What kind of coating on the tongue indicates health problems?
If there is a thickening of the plaque, a change in its color and the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the mouth , this is already the result of the activity of bacteria and fungi. Of course, the body is not a sterile substance and microorganisms are always present in it, but the immunity of a healthy child controls their numbers. When immunity decreases or any disease occurs, there is a significant increase in pathogenic bacteria and fungi, which is accompanied by the formation of plaque on the child’s tongue.
Treatment
Based on the results of the examination, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
In each individual case, the treatment complex is selected individually based on the reasons for the formation of black deposits on the tongue, the patient’s age and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Treatment of black plaque:
- If the cause of the formation of black deposits is dental problems , treatment should be performed by a dentist.
- In cases where plaque has formed due to prolonged antibacterial therapy, the doctor cancels it or prescribes another drug.
- For candidiasis, antifungal drugs are prescribed (Fluconazole, Pimafucin)
- If you have stomatitis and fungal infection, rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions (Chlorophyllipt, Hepilor).
- For gastritis, antacids (Maalox) and drugs to enhance the protective properties of the gastric mucosa are prescribed .
- In case of vitamin deficiency, are prescribed .
- If the cause of the black plaque is poisoning, it is recommended to take sorbents (Enterosgel, Polysorb, activated carbon).
If necessary, the doctor prescribes additional medications:
- probiotics (Acipol, Linex, Bifidumbacterin) and prebiotics (Duphalac, Lactusan) to populate the intestines with beneficial microorganisms and stimulate the production of your own healthy microflora;
- interferons to strengthen the immune system (Cycloferon, Kagocel).
Important! The specialist also gives mother and child recommendations on nutrition and oral hygiene, which must be strictly observed during the period of active treatment and after it.
Causes of plaque on the tongue
There are many reasons why various plaques may appear on the tongue: from the banal consumption of foods that can change the color of the tongue, to serious health problems that require immediate medical attention.
Read also: Computer anesthesia STA – dentistry WITHOUT PAIN!
The very first thing you need to do when you discover strange coatings on a child’s tongue is to remember what the baby ate in the last 24 hours. Very often, sweet carbonated drinks, caramels or other sweets contain active dyes that can give the oral mucosa the most exotic shades: crimson, purple, green, orange and others. Even natural berries and fruits can radically change the color of the tongue. Therefore, there is no need to panic right away. You should ask the child to brush his teeth and tongue, and then evaluate their condition and color. If the plaque has not changed or has reappeared without connection with food intake, then this is a reason to urgently visit your pediatrician.
Causes of turning blue
If a child’s tongue turns blue, then only a doctor can identify the problems that helped provoke the development of such a process. The following reasons are identified due to which a bluish tone is observed on the surface of the organ:
- Kidney diseases, such as total or diffuse cyanosis. There is a decrease in the required volume of oxygen in the body, which provokes the appearance of a blue tint not only on the surface of the papillae, but also on the walls of the oral cavity.
- Diamond-shaped glossitis - with its development, the surface becomes dense in structure and turns blue. The disease tends to occur without symptoms. Therefore, identifying a non-standard color should not be ignored.
- Iron deficiency anemia - a deficiency of vitamin B12, iron, and folic acid is detected in the body. The signal for treatment is not only a specific tone in the mouth, but also excessive pallor of the skin;
- Pathological processes with the lungs or heart muscle - a bluish tone appears on the surface or a deep purple color of the external receptors. If the abnormal color occurs on the lower part of the organ, then the problem lies in the blood circulation, which leads to cardiopulmonary failure.
- Kidney failure - a bluish tint is fixed on the edge of the root, in front of the pharynx.
- A sharp bluish discoloration of the surface may indicate poisoning with heavy metals, especially mercury.
- Inflammation of organs in the abdominal cavity - in addition to the non-standard color of the baby’s mouth, increased body temperature and painful discomfort in the lower abdomen are added.
If the baby begins to feel unwell and becomes capricious, you should more closely monitor not only his well-being, but also carefully examine the oral cavity. In some situations, a child's blue tongue may indicate problems with the respiratory system.
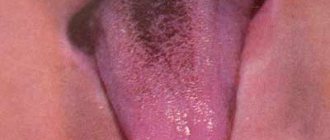
White coating on the tongue
White plaque can be found in the oral cavity of a baby most often.
This phenomenon also happens normally when, after a night’s sleep, a thin white coating without an unpleasant odor is found on the tongue, disappearing after hygiene procedures and not causing any discomfort or unpleasant sensations.
