums.
Remember what foods should not be eaten with artificial teeth - these are hard and stretchy foods. It is their fault that breakages occur and the tightness of the seal to the gums and supporting teeth is disrupted.
Fracture of clasp (metal hook)
In the dental office, the doctor takes an impression of the patient’s mouth along with the prosthesis and sends it to the dental technician in the laboratory. A plaster model is cast along with the prosthesis. The technician removes the broken clasp from the inside of the denture and bends a new one along the supporting tooth. After polymerization of the plastic, it is applied first to the site of the sawn hook, then to the outside of the prosthesis. After a short period of time, excess plastic is removed with a cutter on an electric motor, and the repair area is processed and polished, if necessary.
Professional correction: relining, editing
Adjustment of a removable denture (relining, editing) is an adjustment of its dimensions to the changed anatomy of the prosthetic bed. Since bone atrophy does not stop when wearing such structures, and sometimes even intensifies, over time the base will not fit tightly, will begin to wobble and fall out. To increase comfort, the doctor can file down protruding areas or build up the acrylic base during the appointment - this is a clinical method. It is fast, but there is a higher risk of the patient becoming allergic to acrylic, and lower reliability.
Relocation of removable structures should be carried out according to indications. On average, every 3-6 months, depending on the rate of atrophy and the softness of the base material.
With the laboratory method, new impressions must be taken from the jaws and sent to the dental laboratory along with the prosthetic structure. The technician will modify the product in accordance with the new parameters so that it fits tightly to the atrophied areas. This method is optimal in terms of convenience and durability, plus the risk of allergies is much lower. But the adjustment will take more time - up to 5-7 days.
What to do if the denture rubs the gums?
If the prosthesis begins to rub the gums, pain and discomfort begin, you need to evaluate how intense this pain reaction is.
If these are minor pain sensations: it hurts a little, aches a little, tingles, then you can wait 2-3 days, using pharmacy ointments for pain.
If these sensations do not go away within 2-3 days, or the pain intensifies, then you need to go to the doctor who made this removable denture. The doctor will look at your jaw and in those places where the prosthesis presses too much, he will adjust it and sharpen it so that in this place the prosthesis does not press through the mucous membrane. There may be one or several such corrections, depending on the sensitivity of the patient’s mucosa. Over time, these corrections stretch from one to two to three weeks.
Fixation means
Almost all people who wear removable structures are familiar with fixation cream. Popular brands are Corega, Protefix, Fittydent, LACALUT, PresiDENT. There are also fixing pads and powders based on sodium alginate. All these products are applied to a cleaned, moistened denture, it is installed in place and glued to the gums.
Manufacturers claim that in this way, a poorly fitting structure will gain good fixation for 8-12 hours. But in practice and according to patient reviews, the action lasts only a couple of hours or even before the first meal.
“When they made an acrylic remover for me, I couldn’t use it without cream at all. Food got stuck under my gums, which was not pleasant. The clasps did not cling well to the teeth. Corrections at the dentist also did not help much. So I save myself with cream, although I still can’t chew something tough like shish kebab. And the cream has a specific taste, you need to get used to it.”
Evgeniy Nikolaevich, review from the dentistry.rf forum
An alternative solution is implantation.
Any model of removable denture is not able to stop the process of bone tissue atrophy, which inevitably follows tooth extraction. The only option that can protect against atrophy is dental implantation, which allows you to preserve the existing volume of bone tissue. Using this technique, you can restore not only the crowns, but also the roots of the teeth, as well as the full functioning of the jaw system.
Video review from a patient about lower jaw implantation after long-term wearing of a removable denture
When can you make a repair and when do you need a complete replacement?
The tightness of the fit may deteriorate due to the fact that the clasp (hook for fastening to the tooth) has come off or bent, the attachment has broken, another tooth has fallen out, or another tooth has been removed. In such a situation, you need to contact an orthopedic dentist to repair the structure.
