5204
One of the serious pathologies of the oral cavity structure that needs correction is the shallow depth of the vestibule.
It is impossible to manage with therapeutic measures in this situation, so the patient will have to undergo a surgical procedure - vestibuloplasty.
The technique will help not only restore the aesthetic appearance of the oral cavity, but also reduce the risk of developing severe complications.
Symptoms
The vestibule of the oral cavity is a gap of soft tissue that is located between the lip or cheeks and the elements of the dentition.
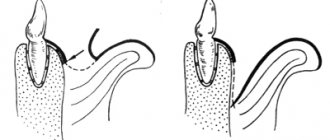
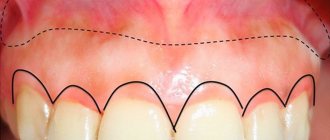
A variant of the norm is the depth of the vestibule from 5 to 10 mm. If this indicator does not reach 5 mm when measured from the end of the gum to the stationary area of the mucous membrane, dentists diagnose a shallow vestibule of the oral cavity.
An anomaly in the size of the vestibule can be identified by the following signs:
- excessive narrowing or complete absence of the attachment zone of the mucous membrane;
- tension of the gum tissue in the area of the periodontal junction;
- inflammation and bleeding of the gums;
- increased sensitivity of incisors;
- exposure of the necks and roots of bone organs in the area of attachment of ligaments;
- dentofacial deformities;
- the presence of a short frenulum;
- violation of diction.
With a decrease in the size of the upper vestibule, incomplete closure of the lips, their partial immobility, as well as malocclusion and a reduced size of the upper jaw compared to the lower jaw may be observed.
What is the vestibule of the oral cavity?
The oral cavity is the beginning of the digestive canal. Many functions that are responsible for the process of food entering the body depend on it.
It consists directly of the vestibule and the oral cavity itself. The vestibule is the space that is located between the teeth and gums on the inside and the lips and cheeks on the outside. This is the soft tissue through which the mouth opens. There are a large number of small salivary glands and ducts of the parotid glands located here.
Causes
A small vestibule of the oral cavity can be the result of both surgical intervention and congenital pathology.
Acquired pathology is a consequence of the following points:
- surgery to correct nonunion of the upper lip;
- surgical interventions to eliminate the consequences of burns, mechanical trauma to soft tissues, and removal of tumors.
The cause of a congenital reduction in the size of the vestibule is most often heredity and the presence of certain pathologies in the development of the dentofacial apparatus.
What is a crooked jaw and methods for straightening it.
We will tell you here about how long the swelling lasts after compactosteotomy.
At this address https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/zubov/polozheniya/etiologiya-razvitiya-i-metodyi-korrektsii-protruzii.html we will discuss why tooth protrusion occurs after braces.
Structure
In the oral cavity, the excretory ducts of the salivary glands open: sublingual, submandibular and parotid. In addition, there are a large number of small glands. The glands that make up the vestibule of the oral cavity and the oral cavity itself can be of three types depending on the nature of the secretion: serous, mucous and mixed.
Large salivary glands, which extend beyond the mucous membrane, reaching large sizes, maintain a connection with the oral cavity through their excretory ducts. These include:
- Parotid gland (Glandula parotidea). It is the largest gland of the serous type and is also a complex alveolar gland. It is located on the lateral side of the face in front and just below the ear. It is covered with fascia and has a lobular structure.
- Submandibular gland (Glandula submandibularis). It has a mixed alveolar-tubular character and is the second largest.
- Sublingual gland (Glandula sublingualis). Complex alveolar-tubular mixed type of iron. It is located at the bottom of the mouth, forming a fold.
Consequences
The depth of the vestibule and the attachment of the gums play an important role in the process of protecting the marginal periodontium from external influences.
In case of insufficient attachment or complete absence of attached gum tissue, the following problems may arise:
- trauma to the marginal periodontium while eating food;
- increased muscle tone of the chin;
- impaired blood supply to gum tissue;
- formation of pathological bite;
- partial decrease in lip mobility;
- slower growth of the upper jaw row;
- loosening of teeth;
- inflammatory diseases of the gums, their atrophy;
- development of periodontitis.
