Formation of permanent teeth
Molars are formed from the epithelial dental plate. The appearance of their rudiments occurs only closer to the 5th month of fetal development inside the mother’s womb.
There are two groups of molars:
- Substitutes. This includes canines, incisors and premolars, which have temporary analogues.
- Additional. This group includes molars that do not have milk predecessors.
The growth of the primordial teeth of the replacement type occurs in the same alveolus as the temporary teeth; they are located behind the lingual surface of the primary teeth. Only after some time does the volume of bone tissue increase, ensuring their insulation.
Additional teeth are formed only after a year, since for this the jaw must reach the appropriate size.
At what age do they appear?
Statistics show that the beginning and completion of the change from temporary teeth to molars in most children occurs at approximately the same time. There are minimal differences only among children in different regions. The warmer the climate, the sooner the child will have permanent teeth.
The table shows age parameters that can be used to determine the approximate beginning of the eruption of molars according to several well-known authors.
| Set of teeth | Period of eruption of permanent teeth in children (in years) | ||
| according to Vinogradova | according to Lukomsky | according to Novak | |
| Central incisors | 5-6 | 6-9 | 6-9 |
| Lateral incisors | 7-9 | 7-10 | 7-10 |
| Fangs | 12-13 | 9-14 | 9-14 |
| First premolars | 9-11 | 9-13 | 9-13 |
| Second premolars | 9-11 | 9-15 | 10-14 |
| First molars | 4,5-7 | 7-8 | 5-8 |
| Second molars | 12-13 | 10-15 | 10-14 |
| Third molars | 18-25 | 15-24 | 18-20 |
The differences in the age at which permanent teeth appear depending on the author are due to the fact that they present the results of studies in different regions that were carried out with a serious difference in time (several decades).
Competition "bio/mol/text"-2017
This work was published in the “Free Topic” category of the “bio/mol/text” competition 2017.
The general sponsor of the competition is: the largest supplier of equipment, reagents and consumables for biological research and production.
The sponsor of the audience award and partner of the “Biomedicine Today and Tomorrow” nomination was.
"Book" sponsor of the competition - "Alpina Non-Fiction"
...They say evil has no face. Indeed, no feelings were reflected on his face. There was not a glimmer of sympathy on him, but the pain was simply unbearable. Can't he see the horror in my eyes and the panic on my face? He calmly, one might say, carried out his dirty work professionally, and at the end he politely said: “Rinse your mouth, please...”
This is how Dan Andrews describes a visit to the dentist in his short story “Wretched.” Indeed, since childhood, we have been in incredible awe of such specialists as dentists. Parents do everything they can to force their children to at least go to the doctor’s office, trying not to think about what awaits them next. And sometimes an adult’s soul sinks at the sight of numerous tools. Sometimes just the sight of a dental clinic is enough to do this.
As a result, the state of the oral cavity and dental hard tissues around the world does not inspire hope for a future without caries. Despite advances in dental treatment, tooth loss remains one of the most significant problems. Thus, according to WHO, the main causes of tooth loss are caries and periodontitis. Complete tooth loss is particularly common among older people. Globally, approximately 30% of people aged 65–74 years are missing teeth due to inflammatory periodontal diseases and pathology of dental hard tissues [1].
Therefore, it is not surprising that the state of the oral cavity of the population not only in Russia, but also in the world represents a serious problem, offering opportunities both for study and, more importantly, for the search for new treatment methods. One of them was tissue engineering , an interdisciplinary branch whose goal is to create biological substitutes that restore and maintain the functions of a tissue or organ. The fairly high efficiency of tissue engineering methods and their potential have attracted the attention of many scientists. This also contributes to their unfading popularity in various fields of medicine to this day.
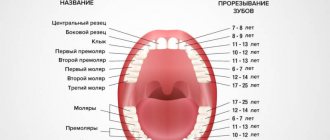
Teething sequence
Almost all parents believe that the first molars should be incisors, which replace temporary elements of the dentition. But this opinion is wrong. Even before baby teeth fall out, at the age of 5-6 years, children receive their first molars, which are not on the list of primary teeth.
After this, the sequence of formation of a permanent bite is almost no different from the order of eruption of primary teeth:
- the lower and upper central incisors grow;
- lateral incisors appear on both jaws;
- lower and upper first premolars;
- fangs;
- upper and lower second premolars;
- second and third molars (you must understand that the so-called “wisdom teeth” sometimes do not penetrate the surface of the gums at all).
