What causes inflammation of the tonsils (tonsillitis)
The tonsils (tonsils) become inflamed when their lymphoid tissue, which is involved in the formation of immunity, is unable to cope with the infectious agent. In this case, adults and children develop acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis), which can develop into chronic.
Other causes of chronic tonsillitis include [2]:
- frequent and untreated pharyngitis;
- prolonged difficulty in nasal breathing due to curvature of the nasal septum, infectious diseases of the nasal mucosa and paranasal sinuses (rhinitis, sinusitis, the occurrence of polyps, etc.);
- diseases of teeth and gums;
- allergic reactions.
As a result of tonsillitis, inflamed tonsils turn into a source of infection, which leads to decreased immunity and frequent respiratory diseases and can cause complications of existing chronic diseases, the development of allergies and serious diseases of the cardiovascular system, liver, kidneys, and joints [2].
Symptom of "coma in the throat"
Murzaeva Irina Yurievna
Endocrinologist, Preventive Medicine Doctor
December 15, 2016
This is one of the most common complaints with which a person comes to an endocrinologist.
A lump in the throat can be described as a non-painful sensation of the presence of a voluminous foreign body in the throat, usually in the area of the jugular fossa, this is a “hollow” between the collarbones.
This may feel like a “tickling” in the throat, a “stuck pill” feeling. This symptom differs from the symptom of dysphagia by the free passage of food through the esophagus without choking or choking.
Essentially this is a neurosis of the pharynx. But to understand this, you need to understand the criteria. According to medical parameters, the symptom of “coma in the throat” is set according to the following Rome III recommendations (provided that the symptoms have been present for at least 3 months, this is not a “one-time action”.
- constant or periodically occurring non-painful sensation of the presence of a voluminous foreign body in the throat;
- the appearance of a lump in the throat between meals;
- lack of evidence that this symptom is caused by gastroesophageal reflux;
- absence of histopathological changes (according to FGDS) that could affect the motility of the esophagus.
“Lump in the throat” is a functional condition (usually associated with stress of the globus hystericus type, and not a disease. To prove this, it is imperative to exclude diseases that are masked under it. And this is:
- esophageal motility disorder;
- head and neck tumors;
- diseases of the thyroid gland with goiter;
- cervical lymphadenoaptia;
- GERD;
- hiatal hernia;
- chronic tonsillitis, pharyngitis or laryngitis;
- esophageal stenosis;
- spondylosis of the cervical spine;
- psychological disorders;
- increased tone of the upper esophageal sphincter.
To diagnose these conditions you need to undergo:
- ENT doctor, sometimes with video endoscopy of the larynx
- FGDS with determination of stomach acidity (ph-metry) followed by consultation with a gastroenterologist
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland and blood tests for hormones
- consultation with a neurologist
- psychotherapist.
Actually, globus hystericus can be supplemented by other complaints that confirm its psychogenic nature, and these are:
- cardiopalmus
- increased sweating
- loss of appetite
- insomnia
- increased excitability
- irritability.
The concept of dysphagia is qualitatively different from the “coma in the throat” symptom. These are different concepts. Dysphagia is a feeling of stuck solid or liquid food, delay or disruption of its passage through the esophagus. And there are many more reasons that cause this condition and they are more severe. I will give just a few examples. Dysphagia occurs with strokes, multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, butulism (mushroom poisoning), amyloidosis, esophageal diverticula, etc.
These are different concepts. Dysphagia is a feeling of stuck solid or liquid food, delay or disruption of its passage through the esophagus. And there are many more reasons that cause this condition and they are more severe. I will give just a few examples. Dysphagia occurs with strokes, multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, butulism (mushroom poisoning), amyloidosis, esophageal diverticula, etc.
Therefore, dysphagia is divided according to the level of occurrence, which facilitates diagnosis:
- oropharyngeal: cerebral, neuromuscular, mechanical obstruction of food passage and esophageal.
For diagnostic purposes, the doctor can interview the patient using a special medical “Mayo Clinic Dysphagia Questionnaire . On the basis of which it is decided which diagnostic measures to apply in a particular case.
Dysphagia, unlike “a lump in the throat,” is always based on a specific disease.
Treatment depends on the identified cause.
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis
The main symptoms of the disease include [2]:
- elevated temperature for a long time, especially in the evening;
- headache, sore throat and joint pain;
- loss of appetite;
- bad breath;
- inflammation of the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes;
- frequent relapses of sore throat.
When examining the throat, the ENT will find [2]:
- enlargement, looseness, swelling of the tonsils;
- accumulation of plugs (white cheesy mass) in the lacunae of the tonsils.
