Restoring the jaw, increasing aesthetic appeal, and replacing damaged areas of the masticatory organs is usually performed by a qualified doctor. However, to make the right decisions, the patient must know: what materials, types of prosthetics and designs exist for removable and permanent dentures in dentistry.
You should know that you need to visit the doctor twice a year, and not when everything in your mouth starts to hurt. Pain is a direct sign that caries is developing with other complicating diseases, chips, cracks and other damage appear that require immediate intervention. Timely prevention prevents bacterial development, allows you to find the problem at an early stage, and prevent large-scale destruction. Everyone should understand: neglecting the advice provided leads to the development of big problems.
Main categories
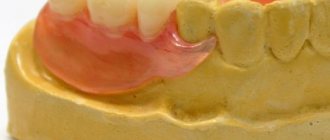
What is a denture? It is an artificial implant that replaces living bone. They are divided into the following types: removable, non-removable and partially removable. To choose the right one, it is necessary to diagnose dental damage and determine the method of treatment.
Only a dentist can prescribe certain actions (operations) in the oral cavity. Self-medication is more likely to only cause harm and cause the situation to worsen.
Filmed
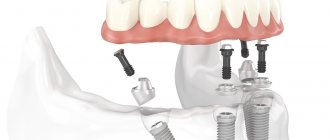
Used after the loss of a large number of living teeth. The main feature of such prostheses is the ability to take them off and put them on yourself at home.
This type of prosthetics solves two problems:
- Restores a section of a row - an acrylic or nylon implant is fixed to living supporting teeth (important requirements for the constituent components: lightness and strength).
- Restores the bite in cases of complete edentia - small implants are installed in the oral cavity and serve as the basis for the movable part. Two years later, after the onset of alveolar atrophy, the entire chewing area needs to be replaced (discomfort or pain may appear).
Fixed type of dentures
- The metal-ceramic structure is expensive and durable, and in terms of aesthetic indicators it is 100% similar to the original, living units.
- The metal base is quite strong, but does not look so beautiful.
- Ceramics - looks expensive, loses in the long run.
- Zirconium dioxide is a modern component, enhanced with ceramic components (it is often used, but the human body can reject it).
- Plastic is fragile, short-lived (up to 5 years), used only for small loads, unstable color spoils aesthetics (advantage: low cost).
Fixed dentures evenly distribute pressure on the jaw, help preserve speech without defects, preserve beauty for a long time, and strengthen the resistance of the oral cavity to external damage.
The main disadvantage of this approach is expensive installation, possible painful sensations during operation, and exacerbation of allergic reactions. Before making such a choice, you should consult with a qualified dentist.
To learn everything about dental prosthetics, types and features, you can sign up for a consultation through the Dentika clinic website.
Conditionally removable
The patient can independently remove the jaw restored with such a prosthesis, or contact a dentist for these manipulations. The method is used where bridge orthopedics is powerless and there are contraindications to it.
The advantages include: ease of use, reliable fastenings, increased durability, beautiful aesthetics, elimination of any deformation.
The complexity of the installation of such systems, the high cost due to the addition of additional procedures, caring for the mechanism requires regular visits to the doctor, the clamps must be replaced every year - these are the disadvantages of this method.
Types of implants
Classification by type of use is not the only thing that needs to be taken into account when carrying out such work. Quality and durability depend on the materials for removable and permanent dentures.
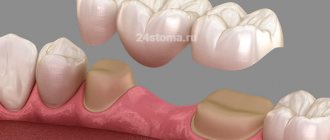
Bridge-like
The complex system is attached to supporting (undamaged) elements. It consists of clasps with special tabs onto which artificial implants are fixed.
Bridges are divided into separate groups according to their components: plastic, metal-ceramics, ceramics, metal. The last three materials should be highlighted due to their beauty, good strength and durability.
In the absence of contraindications, the inner part of the root is made of zirconium dioxide. Durable, resistant to the aggressive environment of the oral cavity, the material completely imitates enamel.
Only a dentist can determine the advisability of using this approach, based on individual components: tolerance to various substances and characteristics of the jaw, including the strength and shape of the bite.
On implants
Metal connects living tissues with a future artificial organ. Available only in non-removable versions. The rods serve as a reliable fastening for installation.