Teeth cutting in this order does not happen just like that, because it ideally corresponds to the speed of development and formation of the maxillofacial system. If the optimal sequence is followed, correct bite development occurs.
Timing of teething in children
Teething is physiological and serves as an indirect indicator of the correct or impaired development of the child. As a physiological act, teething is not a painful phenomenon and cannot cause any diseases. It is in direct connection with the general health of the child - timely growth of teeth in a certain sequence indicates the normal development of his body. A delay in teething may be a consequence of rickets, an infectious disease, prolonged dysfunction of the intestines and changes in metabolism. Earlier teething - endocrine disorders. A discrepancy in the time of the beginning of the eruption of the central incisors by 1-2 months from the conditional period cannot be considered as the effect of any pathology.
The newborn does not have a single tooth, although in rare cases their intrauterine development is observed. Between 6 and 8 months of life, the central incisors of the lower jaw begin to appear, and then the upper. By 8-12 months, the lateral incisors are formed first on the lower jaw and then on the upper jaw. By 12-16 months, the first molars erupt, by 16-20 months - the canines, and by 20-30 months - the second molars, which complete the formation of the primary bite.
The eruption of baby teeth often affects the child’s well-being. In weakened children, this physiological process is accompanied by general malaise, poor sleep, restless behavior, crying, and moodiness. Sometimes the temperature rises to 37.50C, the nature of bowel movements changes, short-term rashes on the body and redness of the facial skin are possible. The child's weight gain is temporarily suspended and immune defense is reduced. To establish the true cause of the malaise, a consultation with a pediatrician is necessary.
At the 7th year of life, the replacement of baby teeth with permanent ones occurs, the time of eruption of which, as a rule, coincides with the resorption of the roots of baby teeth and their loss. In contrast, the formation of a permanent bite begins with the appearance of the first molars of the lower jaw and normally ends by 15-18 years. The central incisors (8-9 years), first premolars (9-10 years), canines (10-11 years), second premolars (11-12 years), second molars (12-13 years) sequentially erupt. The third molars of the lower jaw, or as they are sometimes called “wisdom” teeth, grow later, often after the age of 20-25 years.
A correctly and timely formed bite plays a big role in the normal development of the child’s body. Violation of the timing of teething (early or late), the order, as well as the absence of one or another tooth require the attention of a pediatrician and dentist, since they are evidence of pathology not only of a local, but often of a general nature (the result of diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy, or any anomalies in the child’s health).
For various reasons, a number of deviations can occur in the structure of teeth, their location and development: the absence of a rudiment of a tooth, an incorrect position of the tooth axis (horizontal or oblique), which is why it erupts outside the arch of the dentition or remains in the thickness of the jaw bone. In addition, the incorrect formation of the tooth itself - size, shape, position, color, lack of enamel coating, etc. Such changes should be analyzed by a specialist.
Timing of teeth eruption, formation of rudiments and roots, maturation of enamel
Baby teeth
| Teeth | Period of eruption, months. | Timing of root formation | Beginning of root resorption | Root resorption time |
| I | 6 — 8 | +2 years | from 5th year | in current 2 years |
| II | 8 — 12 | +2 years | from 6th year | in current 2 years |
| III | 16 — 20 | +3 years | from 8th year | in current 3 years |
| II | 8 — 12 | +2 years | from 6th year | in current 2 years |
| V | 20 — 30 | +3 years | from 7th year | in current 3 years |
Permanent teeth
| Teeth | Timing of eruption | Timing of root formation | Final “enamel maturation” | Bookmark of follicles |
| 6 | 5 — 6 | at 10 | at 1 - 3 years | at 5 months intrauterine development |
| 1 | 6 — 8 | at 10 | at 4 -5 years old | at 8 months high-quality development |
| 2 | 8 — 9 | at 10 | at 4 -5 years old | at 8 months high-quality development |
| 4 | 9 — 10 | at 12 years old | at 5-6 years old | at 2 years old |
| 3 | 10 — 11 | at 13 years old | at 6 -7 years old | at 8 months high-quality development |
| 5 | 11 — 12 | at 12 years old | at 6 -7 years old | at 3 years old |
| 7 | 12 — 13 | at the age of 15 | at 7-8 years old | at 3 years old |
For infants, the number of teeth that have erupted is one of the objective criteria by which the baby’s health status is assessed. The timing of teething and the order of their appearance can vary significantly. So, the first tooth can appear as early as 1 month or 1 year, but most often this happens at 6-8 months of life. To calculate the number of baby teeth (N), depending on age, use the formula: N = n-4, where n is the number of months of a child’s life. So, at the age of 12 months, the baby should have 8 teeth.