The appearance of a dense whitish plaque, which is extremely difficult to remove from the surface of the tongue and does not disappear after brushing your teeth, may indicate problems with the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, enteritis or dysbacteriosis). This phenomenon is often accompanied by bad breath. In addition, children may present complaints that may indicate gastrointestinal pathology:
- abdominal pain of various localizations;
- bloating;
- stool disorders;
- change in appetite
In order to get rid of such white plaque, it is necessary, first of all, to examine the digestive system and eliminate even the most minor disturbances in its functioning.
Read also: Drilling teeth? NO thanks, we use ICON!
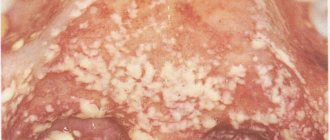
In infants up to 2 months of life, thrush or oral candidiasis is a common occurrence in a nursing mother, especially after taking antibiotics or an error in diet. With this pathology, abundant cheesy white deposits appear on the tongue and cheeks, which are easily removed, and small ulcers are found underneath them. After starting treatment for thrush with antifungal agents and treating the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions, the tongue and other mucous membranes quickly cleanse and regain their previous appearance.
How is diagnosis carried out?
The doctor begins the diagnosis with a visual examination of the patient , assesses the appearance of the tongue and the nature of the deposits, and interviews the child and mother for complaints and associated symptoms.
Next, the doctor prescribes tests and diagnostic procedures:
- clinical blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- blood chemistry;
- culture of microflora from the oral and nasal cavity;
- stool occult blood test;
- Ultrasound of the digestive organs.
If necessary, to clarify the diagnosis, the doctor can give a referral for gastroscopy and colonoscopy .
For your information! A specialist can prescribe all diagnostic procedures in a complex, or several of them separately.
If necessary, the pediatrician gives a referral to see specialists: dentist, otolaryngologist, gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist.
Gray coating on the tongue
A gray coating on the tongue can be a sign of some infectious diseases.
For example, with scarlet fever, on the very first day the mucous membranes become covered with a dirty gray coating, which, starting from the tip of the tongue, gradually disappears and reveals a “raspberry tongue” - enlarged papillae on a bright red background, which is very reminiscent of raspberries.
With diphtheria, gray filmy deposits can be found on the root of the tongue, which are difficult to separate. Such plaques spread to the mucous membranes of the throat, palatine arches and are accompanied by coughing and attacks of suffocation.
Treatment of such infectious diseases is carried out only in a hospital setting. After healing, all plaque on the tongue disappears.
Dehydration in a child can also lead to the formation of a gray coating on the surface of the tongue. At the same time, the mucous membranes look dry and dull. Replenishing the required volume of fluid quickly eliminates this symptom.
What it is
In a healthy child, the tongue has a uniform pink color without spots or plaque. But in the presence of any pathology, spots of various colors and sizes may appear, which represent:
- An uneven accumulation of plaque on the surface of the tongue, which consists of exfoliated epithelium, tiny food particles, and microorganisms.
- Excessive proliferation of epithelium in certain areas of the mucous membranes.
- Limited inflammation.
- Benign or malignant neoplasms.
Let's look at the main reasons for the appearance of various spots and methods of treating them.
Yellow coating on the tongue
A dense yellow coating on the tongue indicates pathology of the liver or biliary tract.
Often in children, diseases of the biliary system occur without a clear clinical picture, and the presence of bile stagnation can only be suspected by a change in the color of deposits on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
If a child has a yellow coating on the tongue , it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor and have an examination of the internal organs and the biochemical composition of the blood.
Read also: Medication sleep - WHAT? For what? HOW?
Bald
Normally, the lingual surface is covered with a large number of small taste buds, which give it a velvety appearance. If such papillae die or atrophy for any reason, “bald” spots appear. They are pink in color, irregular in shape and do not spread to the mucous membranes of the cheeks, lips or gums.
Reasons that can cause the appearance of such pink “bald” spots:
- Inflammatory diseases (glossitis, stomatitis).
- Tongue injuries.
- Burns from heat or chemicals.
“Bald” spots do not cause any inconvenience to children, but may slightly change the taste sensations. It is impossible to cure such formations, since the taste buds cannot be restored.
If you find that your one-year-old or older child’s tongue has become spotted, you should not panic and try to treat it yourself. Also, the appearance of spots on the tongue should not be ignored, as they may indicate the presence of serious diseases. It is necessary to consult a doctor who will find out the exact cause of such changes and, if necessary, select appropriate treatment for the child.
Green coating on the tongue
The appearance of a green coating on the mucous membrane of the tongue often frightens parents, especially if it is found in a newborn or infant.
The most common cause of this phenomenon is candidiasis - a fungal infection of the oral cavity that occurs due to imperfect immune defense in the body of a 1-year-old baby or while taking strong antibacterial drugs.
This plaque has varying color intensities and can spread to other parts of the oral cavity, found on the cheeks, palate and lips. After removing it, you can see the red surface of the tongue with small blisters or ulcers, which cause discomfort to the child.