Capital, with a neat appearance, anti-allergenic, durable - implants are inferior only in cost, rehabilitation process and contraindications (for example, weak gums).
Butterfly dentures
A complex design that requires a careful approach to insertion and operation. It got its name because of its resemblance to an insect, and is used only for fragmentary restoration. It is attached to adjacent teeth, so it cannot be used if they are completely or partially lost.
Simple and cheap to install, they have a short service life and cause some discomfort to their owner.
Coronal
Preserve the root while restoring the outside. The solution allows you to extend the life of your natural teeth and has the following advantages:
- Complete resemblance to a real chisel (impossible to distinguish).
- Effective where fillings and extensions do not work.
- Uniform load distribution helps to preserve adjacent elements.
- A bridge allows you to simultaneously restore your bite.
- There are virtually no side effects.
Any damage to the root prohibits the use of a crown. Turning an entire part is a complex job that must be carried out by a qualified specialist.
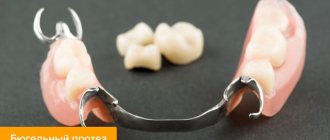
Clasp
Stainless steel (nichrome) is used to make the frame. According to the principle of treatment and application, it is completely similar to plastic options.
The system is attached to the supporting parts using locks. Implants can be used, which allows the use of clasps in case of complete loss of teeth. It preserves taste buds, and the prosthesis is very reliable thanks to the locking fixation.
This type should be carefully determined for use - it has contraindications due to the metal insert, and the frame is visible to others.
Lamellar
The jaw is divided into two components (upper and lower plates). The removable base is attached to the gums through suction cups, the cost of which depends on the quality of the components.
They are easy to produce, low in price, and can be used for extensive lesions - they cause great discomfort (increased load on the alveoli, may fall out), have side effects and a short service life. In the laboratory, the model is recreated for each person using a unique cast.
There is no point in choosing expensive components for plates, since the model wears out quickly.
Sandwiches
A hybrid that brings together all the best from clasp and plate types of prosthetics. Without visible fragments, such plates are easy to use (even with complete edentia).
Putty knife
Description, purpose
This is a tool that is used for mixing various materials and modeling prosthetic structures.
Therapeutic spatula is used for mixing:
- cement, fillings;
- medicinal dressings.
Mixing the components of the material to the required consistency is done with spatulas, rubbing them on the glass. The laboratory spatula is designed for mixing impression materials, plaster, and casting plaster models. Modeling spatulas, dental and therapeutic metal spatulas are used to model the prosthesis with wax. An electric dental spatula is also used.
Kinds
The spatula can be:
- metal or plastic;
- therapeutic, laboratory, modeling;
- one- and two-sided.
The metal instrument is made of medical steel. Plastic is used when mixing materials that may change color (for example, a chemical composite).
Dental spatula in the photo:
Manufacturers and cost
Manufacturers: HLW Dental Instruments (Germany), IVOCLAR VIVADENT (Liechtenstein). Price – from 120 rubles.
Varieties by type of fastening
Artificial restoration of the bite is completed after the installation of implants. Depending on the methods of fixation, the components used and the design, there are several types in the classification of dentures and dentures:
- spherical - convenient for using partially removable systems; two supports are enough to evenly distribute the load on the closed jaws;
- beam – screwing points for implants are determined (based on the force of pressure on the gums), a beam is fixed to the holders;
- clasp - installed on supporting organs using hooks;
- on implants - it is recommended to use metal retainers as opposed to cement when there are no contraindications;
- micro-locks – the main advantage is the ability to install locks on crowns and entire areas without preliminary grinding;
- suction cups - light and short-lived with a fairly cheap implementation.
Smoothers for restoration
Smoothers for restoration
Our website presents a wide range of smoothing pads for dentists:
- Tool for modeling fissures light green Silicon Black - designed for modeling the surface of the tooth, forming fissures, tubercles;
- Double-sided plugger, gray Silicon Black, is used to introduce the composite into the formed cavity and distribute it along the walls;
- Double-sided blue trowel Silicon Black - for introducing and distributing the composite into cavities, as well as for forming restoration cusps;
- Brown Silicon Black reverse trowel - for introducing and distributing the composite into cavities, as well as for forming restoration cusps;
- Double-sided trowel with a turn, blue Silicon Black - for introducing and distributing the composite into cavities, as well as for forming restoration cusps;
Also our new ironers made to order, especially for our customers:
- Universal smoother for working in the area of the front teeth, yellow Silicon Black
Bright design, silicone handle with anti-slip effect. It has a wide leaf-shaped shape with a pointed tip for convenient modeling with a composite in the front group of teeth. A thin working part, with two different bends on opposite sides, depending on the surface on which the work is being done. It has a black anti-reflective matte coating for convenience when working with optics. For comfortable work on both vestibular, oral and proximal surfaces.
