Stages of sedation Types When treating children Possible complications Indications Preparation for the procedure Contraindications Anesthesia Alternatives
There are few people in the world who are not afraid of a visit to the dentist. Against the backdrop of such a widespread phobia, calls are increasingly being made to undergo treatment under sedation, without pain. What is it and is this method as safe as they say?
Dental treatment under anesthesia in adults is carried out in rare cases, more often in hospitals. But sedation is more common. This method causes inhibition of the nervous system to reduce panic and stress during the procedure. There is contact with the doctor, the patient is able to respond to stimuli. With this method of anesthesia, the patient breathes on his own, all his reflexes are preserved. This is the main difference between sedation and anesthesia, in which the degree of inhibition reaches such a level that consciousness turns off, reflexes are not preserved, and the patient does not respond to physical and verbal stimuli. The main purpose of anesthesia is to put the patient into a state in which he does not feel anything.
The main goal of sedation is not to harm the patient’s health, so before the procedure it is necessary to do a full examination of the body and obtain a conclusion from a general practitioner and anesthesiologist.
Sedation will help:
- relax during an unpleasant or painful procedure;
- perform local anesthesia without tension and fear;
- provide comfort, moral and physical;
- create a calm environment for the dentist to work.
Stages of sedation
- Easy
. The patient is in a state of relaxation, but is awake and makes contact with the doctor. Although his reactions and coordination are slightly reduced. This type of sedation is also called superficial. - Average
. A state of consciousness in which patients respond to tactile stimuli, all functions are preserved, reflexes work, and there is interaction with the doctor. - Deep
. The patient reacts only to strong stimulation; the patient does not respond to a call, but the cardiovascular system works normally. Breathing may become irregular
The next stage is complete anesthesia. With it, there is no reaction even to strong painful stimuli. Respiratory support is often needed.
Modern anesthesia in dentistry: contraindications for use
The main contraindication to anesthesia in dentistry is an allergy to its components; side effects should also be taken into account, which are most often associated with the presence of additional substances in the anesthetic solution: vasoconstrictors, preservatives and stabilizers. In particular, it is necessary to especially carefully select drugs for patients with cardiovascular diseases, arterial hypertension, and decompensated forms of endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis, and others). To determine which substances a person has a negative reaction to, the doctor sends him to the Institute of Allergology to perform tests. In accordance with these data, a safe drug for local anesthesia is selected, and in case of reaction to all groups of anesthetics, general anesthesia is used.
Types of sedation in dentistry
There are quite a few ways to administer relaxing drugs, but only a few of them are used in dental clinics:
- Inhalation
. The most common mind control technique. The advantages of dental treatment under sedation through inhalation: quick effect, the process is easy to control, consciousness is restored in a very short period of time. The most common use is nitrous oxide. It has a relaxing effect, reduces motor activity and has some analgesic properties. Subject to the rules of supply and percentage of gases, there are practically no side effects. - Injection
. The drug is administered once, as an injection or gradually, through an intravenous infusion system. The most well-known drugs are profopol and medazolam. Their hypnotic effect allows dental treatment to be performed while you sleep, while maintaining basic reflexes and spontaneous breathing. Recently, dexmedetomidine has been increasingly used because it does not lower blood pressure. - Oral medication
. If the patient is afraid of the needle, but calmly takes the pills, they can be used. - Intranasal dispersion
. An anesthetic is sprayed into the nasal passages. So the drug, through the taste buds, immediately enters the brain. Quick effect, bioavailability, central action and ease of use make sprays very popular.
No longer than an hour
General anesthesia can be intravenous or inhalational. Its action is aimed at suppressing the patient’s reflexes so that the doctor can perform various manipulations, sometimes quite painful, during dental treatment.
— In any case, we start with inhalation anesthesia using a face mask.
When the child or adult falls asleep, we catheterize the vein and switch to intravenous anesthesia. We are working with a very good drug - propofol. But in some cases, when the treatment is planned to be short - 10 - 15 minutes, we can only use a nasal mask. There is another option that is sometimes offered to adults who are terrified of the dentist: sedation. Interestingly, this method is now widely advertised in private medical clinics, but this name means general anesthesia while the patient is asleep.
Meanwhile, sedation is the effect on the body of special relaxing drugs, such as dormicum, due to which the patient ceases to experience feelings of fear or panic, but is at the same time conscious. By the way, sedation does not relieve pain, so if necessary, the dentist performs additional local anesthesia.
A team of four people is with the patient during treatment, which includes an anesthesiologist, a nurse anesthetist, a dentist and a dental nurse. Both sedation and general anesthesia are observed for an additional two hours. In this case, even an adult should be accompanied by one of his relatives or friends, because his coordination of movements may be impaired for some time.