You should start treating green plaque only after consulting a doctor. Therapeutic measures will consist of taking special drugs with antifungal action and local antiseptics to treat thrush and prevent bacterial complications.
Read also: How bite affects posture and spinal health
Main and rare types of disease
Increased bilirubin in infants is considered normal, but only in the first few days. Gradually the figures are decreasing. If this does not happen, we are talking about the development of a pathological process.
Types of jaundice in newborns (depending on the reasons for its occurrence and severity):
- physiological;
- hemolytic;
- conjugative;
- neonatal;
- nuclear;
- parenchymal;
- obstructive;
- pathological4
- mechanical.
Classification of newborn jaundice allows you to accurately diagnose and determine the direction of treatment. In uncomplicated cases, health is good. Physiological jaundice occurs in 60-70% of infants. It is also called temporary conjugation. Appears on days 3-4 (in premature infants on days 5-6) after birth without signs of anemia and hemolysis. It goes away within 7-14 days.
Conjugation jaundice develops due to the immaturity of any component of the bilirubin metabolic system. Occurs from 2 to 10 days after birth. The disease lasts from 14 to 30 days. Differential diagnosis is difficult, and symptoms may be similar to other types of jaundice. Inpatient monitoring of the young mother and baby is recommended.
Hemolytic jaundice in newborns occurs due to a history of other diseases. These may be: pulmonary infarction, liver damage, septic endocarditis, malignant tumors, malaria. Toxic effects on the body can also cause the development of this form of the disease. Diagnostics shows an increased level of stercobilin in feces and the presence of hyperbilirubinemia.
Neonatal jaundice of newborns is provoked by immaturity of liver cells, increased production of bilirubin and low ability of blood serum to bind it. If a decreasing trend in indicators is not observed, diagnostics are necessary to determine the causes. Neonatal jaundice is characterized by insufficient amounts of enzymes that are needed to neutralize excess bilirubin in the blood.
A severe form of the disease is considered to be kernicterus, which affects the brain, which is not bound by bilirubin. Symptoms develop rapidly during the first two days after birth. The baby has a mask-like facial expression, convulsions, tension in the muscles of the neck and head, and wheezing when listening. This type of jaundice in newborns has serious health consequences.
Parenchymal type is a severe form of the disease that requires immediate medical attention. It is of hepatitis origin. Obstructive jaundice is a pathological syndrome, the cause of which may be disturbances in the metabolism of metals, proteins, anatomical defects and obstruction of the bile ducts. It appears from the first days of life. Recovery is possible by the second half of the year, provided the form of the disease is uncomplicated.
The obstructive (subhepatic) form of the disease develops against the background of bile duct obstruction. There may be a history of abdominal tumors. In infants, the skin color has a greenish-yellow tint, stool is whitish, and urine is dark. Pathological jaundice in the neonatal period develops rapidly - in the first days after birth. An enlargement of the spleen and liver, and the occurrence of spontaneous bruises on the body are diagnosed. Increased hemolysis may occur if there is a history of Rh factor incompatibility between mother and baby.
Brown coating on the tongue
A brown tongue in a child is not such a rare occurrence. There can be many reasons for this:
- Severe diseases of the digestive system , accompanied by inflammatory changes, stagnation of bile in the bile ducts, and disruption of the digestive processes.
- Constant dehydration of the child's body due to high ambient temperatures or insufficient fluid intake.
- Insufficient intake of B
- Taking certain medications : antibiotics, antiseptic solutions, concentrated herbal decoctions.
It is very difficult to establish the exact root cause of the appearance of such a dark plaque. This can only be done by an experienced doctor, who, after additional examinations, will be able to prescribe the optimal treatment.
Causes of tongue redness
All existing causes of external changes in the language, including its color, can be divided into two groups. The first group of factors are easily solvable problems that do not signal internal disorders and are not a cause for concern on the part of parents. These include:
- consumption of coloring foods and drinks,
- eating too hot (cold) food;
- mechanical trauma from a brush, teeth, lollipop, etc.
The second one combines negative causes that are inextricably linked with pathological processes that are hidden or obvious in the child’s body:
- inflammation of the taste buds;
- any inflammatory processes caused by viruses or infection;
- intoxication of the body due to poisoning;
- taking medications (antibiotics);
- allergic reaction to food, medications.
- lack of vitamins and microelements.
Only a doctor can identify the true cause of changes in the color and texture of the tongue. Parents should not engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication; this will only mask the problem and complicate the doctor’s work.
Black coating on the tongue
The presence of a black coating on a child’s tongue looks quite scary, and there may be several reasons for this phenomenon:
Bacterial sore throat is often accompanied by the appearance of dark plaques on the mucous membranes, even black. In this case, the child will have signs of inflammation in the tonsils: red throat, high fever, pain when swallowing, weakness.
