Herpangina is one of the most common viral diseases in children. Almost everyone experiences this disease in childhood, although this diagnosis also occurs in adults. From a scientific point of view, the very name “herpetic sore throat” was incorrectly given to the disease. Previously, the disease was little studied. Scientists, noticing the similarity of rashes during the disease with those of herpes, came to the conclusion that the causative agent of the disease was the herpes virus, and gave the disease a name that has stuck and is found in the medical literature in exactly this form. Although the disease has nothing in common with herpes infection. It has been established that the cause of herpetic sore throat is enteroviruses - Coxsackie viruses of groups A and B and ECHO viruses (echoviruses). In medical reference books you can find different versions of the names of this disease: aphthous tonsillitis, vesicular pharyngitis, herpetic tonsillitis, herpangina, etc.
As already mentioned, children under ten years of age are at risk: infants, preschoolers and children of primary school age. The severity of the disease depends on the age of the child. The disease is most severe in children in the first year of life. Preschoolers are more often infected because at this age they do not pay due attention to hygiene, have contact with animals and are often in children's groups. To become infected, it is enough to eat unwashed fruit. This should also include the immaturity of immunity at an early age. The disease is highly contagious, and often its outbreaks become epidemic. It is noteworthy that this disease does not occur in babies in the first months of life - the antibodies found in mother's milk create some kind of immunity to herpangina.
One can trace the obvious seasonality of herpetic sore throat: the peak occurs in summer and autumn. As a rule, having been ill once, a child becomes immune to re-infection, so this disease is less common among adolescents and adults.
Infection can occur in one of three ways:
- airborne
- contact
- fecal-oral.
With the airborne method, infection occurs by sneezing, coughing, or talking with a carrier of the virus. In case of contact - through discharge from the nasopharynx. With the fecal-oral method - through dirty hands, through unwashed food, toys and pacifiers, which is especially typical for children.
Even a recovering person can still spread the infection around him for about a month, so it is believed that herpes sore throat is highly contagious: a child can easily become infected in kindergarten from a baby who does not even have obvious symptoms of the disease. If one family member gets sick, most likely everyone will suffer from the disease.
How does infection spread throughout the body? First, the virus from the nasopharynx reaches the intestinal lymph nodes through the lymph flow. Already in the intestines, the virus gains strength and enters the blood, and severe inflammation begins in the oropharynx.
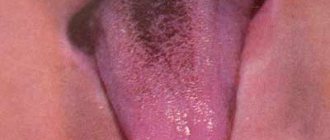
What are white dots on the tonsils
Plaque can take the form of single white dots of varying sizes - from one to several millimeters. Their consistency can be soft, cheesy (caseous), dense or hard.
Every day, the tonsils encounter microbes that enter through the nasopharynx. In the lacunae, pathogenic microorganisms come into contact with the epithelium of the tonsils. In response to the penetration of bacteria, local inflammation develops. It activates the immune system and the production of antibodies.
The epicenter of resistance to infection is the follicles of the tonsils. They are groups of lymphoid immunocompetent cells. The result of the struggle is accumulation of destroyed cells and bacteria in the lacunae and at the site of the follicles. Gradually the plugs are impregnated with calcium salts and harden.
The resulting white dots on the tonsils consist of:
- from the remains of dead leukocytes;
- destroyed epithelial cells;
- microbes;
- calcium salts.
Bacterial examination of the contents of plugs reveals streptococci, staphylococci, and pneumococci.
What kind of disease is this and what are its causes?
Chronic tonsillitis is the most common cause of plug formation.
In addition, white lumps on the tonsils may appear:
- with weakened immunity;
- frequent sore throats;
- herpetic infection;
- fungal infection - candidiasis;
- caries;
- viral infections - influenza, ARVI.
With and without fever
The appearance of white spots on the tonsils may be accompanied by an increase in temperature. This is observed:
- with follicular or lacunar tonsillitis;
- influenza and acute respiratory viral diseases;
- herpetic infection;
- exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis.
