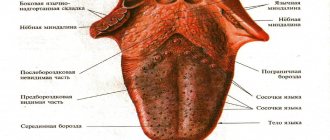
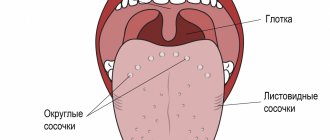
- What does a normal tongue look like?
- White spots on a child's tongue
- Red spots on a child's tongue
- How to treat spots on the tongue
- Imudon® in the fight against inflammatory diseases
The tongue is considered an indicator of health, so the appearance of spots on it should alert parents, even in the absence of other manifestations. However, before you begin to calculate the reasons that caused the formation of plaque, analyze your baby’s diet. Very often, tongue spotting is caused by eating dyes or foods containing chemical dyes3.
Spots in the oral cavity of children are formed from the influence of various factors. This symptom does not always indicate a disease in the oral cavity. Parents' attentiveness to the baby's condition allows the disease to be quickly detected and eliminated.
What it is
In a healthy child, the tongue has a uniform pink color without spots or plaque. But in the presence of any pathology, spots of various colors and sizes may appear, which represent:
- An uneven accumulation of plaque on the surface of the tongue, which consists of exfoliated epithelium, tiny food particles, and microorganisms.
- Excessive proliferation of epithelium in certain areas of the mucous membranes.
- Limited inflammation.
- Benign or malignant neoplasms.
Let's look at the main reasons for the appearance of various spots and methods of treating them.
White
In a baby, the appearance of white spots on the tongue most often indicates thrush - a fungal infection of the mucous membranes due to a decrease in immune defense in the body or when taking antibiotics. Such spots are located asymmetrically, can have a variety of sizes, and are often covered with a cheesy coating.
If a child shows signs of thrush on his tongue, then it is necessary to visit a pediatrician who will find out the reasons for its appearance. Delay in treatment can cause progression of the disease and inflammation of the mucous membrane, which will cause pain and discomfort in the child. You cannot try to remove the plaque on your own; this can lead to additional trauma. To eliminate such white spots, it is most often recommended to treat the child’s oral cavity with a weak solution of baking soda or ordinary brilliant green. In more severe cases and with relapse of the disease, it may be necessary to take antifungal drugs.
Types of plaque and reasons for its appearance
To understand why the tongue becomes spotted, you need to take a closer look at the plaque covering it. Usually it precedes spots that form as a result of a violation of its structure or after the plaque “peels off.” The film on the tongue of an infant or older child can be of the following shades:
- Thrush
Thin white coating
. Often observed in newborns and children in the first year of life. Appears in the morning, structurally it is a thin, transparent film of whitish color. It is enough to remove the deposits with a damp gauze swab so that they no longer appear during the day. This plaque is an allergic reaction of the baby to an artificial formula or to foods that make up the mother’s diet (during breastfeeding).
- Curdled white coating.
A dense film of rich white color with hidden ulcers, foul-smelling and difficult to remove - a symptom of thrush (candidiasis) or stomatitis. In infants with such diseases, instead of a solid plaque, white spots of very impressive size often form. - Yellow plaque
. Formed when there is a malfunction of the child’s liver, kidneys or bile ducts. - Fungal infection of the tongue
Gray plaque
. The initial sign of dangerous childhood diseases - scarlet fever and diphtheria. Sometimes this appearance of the taste organ indicates severe dehydration. In both cases, you need to start treating the root cause of the symptom as soon as possible, since such diseases are dangerous not only for the health, but also for the life of the baby.
- Plaque in the form of green spots
. The manifestation indicates a fungal infection in the oral cavity of a small patient. Usually the rash spreads to the palate, cheeks, and mucous membranes of the lips. - Brown deposits
. The result of a malfunction of the digestive system, accompanied by stagnation of bile in the bile ducts. In infants, the symptom often signals dehydration; in older children, it indicates a deficiency or malabsorption of B vitamins. In addition, if brown spots appear on the baby’s tongue, an allergy to herbs can be suspected, even if the nursing mother takes them. - Black deposits
. They are a consequence of taking certain antibiotics, overdose or the body’s rejection of the drug. Sometimes the reasons for the appearance of black plaque lie in intestinal disorders: colitis, enteritis and gastritis.
Geographical
If red spots and a white coating along their edges appear on the tongue, then this is a sign of a geographic tongue - desquamative glossitis. The disease is not inflammatory in nature and may indicate some hormonal disorders, worms and problems in the digestive system. Such spots do not have smooth outlines, they quickly change their location and do not bother the child in any way. They can be oval, round or have fancy shapes.
