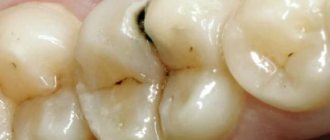
Although orthopedics as a science was formed not so long ago, people have been practicing dental prosthetics since ancient times. Animal bones, semi-precious stones, hard wood - everything that ancient doctors did not use as prosthetic material. But the methods of fastening were quite monotonous - using gold, less often silver, wire.
What are dentures made of now? The composition for prosthetics is selected for a specific clinical case, taking into account the patient’s wishes, indications and contraindications.
Content
- Composite
- Ceramics. Metal ceramics
- Ceramic dentures
- Metal alloys
- Plastic
Modern materials for prosthetics help facilitate this process. Today, dentures are high quality structures that are barely distinguishable from real teeth and are comfortable to wear. They are made from various materials.
Modern prostheses:
- High quality;
- Wearable, with a long service life;
- Aesthetic;
- Ensuring the full functioning of the dental system.
Each of the materials from which dentures are made has its own characteristics.
This group includes:
- Ceramics;
- Metal ceramics;
- Plastic;
- Composites;
- Metal alloys.
The choice of the optimal option is carried out taking into account many factors.
PROMOTION
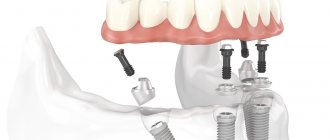
All-on-4 prosthetics turnkey!
120,000 rub.
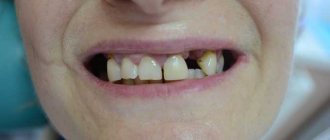
What are dentures?
These are unique structures used in dentistry that replace a person’s own teeth. They come in two types: removable and non-removable. The name “removable” speaks for itself: such dentures are removed from the mouth to clean and remove food debris. This is quite convenient, but at the same time, this property can also be considered a disadvantage, because for some, the need to clean the prosthesis every day can be tedious. Therefore, many people resort to permanent dentures. These include:
- Veneers are used mostly to correct aesthetic imperfections of teeth.
- Crowns placed on a tooth to prevent further decay.
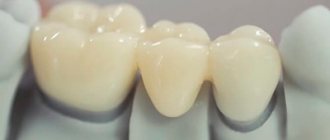
- Bridges are several interconnected crowns that are installed when two or more teeth are missing.
Teeth perform a number of very important tasks. In addition to the obvious chewing function, without which people would not be able to chew food as necessary for its normal digestion and smooth functioning of the digestive system, they perform an aesthetic function. A person feels much more confident in communicating with others, having healthy teeth and a beautiful, attractive smile. Therefore, if you have any problems with your teeth, you should not delay treatment. Properly selected dentures can help restore an attractive smile.
What should we do to find a prosthesis that would fully meet our requirements and be comfortable and safe? First of all, you need to know what materials quality products are made from.
Composite
The composite is durable and has a long service life. Its only drawback is the high price. But if you need a prosthesis for life, it makes sense to resolve the issue in favor of this composition. Composite is a polymer with many additives that provide exceptional strength and make artificial teeth look like real teeth.
Prosthetics are carried out according to the following algorithm:
- A polymer composition is applied to the prepared area in layers, giving it the shape of a lost tooth;
- Each layer is dried with a special lamp.
As a result of this build-up, the tooth becomes stronger and regains its lost shape. The doctor may use a pin to strengthen the structure. The pin is installed into the remains of the tooth or directly into the root canal.
Which prostheses are best to choose?
Dentists can cope with tasks of any complexity. The choice of prosthetic method, material, approach to treatment, its duration and other nuances are determined only by the doctor.
According to indications
The main condition for determining approaches to therapy is the patient’s clinical condition. A professional will, first of all, focus on these conditions.
By price and budget
The second most important criterion. In dentistry, one problem can be solved in several ways. From those presented, the client can choose the option that is suitable in terms of cost, time and other criteria. This indicator also depends on what the dentures are made of.
By service life
The quality of the components used directly affects the wearing comfort and durability of the products. This factor should be taken into account when choosing an affordable option. The criterion must be on the same level as the price determination.
With complete or partial edentia
This criterion applies to diagnostics according to indications. Because the different conditions of the oral cavity and gums determine the possible destinations. A complete absence of masticatory organs requires one approach, a partial absence requires another.
