- Characteristics of osteoplastic material in dentistry
- Classification of osteoplastic materials
- Necessary procedures before bone augmentation
- Type of osteoplasty
- Surgery with osteoplastic material at A-Medic
The use of bone material in dentistry is widespread. With its help, it is possible to perform osteoplasty - to restore the lost volume of the alveolar ridge. This allows you to avoid further destruction of bone tissue and the appearance of a number of negative consequences that arise against the background of changes in appearance and deterioration of human health. The procedure is often used before installing implants when the patient’s bone tissue is insufficient. Let's take a closer look at the specifics of the materials that make it possible to carry out these events.
Characteristics of osteoplastic material in dentistry
Osteoplastic materials in surgical dentistry must be of high quality and have the following characteristics:
- safety for human health (the use of artificial bone tissue that can harm the body is prohibited);
- high efficiency;
- porosity (ensures the germination of new bone tissue);
- full compatibility with the tissues into which the materials will be implanted;
- ridding the bone tissue of the defect by filling it.
Currently, there are many types of osteoplastic materials on the market. When choosing the most suitable material, all the above characteristics must be taken into account. In addition, it must be ready for immediate use and have high adhesion rates so that the implant can adhere to the bone as closely as possible.
How does the procedure work?
Before surgery, the patient must have a blood test and x-ray. If it is necessary to clarify in which area of the jaw the defect is localized and what its dimensions are, a computed tomography scan is performed. It allows you to determine the exact location of the damage.
The procedure is painless, thanks to local or general anesthesia (at the dentist’s discretion).
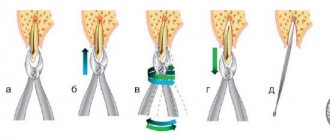
Implantation is carried out in three main stages:
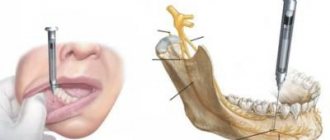
- The gum and periosteum are cut. Tissues are separated from the bone and moved away from the operation site;
- The defective cavity is filled with plastic material;
- Plastic surgery of the defective area is performed, after which the edges of the wound are sutured with special self-absorbable threads.
Sometimes after surgery, drainage is placed in the wound for a day. It ensures the outflow of blood and secretions from the wound.
Classification of osteoplastic materials
Osteoplastic materials are implants that promote bone formation. At the same time, they provide local osteoconductive, osteoinductive or osteogenic activity. According to their origin, all osteoplastic materials are divided into four main groups:
- autogenous (the patient is the donor);
- allogeneic (the donor is another person);
- xenogeneic (the donor is an animal);
- synthetic (made from calcium salts).
Let's take a closer look at the features of each group separately.
Autogenous
Autogenous bone replacement material is used more often than others in dentistry. Autologous bone is obtained by harvesting from a donor intraoral or extraoral site and then transplanting it into a receiving site. In a number of clinical studies, it has been proven that it promotes accelerated replacement of postoperative and other bone defects with newly formed tissue. It is characterized by plasticity and does not have the properties of immune incompatibility. At the same time, the financial costs associated with its fence are small.
According to their origin, two types are distinguished - endochondral (cartilaginous) and ectomesenchymal (membrane) origin. Disadvantages include the likelihood of infection, the traumatic nature of obtaining autologous material, and the long duration of the surgical intervention itself. Often, autologous bone is used in combination with other materials, for example, allobone or xenobone. This avoids shrinkage of the autologous bone.
Allogeneic
In accordance with the legislation, allogeneic bone material is not used for sinus lifting in the Russian Federation. Allogeneic implants are osteoplastic materials that are obtained from human corpses and subsequently subjected to special processing. This may be cortical and cancellous ilium or a demineralized lyophilized bone allograft. The main advantages of this group in comparison with automaterials include:
- pronounced osteoinductive potential;
- no trauma when obtaining the material;
- good adhesion to the recipient bed;
- short duration of surgical intervention;
- good micro- and macroporous structure (guarantees rapid angiogenesis).
In addition to ethical problems, the disadvantages of using these materials include the likelihood of possible infection of recipients with HIV infection and hepatitis.
Xenogeneic
In extremely rare cases, specialists resort to the use of xenogeneic bone material for implantation. It has osteoconductive properties and preserves the original mineral structure of the bone. Xenobone (natural hydroxyapatite) is obtained from mammalian bone tissue. The structure of animal bones is identical to human bones, which allows them to be used in dental practice. Xenobone is preliminarily subjected to special treatment and deantigenization. This allows you to eliminate from its composition all factors that provoke the development of an immunological and allergic reaction.