The tonsils enlarge, their hyperemia and swelling are revealed, their surface loosens.
White spots on the tonsils may appear without fever. This happens:
- with candidiasis;
- with chronic tonsillitis without exacerbation.
To establish the cause of white dots on the tonsils, it is necessary to do a bacteriological analysis of them.
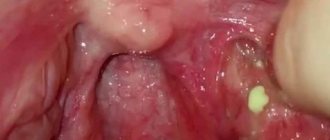
White lumps with an unpleasant odor
With chronic tonsillitis, white lumps with an unpleasant odor appear in the tonsils. They often have a cheesy or hard consistency. They are called tonsilloliths. The putrid odor is caused by the activity of pathogenic microorganisms. The disease occurs without sore throat.
With inflammatory processes in the throat or nasopharynx, tonsillitis increases.
Other symptoms
With exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, follicular or lacunar tonsillitis, in addition to plaque on the tonsils, there is a sore throat, difficulty swallowing, enlargement and tenderness of the submandibular lymph nodes. Symptoms of intoxication appear: headache, weakness, lack of appetite. At night there may be heavy sweats and sleep disturbances.
With acute respiratory viral infections, patients complain of body aches, pain in the muscles and when moving the eyeballs, cough, runny nose, and chest congestion.
Reasons for appearance
There are several reasons why white plaque appears on the tonsils. So, a white spot on the tonsils may indicate a pathology developing in the body.
Thrush
Candidiasis (thrush) is a disease caused by fungal bacteria Candida Albicans. These bacteria thrive and thrive in warm, high-sugar environments, so the oral cavity is a good place to be.
The mucous membrane of the throat is often subject to candida attack, the symptom of which is the appearance of white plaque and spots on the tonsils.
Stomatitis
Stomatitis is a common inflammatory process of the oral mucosa. The main manifestation of the disease is white plaques in different parts of the oral cavity, as well as on the tonsils.
So, spots can affect: the tongue, the inner sides of the cheeks and lips. The formations are painful and cause considerable discomfort to the person.
- What should you do if white lumps with an unpleasant odor come out of your throat?
The risk group for infection includes children and pregnant women.
Angina
Sore throat is an infectious disease.
Symptoms of the disease are:
- pain in the throat;
- white dots on one tonsil or both;
- temperature rise to +38…+39°C.
Plaque on the tonsils without fever may be a harbinger of developing purulent tonsillitis.
Diphtheria
Another disease that can cause the appearance of white spots on the tonsils is diphtheria. The cause of the disease is the entry of harmful microbes into the human body.
Symptoms of diphtheria include:
- enlarged cervical lymph nodes;
- difficulty breathing and swallowing food;
- the presence of a gray-white film on the tonsils.
Diphtheria differs from tonsillitis in the absence of high fever.
After ARVI in a child
Children suffer from acute respiratory viral diseases quite often. This is due to:
- immaturity of the child’s immune defense mechanisms;
- high crowding in children's groups.
Sometimes after an acute respiratory viral infection, white dots or spots are found on the child’s tonsils, enlargement, swelling of the tonsils, and redness of the palatine arches. This indicates the addition of a bacterial infection and the development of a sore throat. In this case, you should immediately seek medical help.
Timely and correct treatment of sore throat will protect the child’s body from complications.
A white coating may appear on the child’s tonsils without fever. This happens when oral thrush occurs. Thrush is a fungal disease caused by pathogenic fungi of the genus Candida. Candidiasis often develops during antibiotic treatment. The diagnosis is made based on examining a smear from the tonsil under a microscope. Specific antifungal drugs are used in treatment.
White spots in a child's throat
In infants, the main cause of whitish plaque on the oral mucosa is candidiasis. This is due to the complete sterility of the baby’s skin and mucous membranes at birth.
Therefore, by inhaling air, receiving mother’s milk or formula from a bottle, or putting his fingers into his mouth, the baby populates the oral cavity with microflora. Sometimes in this way he becomes infected with a fungal infection, which causes unpleasant symptoms.
