Chief editor of the site:
Snitkovsky Arkady Alexandrovich
Chief physician of the professorial dentistry “22 Century”, dentist, orthopedic dentist
Author of the article:
Scientific team of dentistry “22 Century”
Dentists, candidates and doctors of medical sciences, professors
Dental treatment under general anesthesia
Panic fear, a strong gag reflex, allergic reactions to anesthetics and many other conditions are indications for the use of general anesthesia during dental procedures. The patient’s condition after such an intervention is somewhat different from his normal state of health, and this article is devoted to how to behave for the first time after treatment under anesthesia or drug sedation in dentistry .
Indications for general anesthesia
Under general anesthesia in dental practice, it is possible to eliminate almost all problems that arise in the oral cavity - from simple dental caries to complex maxillofacial operations. The patient seeks this type of help, most often, not because of pain, but because of severe fear or medical conditions that interfere with the doctor’s work (allergies, gag reflex, mental illness, etc.). More information about the types of anesthesiological support and how treatment is carried out with switched off consciousness can be found on our website. Here we will talk about the process of postoperative restoration of the patient’s activity , depending on the method of pain relief and the medications administered.
About the period after anesthesia
Common adverse reactions and complications after anesthesia:
- Pain
After the end of general anesthesia, you may feel pain in the surgical area. If upon arrival in the recovery room you still feel it, then inform the medical staff about this - you will be given painkillers.
- Nausea
This is a very common consequence of anesthesia, occurring in approximately 30% of cases. Nausea is more common with general than with regional anesthesia. Here are some tips to help reduce your risk of nausea:
- During the first hours after surgery, you should not be active - sit down and get out of bed;
- Avoid drinking water and food immediately after surgery;
- good pain relief is also important as severe pain can cause nausea, so if you experience pain, tell your healthcare team;
- Deep breathing with slow inhalation of air can reduce the feeling of nausea.
- A sore throat
The endotracheal tube at the stage of awakening from anesthesia can cause an unpleasant feeling of discomfort and sore throat. You need to take this calmly, try to breathe evenly and, most importantly, follow all the instructions of your anesthesiologist. Discomfort, dry mouth, and pain when speaking or swallowing may also be felt for several hours after surgery, but may persist for two or more days. If the above symptoms do not go away within two days after surgery, contact your doctor. A sore throat is only a consequence of anesthesia.
- Shiver
Trembling, as a consequence of anesthesia, is a fairly common problem, as it causes great discomfort, although most often it does not pose a danger to the body and lasts about 20-30 minutes. Trembling can occur after general anesthesia and can also occur after epidural and spinal anesthesia.
- Sensory impairment
During anesthesia, there is a lack of muscle tone, which may result in positional compression of the nerve, which can cause sensory disturbances at the site of compression that last for several weeks. After an operation performed under spinal or epidural anesthesia, the legs become numb for several hours, and emptying the bladder may also be difficult; if necessary, a urinary catheter is installed.
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
The residual effect of anesthetics may manifest itself in the form of a slight decrease in blood pressure, in addition, dehydration, which is not so uncommon after surgery, can lead to the same effect. A decrease in pressure can cause dizziness, weakness, and faintness.
- Headache
There are many reasons that can cause a headache. These include the medications used for anesthesia, the surgery itself, dehydration, and patient anxiety. Most often, the headache goes away within a few hours after anesthesia and can be easily controlled with painkillers. Severe headaches may be a complication of spinal or epidural anesthesia, and treatment may require bed rest for several days.
- Itching
This is usually an adverse reaction to anesthesia medications, but itching can also be an allergic reaction, so be sure to tell your doctor if it occurs.
- Back and lower back pain
During surgery, the patient lies in one constant position on a hard operating table for quite a long time, which can cause the back to become “tired” and ultimately lead to lower back pain after surgery.
- Muscle pain
These pains are most common in young males and are most often associated with the use of drugs to relax muscles during anesthesia. Muscle pain is a consequence of anesthesia (general anesthesia), it is symmetrical, most often localized in the neck, shoulders, upper abdomen and lasts approximately 2-3 days after surgery.
After surgery in the intensive care unit
Depending on the severity of the surgery, postoperative monitoring in the intensive care unit may be necessary. As needed, you will be prescribed medications, possibly in the form of injections/drips. Unfortunately, it is inevitable that the wound after surgery will hurt for some time. If you feel severe pain, you must immediately inform the staff so that the necessary measures can be taken.
Depending on the operation performed, you may have a gastric tube, drainage and a urinary catheter installed.
- Gastric tube
Probes are used to evacuate the contents of the gastrointestinal tract. This is a necessary measure and it is necessary to understand the importance of this procedure. A gastric tube helps you avoid vomiting in the postoperative period, because... all gastric contents will flow through it into a special container. You may experience discomfort and sore throat.
If necessary, enteral nutrition is provided through a tube, i.e. introduction of balanced mixtures to provide your body with nutrients and vitamins. In the first day (and in some cases longer) after the operation, you should not drink or eat. You will receive all the fluid your body needs through an intravenous infusion and tube.
- Drains
Drainage is a treatment method that involves removing discharge from wounds, natural, purulent and other pathological cavities, and the contents of hollow organs.
Drainage - rubber or plastic tubes of various diameters, thin rubber strips, dry aseptic swabs.
- Urinary catheter
If you are unable to urinate on your own, a urinary catheter may be inserted into your bladder to make urination easier.
(See About the Intensive Care Unit) (Active link)
The department team wishes you a speedy recovery!
How long does it take to recover from anesthesia?
