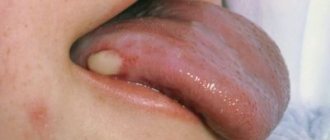
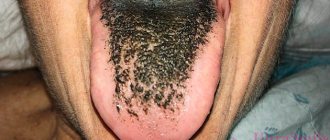
We are used to the fact that we need to go to the dentist if we have problems with our teeth or gums. What to do if you have inflammation of the tongue or glossitis? Dentists identify more than 10 types and subtypes of infection. The infection can be caused by both fungus and bacteria. Viral infection is less common. Inflammation can be caused by a lack of certain vitamins and minerals, or hormonal changes. There are many reasons for the disease, so it is important to identify what exactly caused the inflammatory process.
Causes of glossitis
- improper oral hygiene;
- bacterial infection;
- fungal infection;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- congenital pathologies of the tongue (folded tongue);
- allergic reaction;
- tongue injury (often caused by malocclusion);
- oral infections;
- lack of iron in the body;
- burn of the mucous membrane (hot food or drinks);
- infectious diseases (AIDS, tuberculosis, scarlet fever, measles).
Possible reasons
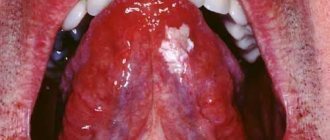
- Mycoses. Most often, red dots in the mouth are symptoms of oral candidiasis. Fungi of the genus Candida are considered opportunistic. They live in the intestines and do not cause harm to the body. However, when they enter the oral cavity, they quickly multiply and provoke inflammation of the mucous membrane. Spots of different shades of red can form on the gums, palate, cheeks, tongue, and tonsils.
- Bacterial infections. One of the main pathogens is streptococci. They change the structure of the mucous membrane and lead to inflammation of the soft tissues. They provoke the development of pharyngitis and tonsillitis.
- Viral diseases. Acute respiratory viral infections can also be accompanied by the formation of red spots on the oral mucosa. Pathogens enter the oral cavity through the nose. The gums and palate become inflamed, local hyperemia appears. If the spots become covered with a white coating, we can talk about a fungal or bacterial infection.
- Neoplasms. Suspicious spots on the gums may turn out to be benign tumors. The most common include papillomas and granulomas. Also, the risk of malignant neoplasms cannot be excluded.
The most common types of glossitis
The most common occurrences in dental practice are:
- acute catarrhal glossitis;
- tongue abscess;
- desquamative glossitis.
Acute catarrhal glossitis is the most common type of inflammation. Inflammation can be caused by microbes or mechanical damage to the tongue. The predominant symptoms are pain, redness and swelling.
A tongue abscess is the appearance of an abscess in the tongue. The abscess can be superficial, under the mucous membrane, or maybe in the thickness of the tongue. Abscesses in the thickness of the tongue, in addition to pain in the tongue, can cause a disturbance in the general condition. A person develops a fever, a headache, and weakness. Most often occurs due to injury to the tongue.
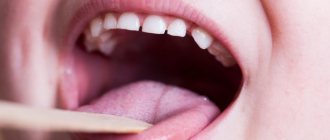
Desquamative glossitis, also known as “geographic tongue,” most often appears in children. It appears in the form of various spots on the tongue, which look like a white coating, alternating with areas of pink mucous membrane. There are no changes other than appearance. Scientists have identified a clear reason for it. The main factors are believed to be bacteria, allergic reactions and hormonal imbalances.
How does burning in the mouth and tongue manifest?
The symptom is clearly noticeable, may occur sporadically and disappear on its own. This happens when taking bitter medicines or eating spicy foods (“fire” in the mouth). A slight irritation of the mucous membrane may bother you after dental procedures; this is quite normal.
True diseases can be assumed if:
- Dryness and burning in the mouth often appear in certain areas of the oral cavity
- Unpleasant sensations intensify and are accompanied by numbness
- The tingling becomes constant
In most patients, the burning sensation manifests itself in the morning, intensifies during the daytime and subsides towards night.
Symptoms of glossitis
- increased salivation;
- swelling and redness;
- pain and burning when eating;
- plaque on the tongue in the form of spots;
- bad breath;
- papillomas or warts on the tongue;
- speech disorder;
- foreign body sensation.
Prevention of glossitis - high-quality oral hygiene and no bad habits. It is important to undergo timely preventive examinations and also eat well. All these factors actively contribute to the development of the disease and bring a number of problems.
