Statistical studies based on the results of diagnostic procedures performed in clinical settings show that occlusal deviations occur in the majority of people. Quite often, patients are unaware of the presence of a problem, turning to orthodontists solely out of a desire to improve the aesthetics of their smile, but in fact, the pathological condition can provoke more serious consequences. The correct ratio of the upper and lower rows is characterized by close contact of the antagonists, a small (no more than a third of the height of the crowns) overlap, as well as a natural anatomical arrangement of the elements. Malocclusion, the types of which are classified based on characteristic symptoms, requires proper treatment.
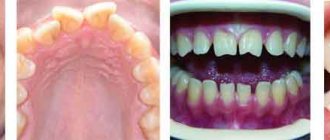
Crossbite
It can occur in both children and adults. It is a horizontal intersection of the dentition or jaws.
It is strongly expressed visually, which brings moral discomfort. Occurs when there is a discrepancy in the development of the lateral parts of the jaws. There are both one-sided and two-sided.
Transversal malocclusions (crossover) are divided into lingual, palatal and buccal.
- Lingual bite is characterized by a displacement of the jaw towards the tongue.
- Palatinal - the jaw is shifted towards the palate.
- Buccal - displacement is observed towards the cheek.
This anomaly occurs for a number of reasons. Among the main ones it is worth noting: traumatic factors, lack of teeth in the dentition, pathologies of the temporomandibular joint, disruption of the teething process.
The most common complaints with crossbite include:
- aesthetic defect;
- problems with chewing food;
- slurred speech;
- frequent gum injury.
How to understand when it’s time to see a pediatric orthodontist
There are many factors that can affect the growth and formation of the dentofacial apparatus: genetics, the habit of chewing the tip of a pencil or sucking a thumb, mouth breathing, past illnesses, injuries and much more. But how do you know when it’s time to show your child to a specialist? First, you need to visually assess how smoothly the teeth grow, whether there are too large gaps between them, and whether the jaws close correctly. Also, experts in the field of orthodontics advise paying attention to the following points:
- bad habits: if a child sucks his thumb or bites a pillow in his sleep, if while writing he unconsciously pulls the tip of a pencil or pen into his mouth - all this is a reason to show the baby to an orthodontist. Such habits very quickly lead to changes in the bite and position of the teeth,
- mouth breathing: when a child breathes through his mouth most of the time, the jaws remain open for a long time, which has a direct impact on the correctness of their formation,
- Difficulty chewing food: You can notice this symptom if you carefully observe how the baby eats. Incorrect positioning of the chewing teeth often leads to the fact that the child has to use the neck muscles while chewing,
- Grinding of teeth during sleep: incorrect development of the jaw apparatus is often accompanied by nocturnal grinding of teeth.
Unfortunately, in orthodontic practice there are cases when hardware treatment alone is not enough. Sometimes, to correct anomalies, the doctor has to resort to surgery, namely the removal of individual teeth. In such a situation, further treatment will involve prosthetics - restoring the integrity of the dentition with the help of crowns and dentures. In order not to start the problem and not bring it to a critical state, parents need to carefully monitor their children’s teeth and the health of the child’s oral cavity, how correctly their dental system is formed.
Sagittal bite
Sagittal malocclusions are often combined with transverse ones. They are characterized by displacement of the jaws in relation to each other. This may be an overdeveloped lower jaw and an underdeveloped upper jaw and vice versa. Such pathologies are divided into mesial and prognathic.
In the first case, a noticeable protrusion of the upper jaw can be observed. The lower one is noticeably underdeveloped, which causes significant deformation of the face in the form of a sloping chin.
In the second case, the lower jaw is noticeably protruded, which causes a significant disproportion.
Such anomalies arise due to a different number of teeth in the jaws, pathology of the development of the alveolar processes, or pathologies of another similar type.
With such defects, the patient experiences difficulty in eating and there is blurred speech. Due to the incorrect position of the jaws, a constantly tense facial expression occurs.
The defect is eliminated in childhood (up to 11 years) with the help of modern technologies, in adults, especially in advanced cases, through surgical intervention.