This disease lasts a long time and often goes away on its own after some time, even without specific therapy. Sometimes antiseptics, vitamins and drugs that accelerate tissue regeneration processes are used to treat geographic tongue. But most experts (for example, Dr. Komarovsky) believe that there is no need to treat geographic spots.
If formed at the tip
If redness in the form of a spot appears at the very tip of the tongue of an infant, then it is most likely caused by a malfunction of the digestive system. In this case, the middle part is often covered with a whitish coating.
In older children, there are a large number of factors that cause such damage. These include common injuries - biting, cuts from hard food or candy, burns from hot drinks or food
.
An improperly formed bite is also a constant source of injury.
, especially some varieties of this pathology. Then, while eating, the child often bites the tip of his tongue.
Reds
The appearance of red spots on a child’s tongue is a sure sign of an infectious or inflammatory process in the oral cavity:
- stomatitis;
- glossitis;
- bacterial dermatosis;
- herpetic infection.
Also, red spots may be due to an allergic reaction or consumption of foods that are bright red in color.
Very often, such formations are accompanied by unpleasant symptoms: pain in the tongue, a feeling of discomfort, increased salivation. Due to pain, children may be capricious and refuse to eat or drink. The general condition may also suffer - body temperature rises.
Only a doctor should treat red spots. After establishing an accurate diagnosis, the following may be prescribed:
- treatment of lesions with antiseptic agents;
- taking antibiotics or antivirals;
- use of anti-inflammatory medications.
How to treat?
Treatment of spots on the tongue without making a correct diagnosis of the disease is prohibited, as it can harm the baby. It is important to know the etiology of their formation.
If your baby has glossitis, stomatitis or other diseases of the oral cavity, the pediatrician may prescribe a consultation with a dentist to select the correct therapy. In most cases, the following drugs are used for this pathology: Stomatidin, Cholisal, Miramistin, etc.
If a gastroenterological problem is detected, the baby must be examined by a gastroenterologist. If spots appear due to microflora disturbances, probiotics (Bifidumbacterin, Linex, Enterol, etc.) can be prescribed.
In severe cases (formation of deep ulcers and lack of effect from treatment), the doctor may insist on surgical intervention.
Each specific case requires an individual approach to therapy.
If the baby has a geographic tongue, the doctor may prescribe: taking multivitamins, treating the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions (for example, Miramistin), as well as drugs that accelerate natural tissue regeneration.
If yellow spots appear, no treatment is required, but the baby needs to be examined to identify the cause of their occurrence.
If a child’s tongue changes due to infectious processes, for example, scarlet fever, you must immediately call a doctor to confirm or refute the diagnosis. Until the pediatrician arrives, you need to isolate the baby. If the disease is confirmed, the following may be prescribed: hospitalization, plenty of warm drinks, treatment of the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions, antibacterial and vitamin therapy, and others (depending on the patient’s condition).
If a baby has red spots that have an allergic etiology, it is most often necessary to prescribe antihistamines (Zodak, Erius, Fenistil) and adsorbents (Polysorb, Smecta, etc.).
Since black spots in most cases are caused by helminthic infestation or long-term use of antibacterial drugs, the use of anthelmintic drugs (after confirmation of the diagnosis) and probiotics (Acipol, Hilak, Bifiform) is recommended.
Dark
Dark spots on the tongue often occur when eating food that contains dark pigments that color the plaque on the surface of the mucous membranes. Such spots do not pose any danger to the child and disappear after hygiene procedures. But there are a number of conditions that manifest as dark spots in the mouth and which can have very serious consequences.
Black
Black spots on the tongue in children most often appear during a long course of antibiotic therapy as a result of the active proliferation of microorganisms and fungi. Blackening of the tongue develops gradually and can last up to 2-3 weeks. The main treatment for this condition is to restore normal microflora in the child’s intestines and oral cavity. For this purpose, eubiotic drugs are prescribed (for example, Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin).
It is extremely rare that black spots on the tongue appear as a result of deep degenerative processes accompanied by necrosis of areas of the mucous membrane. This condition is very dangerous and requires emergency medical attention. The treatment of such spots is often surgical.
Blue
Blue spots in a child's mouth are a rare occurrence. They may appear in the following situations:
- The presence of severe heart failure due to heart disease and defects. Spots on the tongue appear due to stagnation of blood in the venous bed and are accompanied by blue discoloration of the lips and limbs. Their treatment consists of eliminating cardiac pathology and normalizing blood microcirculation in the vessels.
