An abnormality such as bone spurs is often ignored until it actively progresses. Patients often come to the clinic late, which entails complex treatment, including surgery. Exostosis is a pathology in which hardened areas of cartilage tissue protrude above the jaw are formed. The causes of this phenomenon are mechanical damage, trauma, tooth extraction and other diseases. Chewing functions are preserved, and soft tissues are also not damaged. But as the protrusions grow, thinning of the mucous membrane and ruptures occur, causing injury to surrounding areas.
Causes
Reasons for the formation of growths:
- inflammatory, infectious processes, purulent accumulations;
- mechanical impacts, injuries causing bone destruction, jaw displacement and other damage;
- deviations of row segments, formation of nodular hardenings;
- disorders of the endocrine system, hormonal levels.
One of the reasons for the development of pathology is complex tooth extraction. Often, when a wound heals, the tissue around it becomes overgrown with moving areas. If done incorrectly, compactions may appear and exostosis will gradually develop.
Rehabilitation after removal of exostosis
The wound heals completely in about 1 week. For better tissue healing and prevention of complications, it is necessary to comply with the doctor’s requirements.
During the recovery period, you should not exercise or overheat the body. It is prohibited to visit the bathhouse, sunbathe on the beach, or take a hot bath. Otherwise, bleeding from the wound may occur.
In order not to injure the damaged mucous membrane, you should not eat rough, spicy or sour foods. Food should be liquid or pureed, at a comfortable temperature. It is undesirable to smoke, as nicotine constricts blood vessels, which prevents rapid healing.
When brushing your teeth, you should avoid the operated area. The toothbrush should be soft. After eating, you should rinse your mouth with warm water. Daily rinsing with antiseptic solutions, for example, chlorhexidine, miramistin, is recommended. For these purposes, you can prepare decoctions of chamomile, sage, calendula, and oak bark.
In the first few days, pain and swelling of the tissues persist. To relieve acute pain, you can take analgesics. A cold compress will help relieve swelling. Ice or frozen product is wrapped in plastic wrap, cloth and applied to the cheek several times a day.
If the patient is in poor health or has chronic diseases, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
If you ignore the dentist’s requirements, complications may occur: infection and inflammation of the wound, bleeding, suture dehiscence.
Symptoms
The initial stage of the pathology practically does not manifest itself. Symptoms generally have a vague picture, which is why patients rarely see a doctor in a timely manner. But as the condition worsens, the following symptoms appear:
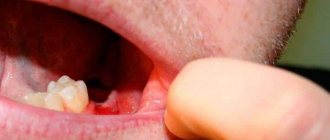
- growths with a pronounced convex shape appear on the tissues; the structure can be embossed or smooth;
- there is a feeling of a foreign object in the mouth;
- pain appears, sometimes quite severe;
- partial jaw dysfunction is observed;
- the shade of the mucous membrane changes to bright;
- capillary obstruction appears in the area of the growth.
What to do if exostosis occurs after tooth extraction
Osteocartilaginous formations in the mouth can only be treated surgically, so if you suspect a pathology, you should consult a dentist. The doctor makes an accurate diagnosis after examining the patient: visual examination and radiography. Differential diagnosis of the nature of the lumps may be required.
Exostosis itself does not disappear, so the doctor decides whether the growth needs to be removed. If the protrusions are small, then the operation can be postponed indefinitely. In this case, you need to undergo regular examination at a dental clinic to monitor changes in tissues.
Indications and contraindications
The growth is treated surgically. Indications for using this option for removing pathology are:
- the bone growth grows quickly;
- pronounced cosmetic changes, progression of pathology;
- physical discomfort, the growth becomes too large;
- before prosthetics.
There are a number of the following contraindications to surgical intervention:
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- adrenal dysfunction;
- diabetes of any form;
- bleeding disorders.
Treatment
Before treatment, the doctor conducts an examination and prescribes a number of diagnostic measures. It is necessary to perform fluoroscopy, determine the level of blood clotting, and determine whether there are contraindications to surgery. If there are no contraindications, the doctor removes the growth:
- anesthesia is performed (for uncomplicated pathology, the operation is performed under local anesthesia);
- the oral cavity is treated with antiseptic drugs;
- an incision is made on the gum, then the mucosal tissue is dissected to open access to the bone;
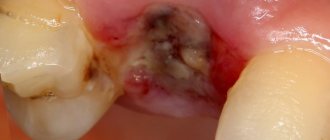
- the growth is removed using a laser beam or chisel (depending on the state of the pathology);
- the bone tissue is smoothed to an even texture, at which time cooled water is supplied to the surface;
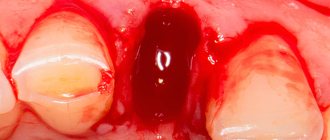
- The tissues are sewn together and a bandage is applied.
The duration of the procedure depends on the complexity of the treatment. For mild cases, the operation takes about forty minutes; for complex pathologies, removal may take an hour and a half.
During the recovery period, the patient must follow the doctor's recommendations. For the first day, the intake of food and solid foods is limited, smoking and drinking alcohol are excluded. It is necessary to avoid physical activity, which can provoke bleeding and cause swelling.