Time to recover from anesthesia
The time to recover from anesthesia after surgery or after caries treatment differs, although not significantly. This is usually 15-30 minutes from the end of medical procedures to the moment when the patient fully regains consciousness and is able to think clearly, talk and walk. This is explained by the fact that the introduction of modern drugs for general analgesia is very effective and their effect can be stopped very quickly. These substances are also quickly eliminated from the body. Of course, the speed at which the body regains consciousness depends both on the patient’s age, his sensations, his somatic diseases, and on the stage of treatment, the period of his stay in medicated sleep, and the method of administering medications. But in any case, the time after anesthesia in dentistry is very short and the patient leaves the clinic on the same day.
How is dental treatment performed under anesthesia?
At the beginning of the procedure, the anesthesiologist injects an intravenous drug or puts a mask on the patient, who inhales a special drug, and within a few minutes he falls asleep. After this, the dentist can begin treatment. The patient wakes up 20-60 minutes after completion of the procedure and in less than an hour, he can go to his home to rest.
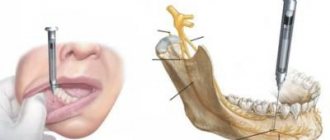
It is worth remembering that if general anesthesia is used during tooth extraction , the procedure can last, as a rule, up to sixty minutes, but in some cases with complex extractions this requires a longer time.
Rule one. You shouldn't endure pain just to avoid anesthesia.
Almost any manipulation associated with causing severe pain is more harmful to the body than anesthesia. Therefore, in the civilized world they adhere to this point of view: where it is possible to relieve a patient of pain, this is certainly done. Modern medicine has very wide possibilities for this.
In addition, anesthesia with the use of artificial respiration devices significantly expands the capabilities of surgeons and allows them to provide assistance to those patients who cannot be helped with other types of surgical intervention. Of course, all contraindications of the patient, his age, and body capabilities are taken into account.
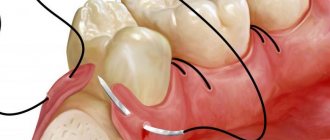
Recommendations from specialists after tooth extraction
To ensure that the treatment is not in vain and you do not experience any complications, you need to follow certain recommendations that will contribute to a speedy recovery and healing.
- The gauze swab should be spat out half an hour after completion of the procedure.
- Under no circumstances should you eat within two hours after tooth extraction.
- Do not rinse your mouth or spit out blood clots.
- It is strictly forbidden to drink alcohol within 24 hours after visiting the dental clinic.
- Refrain from strenuous physical activity.
- If bleeding occurs, apply a gauze pad to the wound site and bite it.
- There is a risk that your cheek may swell after treatment. Want to avoid this? Then you need to apply ice or some cool object to your cheek during the first 24 hours after treatment.
Rule three. Recovery from anesthesia depends on the type of anesthesia and the characteristics of the body.
Typically, the patient recovers from anesthesia within one to four hours, depending on the amount of anesthesia used and his individual characteristics. The fact that recovery from anesthesia was normal can only be assessed by a doctor based on various indicators of the body’s functioning.
The patient himself usually remains half asleep for quite a long time during the day. His relatives who are present should not be afraid. The patient's body is simply under the influence of analgesics. They are necessarily administered in order to alleviate pain after surgery - after all, the anesthesia has ended, but the cause of the pain remains.
Article on the topic
In facts and figures: epidural anesthesia does not work for 1 in 20 patients
There may be another condition after anesthesia - excessive excitement. This usually happens if a person has previously abused alcohol or had mental problems. This complication is also amenable to medical control - the patient will simply be given sedatives and sleeping pills for a while.
Complications of anesthesia
Therapy is carried out taking into account the reasons that caused the pathological condition. In case of respiratory disorders, the composition and volume of the gas-air mixture is adjusted, and the endotracheal tube is sanitized using an electric suction. If it is not possible to completely clear the airways, call the endoscopic team on duty to perform emergency bronchoscopy. To relieve laryngospasm, narcotic analgesics, atropine, antispasmodics, and adrenergic agonists are used. To saturate the blood with O2, the device is set to enhanced oxygenation mode (100%). Maintaining a sleepy state is ensured by intravenous anesthetics.
Cardiac dysfunction is treated symptomatically. For bradycardia, administration of atropine and adrenaline is required. A decrease in blood pressure against the background of weakened cardiac activity is an indication for transferring the patient to the administration of pressor amines through a syringe pump. The dose of anesthetic may need to be reduced. Arrhythmias are stopped using cordarone, amiodarone, procainamide, lidocaine. Fibrillation that is not amenable to chemical treatment requires electrical defibrillation. When blood pressure increases, antihypertensive drugs are administered; when blood pressure decreases, hypotonic drugs, infusion solutions to replenish blood volume, and steroid hormones are administered.
Short-term postoperative psychosis cannot be relieved with medications. In case of severe psychomotor agitation, the prescription of neuroleptics and narcotic analgesics is allowed. Long-term disorders of the central nervous system require therapy with the use of nootropics, antioxidants, and general strengthening agents (multivitamin complexes, adaptogens). Intestinal tone usually recovers on its own within 1-2 days. In case of prolonged paresis, proserin is administered.
Malignant hyperthermia is an indication for the administration of datrolene, a muscle relaxant that can block ryanodine receptors. In addition, symptomatic treatment drugs and physical methods of reducing the temperature are prescribed (ice on large vessels, wetting the sheets and the patient’s body with cold water, ventilating the patient’s body). For allergic reactions, antihistamines, glucocorticosteroids, and symptomatic medications are infused. Severe manifestations require mandatory tracheal intubation and transfer to mechanical ventilation, if this has not been done previously.