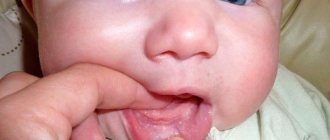
Stomatitis in a child: symptoms, causes
The description of stomatitis in a child deserves special attention. The specificity of stomatitis that occurs in the mouth of a young child is that the disease is a consequence of a weakened or not fully formed immune system. Therefore, the stomatitis reaction manifests itself clearly and the course of the disease is accompanied by severe symptoms.
Symptoms of stomatitis in a child:
- The oral mucosa turns red and swelling appears.
- Characteristic stomatitis ulcers form in the mouth, which are located either singly or in groups. The localization of ulcerative formations during stomatitis in a child is different: wounds and blisters appear on the tongue, on the palate, mucous membrane or in the throat. The nature of the lesions depends on the form of the disease and on what factors triggered the reaction (infections, allergies, vitamin deficiency, etc.).
- The development of stomatitis in the baby’s oral cavity is accompanied by an increase in the child’s body temperature (up to 38-39 degrees).
- The baby’s submandibular lymph nodes increase in volume and become painful on palpation.
- The child becomes lethargic, drowsy, capricious and whiny.
The baby has a hard time suffering from stomatitis in the mouth, and this is a lot of stress for the young body, not to mention the fact that the disease worsens the child’s appetite and disrupts the child’s sleep pattern. Therefore, if you notice the formation of ulcers in the mouth of your daughter or son or identify other symptoms of stomatitis, immediately show your child to a doctor (dentist or therapist).
Studying pictures and photographs of other children with oral stomatitis on the Internet is pointless; you will only waste your time and may come to the wrong conclusions. The doctor will help you understand the reasons that provoked the development of stomatitis in the child’s mouth and prescribe effective treatment for stomatitis.
Treatment of glossitis
A specialist must make an accurate diagnosis and identify the cause of the disease. If you suspect that you have glossitis , and all symptoms indicate this, contact your dental clinic. This is the only way to create the right treatment plan and provide timely assistance. Quite often in such cases, doctors prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and rinsing the mouth with special antiseptic solutions. In advanced stages, glossitis is treated surgically. Deep abscesses must be opened in the maxillofacial department. Under no circumstances should you take medications without a doctor’s recommendation.
You can cure glossitis, caries or any other diseases of the oral cavity right in your sleep. Family Dentistry Center "Medexpert" provides dental treatment under medicinal sedation. Thanks to this approach, the patient falls into a healthy sleep, ceases to feel pain and discomfort, while the vital functions of the body remain unchanged. Sedation is widely used in pediatric dentistry and even helps fight dental phobia. Dental treatment can be comfortable and painless - tested for yourself.
Acute and chronic stomatitis, what is the difference?
There are two forms of stomatitis disease: acute and chronic. For the first time, stomatitis usually manifests itself in an acute form, characterized by the sudden appearance of ulcers on the palate, mucous membranes in the mouth, tongue or throat of a person. The ulcers hurt and cause discomfort when talking or eating.
Acute stomatitis goes away on its own after 7-10 days, even if it is not treated, but in most cases the disease returns in a chronic form. This means that a person develops stomatitis ulcers in the oral cavity from time to time throughout his life. In order to prevent the transition of stomatitis disease from an acute to a chronic form, a person should undergo a course of treatment for the disease at the initial stage. It is very important that a plan and methodology for combating stomatitis in the patient’s mouth is developed by a competent and competent doctor who could take into account all the factors that could provoke this disease and get rid of them.
The LeaderStom clinic invites you to diagnose stomatitis and undergo a course of effective treatment under the supervision of the institution’s experienced dentists. Our doctors know modern methods of combating this disease in patients of different ages and are able not only to solve the existing problem, but also to give valuable recommendations for further oral care in order to prevent the occurrence of stomatitis ulcers on the mucous membrane, palate, throat or tongue of a person again .
Three types of inflammation of the salivary gland
Depending on the disease, there are three types of inflammation, namely catarrhal, purulent and gangrenous. First of all, a swelling forms in the area of the salivary gland, which is often accompanied by pain. The inflamed area becomes red, and the skin there is tense and shiny. The exit site of the gland duct has a limited area of edema and inflammation.