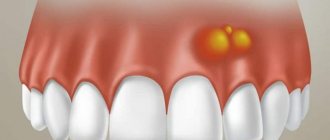
Caseous plugs - remains on the battlefield
Tonsils, or tonsils as they are popularly called, are an organ that protects the body from harmful bacteria.
The palatine tonsils are covered with special depressions (lacunae), in which the immune system kills microbes that enter the mouth along with air and food. After the fight, “corpses” of microbes, leukocytes, and food residues remain on the battlefield. But the tonsils of a healthy person are quickly cleared of debris and continue to perform their function. And caseous plugs (tonsillitis) appear when the tonsils are inflamed. Their composition is almost identical to pus, so they cause concern for patients. In fact, the deposits themselves are not dangerous, but they signal the presence of an infection in the oral cavity.
The most common causes of traffic jams are untreated tonsillitis and chronic tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils). In addition, deposits can be caused by the following factors:
- chronic runny nose;
- sinusitis;
- adenoids;
- untreated caries;
- smoking;
- hypothermia;
- low immunity.
The disease often occurs in young people under 30 years of age. Sometimes tonsillitis may not make itself felt at all, but in some cases it causes bad breath and interferes with eating.
In addition, as orthodontists note, chronic otolaryngological diseases can cause malocclusion.
Moreover, since everything in the body is interconnected, the situation can turn in the opposite direction. In particular, if care is not taken to straighten teeth in cases of serious anomalies, ENT diseases may also follow.
Therefore, if you are faced with a problem such as caseous plugs, it would not be superfluous to make an appointment with an orthodontist. Your doctor will likely prescribe short-term treatment for your malocclusion with Invisalign aligners.
Such an integrated approach will eliminate the problem on both sides once and for all.
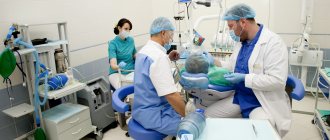
Indications for tonsillectomy
After collecting anamnesis and a complete examination, the doctor will prescribe a tonsillectomy if there is [1, 2]:
- frequent relapses of tonsillitis (if we talk about children - from seven exacerbations per year to five or three exacerbations over two and three years, respectively), convincing of the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment;
- decompensated form of chronic tonsillitis, when the tonsils are unable to perform their protective functions and inflammation leads to diseases of other organs;
- chronic tonsillitis with toxic-allergic phenomena, when the risk of complications and other infectious-allergic diseases increases;
- sleep apnea syndrome, when inflamed tonsils cause dysfunction of breathing and swallowing;
- purulent complications in the tonsils themselves and peritonsil tissue;
- Marshall syndrome (PFAFA syndrome) is a regularly recurring fever with complications that occurs mainly in children.
There is a lump in the throat: reasons
Many people feel a lump in their throat after eating, the reasons for this may lie in:
- formation of an abscess in the pharynx,
- formation of neoplasms,
- pathologies of the thyroid gland,
- dysfunction of the cervical spine.
If you feel a lump in your throat with nausea, the reasons for this most often lie in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Signs such as pain when swallowing, a feeling that a foreign object is stuck, suffocating and causing other types of discomfort are observed:
- with gastritis;
- with reflux esophagitis;
- when a hernia forms in the esophagus.
In addition to the fact that there is a lump in the throat, patients are often annoyed by:
- pain in the chest in the center or right, particularly in the esophagus, with difficulty swallowing and breathing;
- belching after eating;
- severe heartburn;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- nausea;
- feeling that there is air in the stomach;
- an unpleasant sour taste in the mouth and a sore throat provoked by it.
Sign up for the First Family Clinic of St. Petersburg to find out how to get rid of a lump in your throat. We offer you a full range of diagnostic measures and consultations with high-level gastroenterologists, thanks to which we can accurately determine the reasons why there is a lump in the throat. We are waiting for you at the multidisciplinary clinics of the Primorsky and Petrograd districts.
Contraindications to tonsil removal
The operation is impossible if the patient [1, 2, 3]:
- diseases of the blood system that occur with increased bleeding (hemophilia, agranulocytosis, leukemia, leukemia, hemorrhagic diathesis and others);
- vascular anomalies of the pharynx (angiodysplasia, aneurysms, submucosal pulsation of the vessel);
- active form of tuberculosis;
- decompensated form of diabetes mellitus;
- severe progressive diseases of the cardiovascular system, kidneys, liver, lungs;
- severe forms of mental disorders.
There are also relative contraindications that can negatively affect the outcome of the operation - therefore, tonsillectomy should be postponed until they are eliminated or completed [1, 2, 3]:
- acute infectious diseases;
- menstruation;
- caries;
- inflammation of the gums;
- pyoderma (pustular skin diseases);
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- exacerbation of dermatitis;
- pregnancy starting from the 7th month.