What is the importance of orthodontic treatment for children?
Some parents believe that baby teeth do not need any treatment or correction of their position. Why put your child through additional stress if the temporary teeth are going to fall out anyway? This is a deep misconception, due to which the health of the permanent dentition often suffers. If a child has had certain anomalies in the structure of the jaw apparatus and the position of the teeth since childhood, treatment should be started immediately. Age plays an important role in orthodontics and bite correction, because it is in childhood that bones are more plastic, due to which correction is easier and much faster.
The importance of orthodontic treatment in childhood is due to the following reasons:
- timely correction will help prevent many problems with teeth and the child’s health in general,
- at an early age, correction of defects takes much less time, while for an adult, treatment of similar anomalies requires twice as much time, despite the fact that the guarantees of the result will be very vague,
- The specialist gets the opportunity to control the direction of growth and the process of tooth formation, and make the necessary adjustments in a timely manner.
If you notice that your child’s teeth are overlapping each other or, for example, one of the jaws is protruding forward, be sure to make an appointment with the orthodontist. After a visual examination, the specialist will be able to identify a specific problem, assess its severity and prescribe timely treatment.
Children's bite defects
According to statistics, approximately 70% of children have malocclusions. Most of them require treatment using complex techniques. Specialists experience significant difficulties when working with children. This is due to the attitude of young patients towards the event. They do not always follow doctors' recommendations, which is why treatment is ineffective.
About a third of children do not receive the necessary therapy, which subsequently causes a relapse of the disease. Bite pathologies in school-age children are in most cases accompanied by numerous carious lesions of the teeth, as well as various concomitant diseases, such as periodontal disease. Therefore, treatment must be carried out on time.
Important! Orthodontic diseases in children require long-term treatment. On average, it lasts from 10 months to one and a half years. During this period, you must carefully follow the doctor’s recommendations and come for scheduled examinations on time. They are necessary to evaluate treatment results and correct methods.
Malocclusions in children are classified into 5 types:
- cross;
- deep;
- open;
- mesial;
- distal.
Cross occurs due to unilateral or bilateral underdevelopment of the jaws. As a result, the dentition overlaps.
A deep bite appears due to underdevelopment of the lower jaw. As a result, the upper row of teeth significantly overlaps the lower one.
An open bite is characterized by non-occlusion of the dentition over a significant segment. This pathology can appear both in the front and side of the jaw.
Mesial occlusion is characterized by an overly protruded lower jaw, which causes significant overlap of the upper dentition.
With a distal bite, the upper jaw is pushed forward, which causes the effect of a slanted chin.
All these types of malocclusion in preschoolers have certain causes. The main factors influencing the development of the jaws and the formation of the dentition are:
- Genetic factor.
- The presence of chronic diseases accompanied by difficulty in nasal breathing.
- Habit of thumb sucking and lip or tongue biting.
- Late weaning from the pacifier.
- Lack of calcium in the body.
- Injuries and damage to teeth and jaws.
- Numerous carious lesions.
- Extracting baby teeth too early or too late.
Important! Bite pathologies in children should be treated as early as possible. An advanced disease can lead to significant complications, as well as problems with chewing and speech.
How much will the treatment cost?
As for the prices for orthodontic treatment, it all depends on the chosen method, the system used, as well as the degree of complexity of the anomaly, which, in turn, determines the duration of the course. For example, treatment using a set of aligners designed for a year can cost the patient a tidy sum of 180 to 300 thousand rubles. In the case of braces, the exact cost will depend on the type and brand of the device.
The most expensive are lingual systems (plates are located on the inside of the dentition), as well as sapphire and ceramic - here the price tag varies from 100 to 250 thousand rubles for a lingual model (prices are for installing braces on one jaw, a one-year turnkey course) . Removable plates, which are indicated for correcting malocclusion specifically in childhood, will cost much less - from 6 to 25 thousand for an expanding model (for one jaw). The price will also be directly influenced by the level of prestige of the dental center whose services you decide to use.
Tests to determine malocclusion
When diagnosing bite pathologies, specialists use various research methods. There are already developed tables with which you can identify even minimal deviations and prevent its development at an early stage.
