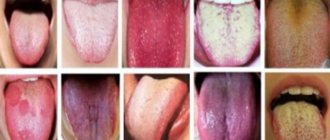
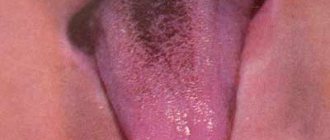
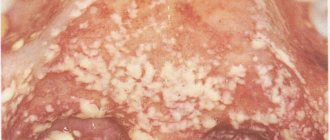
A healthy child's tongue has a soft pink tint , but sometimes a dark gray or black coating appears on the surface of the baby's taste organ.
A change in the color of a child's tongue makes parents seriously worried.
There is no need to panic right away - black coating on the tongue in children is not always pathological .
Why might it appear?
Keep in mind! Most often, a child’s taste organ darkens for the following reasons:
- Eating large amounts of food containing natural or synthetic dyes . Candies, tea, lemonade, dark berries (currants, blackberries, blueberries, mulberries), as well as jams and compotes based on them, can color your tongue dark.
- Taking certain medications. This organ is often colored dark by iron preparations in the form of drops, which are prescribed to the baby to treat anemia. Also, the color of the taste organ often changes during prolonged treatment with antibiotics, or when taking activated carbon.
In rare cases, the tongue darkens for reasons unknown to modern medicine.
Thus, the surface of the taste organ may darken due to excessive growth of the papillae of the tongue, followed by their keratinization and darkening .
Stay up to date! This phenomenon is called “villous tongue”; in the absence of complaints, special treatment is not required, and the condition of the taste organ is normalized within a few weeks.
Less commonly, the cause of darkening of a child’s tongue is various pathological conditions of organs and body systems:
- gastritis;
- colitis;
- enteritis;
- pathologies of the gallbladder and pancreas;
- acute deficiency of B vitamins and vitamin PP;
- dysbacteriosis;
- stomatitis;
- caries;
- oral candidiasis;
- Crohn's disease;
- lead poisoning;
- immunodeficiency, HIV;
- severe dehydration;
- infectious diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract: sore throat, ARVI, bronchitis.
Note! The cause of dark plaque in a baby can also be acidosis - a shift in the acid-base balance of the body towards increasing acidity.
Causes of reactive pancreatitis in children
Unlike adults, children more often react to infections and inflammations by disrupting the functioning of the pancreas.
The most typical causes of reactive pancreatitis in children are1:
- gross violation of diet;
- regular consumption of fatty and sweet foods, foods high in preservatives and dyes;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics;
- frequent ARVI, flu, colds;
- repeated infection with helminths;
- allergic reaction (to food or medicine);
- congenital pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, contributing to the development of inflammation of the pancreas;
- stress, emotional overload.
Medical practice shows that the key causes of reactive pancreatitis in children are related to nutrition. Namely, with violation of his regime, introduction of harmful foods into the diet, and passion for fast food.
Products that can provoke reactive pancreatitis in children:
- fried foods (both vegetable and butter);
- fatty foods;
- smoked meats;
- spicy seasonings;
- fast food (burgers, chips, French fries, crackers);
- sweets with dyes and artificial additives;
- carbonated drinks;
- packaged juices.
Associated symptoms
If a black coating is detected on the child’s organ of taste, you should pay special attention to the child’s accompanying symptoms and complaints.
Possible symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting;
- diarrhea with particles of undigested food;
- loss or abnormal increase in appetite;
- stomach ache;
- dry or bitter mouth;
- weakness;
- temperature increase;
- headache;
- redness of the mucous membranes of the mouth and tonsils;
- pain when swallowing.
It is worth noting! Sometimes, even in the presence of dark gray and black deposits on the tongue, the child voices absolutely no complaints.
The complete absence of accompanying symptoms is characteristic of fungal infection of the mucous membranes of the mouth, as well as when plaque occurs for non-pathological reasons.
What to look for when examining your tongue
An adult brushes his teeth every day. The same mandatory rule for any person should be a daily inspection of the tongue.