Dimensions and depth
The depth of the vestibule of the oral cavity can be shallow (less than 5 mm), medium (8-10 mm) and deep (more than 1 cm), which depends on the distance between the moving part and the fixed gum area. If the vestibule is small, this is fraught with the development of gingivitis or marginal periodontium. In this case, a kind of periodontal pockets may form, that is, a depression between the tooth and the gum. The cause of this condition can be a normal conversation, brushing your teeth or the process of eating food. With increased mobility of the nipples and retraction of the free end of the gum, periodontal disease may occur.
If the size of the vestibule deviates from the norm, operations called vestibuloplasty are performed. They can be either open or closed and carried out in various ways.
Indications for surgery
Vestibuloplasty is indicated in the following cases:
- absolute absence of gum attachment;
- a symptom of tension, the signs of which are pallor and displacement of the gingival margin when the lip is pulled back;
- lack of attached gum zone – distance less than 1 mm;
- signs of inflammation of the gum tissue;
- preparation for orthodontic therapy - installation of a structure to correct the bite will not bring the required effect with a small vestibule due to the fact that the alveolar processes of the incisors will return to their original position due to gingival tension;
- the need for further prosthetics;
- elimination of recession or atrophy of gum tissue.
The small vestibule of the oral cavity is often diagnosed not only in adults, but also in childhood. In this case, during the mixed dentition, observation of the child by the dentist is indicated. The operation is permissible after complete eruption of all teeth.
Functions of the human oral cavity
The structure of the human oral cavity, which is in direct contact with food and is responsible for digestion processes, performs a number of basic functions. Namely:
- Crushing food. Dividing food into pieces, grinding small and solid particles.
- Softening. That is, maximum grinding of food products, even soft ones. Everything is thoroughly chewed so that later the food can be quickly processed by saliva and gastric juice.
- Wetting food. Even a piece of soft bread will not just pass into the larynx. It is saliva that contains the necessary enzymes for the digestion of all substances.
- Analysis of food composition. This process involves the tongue, which contains various receptors that transmit information about food (temperature, taste) to the brain.
Course of action
Before proceeding with surgery, the dentist conducts a thorough examination of the patient’s oral cavity using certain instruments and equipment.
This allows you to identify associated problems and determine the most suitable vestibuloplasty technique among the many existing ones.
Before the operation, the dentist also professionally removes mineralized plaque from the front surface of the dentition.
During preparation for surgery, the patient is required to comply with the following rules:
- refusal to take painkillers and other medications not prescribed by the dentist;
- refraining for 6 hours before surgery from consuming foods that can cause mechanical injury to the gum tissue.
Vestibuloplasty is performed with preliminary anesthesia of the treated area. Anesthesia can be either local or general, at the request of the patient.
There are many options for performing surgery to change the size of the vestibule, which can be divided into several large groups.
Open method
Open vestibuloplasty techniques are based on changing the depth of the vestibule in such a way that a wound is formed on the surface of the lip and alveolar process, which takes about two weeks to heal.
The key disadvantage of such methods of surgical intervention is the formation of scars on the soft tissue, which in the future can contribute to the re-development of the pathology.
The open method is carried out as follows:
- a dissection of the mucous membrane of the lower lip is performed using an incision in the sector of the front teeth;
- an apron-shaped flap is peeled off, the base of which is a transitional fold in the area of the incisors;
- soft tissues are displaced to the prescribed depth, which helps to increase the depth of the vestibule;
- the detached flap of tissue is placed in the area of the alveolar process of the lower jaw, after which it is fixed with suture material;
- the wound formed on the mucous membrane is sutured and healed due to secondary intention.
Closed
Plastic surgery using a closed surgical technique involves closing the wound surface formed after enlargement of the vestibule using local soft tissue.
The essence of the method is that soft tissue is cut off through a small vertical incision.
The mucous membrane is practically not damaged. Thanks to this, the recovery process proceeds more quickly.
Dentists note a significant drawback that is inherent in closed operations - the possibility of relapse of the disease. According to statistics, three years after the operation, the size of the vestibule is again reduced by almost half.
Patchwork
The key indication for flapplasty is the exposure of the necks and roots of the teeth due to the strong tension of the soft tissue, which over time can lead to inflammation of the gum tissue and loosening of the teeth.