But it is not always possible to glue an existing prosthesis with cream (it simply does not stick), repair or reline. For example, nylon stretches very quickly due to increased elasticity, and cannot be repaired. Repair will not help if the orthopedic structure is cracked in several places. Or it has completely lost its qualities and has served its entire service life. Another option is that all the teeth were removed, and the person had a partial orthopedic structure: clasp, acetal, Quattro Ti (“Quadrotti”), sandwich denture. Complete absence of teeth is a contraindication to wearing them. In all of these situations, a new product must be manufactured.
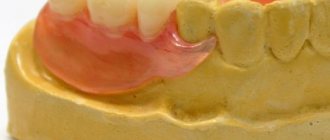
Types of partial dentures
Despite the fact that most removable dentures are very similar, experts divide them into several types. The main parameters are the number of teeth to be replaced and the material of manufacture.
Butterfly prosthesis
So named because of its shape, which resembles the wings of a butterfly. In most cases, a butterfly denture is installed when 1–2 teeth are missing in a row.
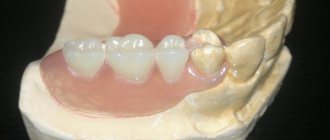
Partial removable clasp denture
A design that has an all-metal frame. Due to the metal arch, the clasp denture looks compact, but is less aesthetically pleasing than metal-free structures. In addition, metal can cause an allergic reaction.
Partial removable laminar denture
A removable lamellar prosthesis does not contain metal parts (fastening elements can be made of metal) and, in comparison with clasp structures, has a wider soft base.
Partial removable plastic denture
It is the cheapest design, which is often used as a temporary measure (for example, after implantation). A prosthesis made of acrylic plastic has the necessary rigidity, but is less comfortable than softer systems and can cause allergies.
Removable nylon partial dentures
Modern, comfortable and soft nylon prostheses, which, however, are significantly more expensive than plastic structures.
Dental implantation as an alternative
It often happens that a removable denture, after all the measures taken, is still uncomfortable, and a person cannot use it normally. But going without teeth is not the best solution, because... The quality of life is greatly reduced. There are several options here - either change the doctor/clinic, or think about implantation. Teeth on implants hold as firmly as your own, do not wobble, and are easy to get used to. It is even possible that an old acrylic prosthesis for the entire row (which the patient already wore) can be installed on implants using the All-on-4 or “All-on-4” method. But the design must be “no older than” 2 years and have no flaws.
[1]Fleece P.S. Technique for making removable dentures, 2008.
QUESTION ANSWER
QUESTION I have been wearing a removable jaw for about 2 years, and at the right time I go to the dentist to adjust the denture. But I still can’t chew properly with it, it quickly becomes loose and tries to jump out of my mouth. What can be done? Svetlana R.
ANSWER Hello, Svetlana. Poor fit occurs with all removable dentures. Because they do not stop the loss of jaw bone and gums. Because of this, a gap appears under the prosthesis and it is less secure. You may be atrophying too quickly for adjustments to last long. Or maybe the material of the prosthesis is too elastic and stretches quickly. What can you suggest to solve the problem? Undergo a thorough diagnosis - x-rays, taking dynamic parameters. You can try going to a larger clinic or another dentist. You can consider another type of prosthesis that will suit you better and has a more reliable degree of fixation. The doctor should suggest options after diagnosis. For example, instead of a clasp on clasps, choose a clasp on attachments. If you have completely missing teeth in a row, then all removable dentures will not attach very well. However, there is an option - to undergo implantation. Dentures on implants have the most reliable fastening, do not wobble, and you can chew any food with them.
Author: Chorny S.V. (Thank you for your help in writing the article and the information provided)
Repair, correction, relining of full-arch removable dentures
All inaccurately made full dentures can cause various lesions of the oral mucosa and inflammatory growth, so repairing, adjusting and relining dentures in such cases is very important.
Repair
A fracture of the prosthesis can occur either during its use or when it hits a hard surface. Thus, the key point of repair will be the exact matching and connection of the broken parts in the original position.