Tests for malocclusion are performed both by direct examination and by dental impressions. In the process, measurements are taken in various planes, and attention is paid not only to the dentition as a whole, but to the presence and location of each tooth, as well as their general condition.
Important! Even if there is no visually noticeable bite pathology, it is imperative to visit a specialist and undergo testing. It will help identify the development of anomalies at the initial stage, when deviations are minimal.
Orthodontic diagnostic process
Before correcting the bite, the orthodontist organizes a step-by-step diagnosis:
- conducts an examination of the oral cavity;
- Visiographic photographs are taken;
- takes impressions and makes diagnostic models;
- takes a photo of the patient’s teeth, face and smile (determines the appearance, symmetry of the face or the influence of identified bite pathologies on these factors).
How to prevent bite pathologies
To prevent the development of anomalies, you need to follow a number of simple rules:
- During pregnancy, you need to carefully monitor your health and eat foods rich in calcium.
- After the birth of a child, do not transfer him to artificial feeding unless necessary. Bottle feeding affects the formation of the bite.
- After teething, monitor their condition and visit the dentist on time.
- Do therapeutic exercises that provide the necessary load on the facial muscles.
Prevention of malocclusion is necessary for both children and adults. Pathology can manifest at any age if appropriate factors are present. Therefore, regular examinations are necessary. If a specialist identifies a predisposition to the development of a certain disorder, he will recommend appropriate means of preventing malocclusion.
To prevent the disease, more complex measures may be needed than therapeutic exercises and compliance with a number of the rules described above. In some cases, you will need a set of devices for the prevention of malocclusions, which the doctor will select depending on the situation.
You cannot use devices to prevent malocclusions on your own, only on the recommendation of a specialist. Their unsystematic use can significantly worsen the current condition and provoke the development of pathology.
Treatment of malocclusion in children - modern methods
Parents need to understand that the defects in question do not go away on their own. To correct them, appropriate treatment is required under the supervision of an orthodontist. Today, functional orthodontics has a wide range of various corrective devices to solve various clinical problems.
On a note! For the youngest patients, experts offer special orthodontic pacifiers with beveled papillae. To grasp such a pacifier, the child has to push his upper jaw a little further, exactly the same as he does when grasping his mother’s breast. This pacifier promotes proper growth of the jaw apparatus, strengthening of the lower jaw, and correct formation of the temporomandibular joint.
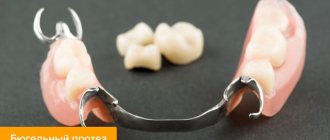
Modern methods for correcting abnormalities of the jaw apparatus involve the use of various corrective structures. The most common devices include the following systems:
- plates - this type is usually used for children, including those with a milk bite. The device is a structure made of metal arches with a plastic base and a screw for correcting the force of pressure on the teeth,
- Trainers and aligners are elastic, removable aligners that have special recesses in their design for each tooth. The full course involves the step-by-step use of different variations of mouthguards, included in one set and designed for different periods of treatment,
- Braces are the best option for teenagers and adults. A non-removable device, which is usually installed for a period of six months to several years, depending on the severity of the pathology. This is a more complex design that includes an arch, plates that are attached directly to the teeth, as well as fastening elements in the form of locks or ligatures - elastic bands. In this case, braces can be made of metal, plastic, ceramics and even sapphire. According to patient reviews, the best and fastest treatment option for the child would be to install a standard metal model. The choice of one model or another directly depends on the defects present and the financial capabilities of the patients.
In addition to the devices listed above, additional components such as face masks, arches and blocks are widely used in orthodontic practice. They can be used not only as auxiliary elements, but also as independent devices.
Dental defects
The teeth may have an incorrect position relative to three mutually perpendicular directions. That is, move forward or backward, up or down, and also rotate around its axis.
The following anomalies occur:
- Rotation. This means a change in the orientation and position of the dental unit in the arch. The degree of rotation can be different - in severe cases, reversion of the cervical and lingual surfaces is observed. But most often there is a slight rotation, which can be noticed with crowded teeth. As a result, some teeth may turn to the side.