- With the growth of a benign vascular tumor - hemangiomas. This blue spot is most often single. Treatment is only possible through surgery.
Aphthous stomatitis in children
Manifests itself in the form of small individual ulcers on the lips and oral mucosa. Its appearance is provoked by:
- allergic reactions of various types (to food, medications, etc.);
- staphylococci (there are many of these bacteria in carious formations and dental plaque);
- immunity disorders;
- liver diseases.
Aphthous stomatitis in children: symptoms and treatment
Exacerbation occurs mainly in autumn and spring. Ulcerations most often form on the lips, tongue and inside the cheeks (in these places the mucous membrane comes into contact with food and can be injured by the teeth).
Sometimes weakness in the body and fever appear, but often the general condition of the body remains normal.
The size of the ulcers (ulcers) is 5-10 mm. They are covered with a grayish coating and are surrounded by a red, inflamed rim of mucous membrane. There is pain when touching them. It happens that only 1 ulcer forms.
Aphthous stomatitis in children: treatment
The causes of stomatitis in children will influence the nature of treatment. Immediately after the first symptoms appear, it is necessary to adjust the child’s menu, completely eliminating the main allergens (chocolate, honey, berries, citrus fruits, etc.). During illness, you should also not eat spicy foods with added spices.
Often, aphthous stomatitis becomes a reaction of the body to medications, so if a child is taking medications, it would be a good idea to consult a doctor.
Treatment methods:
- Antiallergic drugs. The most frequently prescribed are Suprastin, Diazolin and many others like them.
- Treatment of ulcerations. At the initial stage of the disease, “Miramistin” (they are recommended to spray the aphras using a special sprayer that comes with the drug) and “Cholisal” (ulcers are treated with gel at least 3 times a day) perform well. When the acute symptoms of the disease pass, you can use Solcoseryl, a gel that accelerates the healing of mucosal defects and has an analgesic effect.
- Exposure to UV rays in a physiotherapy room.
- Use of immunomodulators. Firstly, it is worth purchasing a special toothpaste based on lactoferrin, and secondly, you can take a course of Imudon.
- Sanitation of the oral cavity. Since one of the causes of stomatitis is microorganisms, all carious formations must be cured and plaque removed.
Bald
Normally, the lingual surface is covered with a large number of small taste buds, which give it a velvety appearance. If such papillae die or atrophy for any reason, “bald” spots appear. They are pink in color, irregular in shape and do not spread to the mucous membranes of the cheeks, lips or gums.
Reasons that can cause the appearance of such pink “bald” spots:
- Inflammatory diseases (glossitis, stomatitis).
- Tongue injuries.
- Burns from heat or chemicals.
“Bald” spots do not cause any inconvenience to children, but may slightly change the taste sensations. It is impossible to cure such formations, since the taste buds cannot be restored.
If you find that your one-year-old or older child’s tongue has become spotted, you should not panic and try to treat it yourself. Also, the appearance of spots on the tongue should not be ignored, as they may indicate the presence of serious diseases. It is necessary to consult a doctor who will find out the exact cause of such changes and, if necessary, select appropriate treatment for the child.
Preventive measures to prevent stomatitis in children
To minimize the risk of developing stomatitis you need to:
- wash the child’s toys, bottles and other things regularly, and do not forget to thoroughly wash the baby’s hands;
- strengthen the child’s immunity;
- do not let your child bite his nails;
- create a balanced menu containing all the necessary minerals and vitamins. The diet should be followed;
- promptly treat diseases such as tonsillitis, gastritis and other gastrointestinal diseases. If you extinguish the outbreak in time, this will prevent stomatitis from developing;
- At least once a year, and preferably twice, visit the dentist for a detailed examination of the oral cavity.
All these simple recommendations will help avoid the occurrence of stomatitis, because any disease is much easier and cheaper to prevent than to treat it later. If it was not possible to avoid the disease, at the first signs of it, you must consult a doctor to prescribe effective treatment. If stomatitis appears again and again, a thorough immunological examination is required. The child should be examined by a pediatrician and an immunologist; it is also advisable to contact an endocrinologist and gastroenterologist (perhaps they will identify a chronic disease leading to relapse of the disease).
It is equally important to teach your child proper oral hygiene. If the teeth are affected by caries and covered with plaque, and there are fistulas on the gums, the fight against stomatitis will not be successful. A child must be taught how to properly brush his teeth and gums by buying him a brush and toothpaste appropriate for his age.