Depending on the type of processing, a distinction is made between xenomaterials with low-temperature processing, xenomaterials with high-temperature processing and xenomaterials based on enzyme technologies. There are two main methods of deantigenization. The most effective and popular is heat treatment at elevated temperatures (about 700-1000 C°), after which all organic substances evaporate. Xenobone does not shrink. Due to the synchronicity of the processes of bone destruction and restoration, physiological replacement of artificial bone granules with natural bone occurs, without loss of volume.
Synthetic
Synthetic bone material is made on the basis of calcium salts. In particularly complex clinical cases, when it is necessary to build up large volumes of bone in the horizontal or vertical direction, xenogeneic bone tissue is combined with autogenous bone in equal proportions. Synthetics are a worthy alternative to auto-, allo- and xenomaterials. In some respects, they are superior to osteoplastic materials of natural origin (for example, there is no need to harvest bone tissue, and the possibility of infection with infectious pathologies is excluded).
The main disadvantage of most synthetic materials in comparison with auto-, allo- and xenomaterials is the lack of osteoinductive properties (the ability to cause ectopic bone tissue formation). If components are added to their composition that will stimulate bone tissue regeneration (for example, collagen), they can acquire osteoinductive properties.
Selection of materials for plastic surgery: why bone chips are needed
Bone shavings are used in various types of plastic surgery. First of all, this is a bone block transplant, which is needed if the scale of resorption is large and it has developed in width and height. The graft is compacted with shavings before covering with a membrane so that it takes root better. The procedure for taking it from the patient himself is much less traumatic than removing the block, and granules are used instead if the scale of the problem allows it.
Material obtained from cattle bones is used for directed regeneration. The original transplant must be thoroughly crushed, sterilized, and washed with acid so that there are no viable cells in the freeze-dried shavings. In this case, the chance of successful engraftment is also quite high. However, not as much as when using an autograft.
Despite the wide use of shavings from animal or donor bones, our own material has a significant advantage - it contains viable cells identical to the patient’s tissues, which help grow the jaw bone after surgery. The harvest of your own graft is carried out, even if the surgeon works with osteoplastic materials to mix with them or fill the cavity around the implanted block.
Necessary procedures before bone augmentation
Once a molar or premolar is removed, the bone is no longer subject to regular stress, which over time causes it to atrophy and lose volume. Along with this, inflammatory processes appear in periodontal tissue. As a result, the more days that pass after the loss of a molar or premolar, the more the bone begins to become deficient. Against this background, it becomes much more difficult to carry out implantation.
The technique used to increase bone tissue volume is selected individually in each clinical case. To do this, the dentist first evaluates the oral cavity and, if necessary, prescribes instrumental diagnostics. It often happens that the need to use another technique arises only during the period of surgical intervention. Due to this, the specialist must be aware of all types of osteoplasty and be able to apply them in practice.
Rehabilitation period
After surgery, the doctor can prescribe the patient a course of antibiotics for 7-10 days, if necessary.
For 2-2.5 weeks, the patient is recommended to exclude solid foods, cold and hot dishes from the diet. Do not chew on the treated part of the jaw.
It is also recommended to contact your dentist if you experience the following symptoms:
- increased temperature (especially if it lasts more than a day);
- increased swelling;
- the occurrence of pain;
- change in the color of the discharge (they have an unusual shade, a sharp unpleasant odor appears).
Implants are installed six months after the procedure. Before implantation, a repeated examination is performed and, if there are no contraindications, the implant is implanted.
Type of osteoplasty
Below are the main types of osteoplasty to understand for which surgical interventions a specific type of material is used:
- autotransplantation. This is a procedure that involves moving a tooth from one place to another in order to fill a visually and functionally significant defect. Eighth molars (wisdom teeth) are most often transplanted. As a result of the operation, the bone tissue becomes significantly wider;
- sinus lift. This is a surgical intervention that is performed on the upper jaw in order to increase the length of bone tissue in case of its deficiency.
It is possible to increase the volume of bone tissue through the use of materials of synthetic origin. Barrier membranes are used to fix transplanted bone tissue or to protect a person’s bone tissue after a molar or premolar has been removed. Allografts are used to restore bone tissue. The most common are autografts.
Osteoplasty – what is it and why is it needed?
When introducing a titanium root, it is very important that it is surrounded on all sides by bone. If there is a deficiency of tissue, the titanium pin will be rejected. Moreover, if the root is installed in the upper jaw, there is a risk of touching the maxillary sinuses, which can lead to serious ENT diseases. Also, if there is insufficient bone, the implant will become loose and sink below the gum, which will affect the aesthetics of the prosthesis and the overall picture.