- Universal smoother for working in the area of chewing teeth, black Silicon Black
The smoother is universal for working in the area of chewing teeth; it has a black coating with an anti-reflective effect for comfortable work with optics. The smoother has a silicone handle with an anti-slip effect. On one side there is a plugger for compacting the composite into the tooth cavity, on the other there is a tool with a sharp tip for modeling fissures on the chewing group of teeth.
- Green filler trowel Silicon Black
Ergonomic design for applying the composite and its subsequent modeling on the tooth surface.
All instruments are made of stainless medical steel AISI 410 and have a comfortable silicone handle, which is very dense and can withstand a huge number of sterilization cycles.
Additionally, you can order your own personalized engraving on any instrument.
We recommend that you adhere to sterilization standards so that your instruments last a long time.
You can order dental instruments at affordable prices separately or in a set on our website dentins.ru.
Components for the production of implants
Laboratories are working to create new approaches that will determine the quality of the future product, service life, owner comfort, the development of allergic reactions and other indicators. Which material is better for dentures for dental prosthetics?
Acrylic
Affordable – the most common today. Fixed to the surface via a hook, eliminating grinding. Using this option is justified only for temporary solutions, pending the manufacture of a permanent filling or part of it.
Acry-free
The acrylic-free polymer component is resilient and elastic and does not cause any discomfort to its owner. Scientists claim a service life of 10 years, which adds points. However, it is rarely used for long-term artificial jaws, despite the fact that the transparent base is invisible to others.
At the initial consultation, the doctor will tell you what material and type of prosthesis is best to use for dental prosthetics in each individual case.
Nylon
Widely used in any medical practice due to its lightness, flexibility, as well as elasticity and elasticity.
But even distribution of the load on the chewing organs is impossible due to their great softness (which leads to the need for immediate replacement). Recommended for temporary solutions while work is underway on a permanent prosthesis.
Zirconium dioxide
A biologically compatible artificial component that is comparable in strength to metals. Used for the manufacture of crowns, implants, and various systems for a long time.
Ceramics
Ideal for the outside of teeth on a zirconia or other metal framework. Cheaper than analogues, has an average service life - which makes the material the most widely used.
Metal alloys
The composition includes durable hypoallergenic components. The main property is oxidation resistance. Used for clasp, frame and beam implants. After ceramics, the most common option. Before carrying out work, it is necessary to consult with qualified dentists, due to the risk of material rejection.
Manual preparation in the practice of a modern dentist
In most cases, the preparation of carious cavities is carried out using the traditional method using a drill. The fear experienced by patients (usually children, pregnant women, elderly and somatically burdened patients), pain during the preparation process arising from the vibration of the bur, its pressure on the tooth, the unpleasant sound of the dental unit: all this affects the patient’s behavior, leading to to the development of dental phobia [1, 3—5]. To reduce the level of psycho-emotional stress in patients, special preparation methods have been developed in accordance with the rules of biological expediency.
In 1994, the Dutch doctor Taso Pilot proposed the ART technique (atraumatik restorative treatment - atraumatic restorative treatment) not as an alternative, but as an addition to the machine method of preparation [1, 3, 4]. Since 1994, the ART technique has been recommended by the World Health Organization for providing dental care to residents of economically backward regions, low-income populations, refugees, and emigrants.
There are general and local indications for the use of the ART technique.
Are common:
- children's, elderly and senile age;
- patients for whom machine preparation is not indicated (with severe diseases of the cardiovascular system, in the post-infarction state, with diseases of the nervous system accompanied by increased excitability);
- patients in a state of prolonged immobilization, disabled people;
- pregnant women, patients with increased individual sensitivity to anesthetics or who have contraindications to their use;
- preparation in field conditions (military conditions, agricultural work, etc.);
- insurmountable fear, categorical refusal of machine dissection at any age [1].