Signs of physiological teething
- Teething at certain average times
- Eruption pairing
- Teething in a specific order
Causes of delayed teething:
- rickets and other disorders of calcium-phosphorus metabolism;
- decreased activity of the endocrine glands (hypothyroidism);
- disturbances in the digestion and absorption of nutrients;
- severe eating disorders;
- chronic infections;
- hereditary disorders of mineral metabolism and diseases of osteochondral tissue;
Difficult teething with increased body temperature, catarrhal symptoms, and indigestion is most often caused by an infectious disease. Therefore, the appearance of such symptoms in a baby during teething requires a mandatory medical examination and observation!
Possible features of teeth in children at the teething stage:
- Expansion of spaces between teeth. It may reflect increased jaw growth and during the transition period from baby teeth to permanent teeth is regarded as a normal condition. A wide gap between the front incisors on the upper jaw is usually associated with a deep-lying maxillary frenulum. The tactics for monitoring and treating wide gaps between teeth are determined by an orthodontist.
- A blackish edging on the neck of the tooth can be due to the use of soluble iron preparations or a chronic inflammatory process (precipitation of bacteria of the leptotrichium group);
- Yellowish-brown staining of teeth is most often associated with the use of antibiotics by the mother in the second half of pregnancy or by the child during the period of teeth formation.
- A yellowish-greenish color develops in severe disorders of bilirubin metabolism and hemolytic (destruction of red blood cells) conditions;
- Reddish staining of tooth enamel is characteristic of a congenital disorder of pigment metabolism - porphyrin. This disease is called porphyria;
- Malocclusions occur due to uneven growth of the jaws, due to prolonged sucking of the nipple;
- Anomalies in the location of teeth occur for constitutional reasons (small jaw size), due to trauma, congenital disorders of connective tissue metabolism, and tumors of the alveolar process of the jaw.
The absence of teeth before 1 year of age is extremely rarely associated with edentia - the absence of their rudiments. You can check the presence of tooth germs using a special radiovisiography method prescribed by a pediatric dentist.
Duration of growth
Typically, children say goodbye to their last temporary teeth at about 12-13 years of age, although the roots of baby teeth dissolve even earlier. By that time, the oral cavity already has molars that are actively growing, and their roots are at different stages of formation.
It is necessary to understand the approximate timing of growth and root formation in case of deviations. It is these indicators that are taken into account when choosing a treatment method.
Experts distinguish two main stages of development of the roots of permanent teeth:
- Stage of unformed apex.
- Unclosed apex stage.
At the first stage, the length of the root becomes maximum, but its walls are parallel to each other. The channel is of sufficient width; it ends in the area of the future apex with a bell. The periodontal gap can be seen only on the sides of the tooth root.
At the next stage, there is a gradual formation of the upper part of the root, the convergence of the root walls and the release of the periodontal fissure, the apical region of which is slightly enlarged.
Root canal treatment in children
The roots of children's baby teeth are filled with a special paste. It has the ability to dissolve in parallel with the process of resorption of hard tissues. This is the only way to ensure that the order of changing teeth is not disrupted and that there are no obstacles to the resorption of milk roots.
Once the root canals are treated, they are closed with a filling. Sometimes the doctor decides to use temporary filling material. This measure is justified if the likelihood of complications is high and you need to make sure that the inflammation has subsided. Only when the dentist is sure that everything is in order will he install a permanent filling.
The completion of tooth root formation occurs at approximately this age:
| Teeth | Upper jaw, age | Lower jaw, age |
| Central incisors | 9-13 | 7-11 |
| Lateral incisors | 9-12 | 8-11 |
| Fangs | 9-12 | 9-12 |
| First premolars | 11-13 | 11-13 |
| Second premolars | 11-13 | 11-13 |
| First molars | 9-12 | 9-12 |
| Second molars | 14-15 | 14-15 |
Since the eruption of third molars does not occur at a specific time, it is impossible to establish a clear age at which their roots are formed.
X-ray results confirm the completion of the process of tooth root formation. The key signs are the absence of an opening at the apex, as well as a pronounced periodontal contour.
Thus, completion of dental growth, including full maturation, usually occurs only between the ages of 15 and 18 years. It is at this time that the maxillofacial apparatus already has the same dimensions as in adults.