In most cases, a specific liquid is released from it, similar to saliva or pus. Body temperature rises sharply to 39 degrees. Opening your mouth becomes more and more difficult and painful. If treatment is not started on time, the disease will develop into a more severe form with serious consequences.
In the human body during normal development there are three pairs of salivary glands
The parotid gland is most often affected by various diseases. There are a number of diseases in which the sublingual and submandibular salivary glands become inflamed. If you do not start treatment on time or undergo inappropriate therapy, then serious complications may occur after such diseases, such as encephalitis, orchitis, meningitis, nephritis, neuritis and pancreatitis. However, do not worry, treatment often gives positive results. To avoid inflammation of the salivary glands, you just need to follow a few recommendations.
It is very difficult to diagnose this disease in the early stages.
In most cases, patients notice that something is wrong when the stone prevents the complete drainage of fluid. All this is accompanied by sharp pain, similar to salivary colic. At the site of inflammation, the tissues swell and become swollen. These symptoms are not constant, the pain either increases or disappears. During treatment, the stone is removed; if the situation is too advanced, sometimes the entire gland is removed.
The salivary glands under the tongue extremely rarely. But at the same time, the disease develops at a rapid pace and can have adverse consequences.
In order to maintain your health, first of all, you must adhere to the rules of hygiene and if you experience the slightest discomfort, immediately consult a doctor.
Inflammation of the salivary gland under the tongue
Causes, symptoms and types of stomatitis on the tongue
Modern medicine has a huge variety of causes of stomatitis. As a rule, they are either bacterial or viral in nature. Not only adults, but also children can suffer from stomatitis on the tongue. Here are the most common causes of stomatitis on the tongue:
- Infectious diseases: diphtheria, influenza, scarlet fever, measles, acute respiratory infections. Such diseases are usually accompanied by acute stomatitis. Its development is facilitated by constant irritation of the mucous membrane during smoking, alcohol abuse, and regular consumption of too cold, hot or spicy foods. Among stomatitis caused by infection, herpetic stomatitis (herpetic sore throat) or stomatitis in the throat is distinguished. It is caused by various enteroviruses. In addition to stomatitis in the throat, this virus can cause enteroviral vesicular stomatitis with exanthema, acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis, and aseptic (serous) meningitis. If you suspect that you have stomatitis in the throat or herpetic sore throat (white or grayish-yellow blisters in the throat), contact your doctor immediately to clarify the diagnosis.
- Diseases of the digestive system and stomach.
- Bad habits.
- Dental damage: tartar, caries, periodontitis, bleeding gums.
- Various types of damage: mechanical or chemical. For example, low-quality dentures, chipped teeth. Such violations can lead, first of all, to the appearance of stomatitis on the lip. The thin, delicate skin of this area is injured (burn, chapping, etc.), through microcracks in the thin and delicate skin of this area, an infection enters the body, causing stomatitis on the lip.
- Worm infestation.
- Weakened immunity, vitamin deficiency.
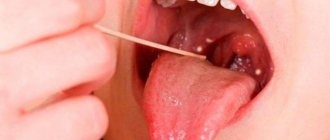
Characteristic signs that you have stomatitis are a white-yellow coating. Then gray spots appear on the tongue, reaching up to 0.5 mm in diameter. Sometimes they change shape or merge into one large spot. By the way, they may not hurt or bother you at all, and ulcers may not appear either. But, nevertheless, even if there are no pronounced symptoms of stomatitis, treatment is necessary, otherwise stomatitis can become acute. In addition, the lack of proper and timely treatment can provoke recurrent stomatitis - an inflammatory disease of the oral cavity that is chronic, but has periods of remissions and exacerbations. Sometimes it occurs as an independent disease.
One of the common manifestations of stomatitis in both children and adults is severe swelling of the tongue, which thickens and becomes covered with ulcers. After epithelial detachment, red, atrophied areas of skin remain, which cause a burning sensation. It becomes painful to eat and talk. One of the symptoms of the disease in a child is often tearfulness, moodiness, and restless behavior. If they appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. As a rule, stomatitis in children develops much faster and more painfully.
There are several types of stomatitis on the tongue:
- Catarrhal: characterized by high fever and profuse salivation, and may cause bad breath.
- Aphthous: the appearance of small ulcers (aphthous) that are covered with a yellowish coating.
- Ulcerative-necrotic: characterized by the appearance of ulcers covered with a gray coating.