Preparing for surgery
The decision to remove the palatine tonsils, as well as the choice of treatment tactics and anesthesia, is made by the otolaryngologist after collecting anamnestic data and conducting a thorough clinical examination [2]:
- taking tests (general blood and urine analysis, biochemical blood test, determination of blood group and Rh, coagulogram (assessment of blood clotting), etc.);
- other examinations (electrocardiography, fluorography, etc.);
- in the presence of pathologies, consultation with specialized specialists and additional examinations;
- prescribing medications that reduce the risk of bleeding, and, if necessary, other drug therapy and taking sedatives.
This treatment method has been used for more than 2000 years and remains one of the most common surgical interventions to this day.
During the time that has passed since the first tonsillectomy in children, surgical tactics, pre- and postoperative preparation of the patient, as well as the possibilities of pain relief have changed significantly. Polunina T. A, Ph.D., ENT, employee of the Scientific Center for Children's Health of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Moscow [1]
A few days before surgery, you must give up alcohol, smoking, and eating heavy, spicy, and fatty foods. You should not eat or drink directly on the day of surgery.
How to treat caseous plugs
What you absolutely should not do is try to remove the plugs yourself. “Picking” your tonsils with your finger or foreign hard objects will not only not relieve you of the disease, but will also aggravate it. The deposits will clog even deeper, and the infection will only grow.
Rinsing in this case is also not an option. Although patients note some relief, the medicinal solution only washes the surface of the tonsils, but, unfortunately, does not “wash out” the plugs.
Therefore, with this problem you should contact an ENT doctor, therapist or dentist. At some stages, treatment of the disease is not required, but if necessary, a specialist will perform professional cleansing of the tonsils. This procedure can be carried out in two ways:
- manually - the doctor rinses the recesses in the tonsils with a syringe with a special solution;
- using devices - vacuum suction, ultrasound, etc. are used.
As a rule, the treatment of caseous plugs is approached in a comprehensive manner, adding medications and physiotherapeutic procedures to cleansing the tonsils.
Patients who notice white deposits on their tonsils, bad breath, or a sore throat should definitely consult a doctor. After all, in the early stages it is much easier to eliminate the disease.
Surgical options
Today there are many methods for removing tonsils, but the most common include [1, 3]:
- Classic (standard) tonsillectomy. Enucleation of tonsils using surgical instruments.
- Extracapsular tonsillectomy. The doctor, using scissors and a loop, cuts off the palatine tonsil along with the capsule, then applies sutures. The main disadvantage of this method is the high risk of bleeding both during and after surgery.
- Using an ultrasonic scalpel. Thanks to high-frequency sound vibrations, the temperature of surrounding tissues remains low enough to avoid serious damage.
- Coblation (bipolar radiofrequency ablation). This method has become widespread in otorhinolaryngology due to the minimization of pain and postoperative risks, as well as the reduction of the recovery period. This is due to the absence of thermal effects: the radiofrequency energy used separates the molecular bonds between tissues, allowing them to be cut almost painlessly and bloodlessly.
Possible complications after tonsil removal
Thorough preoperative examination and preparation, modern equipment and adherence to doctor's recommendations during rehabilitation after tonsil removal can minimize the risk of complications after tonsillectomy. However, the following cannot be excluded [2]:
- bleeding, which can occur both directly during surgery (primary) and several hours and days after tonsillectomy (secondary);
- sore throat, difficulty swallowing;
- taste disturbance;
- inflammation of the wound;
- increased body temperature;
- swelling of the soft tissues of the neck and larynx.
Therefore, the first few days after removal of the tonsils, the patient most often remains in a hospital under the supervision of specialists, where if his health worsens, he will be provided with qualified assistance.
Postoperative period after tonsillectomy
The duration of the recovery period after tonsillectomy directly depends on the chosen method of operation; the wound itself heals on average in 3–4 weeks. For rehabilitation to be successful, it is necessary [2]:
- follow all doctor's recommendations;
- stick to bed rest for the first few days;
- limit physical activity, visiting the sauna, hot bath, swimming pool;
- take prescribed medications;
- for the first 5–7 days, avoid eating irritating foods (hot, cold, sour, spicy), carbonated drinks;
- Carefully monitor your condition and, if any deviations or complications appear, seek the help of specialists.
After surgery to remove the tonsils as a source of infection, the frequency of colds and the risk of developing serious complications are reduced. Therefore, if conservative methods of treating tonsillitis do not produce results, it is necessary to contact a specialist and discuss the possibility of surgery.