On the upper or lower jaw
Different anatomical functions make adjustments to dental procedures. The doctor must take this factor into account when selecting a variety of suitable solutions.
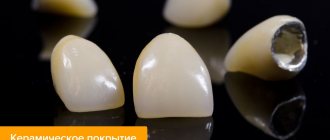
Ceramics. Metal ceramics
Ceramics for many years was considered the main material for prosthetics, despite the lack of high strength. This delicate material deteriorated over time, and prosthetics had to be started all over again. Modern ceramic and metal-ceramic prostheses have changed - they are reliable and strong.
The advantage of the material is lightness. Teeth made from it are almost not felt in the mouth. Aesthetic indicators are the best. Ceramics are used for both molars and front teeth.
When performed professionally, prosthetic structures are durable, their shade, translucency and shape are indistinguishable from natural teeth. The manufacturing process does not require much time and lengthy preparation. Treatment is carried out relatively quickly. Ceramics are suitable for patients prone to allergic reactions.
Main categories
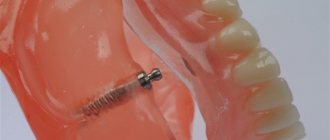
What is a denture? It is an artificial implant that replaces living bone. They are divided into the following types: removable, non-removable and partially removable. To choose the right one, it is necessary to diagnose dental damage and determine the method of treatment.
Only a dentist can prescribe certain actions (operations) in the oral cavity. Self-medication is more likely to only cause harm and cause the situation to worsen.
Filmed
Used after the loss of a large number of living teeth. The main feature of such prostheses is the ability to take them off and put them on yourself at home.
This type of prosthetics solves two problems:
- Restores a section of a row - an acrylic or nylon implant is fixed to living supporting teeth (important requirements for the constituent components: lightness and strength).
- Restores the bite in cases of complete edentia - small implants are installed in the oral cavity and serve as the basis for the movable part. Two years later, after the onset of alveolar atrophy, the entire chewing area needs to be replaced (discomfort or pain may appear).
Fixed type of dentures
- The metal-ceramic structure is expensive and durable, and in terms of aesthetic indicators it is 100% similar to the original, living units.
- The metal base is quite strong, but does not look so beautiful.
- Ceramics - looks expensive, loses in the long run.
- Zirconium dioxide is a modern component, enhanced with ceramic components (it is often used, but the human body can reject it).
- Plastic is fragile, short-lived (up to 5 years), used only for small loads, unstable color spoils aesthetics (advantage: low cost).
Fixed dentures evenly distribute pressure on the jaw, help preserve speech without defects, preserve beauty for a long time, and strengthen the resistance of the oral cavity to external damage.
The main disadvantage of this approach is expensive installation, possible painful sensations during operation, and exacerbation of allergic reactions. Before making such a choice, you should consult with a qualified dentist.
To learn everything about dental prosthetics, types and features, you can sign up for a consultation through the Dentika clinic website.
Conditionally removable
The patient can independently remove the jaw restored with such a prosthesis, or contact a dentist for these manipulations. The method is used where bridge orthopedics is powerless and there are contraindications to it.
The advantages include: ease of use, reliable fastenings, increased durability, beautiful aesthetics, elimination of any deformation.
The complexity of the installation of such systems, the high cost due to the addition of additional procedures, caring for the mechanism requires regular visits to the doctor, the clamps must be replaced every year - these are the disadvantages of this method.
Metal alloys
As a rule, it is a compound of chromium, nickel and cobalt. The advantage of such materials is their increased resistance to mechanical stress.
Disadvantage: high allergenicity. In patients prone to allergic manifestations, adverse reactions occur frequently.
The preferred material is an alloy of platinum, palladium and gold. The prosthesis from it will be:
- Expensive, but safe and durable.
- Be comfortable and give a feeling of naturalness;
- With a ceramic coating, it will completely match the appearance of natural teeth.
Titanium is a popular and most modern solution in prosthetics.
Titanium prostheses:
- Durable;
- Safe;
- Lungs.
The only drawback is the lack of full compliance with aesthetic requirements. Titanium crowns are placed on the far molars. Here they are not visible to others, but they perform their task flawlessly.