- Axis change. Normally, all teeth have a certain inclination. For example, the front teeth are slightly tilted outward to provide convexity to the surface of the lips and the correct profile of the face. However, often the units have an abnormal inward slope (oral position) or a strong outward slope (vestibular position).
- Ectopia (ectopic eruption). This term refers to the eruption of one or more teeth outside the line of the dental arch. This usually occurs due to lack of sufficient space. As a result, the teeth form a “double” row. The picture is especially often observed when baby teeth are retained (that is, when they have not completely erupted). As a result, molars begin to grow from the lingual edge of the arch.
- Migration. This type of dental anomaly is characterized by the displacement of an unerupted unit into an incorrect position within the jaw. And, as a rule, migrated teeth do not erupt, but even in this case they cause a number of problems.
- Transposition. As a result of such a defect, two adjacent teeth change places. That is, one of them occupies the normal position of the other on the dental arch. Often transposition indicates the presence of any obstacles to the normal eruption of a tooth. For example, a canine tooth changes with an adjacent premolar.
- Translocation. In this case, the tooth erupts in an unusual place, but remains within the dental arch. This may occur due to the absence of congenital rudiments of some teeth, as a result of which the free spaces are occupied by other units of the row.
- Distal displacement. This type of anomaly is characterized by displacement of one or more units in the distal direction. That is, the teeth “slide” into the back of the arch. This often happens when molars are removed.
- Partial eruption (infraocclusion). In this case, the tooth does not reach the required occlusal plane, that is, it appears incompletely. This is often due to an obstruction (such as insufficient space). Also, the cause of the defect may be underdevelopment of the root structure.
- Pushing out teeth (supraocclusion). The situation is the opposite of infraocclusion. The erupted tooth is located above the line of the entire row. Most often this is caused by the absence of an antagonist tooth, that is, a unit on the opposite jaw. Moreover, both upper and lower units can be pushed out. Often the problem is caused by root caries or periodontal defects.
Various dental anomalies are often combined with each other, resulting in the formation of complex pathologies. Severe crowding of teeth occurs, which makes normal oral hygiene impossible. Additionally, problems arise with tartar, caries and blood supply to the gums.
Possible consequences
Malocclusions often cause psychological discomfort to a person. Many experience embarrassment, problems with communication, and often anomalies lead to facial asymmetry and changes in profile. But, as you understand, the negative consequences of pathologies do not end there.
Bite and dental defects affect health in the following ways:
- The risk of developing periodontitis and periodontal disease increases.
- Plaque and tartar form, which leads to caries and other oral diseases.
- Inflammation of soft tissue occurs.
- Improper distribution of load on teeth leads to increased wear and increases the risk of chips and cracks.
- Speech defects and serious speech therapy problems appear.
- Chronic headaches occur, which are caused by impaired tone of the masticatory muscles.
- Metabolism is disrupted, which leads to gastrointestinal diseases.
This is why experts recommend correcting malocclusions and teeth, and it is best to treat the problem in childhood/adolescence. However, it is worth noting that modern techniques can solve the problem even in adults.
Diagnostic methods
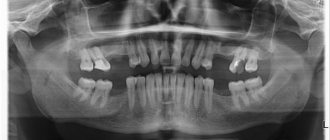
Most bite and dentition defects are noticeable even during a visual examination of the patient. In the future, the orthodontist can only confirm or refute his assumptions. As for hidden anomalies (associated with unerupted teeth), their diagnosis will require the use of X-ray diagnostic methods.
All patients are required to undergo an orthopantomogram - a detailed x-ray of both jaws. An additional computed tomography scan is also performed, which is necessary to draw up a treatment plan. To visualize local disorders, targeted intraoral photographs are taken.
Correction methods
In modern dental practice, several treatment options for dental and jaw abnormalities are used. These include the following:
- Hardware techniques. This therapy involves the use of special correction systems. These are well-known brace systems, as well as various non-removable devices. The treatment period can be up to 3–4 years, but it is possible to achieve complete correction of the bite and displacement of the teeth into the correct position in the row.
