We all love to sleep soundly at night - and we do it right, because, as neurologist Alexey Danilov, professor of the department of nervous diseases of the First Moscow State Medical University, explains in his interview, lack of sleep leads to worsening mood, depression and decreased concentration, increases the risk of obesity and the development of a number of chronic diseases. diseases. To be in shape, a person needs to sleep a certain number of hours. But sometimes we wake up in the middle of the night, and one of the main reasons for this is dry mouth. If you have ever encountered this problem, it will be useful for you to know what causes it, how to deal with it, and when you should see a doctor.
Symptoms of dry mouth
Common symptoms include dry tongue and throat, cracked lips, and a sticky, sticky feeling in the mouth. Some people with dry mouth have difficulty recognizing the taste of food, chewing and swallowing food, have difficulty speaking, have sores, and have a burning sensation in the mouth. If you have several symptoms of dry mouth, consult your dentist or physician - such symptoms may be a sign of diseases that require medical attention.
What is xerostomia
Xerostomia is dryness, itching, and discomfort in the oral cavity, caused by a decrease or cessation of salivation. Insufficient functioning of the salivary glands is often a sign of various diseases or the body’s reaction to stress or a negative external environment.
Every fifth person complains of xerostomia. The symptom occurs more often in women (about 30%) than in men. The proportion of patients among the elderly is half.
What causes dry mouth?
It is important to know not only the symptoms, but also the causes of dry mouth at night. It may occur due to snoring or sleeping with your mouth open, smoking, drinking alcohol, or experiencing stress and emotional overload. In addition, dry mouth at night may be a sign of Sjögren's syndrome or a side effect of medications such as sinusitis, anxiety and depression.
Which doctor should I contact?
Since xerostomia is not a disease, but a symptom of one or more disorders, the patient can go to a general practitioner (family doctor or therapist) or dentist with a complaint.
You should not postpone a visit to the doctor if other symptoms appear at the same time:
- complicated caries (tooth pain is severe);
- rashes, redness on the face and body;
- dehydrated, tight skin;
- irritated, dry eyes;
- pain in muscles, joints.
To clarify the cause, the doctor may additionally refer the patient to a gastroenterologist, gynecologist, rheumatologist or endocrinologist.
The Best Strategies for Combating Dry Mouth
The first thing you should do is talk to your dentist, who can determine the causes of dry mouth and, if it is a symptom of a medical condition, offer you treatment options. While waiting for your visit to the clinic, try to relieve your condition on your own:
- Keep a glass or bottle of water on your bedside table to quench your thirst at night
- Dentists also recommend using sugar-free chewing gum or sugar-free candy throughout the day.
- Use a humidifier in your bedroom at night
- Reduce your caffeine and soda intake
- Quit tobacco and alcohol
- Drink more fluids throughout the day to avoid dehydration
In addition, careful care of your teeth and gums provides significant assistance in the fight against dry mouth. Be sure to use an alcohol-free mouthwash, brush your teeth twice a day, and floss, which helps remove food particles stuck between your teeth in areas that are hard to reach with a toothbrush.
Don't let dry mouth interfere with your night's rest. Take the necessary steps and wake up in the morning in a good mood, fully prepared for the new day.
Treatment with home remedies
Xerostomia, which is not a symptom of a serious disease, is treated with traditional methods.
The following recipes moisturize the mucous membrane, increase saliva production, and help with inflammation:
- Dissolve aloe juice in water (40-50 ml per glass). Rinse your mouth 3 times a day.
- Chew 1 tsp after eating. pharmaceutical dill. Repeat for 2-3 weeks. Due to the high content of flavonoids, the plant stimulates salivation.
- Before meals, take 15 drops of wormwood tincture. Repeat every day for three weeks. Bitter herb irritates the receptors, increases the sensitivity of the hunger center, which causes an increase in the amount of saliva.
- Prepare rosemary infusion. Pour 300 ml of boiling water over 15-20 leaves of the plant. Leave for 1-1.5 hours. Rinse your mouth daily before eating.
- Grape seed oil has a gentle effect on the oral mucosa, moisturizes and heals small cracks. Apply before bed to the tongue, inner surface of the cheeks, lips. The oil removes tightness, envelops affected, injured tissues, and facilitates swallowing.