Hidden forms of diabetes mellitus, which lead to persistent disruption of the acid-base balance in the body. Excess acid or acidosis will cause darkening of the tongue.
Taking some antibiotics causes the growth of pathogenic microflora in the mouth, which causes the mucous membranes to become permanently stained black.
Treatment of such plaque will consist of eliminating the causes that caused its appearance. After a sore throat is treated, medications are stopped, or diabetes is identified and compensated for, this symptom will most likely go away on its own.
Dark
Dark spots on the tongue often occur when eating food that contains dark pigments that color the plaque on the surface of the mucous membranes. Such spots do not pose any danger to the child and disappear after hygiene procedures. But there are a number of conditions that manifest as dark spots in the mouth and which can have very serious consequences.
Black
Black spots on the tongue in children most often appear during a long course of antibiotic therapy as a result of the active proliferation of microorganisms and fungi. Blackening of the tongue develops gradually and can last up to 2-3 weeks. The main treatment for this condition is to restore normal microflora in the child’s intestines and oral cavity. For this purpose, eubiotic drugs are prescribed (for example, Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin).
It is extremely rare that black spots on the tongue appear as a result of deep degenerative processes accompanied by necrosis of areas of the mucous membrane. This condition is very dangerous and requires emergency medical attention. The treatment of such spots is often surgical.
Blue
Blue spots in a child's mouth are a rare occurrence. They may appear in the following situations:
- The presence of severe heart failure due to heart disease and defects. Spots on the tongue appear due to stagnation of blood in the venous bed and are accompanied by blue discoloration of the lips and limbs. Their treatment consists of eliminating cardiac pathology and normalizing blood microcirculation in the vessels.
- With the growth of a benign vascular tumor - hemangiomas. This blue spot is most often single. Treatment is only possible through surgery.
Blue coating on the tongue
A blue tongue is a sign of blood stagnation.
Very often, various diseases of the cardiovascular (congenital heart defects, arrhythmias, heart failure) and nervous system (hemorrhages, cysts, epilepsy) lead to the fact that blood flows through the tissues more slowly than it should - cyanosis or cyanosis appears on the limbs, lips and language. Therefore, if you notice such a symptom in your child, you should urgently contact your doctor for advice.
Read also: Now the beauty and health of your child is completely in your hands
conclusions
- there are both pathological and non-pathological causes of darkening of the tongue in a young child;
- plaque formation may be accompanied by alarming symptoms, such as vomiting and fever, or may occur without the appearance of additional symptoms and complaints;
- if the plaque does not disappear on its own, but appears again after cleaning the tongue, you should make an appointment for the child to see a doctor;
- Treatment can be prescribed only after a comprehensive examination and clarification of the causes of darkening of the tongue;
- the appearance of the taste organ will return to normal when the causes of the formation of black plaque are eliminated.
Prevention
In order to prevent the appearance of plaque on a child’s tongue, there are a number of preventive measures that many experts focus on:
- The room in which the child lives should always be clean, well ventilated and humidified.
- You should not prescribe antibiotics to your child yourself. The use of such medications must be strictly justified.
- It is necessary to closely monitor the baby's health. If the slightest symptoms appear that indicate a possible disease from the internal organs, you should urgently seek medical help.
- Limit your child's consumption of sweets containing synthetic coloring pigments: sweet carbonated drinks, candies, chewing gum. This will not only prevent the appearance of active staining of the tongue, but will also preserve the health of delicate children's teeth.
If plaque does appear on the tongue, there is no need to try to remove or treat it yourself. Consult your doctor about the possible causes of this phenomenon and the necessary treatment for it.
Posted in For parents by biglamed
What diseases does a red tongue hide?
A red tongue can be a symptom of diseases of various etiologies, including:
- angina;
- flu;
- chickenpox,
- scarlet fever;
- stomatitis;
- glossitis;
- pneumonia;
- Kawasaki disease;
- gastritis;
- severe poisoning;
- renal failure;
- vitamin deficiency (vitamin B deficiency).
As you can see, the list of diseases is quite wide and requires visiting not only an otolaryngologist, but also, if necessary, other specialized specialists: dentist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, etc.
Hypovitaminosis
In the course of careful research, it was discovered that with a lack of vitamins PP and B vitamins in the child’s body, the mucous membrane of the tongue changes its color. Black plaques or spots appear.
Special cases
Difficult to explain cases include the so-called “black hairy tongue.” The nature of this phenomenon is still being studied, and today doctors cannot give a comprehensive explanation. The picture looks like this: at the tip and root of the tongue, the normal pink color remains, while multiple dark papillae grow on the back.