- Surgical methods. Some severe and combined pathologies can only be treated surgically. However, this is required extremely rarely, only when treatment with devices is impossible.
- Gymnastics and exercises. Preventive and additional measures that allow you to consolidate the results of treatment, get rid of speech therapy difficulties, etc.
In any case, the necessary treatment option is determined only after consultation with an orthodontist and a full diagnosis.
Remember that proper bite is the key to your overall health, so do not delay treatment. The sooner you take the necessary measures, the faster you will be able to get the desired result.
Still have questions? Consult with the orthodontists of our Clarimed clinic - use the appointment on the website or call us at the numbers provided!
Reasons for the formation of pathology
There may be several components that provoke the formation of pathology.
Internal:
- Provided that the child’s parents are diagnosed with an incorrect bite relationship of the jaws; teeth with non-standard anatomy, size or location - with a high probability the pathology will be inherited.
- Disorders of intrauterine fetal formation, diseases of women during pregnancy (anemia, intrauterine infections), trauma during childbirth.
External:
- Failure to comply with the rules of natural and artificial feeding by parents in infants is fraught with the formation of pathological closure of the HF and LF. The hole in the nipple should be small so that the baby can perform chewing and sucking manipulations.
- It is important to pay attention to bad habits at home, because psychosomatics are involved. Make sure that when sleeping on the side the child does not place his hand under his cheek - there may be a danger of developing a unilateral defect. Tension in your sleeping position can also interfere with the smooth development of your mouth. A child’s harmful habit of constantly sucking a finger, pacifier, and other objects threatens to form a malocclusion.
- It is necessary to monitor the nutritional balance in children at any age. It is important to maintain optimal amounts of fluoride, calcium and other minerals in the body. If you determine a violation of their metabolism, contact your pediatrician.
- Poor posture in a teenager, when the head goes forward and the back goes back, leads to a greater development of high frequency than low frequency.
- Problems with nasal breathing, together with ENT pathologies, lead to pathologies in the formation of the jaws.
- It is important to promptly treat caries and maxillofacial pathology, restore early loss of milk units; Avoid injury, fractures, and prosthetic errors.
- You should pay attention and monitor the formation of the rudiments of wisdom teeth (eights), remove them in time to prevent displacement of the dental units.
Bite in the absence of teeth
It’s interesting, but even if you have no teeth at all, there is no guarantee that with prosthetics you will be able to create the right jaw . It all depends on how damaged the dental system was before removing all its elements. If the jaws are within normal limits relative to each other, the doctor will be able to make adjustments to the prosthesis. If there are also problems with the bones, more complex methods of restoring the dentition will be necessary.
In the absence of teeth, the bite in people is determined using special wax rollers that are placed in the mouth and allow measurements to be taken. The instruments used are a ruler arc and an intraoral plate. Next, a plaster and then a regular prosthesis is created.
Bite after wisdom tooth removal
In modern man, wisdom teeth are an atavism, that is, an element that seems to be there, but is not required in life. They do not affect the correct closure of the teeth and do not harm the dentition in any way if they erupted correctly. This is why dentists recommend not touching wisdom teeth and not removing them unless necessary.
But if you decide to form the correct bite of your teeth as an adult, useless “eights” can serve you well. The fact is that after their removal, the dense dentition becomes freer, so that the remaining teeth can be positioned correctly.
Kinds
In dentistry, such anomalies are usually classified in detail. Orthognathic closure of the teeth allows the chewing pressure to be evenly distributed; in this position, the upper units overlap the lower ones by 1/3 of the coronal part, which is the norm.
Malocclusion is divided into types:
- Distal. It is determined by a strongly advanced high frequency or underdeveloped (pushed back) low frequency.
- Mesial. The LF has a forward position, surpassing the HF in development.
- Deep. A pathology in which the frontal group of the upper units, overlapping the lower ones, injures the gingival tissue.
- Open. Most of the dental units of the HF and LF do not close.
- Cross. An anomaly in which several LF units overlap HF sections and vice versa.
- Dystopia. Teeth are out of place.