Zirconium oxide remains the traditional choice:
- Lasting;
- Stable;
- Biologically compatible and safe;
- Meeting high aesthetic requirements;
- The color matches the natural enamel of the teeth.
Thanks to laser processing, artificial teeth made of zirconium dioxide completely match the natural shape of the tooth being restored.
What is the best material for prosthetics?
As you can see, the choice of modern materials for dentures is quite large. It is impossible to say definitively which material is better, since each is suitable for a specific purpose. For installing crowns on the front teeth, the best materials for dentures are ceramics, and for molars, metal-ceramics or zirconium oxide are more suitable. A specialist will help you choose which denture material is right for you.
Another important question is what is the compatibility of dentures made of different materials with oral tissues? According to medical research, the most biocompatible bases for artificial teeth are ceramics and zirconium dioxide. Such crowns never cause allergies, this is another big advantage.
Correctly selected alloy for dental prosthetics
V. V. Nosov private dentist, Krasnodar
High-quality prosthetics are distinguished not only by a pronounced aesthetic effect. Along with such requirements as high strength and stability, the denture must optimally fit the patient and also be biocompatible with body tissues. The main criteria were and remain durability of the structure and complete restoration of function.
Which alloy to choose for the future prosthesis? An urgent issue in the context of declining patient solvency and growing competition. Alloys based on base metals are an acceptable alternative for patients who want to save money. They are popular among patients due to their high safety and good treatment prognosis. They are characterized by good biocompatibility with body tissues and do not corrode. A stable layer of chromium oxide provides additional reliable protection to the surface of the prosthesis. In my work, I have been successfully using the standard alloy from BEGO Wirobond C for many years (Fig. 1). The distinctive features of this alloy are increased mechanical stability and good tolerance by the body. Due to their low thermal conductivity and relatively light weight, clasp dentures made from the Wironium plus alloy (Fig. 2) are characterized by increased comfort for patients. However, in combined prosthetics, in the manufacture of telescopic crowns, as well as superstructures, preference is usually given to gold-containing alloys.
Rice. 1. Metal for ceramic cladding
Rice. 2. Metal for clasp dentures
Gold-containing alloys are suitable, among other things, for the manufacture of dental crowns, bridges and inlays (Fig. 3-5).
Rice. 3. Gold alloy frame with Minicon lock
Rice. 4. Frame made of gold-containing alloy with Minicon lock on the lingual side
Rice. 5. Frames for ceramic cladding, disassembled
On frames made of precious metal alloys, it is possible to apply layer-by-layer ceramics - a material whose structure best imitates the anatomy of a natural tooth. The high strength of the connection between the frame and the ceramics allows you to achieve the most pronounced natural effect.
Alloys based on noble metals have excellent mechanical properties, which has a positive effect on their processing. These benefits are especially noticeable when installing inlays or partial crowns made of gold. Their precise fixation on the tooth surface is carried out using a special polishing method. In this way, the dentist achieves a strong connection between the crown and the natural tooth prepared for the crown. Gold inlays not only have good technological properties, they are also distinguished by excellent biocompatibility with body tissues. With proper care, inlays can last a lifetime.
For demanding patients, gold is the most popular material for making a prosthesis frame. Pure gold is considered a soft metal and for this reason is not used for dentures. It is used in dentistry, usually in the form of an alloy with other metals. Such alloys regularly undergo strict quality control in accordance with international standards.
Using a clinical case as an example, we will demonstrate the restoration of function in the lateral part of the oral cavity when working with a face bow in an articulator.
The work always begins with plastering diagnostic models into an articulator for the orthopedic dentist to plan the future orthopedic design and draw up a financial treatment plan (Fig. 6). This is followed by an order to the dental laboratory to perform Wax-Up using the occlusal compass. Based on the wax modeling, teeth are prepared, impressions are taken and temporary crowns are made.
Rice. 6. Diagnostic models plastered in an articulator
The impressions and facebow fork are sent to the laboratory (Fig. 7). The dental technician makes high-precision models and plasteres the upper jaw model into the articulator using a facebow fork (Fig. 8). Using habitual occlusion recorders, a model of the lower jaw is plastered (Fig. 9). When re-modeling prepared teeth, the technician must copy the Wax-Up (Fig. 10).