On the throat of a preschool child, a white coating most often forms against the background of acute tonsillitis.
Sore throat is an exclusively bacterial disease, fraught with serious complications, therefore it must be treated with the utmost care and not neglect antibiotics.
A red throat with white dots in a child rarely indicates the presence of diphtheria, since most modern people are vaccinated against this extremely dangerous infectious disease.
- Thick white snot in adults and children - causes and treatment
Attention
If you suspect the development of this pathology, you should immediately call an ambulance and go to the hospital inpatient department for the administration of anti-diphtheria serum. This can save a child's life.
In any case, if a child has spots on the tonsils, especially against the background of fever and poor general health, he should be seen by a doctor immediately.
How to remove white dots
In order to remove white lumps in the tonsils, use local antiseptic bactericidal agents. They are available in a wide range in the form of sprays, lozenges or tablets. Rinsing helps a lot. Traditionally, solutions of soda, table salt with iodine, furatsilin, chamomile and sage decoctions are used for this. You can use a solution of Metrogyl, Miramistin.
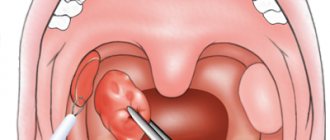
It is impossible to clean the tonsils from white lumps at home. This is done by an otolaryngologist by vacuum extraction of plugs or washing the tonsils with antiseptic solutions.
It is not recommended to remove a white dot containing pus from the tonsil on your own. In the acute period of the disease, this is prohibited.
Tonsillomycosis as a cause of white spots in the throat
Tonsillomycosis is a fungal infection of the tonsils . In common parlance, this disease is called fungal tonsillitis, but this is not entirely correct.
Sore throat is an inflammation in the tissues of the tonsils, but with tonsillomycosis the inflammatory process does not occur. There is no sore throat or fever. Tonsillomycosis affects the pharynx and tonsils.
The causative agent of the disease is usually a fungus of the genus Candida, which can cause such a common disease as candidal stomatitis. Candidiasis can also cause white spots on the tonsils, but in this case they are not the only ones affected. White spots can spread to the surface of the gums, palate, tongue, and cheeks.
Candida fungi are classified as opportunistic. This means that they can be present in the body of a completely healthy person, without causing him any discomfort up to a certain point. When unfavorable factors occur, fungi begin to multiply intensively, causing the development of the disease. These factors include: decreased immunity, taking antibiotics, untreated colds.
Tonsillomycosis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of beige or white spots and dots of various sizes on the tonsils, soft palate and arches;
- when trying to remove white plaque in the throat, this can be done quite easily, but reddened mucous membrane usually remains underneath;
- redness of the throat;
- epithelial detachment occurs in the affected areas.
With tonsillomycosis, the patient complains of discomfort when swallowing saliva and food, a sore throat, the body temperature may rise slightly, pain radiating to the ears occurs, and general health deteriorates.
Treatment of tonsillomycosis
Treatment of white spots on the tonsils should only be prescribed by a doctor after conducting a microbiological examination of the plaque, taking an analysis for the sensitivity of the fungus to drugs, and a blood test for the presence of an inflammatory process.
At home, unpleasant symptoms can be reduced by rinsing with various solutions: soda, honey, aloe juice, as well as calendula decoction, tea tree essential oil.
White spots in the throat can be eliminated with pharmaceutical antiseptics such as Miramistin and Chlorhexidine. Sore throats are also relieved with the help of lozenges and aerosols, for example, Stopangin, Hexoral, Tantum Verde.
Correct treatment
For the treatment of sore throat, or exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, in an adult the following is prescribed:
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- Irrigation or washing of the tonsils with an antiseptic solution.
- Gargling with bactericidal agents.
- Complex vitamin therapy to improve immunity.
- Physiotherapy.
White lumps on the tonsils are removed by vacuum cleaning the tonsils.
Accurate fulfillment of all doctor’s orders contributes to a quick recovery. Incorrect or self-treatment can lead to the development of complications.