- Refreshes, moisturizes and accelerates the healing of minor damage to the mucous membrane with a herbal collection of calendula, peppermint, chamomile, and plantain. You need to take 1 teaspoon of each herb and mix. Pour the mixture with hot water, about 90º C. Leave for 3-4 hours. Rinse your mouth with the broth every time after eating.
Ginger increases saliva production. It is useful to drink ginger infusion, lemon-ginger tea, or simply add the root to food.
Breathing through the mouth
Nasal breathing is considered to be as correct and natural as possible. But there are a number of reasons why we can breathe through our mouth. For example, poor nasal passages due to a deviated septum, polyps or allergic rhinitis. Even if you just hold your mouth open for a few minutes or talk long enough, you can feel like everything is dry inside. If we add to this the effect of constant air flow, it becomes clear why the mucous membranes dry out so much.
Remedies
Dehydration of the oral cavity in the morning and night hours can be solved with home treatment methods. They do not get rid of the problem, but help reduce discomfort. Full therapy is possible only if the source of the pathological condition is detected.
Getting rid of dehydration
Drinking enough drinking water without additives or sweeteners will help restore balance at the cellular level. The recommended daily volume is at least 1.5 liters of non-carbonated liquid. The following are prohibited:
- tea;
- coffee and coffee drinks;
- carbonated sweet waters;
- energy.
With intense training and prolonged exposure to the sun, the amount of water increases to 2.5 liters, provided that the kidneys are functioning normally.
Changing your usual diet
Fruits and vegetables containing sufficient amounts of water, vitamins and minerals are included in the daily menu. Sour fruits provoke active secretion of salivary secretions. The following products are completely removed from the diet or reduced to reasonable limits:
- astringent fruits;
- salty, smoked, sweet;
- crackers, chips, snacks, crackers;
- sandwiches.
When digesting these species, the body consumes a large amount of liquid. Not all patients can replenish the lack of water due to working conditions and lifestyle.
Treatment of concomitant pathologies
A constantly stuffy nose and forced breathing through the mouth are considered the main causes of dry mucous membranes. Respiratory and colds are accompanied by rhinitis, which interferes with the natural flow of air.
When treating swollen nasal mucosa, it is recommended to use sprays and nasal drops.
Inhalations are carried out using special devices or the classical method: the patient breathes steam from a pan of hot potatoes, covering his head with a towel. Nebulizers are safer - when used, the likelihood of burning the skin and mucous membranes is reduced to zero. Mineral water and physiological solutions are poured into the apparatus and procedures are carried out.
Sources of deviation development
Abnormal symptoms may be caused by temporary changes in condition or indicate serious illness. Doctors distinguish two subgroups of reasons that may cause dry mouth during sleep.
The influence of irritants activates protective reactions, leading to dry mouth during night rest - this subgroup belongs to the physiological type of deviation. The pathological form is caused by a variety of diseases and requires searching for the source of the problem. It is impossible to solve it with standard methods of getting rid of dehydration - first you need to cure the disease.
Non-pathological sources of development
There are a number of reasons for the disruption of the normal state of the oral mucosa. Drying is provoked by the body's response to irritants. Inhibition of the activity of the salivary glands does not require specialized therapy; a change in the usual lifestyle is sufficient.
A few days with auxiliary means can eradicate the problem forever - provided that you follow the drinking rules. If the situation remains the same, then the patient needs professional help.
Increased air dryness and dehydration
The problem is common in city apartments with central heating. Constant operation of radiators leads to a decrease in its level by up to 40%, a person begins to feel thirsty during sleep.
In most patients, dehydration is associated with insufficient fluid intake - less than 1.5 liters per day.
An insufficient amount of fluid in the body is caused by increased ambient or body temperature. Water loss occurs through vomiting, diarrhea, bleeding, and severe burns. People who exercise intensely and do not replenish losses can suffer from dehydration.
Violation of nutrition rules
An excess of sweet and salty foods provokes changes in osmotic pressure and the removal of fluid at the cellular level. The feeling of thirst and drying out of the oral mucosa are provoked by:
- salty foods;
- chips, snacks, crackers;
- sweets, confectionery baked goods;
- coffee and coffee drinks.