During vestibuloplasty, several horizontal and vertical incisions are made, which allow the edge of the gum tissue to be excised to form a flap.
After this, the separated flap is placed in the intended place in the dentition and fixed with suture materials.
Use of the plate
Vestibuloplasty using special plates is practically no different from the methods described above, however, its peculiarity is the use of a forming plate during the final stage.
This vestibular structure is applied to the wound surface after applying the flap and fixing it with sutures. The duration of its use is about two months.
Possible causes of crowded teeth in the lower jaw and ways to eliminate the anomaly.
In this publication we will talk about the reasons for the development of a small lower jaw in a child.
Follow the link https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/ryadov/zuboalveolyarnogo-ukorocheniya.html if you are interested in the operation of dentoalveolar shortening.
How is the examination carried out?
Specialists begin examining the oral cavity from the vestibule, with the jaws closed and lips relaxed. The doctor pulls back the lower lip with a dental mirror and examines the corners of the mouth and the border of the lips first. The walls of the vestibule of the oral cavity should have a pinkish tint, there should be no crusts or scales. In this case, the inner surface of the lip may be slightly bumpy, which is caused by the presence of small salivary glands.
Pinholes may also be visible, that is, excretory ducts with an accumulation of secretion droplets. Next, using a mirror, the inner surface of the cheeks is examined, color and moisture are determined. Teeth imprints may be visible on the mucous membrane. Thus, a malocclusion can be diagnosed by a doctor.
Additionally, the oral cavity is examined to determine the nature of salivation (decreased or increased), whether there is bad breath, and whether the gums are bleeding. In the presence of diseases, the mucous membrane may be hyperemic, swollen, with rashes, which indicates the development of inflammation.
Other treatments
Among the above methods, there are some variations, the choice of a specific one is made by the dentist after examining the patient’s oral cavity.
Edlan-Meicher method
This method is most often used when it is necessary to eliminate a small vestibule on the lower jaw due to its high efficiency.
After anesthesia of the operated area, an incision is made into the mucous membrane along the bend of the bone arch. Next, the mucous membrane and periosteum are peeled off, as well as the submucosal tissue moves to the lateral and anterior sections of the vestibule.
For fixation, sutures are placed on the mucous membrane, after which the wound is covered with a special bandage. The patient's recovery time is about two weeks.
The performance of vestibuloplasty according to Meyhar can be seen in the video.
Schmidt method
The Schmidt technique differs from the previous version of the operation only in that exfoliation of the periosteum tissue is not performed.
The soft and muscle tissues in this sector are also incised along the periosteum. The resulting flap edge is placed deep into the formed vestibule and then fixed.
This method of vestibuloplasty is equally effective for treating both the lower and upper jaw.
Glickman method
Plastic surgery using the Glickman method can be performed both on a limited sector of the oral cavity and on a larger area.
After administering anesthesia, the surgeon dissects the mucous membrane in the area of its attachment to the lip, then detaches the soft tissue and forms a depression.
After this, the detached section of the mucous membrane is attached to the resulting depression.
Clark's method
Plastic surgery of the small vestibule using the Clark method is performed for pathology of the upper jaw row.
After administering the anesthetic drug, a section is made at the border of the junction of the gingival margin and the moving section of the mucous tissue of the vestibule.
Using scissors, the mucous surface of the upper lip is peeled off. The soft tissue of the vestibule is dissected as close as possible to the periosteum and parallel to the curvature of the bone surface. The depth of the cut should not exceed 15 mm.
The previously detached section of the mucous membrane of the lip is placed in the vestibule formed as a result of tissue dissection, and then secured with sutures.
At the end of the procedure, the wound is covered with an iodoform swab.
Tunnel vestibuloplasty
The least traumatic method of plastic surgery, which is used to correct the depth of the vestibule of both jaws, is tunnel vestibuloplasty.
In certain areas of the oral cavity, two horizontal incisions are made along the premolars, as well as one vertical in parallel with the frenulum. After this, the mucosal flap is shifted inside the formed vestibule and secured.
The wound surface during this procedure is significantly reduced compared to other surgical techniques. The duration of the rehabilitation period practically does not exceed 10 days.