When examining the tongue, it is important to pay attention to its:
- color;
- plaque;
- surface structure;
- mobility;
- symmetry;
- the appearance of bubbles, pimples, spots and other inclusions.
If a black coating appears on your tongue, it is also important to remember other symptoms:
- past illnesses or stress;
- temperature increase;
- drug treatment;
- consumption of alcohol, nicotine, etc.
In what case should you consult a doctor and undergo an examination?
If the deposits disappear on their own after rinsing your mouth or drinking, there is no need to go to the hospital, since the cause of the darkening of the tongue is most likely food.
If the plaque does not disappear when rinsing, but appears again after cleaning the tongue, you should make an appointment with a pediatrician.
If the blackening of the surface is accompanied by acute abdominal pain, diarrhea or vomiting, you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance.
You should not try to treat your child yourself or try folk remedies without consulting a specialist and finding out the reasons for the blackening of the tongue.
You should know! Self-medication can cause serious harm to the baby's health.
Causes of black plaque
Factors that cause plaque in adults are associated with the following conditions:
- Acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) and other infectious diseases.
- Long-term use of antibacterial agents, as a result of which the immune system weakens and dysbacteriosis develops.
- Slagging of the body.
- Excess weight.
- Violation of metabolic processes.
- Abuse of fatty foods and high-carbohydrate foods.
Crohn's disease is a rare autoimmune pathology. The melanin pigment is concentrated in the form of dark blue spots on the skin, tongue papillae and other mucous tissues. The condition occurs when the basic function of the adrenal glands is suppressed, and the organs of the digestive canal become inflamed. Treatment is carried out using hormonal and antibacterial agents, as well as immunosuppressants. The color of the tongue is restored as you recover. The plaque cannot be washed off by any other means.
How is diagnosis carried out?
The doctor begins the diagnosis with a visual examination of the patient , assesses the appearance of the tongue and the nature of the deposits, and interviews the child and mother for complaints and associated symptoms.
Next, the doctor prescribes tests and diagnostic procedures:
- clinical blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- blood chemistry;
- culture of microflora from the oral and nasal cavity;
- stool occult blood test;
- Ultrasound of the digestive organs.
If necessary, to clarify the diagnosis, the doctor can give a referral for gastroscopy and colonoscopy .
For your information! A specialist can prescribe all diagnostic procedures in a complex, or several of them separately.
If necessary, the pediatrician gives a referral to see specialists: dentist, otolaryngologist, gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist.
The baby's tongue has turned black
If the baby’s tongue suddenly turns black, but he hasn’t eaten or chewed anything, then the plan of action is obvious. Any such manifestation in children should be a signal to consult a doctor.
As a rule, the doctor in this situation will examine the child and begin by ordering “basic” tests such as a general blood test, urine test and ultrasound of internal organs.
There can be many reasons for a black coating on the tongue. And if this manifestation was not the result of banal contact with food dyes, then there is no need to delay revealing its causes.
Sources used:
- James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. — Saunders Elsevier, 2006.
- Notes of a good dentist / E.G. Aghajanyan. - M.: Omega, 2011.
- Northwestern State Medical University named after I. I. Mechnikov
- Treatment of diseases of gums and teeth using traditional and non-traditional methods / E.L. Isaeva. - M.
Treatment
Based on the results of the examination, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
In each individual case, the treatment complex is selected individually based on the reasons for the formation of black deposits on the tongue, the patient’s age and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Treatment of black plaque:
- If the cause of the formation of black deposits is dental problems , treatment should be performed by a dentist.
- In cases where plaque has formed due to prolonged antibacterial therapy, the doctor cancels it or prescribes another drug.
- For candidiasis, antifungal drugs are prescribed (Fluconazole, Pimafucin)
- If you have stomatitis and fungal infection, rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions (Chlorophyllipt, Hepilor).
- For gastritis, antacids (Maalox) and drugs to enhance the protective properties of the gastric mucosa are prescribed .
- In case of vitamin deficiency, are prescribed .