Excessive consumption of caffeine leads to accelerated removal of fluid from the body. Addiction causes thirst at any time of the day - in the mornings, at night and during the daytime.
Acute and chronic intoxication
To remove toxic substances that have entered the body, a large amount of water is needed. Increased dryness occurs when drinking alcoholic and low-alcohol drinks. During the processing of ethyl alcohol, acetaldehyde is formed, which has a toxic effect.
Nicotine addiction is considered a common source of excessive dry mouth.
The same condition occurs after smoking tobacco products - excessive secretion of salivary secretions provokes drying out of the oral cavity. Toxins are excreted by the kidneys along with biological fluid.
Night snoring, stress, taking medications
Non-pathological types of xerostomia include the body’s reaction to taking certain medications. Non-standard manifestations occur during treatment:
- antidepressants;
- antihistamines;
- diuretics;
- NSAIDs and drugs to lower high blood pressure.
[media=
https://youtu.be/FjUzN83H-IU
]
Rochnopathy during sleep predisposes to increased thirst. Air entering the lungs passes through the mouth and nasal passages, causing excessive drying of the mucous membrane. The same clinical picture is observed under stress.
Avitaminosis, hypovitaminosis and toxicosis
Insufficient intake of vitamins, especially retinol, leads to keratinization of the oral mucosa. Individual particles of epithelium gradually clog the ducts of the salivary glands. Changes in hormonal levels during certain periods of life also disrupt the body’s water balance:
- gestation period;
- premenopause and menopause.
During pregnancy, increased thirst occurs due to toxicosis. Vomiting and nausea contribute to the accelerated removal of fluid from the body.
Pathological sources of development
Dry mouth at night during sleep can appear due to certain diseases. Difficulty breathing due to enlarged adenoids, rhinitis and inflammation of the sinuses becomes the reason why the patient constantly breathes through the mouth.
Diabetes
A dry tongue is the first sign of the development of the disease. Secondary signs of endocrine dysfunction are presented:
- frequent urination;
- weight loss - for no apparent reason;
- general weakness, attacks of dizziness.
The combination of these symptoms indicates serious problems in the functionality of the body. The patient needs a full diagnostic examination with blood donation to check blood glucose levels.
CNS diseases
Pathologies of the nervous system lead to problems regulating salivation. The main diseases include:
- Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease;
- trigeminal neuritis;
- cerebrovascular diseases.
Chronic circulatory failure in parts of the brain leads to impaired functionality of individual organs. Pathologies are more common in older patients who have crossed the 60-year mark.
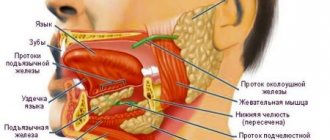
Salivary gland dysfunction
An adult healthy person produces up to one and a half liters of salivary secretion daily. Disruption of the salivary glands is provoked by the following pathologies:
- Sjögren's disease;
- epidemic viral parotitis;
- tumors of malignant or benign etiology;
- salivary stone disease.
Symptoms of a lack of saliva are more pronounced when eating, when the glands must actively produce additional secretions.
Gastrointestinal pathologies
A whitish or yellowish coating on the tongue and dry mouth are the main signs of impaired functionality of the digestive tract. Changes in condition occur when:
- pancreatitis;
- gastroenteritis;
- cholecystitis;
- hepatitis A;
- gastroduodenal ulcers.
Biliary dyskinesia, combined with gallbladder diseases, has additional symptoms. A sign of pathology is considered to be a bitter taste and pain in the area of the right hypochondrium.
Consequences
Dryness itself is not dangerous if it occurs infrequently and does not cause discomfort. But an increase in the symptom can disrupt sleep and prevent sleep at night, cause insomnia and, as a result, chronic fatigue and irritability. Thinned mucous membranes can become damaged, bleed, become covered with ulcers, and interfere with normal eating and drinking.
Constant dryness will worsen the quality of life and affect all areas of it: career, personal life, communication with loved ones. If the disease causing the symptom is not treated, it will become chronic or cause serious consequences.