Local (clinical) indications:
- caries of baby teeth;
- extensive areas of carious softening of hard tooth tissues;
- in some cases - hard-to-reach carious cavities (for example, teeth covered with an artificial crown);
- temporary delayed filling; combined use with classical preparation (machine) [1].
Indications depending on location:
- Class I according to Black - the presence of a wide entrance hole into the carious cavity and softened dentin;
- Class II according to Black - localization of the carious cavity below the equator of the tooth;
- Class III according to Black - localization of the carious cavity in the proximal cavities without damage to the vestibular and palatal walls;
- Class IV according to Black - limited use (in combination with machine preparation);
- Class V according to Black - cervical cavities with access to dentin;
- carious root cavities, including teeth under an artificial crown due to gum recession [1].
Contraindications [2]:
- complicated caries;
- exposed dental pulp;
- the obvious presence of a carious cavity, but at the same time its inaccessibility for processing with machine tools;
- indirect signs of a carious cavity, for example, on the approximal surface, but the impossibility of access to the cavity from the occlusal or approximal surface.
Advantages of the ART method [2]:
- minimal preparation of a carious cavity with maximum preservation of healthy tissue and minimal tooth trauma;
- painlessness, absence of psychological trauma for the patient, reduced fear of dental surgery;
- simplified infection control, as hand instruments are easy to clean and sterilize;
- no need for local anesthesia, expensive dental equipment (dental unit), the ability to use the method in areas remote from industrial centers, rural areas, directly in schools, hospitals;
- high economic efficiency; accessibility of restorative dental treatment for all social groups.
Basic principles of the ART method [2]:
- preparation of a carious cavity only with hand instruments;
- tooth restoration with adhesive filling materials (such as glass ionomer cements - GIC).
Despite the fact that a dental office and electrical equipment are not needed to carry out the method, ergonomic rules are observed when performing it. The operator needs to work while sitting, preferably with an assistant. Good lighting of the oral cavity is necessary. In addition to the standard set of tools (dental mirror, probe, tweezers, excavator and spatula), a dental knife for enamel and a carver for removing excess filling material are required [2]. If there is pain, topical anesthesia can be performed [1, 3].
Stages of working using the ART method [2]:
- Isolate the tooth being prepared from saliva using rollers.
- Remove plaque with damp cotton balls.
- Dry the tooth surface with dry cotton balls; if necessary, expand the entrance to the carious cavity with an enamel knife.
- Remove carious dentin with an excavator starting from the enamel-dentin junction.
- Remove overhanging edges of enamel, lacking dentin support, with an enamel knife.
- Clean the cavity with wet and then dry cotton balls.
- Carefully and carefully remove carious dentin near the pulp of the tooth.
- Clean the cavity again with cotton balls soaked in an antiseptic solution.
- Check the occlusal relationships of the tooth being restored by asking the patient to occlude the teeth in bite.
- Dry the cavity with dry cotton balls.
To improve the chemical bond of GIC with tooth structures, the cavity walls must be carefully processed. Dentin is treated either with the conditioner included in the GIC kit, or directly with the liquid for mixing GIC [2]. Then the cavity and fissures are washed several times with cotton balls moistened with distilled water or saline. After this, the cavity is dried with dry cotton balls. GIC is mixed according to the manufacturer's instructions; introduced into the cavity; condenses. Excess material is removed.
After dental restoration using the ART method, observation and evaluation of long-term results are carried out. The patient is asked about the occurrence of discomfort or pain within 4 weeks after dental treatment. Long-term results are assessed after six months, 1 or 2 years. It must be remembered that the restoration of carious teeth by GIC is only part of the ART method, which includes not only treatment, but also the prevention of caries. To avoid new carious lesions, after dental restoration, the patient is given the following recommendations:
- regular removal of plaque;
- rational nutrition, especially regarding the consumption of carbohydrates;
- applications of fluoride-containing solutions, antiseptic drugs (for example, chlorhexidine);
- fissure sealing [2].
An assessment of the long-term results of treatment of carious teeth using the ART method, carried out in Thailand (1991), showed that 71% of restorations were preserved after 3 years. A similar project in Zimbabwe (1993) led to better results: 85% of restorations were preserved after 3 years [2].