Sedation in pediatric dentistry
Up to 50% of children
[1] hide dental problems due to fear of treatment. This affects their quality of life and oral health both in childhood and when they grow up. Therefore, the use of mind control measures when providing dental care to children is justified, subject to strict adherence to rules and regulations. Most often, medicated sleep during dental treatment in children is achieved using nitrous oxide, but there are studies that have confirmed the effectiveness of the use of other medications. It is worth remembering that sedation should be used only when no other method of dental treatment for a child does not work. This will help avoid harmful consequences.
Anesthetics used for painless dental treatment
A good local anesthetic must satisfy a number of requirements:
- act quickly;
- have little toxicity;
- not absorbed into the systemic circulation;
- do not irritate the gums.
The selection of pain medication always occurs on an individual basis. The doctor takes into account the client’s age, his state of health, the treatment area, the threshold of pain sensitivity, and the characteristics of the existing disease.
More often than others, doctors use drugs containing articaine or mepivacaine.
Medicines based on articaine
Articaine is a local anesthetic belonging to the group of amides. It is characterized by a pronounced local anesthetic effect. Easily passes through the cell membrane into the nerve fiber. Blocks the conduction of nerve impulses along fibers.
Products containing this compound are used for uncomplicated removal of one or more molars, treatment of carious cavities, and grinding of crowns before prosthetics. It produces the medicine under the following trade names:
- "Ultracaine";
- "Ubistezin";
- "Septanest".
Painkillers containing mepivacaine
Mepivacaine is also an amide group anesthetic. It quickly passes through the lipid layer of the nerve cell membrane, is transformed into a cationic form and reacts with membrane sodium channel receptors. The latter are located at the endings of the nerves. Due to this, the conduction of impulses along nerve fibers temporarily becomes impossible.
Mepivacaine causes all types of local anesthesia:
- infiltration;
- terminal;
- conductor.
It acts very quickly and powerfully. Used for complex removal of radical units, during maxillofacial operations, tracheal intubation, esophagoscopy and bronchoscopy. Mepivacaine is used in the production of a medicine called Scandonest.
Don't put off dental treatment because you are afraid of dental pain. Today, doctors can carry out all manipulations with minimal discomfort for the patient, so there is no need to fear severe pain.
Consequences of sedation in dentistry
Specific problems with the use of mind control drugs depend on the route of administration and the mechanism of action of the drugs.
At the beginning of the procedure, you may experience increased activity, physical restlessness, talkativeness, and increased sociability.
A common symptom is an obsessive cough. This problem can be stopped by reducing the dose of the drug. Complications after sedation can appear both immediately and in a delayed period.
Possible short-term complications
- Breathing disorders (slow breathing, lack of oxygen);
- problems with hemodynamics (drop in blood pressure, irregular heart rhythm);
- depression of the central nervous system;
- intestinal dysfunction, vomiting.
Delayed symptoms
- Development of psychoses;
- hallucinatory syndrome;
- paralysis.
Is sedation dangerous? No, if it is carried out by an experienced doctor who has undergone special training, and the clinic is equipped with everything necessary to eliminate the consequences. But this is not a magic pill that can be prescribed to everyone without thinking about the consequences.
Indications
Dental sedation is indicated in a state of increased excitability, fear of treatment, but is not limited to this. This method must be used if there is:
- strongly expressed gag reflex;
- mental problems that exclude interaction with the patient;
- traumatic manipulations.
Like any medical intervention, mind control using medicinal methods requires careful preparation. The decision is made by the doctor taking into account all the data.
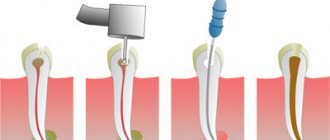
Application of local anesthesia for dental treatment
This type of anesthesia is most often used in pediatric dentistry, as it is performed without an injection. The doctor performs superficial anesthesia of a specific area of the mucosa using a gel or spray.
Since sensitivity in deeper tissues is preserved, local anesthesia is used only for certain dental procedures:
- removal of dental plaque;
- removal of teeth with high mobility;
- disinfection of the mucous membrane before introducing deeper anesthesia;
- pain relief after injection.
Contraindications to sedation
Like any medical procedure, depression of consciousness has contraindications. There are very few of them. The only absolute contraindication is myasthenia gravis (muscle weakness). The remaining states are relative. These are drug or alcohol intoxication, hypotension, a full stomach, a disorder of consciousness that prevents interaction with the patient, pregnancy, a condition after an acute heart attack/stroke. An opinion on the possibility of carrying out this procedure can only be issued by a general practitioner and an anesthesiologist.
The choice of method may also be limited. Thus, inhalation methods are contraindicated for sinusitis and other diseases of the upper respiratory tract. The doctor must know about all diseases in order to select the appropriate drug for a particular one in order to use medicinal sleep in dental treatment without consequences. That is why it is important to treat teeth in a clinic with modern technical facilities. Typically, such dentists employ experienced anesthesiologists and have equipment for first aid.