General idea of exostosis in the mouth
New growths on bone tissue are found in different parts of the body. Exostosis in dentistry according to ICD-10 refers to other specified diseases of the jaw K-10.8. The osteochondral formations look like a protrusion, lump, mushroom or ridge, and can branch and be tortuous. When they grow, they injure the mucous membranes of the mouth, which provokes the development of inflammation.
Zkzostoza on the upper jaw are less common than in the mandibular region. Usually formed on the alveolar process on the side of the cheek. When the size increases, they affect the aesthetics of the face, creating asymmetry. In the lower jaw, exostosis often forms on the lingual side. Protrusions can interfere with chewing food and talking.
You can see what exostosis looks like on the gum or bottom of the lower jaw in the photo. If the formation is small, then it is difficult to notice it visually.
Prerequisites for the occurrence of a lump
Modern medicine has not created a complete list of reasons why bumps may appear. Doctors' reasoning is based on hypothetical cause-and-effect relationships. The appearance of a lump on the palate is caused by:
- Bad habits (smoking, alcohol, oral drugs);
- The presence of micro and macro injuries to the oral cavity (surgeries, scratches of the upper parts of the oral cavity);
- Availability of dentures;
- Viral infections;
- Intrauterine disorders (hemangioma is a congenital disease and acquired from the mother);
- Violation of the activity and integrity of the mucous membrane (typical of angina);
- Congenital and acquired dysfunction of the glands (the main cause of cysts).
There are two more hypothetical reasons for the appearance of malignant tumors:
- Eating too hot and spicy foods, constantly disrupting the structure of the cells of the oral cavity;
- The presence of papillomatosis or leukoplakia - diseases that are precancerous lumps that can develop into an oncological disease.
Diagnostic methods
To determine the method by which a lump on the roof of the mouth will be treated, the causes of its occurrence are studied. The diagnostic procedure is carried out by a dentist.
Regular visits to the dentist are important to prevent the disease and determine whether a lump has appeared on the roof of your mouth. It needs to be treated at an early stage.
For diagnosis use:
- Radiography;
- Biopsy;
- Blood analysis;
- Radioisotope study;
- Ultrasound.
If you comprehensively examine the ball on the roof of your mouth, this will confirm or deny the presence of a malignant formation, and if it is absent, it will determine the exact diagnosis of a benign one.
Varieties of epulis
Conventionally, there are 3 types of epulis:
- Fibrous. The neoplasm is dense, the basis is coarse fibrous tissue. Characterized by slow growth. There is no pain or bleeding.
- Angiomatous. The tumor contains a large number of blood vessels and is localized mainly in the lateral parts of the jaw. With this form of the disease, bleeding is observed even with slight pressure, for example, with a toothbrush or food. When pressed, the tumor is painless and has a soft consistency.
- Giant cell. The tumor can reach large sizes, displacing teeth that are located in the epulis growth zone. The mucous membrane of the epulis is bluish-red in color. On palpation, the neoplasm is painless, but may bleed moderately if injured.
Depending on the nature of the process, epulis can be benign or malignant. In the first case, the neoplasm is characterized by slow development and, as mentioned above, in most cases does not cause pain. The tumor size in this case rarely exceeds 10–20 mm. When the process becomes malignant, rapid tissue growth is observed. In this case, the process is often accompanied by pain, bleeding gums and affects the root canals of neighboring teeth.
Prevention Tips
It is impossible to avoid such a problem with a guarantee, but it is possible to significantly reduce the risk of its occurrence or identify a defect at the initial stage of its formation. To do this, you need to be careful about the condition of the oral cavity, carefully monitor hygiene, do not skip preventive examinations, eliminate traumatic factors if possible and do not trigger dental pathologies - start treatment on time.
Preventive examinations will help to recognize the problem in time
Experts also recommend systematically conducting self-diagnosis - from time to time carefully examining the tissues of the oral cavity for abnormal neoplasms. This should only be done with clean hands, carefully feeling every part of the jaw apparatus, including the palatal area. If you detect a suspicious growth, you should seek help from a dentist as soon as possible.
Treatment of oral fibroids
Surgery remains the most effective and most common therapeutic method. The seal is excised using a laser or radio waves. This procedure lasts about half an hour. If the tumor is very large, after its removal the wound is covered with a flap, which is formed by the doctor from the surrounding tissue.
When pathology is caused by taking certain medications, they should be completely eliminated and replaced with alternatives with similar properties. After discontinuation of drugs in such cases, the appearance of the mucous membranes is often restored without outside help, and the likelihood of relapse approaches zero. However, this does not apply to situations where the disease is advanced.
Surgery can also be avoided in case of traumatic effects of orthopedic structures. For example, when a crown, filling, or prosthesis puts pressure on the tissue. Elimination of the provoking factor often leads to a decrease or complete disappearance of a benign formation. Most likely, it will be necessary to dismantle the old structures and replace them with new ones.
On the Internet you can find stories of healing using home remedies. It is worth remembering that the disease cannot be treated with the help of folk recipes. Herbal decoctions and infusions, and other compositions are used only as an auxiliary element of complex therapy.