Stages of vestibuloplasty and possible complications
Since the ducts of the salivary glands open in the vestibule of the oral cavity, it is important to conduct the examination by determining the height at which the gums are attached. If a specialist determines that the vestibule is still small and vestibuloplasty is indicated, you need to thoroughly prepare for the operation. This will reduce the possible risk of complications in the future.
Principles of preparation:
- complete sanitation of the oral cavity;
- avoiding eating solid food for at least six hours before surgery;
- You should not take medications except those prescribed by the doctor or those necessary to maintain normal human life.
Experts also note that the psychological attitude is important. In general, regardless of the method, vestibuloplasty is a painless operation, since it is performed under local anesthesia and lasts about an hour.
Stages of vestibuloplasty:
- The anesthetic is administered after the doctor discusses with the patient possible intolerance to certain drugs and excludes them. It is the choice of anesthesia that determines how well a person will feel during and after the operation.
- Direct surgical intervention using one of the methods described above. It takes no more than an hour.
- Ice is applied to the site where the operation was performed for 15 minutes to remove swelling and minimize pain after surgery.
After surgery, swelling and redness of the skin is possible, which is considered normal. During the day after vestibuloplasty, the use of painkillers is indicated, but this depends on the patient’s well-being.
Complications, which occur extremely rarely after surgery to deepen the vestibule of the oral cavity, can develop due to non-compliance with specialist recommendations and poor oral hygiene.
Possible side effects:
- increased bleeding, especially at the suture site;
- scarring of tissue;
- low sensitivity;
- severe swelling of the gums.
If this condition is observed for several days after vestibuloplasty, this indicates the development of an inflammatory process. It is worth consulting a doctor for advice.
Rehabilitation
The duration and severity of the rehabilitation process depends not only on the dentist’s manipulations, but also on the patient’s compliance with the following recommendations:
- at the end of the procedure, use a cold compress to relieve swelling from the operated area;
- Avoid eating too hard, spicy or hot foods for two weeks after surgery;
- reduce the amount of dairy products consumed, as they contribute to the formation of persistent plaque;
- use soft-bristled toothbrushes for daily hygiene;
- rinse the mouth with special anti-inflammatory and antiseptic drugs;
- after five days after the operation, begin performing myogymnastic exercises recommended by a specialist;
- visit the dentist on the appointed days to monitor the recovery process.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums, caused by the adverse effects of local and general factors and occurring without disruption of the periodontal junction.
Forms of gingivitis:
- a) catarrhal gingivitis - inflammation of the gingival margin. There are chronic and acute forms of catarrhal gingivitis. The acute form of catarrhal gingivitis often develops against the background of some general infection or intoxication. Often catarrhal gingivitis occurs during the period of spring hypovitaminosis, after suffering from influenza and acute respiratory infections.
- b) ulcerative gingivitis is an inflammatory process characterized by the appearance of ulcers and necrotic plaque on the surface of the gingival margin. The development of ulcerative gingivitis is facilitated by the presence of multiple untreated caries and damaged tooth roots. More common during puberty.
- c) hypertrophic gingivitis - leads directly to gum hypertrophy. There is swelling and inflammation. Patients complain of an increase in the volume of the gums, the color of the gums is slightly changed, there is no pain or bleeding of the gums when irritated. The gum has the appearance of a thickened cushion at the base, the gingival papillae are compacted, and the surface is lumpy.
- d) gingivitis of pregnant women and teenage gingivitis, these are those types of gum inflammation that do not occur against the background of hormonal changes in the body.
Severity of gingivitis:
- light,
- average
- and heavy.
Course of gingivitis:
- spicy,
- aggravated,
- chronic.
results
After correcting the deepening of the vestibule of the mouth in Perovo, dentists minimize the loosening of the incisors and the formation of periodontal pockets. The patient can effectively solve his dental problems and get the following results:
- cure periodontitis;
- securely fix orthopedic structures;
- preventive measures for gingival recession (exposure of tooth roots);
- improve articulation;
- eliminate cosmetic defects;
- correct bite formation;
- pronounce all sounds;
- exclude the development of peri-implanitis.