- If the cause of the black plaque is poisoning, it is recommended to take sorbents (Enterosgel, Polysorb, activated carbon).
If necessary, the doctor prescribes additional medications:
- probiotics (Acipol, Linex, Bifidumbacterin) and prebiotics (Duphalac, Lactusan) to populate the intestines with beneficial microorganisms and stimulate the production of your own healthy microflora;
- interferons to strengthen the immune system (Cycloferon, Kagocel).
Important! The specialist also gives mother and child recommendations on nutrition and oral hygiene, which must be strictly observed during the period of active treatment and after it.
How to treat spots on the tongue?
Treatment of any changes in a child’s oral cavity should be based on eliminating the cause of the problem. Approaches to the treatment of spots on the tongue are varied, since not only dental diseases can cause them.
Most often, the child and parents are faced with stomatitis or a fungal infection of the oral cavity. Principles for treating this problem:
- careful adherence to oral hygiene;
- taking antibacterial or antiseptic drugs, most often local in the form of sprays and rinses;
- taking local antifungal agents (in case of candidiasis, but not for prevention);
- taking local immune activators.
In the case of spots on the tongue as a manifestation of an allergic reaction, you first need to determine what caused it and stop contact with the irritating substance. Additionally, antihistamines are used. In some cases, allergy symptoms appear due to incorrect, too rapid introduction of complementary foods to infants4.
If spots form due to a herpes infection, antiviral agents should be used, most often acyclovir drugs. Treatment of blisters and sores should be carried out using hydrogen peroxide, and then lubricated with an oil solution based on eucalyptus. Vitamin complexes and immune medications will help speed up recovery.
Spots that arise as a result of disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract disappear after exposure to the cause of the problem. Depending on the disease, the child may be prescribed medications that improve gallbladder function, normalize acidity in the stomach, probiotics and live beneficial bacteria to improve intestinal function.
conclusions
- there are both pathological and non-pathological causes of darkening of the tongue in a young child;
- plaque formation may be accompanied by alarming symptoms, such as vomiting and fever, or may occur without the appearance of additional symptoms and complaints;
- if the plaque does not disappear on its own, but appears again after cleaning the tongue, you should make an appointment for the child to see a doctor;
- Treatment can be prescribed only after a comprehensive examination and clarification of the causes of darkening of the tongue;
- the appearance of the taste organ will return to normal when the causes of the formation of black plaque are eliminated.
Is plaque after taking antibiotics normal?
When taking antibiotics, it is normal for .
The symptom disappears within two weeks and does not require specific treatment.
In some cases, the doctor may prescribe antifungal drugs or drugs to strengthen the immune system of a small patient.
The reaction in the form of a black tongue occurs due to the active reproduction of certain types of pathogenic microorganisms.
This effect is provoked by numerous types of medications from the antibiotic category.
Belching in toddlers, general recommendations
The introduction of complementary foods should only be done on the recommendation of a pediatrician.
If belching does not cause concern in the baby, then just be patient. In newborns, the nervous system is not yet fully developed. Therefore, the likelihood of food moving back through the esophagus is high. As you grow, the frequency of regurgitation decreases. Options to solve the problem:
- Normalization of feeding. Some mothers think that the little one is malnourished. Especially if the baby is restless or requires increased attention. The baby will regurgitate excess milk - this is a physiological mechanism of protection against overeating. If the toddler is gaining weight according to age norms, then you should not increase his diet.
- Clothing – tight swaddling is now a thing of the past. Choose loose, comfortable clothes that do not put pressure on your tummy.
- Complementary foods are introduced according to the pediatrician's recommendations. Introduce any new dish gradually, starting with small quantities. Carefully observe your baby's behavior after introducing him to new food. If any alarming symptoms appear, then you will have to wait a while with this dish. This does not mean giving up completely. Just set it aside and try again after a while.
- Smoking is a bad habit. You should generally forget about cigarettes in the room where the baby is. In addition to problems with belching, the toddler runs the risk of problems with the respiratory system and other vital systems.