Clinical example
Patient M., 32 years old, complained of the presence of a carious cavity in tooth 3.6 and pain from thermal and chemical irritants when eating. When collecting anamnesis, it was found that the woman was in the 16th week of pregnancy, there was a threat of miscarriage. Anesthesia is contraindicated. It was decided to carry out ART restoration of the tooth. The examination showed the presence of a deep carious cavity in the 3.6 tooth, filled with softened pigmented dentin. The presumptive diagnosis is pulp hyperemia (deep caries). A spherical diamond bur and a turbine tip were used to open the carious cavity. An excavator was used to remove necrotic dentin (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. View of the carious cavity of tooth 3.6 before filling.
Then antiseptic treatment was carried out. Probing of the bottom confirmed the diagnosis of pulp hyperemia, therefore, before filling the cavity, a therapeutic pad made of a material based on calcium hydroxide was applied to the bottom. The cavity was filled using the classical technique of working with hybrid GIC. The filling was formed using smoothers, fillers and damp, wrung out cotton swabs. After polymerization, the filling was coated with protective varnish (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2. Final appearance of tooth restoration 3.6.
The patient is recommended to undergo a follow-up examination after childbirth. Recommendations on oral hygiene are given.
Thus, the ART method remains relevant today. The method is positively perceived by patients, since dentin preparation is painless or the pain is so insignificant that anesthesia is not required. It is important that the dentist and the patient have a choice: high-tech machine or manual preparation methods, as well as a combination of both.
LITERATURE
- Zapashnik T. A., Gorbachev V. V., Oliferko D. V. Manual preparation in modern dentistry // Modern dentistry. - 2007, No. 3. - P. 55-59.
- Modrinskaya Yu. V., Khramchenko S. N. Methods of minimally invasive treatment of dental caries. ART method. Tunnel restoration / Educational and methodological manual, 2nd edition, expanded. - Minsk: BSMU, 2010. - 31 p.
- Pakhomov G.N., Leontyev V.K. Atraumatic restorative treatment of dental caries. — Incoral, Switzerland.
- Popruzhenko T.V., Yatsuk A.I. // Sovrem. dentistry (Belarus). — 2004, No. 3, 4.
- Chuev V.V., Rachitsky G.I., Al-Alawni S.V., Smetanyak S.M. // Dentist. - 2004, No. 1-3.
Artificial onlays - what are microprostheses?
A description of the types of dental prosthetics with dentures can be found below in the text.
Tabs
They allow you to delay the installation of the crown. A standard procedure can save damaged teeth by placing one cap at the root and another over the gum. The resulting strong base can last quite a long time. The prosthesis is made of porcelain, metal, ceramics, zirconium and various composites.
Veneers
Thin plates are attached to the outside. Designed to hide blemishes, minor defects, and whiten.
Two manufacturing methods:
- Several layers are successively applied to the enamel.
- The veneer is poured (made) in a special mold and then secured in the mouth.
The quality and service life of the finished product directly depend on the components.
Lumineers
They are more similar to veneers, but there are a number of distinctive features:
- Much thinner.
- Follows contours and performs the function of enamel.
- Microcracks are completely eliminated.
- Serve up to 20 years.
- Removable design.
Eliminates cracks, whitens and hides minor defects.
Crowns: what are they?
Depending on the composition they have indications and contraindications. Many people wonder how they are made and what they consist of dentures and their parts. Let's look at each type separately.
Metal
There are cast and stamped. They are widespread due to their low cost, as well as ease of implantation and maintenance, but have lost their relevance due to the use of more modern analogues.
They can be made of nickel, titanium, gold, silver, cobalt. The downside is complete unattractiveness.
Plastic
They are made with or without a finished frame. Attractive and beautiful design, together with simple and cheap installation, can make them leaders in application. Low strength and fragility are the main disadvantages of polymer dentures and structures. In addition, plastic is a highly allergenic component.
Used for restoration, correction of anterior incisors (low load) and temporary solutions, while a permanent option is in development.
Metal-ceramic
Metal base, in the upper layers of which a ceramic coating is applied. The most common: ideal price-quality ratio. Strength, durability, the ability to be inserted into any place are advantages. The disadvantages include a possible change in color over time (requires additional care and protection), may be rejected or lead to inflammation of the gums.