Osteoplasty is recommended in the following cases:
- if it is necessary to install a root in an area where a tooth was removed several years (or months) ago;
- if the patient has anatomically large maxillary sinuses;
- when physiologically a person has a minimum volume of hard tissue.
The operation is not performed if:
- the patient has chronic ENT diseases (sinusitis, sinusitis, rhinitis);
- lack of calcium in the body;
- there are pathologies in the structure of the respiratory system;
- oncology;
- polyps and other formations in the nose;
- diabetes.
Also, osteoplasty is not performed on pregnant and lactating women. Otherwise, the operation is done relatively quickly and with a guarantee.
In many cases, patients are recommended to take a course of hormonal medications and antibiotics before surgery in order to neutralize edema and possible inflammation.
Surgery with osteoplastic material at A-Medic
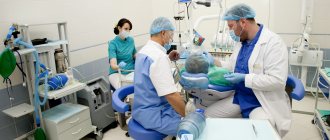
Osteoplastic operations are recognized as one of the most difficult (from a technical point of view) in the field of dental surgery. To avoid a number of negative consequences after surgery, they should be performed only in trusted clinics. Highly qualified dental specialists at A-Medic have been specializing in these operations for many years. The clinic is equipped with modern instruments, modernized equipment and the necessary lighting, which guarantees a positive result of therapy.
Doctors perform high-quality surgical interventions of any complexity using various osteoplastic materials. The cost of the procedure is significantly lower than in other private clinics in Moscow. You can find out more about the price list on the official website. To make an initial appointment with a dentist, just call the clinic at the numbers provided or leave a request online (indicating your name and contact number).
How is plastic surgery performed using bone chips?
The surgical intervention, depending on the technology, lasts up to two hours and is performed under local anesthesia or, in difficult cases, under general anesthesia. Before the operation, the patient is examined and within a few days he begins to prepare - he takes better care of the oral cavity, rinses with chlorhexidine, and cleans dental plaque.
During the intervention:
- part of the gum in the desired area is incised and peeled off to gain access to the bone;
- form a place for installing the material - create a cavity using a membrane to fill it with bone chips;
- the material is inserted into place, immersed in the fabric and the remaining cavity is filled with “natural” shavings (or artificial material);
- the place is covered with a reinforcing membrane barrier or a film on a titanium mesh so that there is no pressure on the new bone from the gums;
- the gum is sutured - the sutures from the soft tissues are removed, as a rule, after 7-8 days.
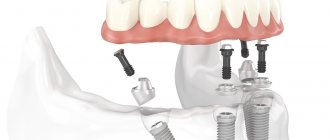
If the surgeon splits the alveolar processes by sawing them along the ridge, the hole into which the implants are screwed is filled with shavings around the rod. It is then covered with a membrane, and the gum flap is sutured. If the implant cannot be fixed immediately, the artificial root is fixed in the bone, but covered with gum and carefully protected from pressure. During the rehabilitation period, the installed material must take root, and your own tissue must “grow” around it.
What is bone grafting during dental implantation?
Dental implantation is an operation to insert an implant into the bone tissue of the patient’s jaw.
The success of this surgical intervention depends entirely on the reliability of the osseointegration of the artificial root. The main condition for obtaining a positive result is sufficient bone density and volume. But, for various reasons, quite often patients exhibit a deficiency of these parameters. Modern dentistry has effective methods for eliminating this defect. This is bone grafting, the purpose of which is to compensate for bone deficiency. Causes of loss (resorption) of jaw bone tissue:
- tooth loss;
- injury;
- dental and periodontal diseases.
Bone grafting during implantation (osteoplasty, augmentation) is a surgical operation to replant osteoplastic materials in the area where the implant is installed when bone deficiency is detected there. Such manipulations have been carried out since 1965, so they have been quite well studied and have received recognition from implantologists around the world. Osteoplasty is an extremely popular procedure for implantation. This is due to the fact that atrophy of the bone structure occurs rapidly. For example, after tooth extraction, the width of the alveolar process in this area decreases to 40% per year. Carrying out augmentation requires great skill and precision from the surgeon.
Please note: the network of “Smile” clinics employs highly qualified surgeons, and the branches are equipped with modern diagnostic and dental equipment. Our specialists successfully perform operations of any complexity.
Contraindications
- HIV AIDS
- Oncology
- Diabetes
- Severe pathologies of the heart and blood vessels
- Poor blood clotting
- Osteomyelitis
- Epilepsy
- Allergy to anesthetics
- Diseases of the ENT organs
- Alcoholism and drug addiction
- Pregnancy
- Dental and periodontal diseases
- Infectious diseases