Rice. 7. Impressions and Protar facebow fork
Rice. 8. Plastering the upper jaw model into the articulator
Rice. 9. Plastering the lower jaw model into the articulator
Rice. 10. Models with Wax-Up and Giroform system
When producing orthopedic structures, it is very important to create a competent occlusal surface; you need to have excellent knowledge and skills in wax modeling (Fig. 11-13).
Rice. 11. Modeling of 36, 37 teeth
Rice. 12. Modeling 46, 47 teeth
Rice. 13. Finalized contact points
Simultaneous casting of both jaws modeled from wax is not allowed; first, it is necessary to cast the dentures of one of the jaws, process, polish and fix them on the model using corrective silicone. It is important to imitate the fixation of dentures on the patient’s teeth using cement and only then add the lost contacts, then you can proceed to casting counter structures (Fig. 14-16).
Rice. 14. Cast crowns of 36, 37 teeth and wax modeling of 26, 27 teeth
Rice. 15. Cast onlays 46, 47 teeth and wax modeling 16, 17 teeth
Rice. 16. View from the lingual side
After casting, processing, polishing, and weighing of the metal follow. The dentures are delivered to the office with the occlusal surface treated with Perloblast (Bego) (Fig. 17-20).
Rice. 17. Finished crowns and onlays for the lower jaw
Rice. 18. Functional design of the chewing surface
Rice. 19. Ready-made crowns, inlays, onlays, veneers for the upper jaw
Rice. 20. Final weighing of metal
Thanks to their special, carefully selected composition, gold-containing alloys meet the highest requirements for alloys for prosthetics. They do not contain copper and palladium, and the content of gold and platinum is higher than in conventional alloys based on noble metals. Environmentally friendly alloys are especially suitable for patients with allergies to certain metals and for all those who care about their health.
Description of the main characteristics of alloys
Hardness as the property of a material to resist the penetration of an indenter—another solid body—into it. This parameter determines the occlusal wear resistance and how the dentist can process and polish the prosthesis.
The yield stress is the stress required to cause permanent plastic deformation in tension. The proof strength is the stress that occurs at a strain of 0.2%. This parameter characterizes the strength of the alloy more than others. This is what people pay attention to first when choosing the design of a prosthesis.
The elastic modulus is another important property that determines the flexibility of a metal frame. An alloy with a high modulus of elasticity bends less under load than an analogue with a low modulus.
Elongation is the ductility of a material, measured as a percentage. The lower this indicator, the more fragile the alloy will be.
The melting temperature range is an important parameter to prevent frame deformation when firing ceramics.
Biocompatibility means that the alloy material is safe for the tissues of the body and humans in general. Non-noble alloys have mixed biocompatibility and should be used with caution.
Manufacturability is the maximum precision in manufacturing and processing of the frame.
The coefficient of thermal linear expansion indicates the compatibility of the alloy with ceramics. The main condition is that the coefficients of the alloy and ceramics must match as much as possible, and there should be no residual stress left in the finished restoration.
How are they attached?
Several fixation methods are used for dentures.
On the closing valve. It is often called a “suction cup”; it is an element of the base, the basis of the structure, which in shape must exactly match the gum. When the denture is placed and bitten, air escapes from the gap between it and the mucous membrane. When completely sealed, a sealed space is formed, and the base is held as if on a suction cup. For more reliable fixation of a complete denture with a closing valve, special gels can be used.
On clasps. This fastening is used for conditionally removable, partial structures; they are mainly made of acrylic. Fixation is performed using metal hooks that are placed on the remaining teeth. Usually these are the incisors in the smile area, and therefore the clasps can be visible. Fixation is reliable, without the risk of displacement or accidental loss, the chewing load is distributed better than when using a locking valve.
On elastic clasps. They are used for structures made of nylon, made of plastic, pink in color, and invisible. Fastening is almost the same as when using metal hooks, but elastic clasps are more convenient, less damaging to the mucous membranes, and easier to get used to.
On attachments. These are composite micro-locks that can be used if the patient has preserved at least part of the dentition. One of the attachment elements is built into the base, the other is fixed to the supporting tooth and covered with a crown. The fixation is reliable, durable, the entire structure is protected from displacement, and transfers the chewing load well. Attachments are used with clasp dentures (having a metal base).