Porcelain
Porcelain implants are made using press casting followed by firing. Aesthetic, strong and durable, while completely anti-allergenic. However, the high price threshold greatly reduces the application.
Zirconium dioxide crowns
After smelting, they are able to completely copy the natural external structure of the teeth. The high cost and the impossibility of subsequent adjustments after smelting the structure make this material rare. However, high strength and durability are its advantages.
Dental smoother
Description, purpose
This is the main tool in therapeutic dentistry, used for filling teeth.
It is a handle with working parts, which are flat spatulas. They have different angles of inclination to the handle.
The smoother is used to introduce filling material into the treated carious cavity and modeling, restoration (by removing excess filling, smoothing).
Kinds
The choice of tool depends on the group of the tooth, the type, location and size of the carious cavity.
Main varieties:
- approximal teardrop-shaped, sickle-shaped, with an elongated working part;
- leaf-shaped approximal (small, long, wide);
- mini-smoothers approximal drop-shaped;
- combined, with a spherical plugger at one end and a trowel at the other;
- medial curved, thin right and left.
The irons are made of medical oxidized steel. A coating (titanium nitride, tantalum) is also used to prevent the filling from being stained by metal particles and sticking to the instrument.
Views in the photo:
with ball filler
mini medial
teardrop-shaped
sickle-shaped
Manufacturers and cost
Well-known manufacturers: Extradent (Russia), 3M ESPE (USA), Voco (Germany). Cost - from 80 to 1800 rubles.
The LM-Arte set of accessories for artistic restoration contains several types of smoothers. Manufacturer: lm-dental. The set was developed together with Style Italiano by a group of doctors involved in aesthetic dentistry. Made from high quality steel. Each device has its own marking depending on the main task. The set contains 5 tools, the cost of each is from 2500 rubles.
Which prostheses are best to choose?
Dentists can cope with tasks of any complexity. The choice of prosthetic method, material, approach to treatment, its duration and other nuances are determined only by the doctor.
According to indications
The main condition for determining approaches to therapy is the patient’s clinical condition. A professional will, first of all, focus on these conditions.
By price and budget
The second most important criterion. In dentistry, one problem can be solved in several ways. From those presented, the client can choose the option that is suitable in terms of cost, time and other criteria. This indicator also depends on what the dentures are made of.
By service life
The quality of the components used directly affects the wearing comfort and durability of the products. This factor should be taken into account when choosing an affordable option. The criterion must be on the same level as the price determination.
With complete or partial edentia
This criterion applies to diagnostics according to indications. Because the different conditions of the oral cavity and gums determine the possible destinations. A complete absence of masticatory organs requires one approach, a partial absence requires another.
On the upper or lower jaw
Different anatomical functions make adjustments to dental procedures. The doctor must take this factor into account when selecting a variety of suitable solutions.
Stopfer
Description, purpose
This is a tool for compacting filling material in a carious cavity and retrograde filling of the root canal.
Kinds
A dental plugger consists of a metal handle and working parts, which have several structural options:
- spherical;
- cylindrical;
- cone-shaped;
- reverse cone;
- three-cornered.
Made from medical steel. Most often it comes with an ironing board.
How to choose a good doctor
Finding a doctor who will restore chewing functions is a responsible task. The qualifications of a specialist directly affect the quality of the work performed, the durability of the structure and the impressions after visiting the doctor. A doctor must combine a master of his craft and a good psychologist in one person. Many people are afraid to go to the dentist, so to create a comfortable environment for the patient, the dentist must be friendly, not fuss, and explain the stages of work. Then your visit will leave only pleasant impressions.
A professional must know: how they are made, from what material removable and permanent dentures are made, and understand the types of fasteners with classification.
The most proven way to find a dentist is to collect reviews from friends. You can also use comments about specialists and clinics involved in bite correction from the Internet. For many years, the Dentika dental center has received only positive reviews from its visitors. The main goal is to make the reception pleasant, high-quality, person-oriented with a mandatory personal approach (to bring joy and health to every patient who comes to us).
At your appointment, you can ask the doctor to show all types of modern materials for high-quality complete dental prosthetics.