Why treat baby teeth?
Even a seemingly insignificant spot can cause the development of caries, pulpitis and spread to neighboring teeth. All this can provoke attacks of acute pain.
Pain and discomfort in the presence of dental pathologies lead to the fact that the child begins to avoid unpleasant sensations - chewing on only one side of the jaw. This can create an incorrect bite.
Diseases of primary teeth negatively affect the rudiments of molars. In this case, permanent teeth grow with defects and will need to be constantly treated.
Anesthesia in dentistry
There are medical terms that in ordinary life lose their meaning or acquire additional meaning. One example is the expression “to treat teeth under anesthesia.” In 99% of cases, this expression refers to ordinary sedation. Due to a common mistake, even dentists sometimes use the term “anesthesia,” although this means depression of consciousness with preservation of reflexes and responses.
Dental treatment under general anesthesia is performed extremely rarely. Its administration requires special equipment and conditions. Usually, this happens in a hospital, by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon, as a procedure accompanying the operation. During manipulation, constant monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and blood oxygen saturation is required.
General anesthesia during dental treatment means a complete shutdown of consciousness, including protective reflexes, which can be dangerous. The patient should not choose the method of pain relief himself; this can only be done by a doctor after a certain examination.
Dental treatment is painful. We destroy myths.
Since childhood, dental treatment has been associated with pain. And even at a more mature age, the thought will certainly itch in the background: what if it hurts? Or will the anesthesia not work?
Pavel Anatolyevich Pazhlakov, a dentist at the Dudko and Sons Dental Implant Center,
answered questions about the possibilities of pain relief in modern dentistry - Pavel Anatolyevich, could you outline what options for pain relief exist in modern dentistry? All methods are divided into local, general anesthesia and their combinations. Local means that it acts only on the area that actually needs to be anesthetized, that is, in our case, on the nerves that directly transmit the pain signal from the tooth. With general anesthesia (or anesthesia), a person falls asleep and does not feel anything. In dentistry, this option is in the vast majority of cases redundant. We always try to adhere to the golden rule: pain relief must be adequate and reasonable - that is, correspond to the specific clinical situation. In each case, you need to choose the most effective and, at the same time, safe method of pain relief. — How can you “turn off” the nerve that transmits the pain signal from the tooth?
For this purpose, local anesthetics are used, what is popularly called “freezing”. These substances block the transmission of signals along the nerve. How to deliver the anesthetic to the nerve? The two most popular options are the so-called infiltration and conduction anesthesia. In the first case, we simply inject the anesthetic into the tissue using a syringe - naturally, it reaches the peripheral nerve endings and blocks them. In the second, we inject the drug in the immediate vicinity of the nerve in the place where all the fibers conducting the signal from the desired area have already gathered into a single bundle. In any case, all the paths through which a message about pain can reach the brain are blocked - and the person does not feel anything. - But the injection itself is not very pleasant either. Some people are afraid of the injections themselves. For this case, there is topical anesthesia. Its essence is that an anesthetic, gel or spray, is applied to the area that needs to be numbed before anesthesia is administered with a syringe. Application anesthesia is not very effective in the sense that it only anesthetizes the superficial layers. But it allows you to “turn off” an area of skin so that the patient does not feel the injection. — Do local anesthesia have side effects? Some people are intolerant to local anesthetics. You may remember that when you go to the dentist, he always asks: “Have you had pain relief before?” This is done to see if the person has had a reaction to the local anesthesia. — If there was such a reaction, what to do? Treat teeth under anesthesia?
No, why so radical right away? Just use a different anesthetic; there are a lot of them available now. Sometimes, however, there are patients who cannot tolerate any local anesthetics at all - then yes, anesthesia or sedation. — It turns out that any patient can be given adequate pain relief? And is there a difference in pain relief for the upper and lower jaws? Yes. There are, of course, difficult cases, but the arsenal of methods is so wide that there is always something suitable. And if we consider the analgesic effect, then a 100% anesthetic effect is not always observed on the lower jaw because bone tissue is more dense. Because of this, it is less permeable to the anesthetic solution. In such cases, we increase the waiting time for the onset of anesthetic pain relief or increase the dose of the drug. - Thank you, Pavel Anatolyevich, after talking with you, it’s almost no longer scary to go to get your teeth treated. But I still really don’t want them to be drilled... And don’t! My advice to patients is to contact dentists before anything starts to hurt. You should try to go for a preventive examination at least twice a year in order to prevent complications that can cause a lot of problems. There is no need to be afraid to go to the dentist, he is not an inquisitor: if you are healthy, no one will try to make extra “holes” in your teeth. And if your teeth need to be treated, today it can be done absolutely painlessly. In order to visit a dentist , you need to: make an appointment by calling +375445450910 or go to the consultation page.
Fear of dentists - first person:
The article was prepared by a specialist: Pavel Anatolyevich Pazhlakov