Median fractures
Causes
- Absence or insufficient relief in the midline
- Resorption of alveolar ridges
Procedure
The broken parts are matched and fixed with sticky wax on the polished surface
- The matching of parts can be strengthened using pins or plastic sticks
- Any undercuts on the contacting surfaces are isolated with wax or plaster
- Gypsum is poured onto the contacting surface. After the plaster has cured, the prosthesis is removed from the model and cleaned of wax residues.
- The edges of the fracture are excised, expanded by 8-10 mm along the fracture line and beveled towards the polished surface to expand the adhesion area
- For a more durable bond, dovetail cuts can be applied to the fracture line.
- The model is painted with the middle part demarcated, then the prosthesis is attached to the model using rubber clamps
- Self-curing resin is applied to the modified fracture line until all voids are filled. The area of the median palatal suture is unloaded.
- If necessary, make corrections
- Rework in some situations
Breakdowns in various parts
Main reasons
Hitting the ground or sink when cleaning
Types
- Floor without defects (repair as described above)
- Floor with part missing
Procedure
- An impression is taken when the prosthesis is inserted into the oral cavity.
- After casting the model, the defect is filled with wax or self-hardening plastic, restoring the lost part. This is followed by packing, replacement, curing, grinding and polishing.
Breakage with fracture or loss of teeth
- Broken teeth are cut with burs
- A sufficient amount of plastic is removed from the lingual side and dovetail cuts are made.
- Teeth of similar shape, size and shade are placed in the correct position and fixed with base wax
- A “key” is made from plaster to register and maintain the position of teeth
- Teeth to be repaired are removed with all surrounding wax
- Subsequently, the teeth are set according to the plaster “key”
- Self-hardening resin is applied from the lingual side until the defect area is completely filled. The surface is covered with thin foil
- After curing, the “key” is removed, the prosthesis is ground and polished
Correction of a complete removable denture
Prosthesis correction refers to manipulations that lead to greater tissue adaptation to the prosthesis by adding new material to the contacting surface without changing the occlusal relationship.
It is used in cases where the prosthesis loses good fixation or adaptation to the underlying tissues, while all other factors, such as occlusion, aesthetics, centric relation, and the basis of the prosthesis remain satisfactory.
- Loss of retention
- Instability
- Food under the denture
- Damaged mucosa
General terms
- Optimal condition of the underlying tissues
- Correctly installed lateral and central occlusion
- Adequate peripheral expansion
Procedure
The patient is forced not to wear the prosthesis for 48 hours to allow the mucous membrane to recover and reduce inflammation due to improper fit of the structure.
Prosthesis correction
- Any undercuts on the base are removed
- Side edges are checked and adjusted
- The edges are rounded and smoothed, and the space is also prepared for filling with new material.
- A hole is made on the palatal side so that excess impression material can come out through it.
- A new impression is taken in centric occlusion and correct occlusal relationship
- A plaster model is cast using the new impression.
- The denture is removed, the old base is carefully cleaned
- The new plastic is packaged and the prosthesis is cured in a setting with water at 45 degrees for 20 minutes. This mode prevents the porosity of the material and its deterioration (releasing internal stress)
- Manual grinding and polishing of the prosthesis is carried out
Relocation
This is the process of readapting the prosthesis to the underlying tissues by replacing the base without changing the occlusal relationship
Indications
When the existing base is of unsatisfactory quality, damaged or has pores
Procedure
- An impression is made using the existing prosthesis, then the model is cast
- Occlusal and incisal indices are established using a duplicator, areas duplicating the lower teeth are attached to the upper teeth to obtain an accurate jaw relationship
- The denture with impression material is removed from the model
- The artificial teeth are separated from the denture and all base material is removed (porcelain teeth are removed under high temperature)
- The teeth are placed and held in the correct position in the index model using adhesive wax on the labial and buccal surfaces
- A sheet of base wax is placed along the edge of the model
- The top of the duplicator closes and the artificial teeth are positioned in the correct position
- The model is deleted and cleared
- After cleaning, the model is attached to the top of the duplicator to check the occlusal relationship
- The occlusion of the relined prosthesis is subsequently corrected in the oral cavity
Author: Dr. Jaouadi Jamila