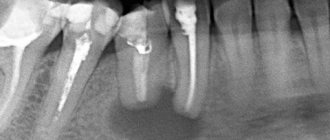
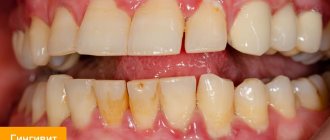
How does a tooth root cyst appear?
The causes of cysts are varied, and among them it is impossible to single out the prevailing ones. So, this may be the result of physical trauma to the maxillofacial bones, or a rare but common medical error, in which the tightness of the root canal was broken, which became the basis for the emergence of a source of infection. A similar situation occurs when a dental crown is installed incorrectly. But the reasons for cyst formation are not limited to this. Untreated infectious diseases (in particular, sinusitis or periodontitis) are no less a provoking factor.
Antibiotics after tooth extraction with a cyst or complex figure eight extraction
After surgery, doctors often prescribe antibacterial and antibiotic drugs. Not in all cases, taking pills is justified, but if there is even the slightest possibility of infection of the wound, then you cannot refuse to take the medication.
Antibiotics are necessary to prevent cyst formation after wisdom tooth removal. It is difficult to remove the figure eight, since the root system is powerful and located deep in the jaw. To extract it, you need to cut the gum, cut off part of the bone, and saw the roots into fragments. With such a complex procedure, tissue is severely damaged and even an experienced surgeon can make a mistake.
Classification of dental cysts
There are not many types of cysts, so understanding them is not difficult. Four main types are distinguished by location:
- wisdom tooth cyst;
— a cyst due to an illiterate (unprofessional) installed dental crown;
- a cyst that arose as a result of the influence of a third-party infectious disease (sinusitis);
- a cyst localized in the area of the front teeth.
At the same time, a classification is used based on previous circumstances preceding the occurrence of the cyst:
- a disease caused by poor-quality removal of one or more teeth;
— periodontal type cyst, provoked by an inflammatory process in the gums;
- a cyst caused by the growth of a wisdom tooth (retromolar or paradental);
- a cyst that occurs in children, first during the period of the appearance of milk (follicular) teeth, and then molars (eruption cyst);
— a cyst that arose as a complication of periodontitis (radicular);
— a situation is also possible in which the tissue forming the tooth degenerates (keratocyst).
Symptoms of cystic lesions
A characteristic feature of a neoplasm under a wisdom tooth is its latent appearance and development. A person does not even realize that there is a growing cyst until it is accidentally discovered during an X-ray or in the dentist’s chair. Education can also reveal itself during colds, in stressful situations and during periods of winter frost.
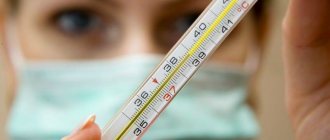
As a rule, a trigger is triggered in the form of severe stress or ARVI, which is the catalyst for the purulent process. When the cyst space fills with pus, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- Painful sensations when touching the affected area;
- Swelling of the face in the area of inflammation;
- Enlarged lymph nodes;
- Body temperature rises;
- Malaise, apathy and lethargy;
If you ignore these symptoms, the disease enters a new phase - flux, osteomyelitis and sinusitis develop. In addition to internal processes, complications can also affect external manifestations - deformation of the dental bite or the appearance of facial asymmetry.
Diagnosis of symptoms of tooth root cyst
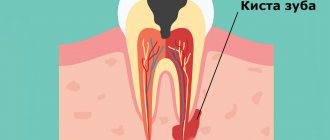
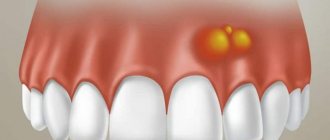
The appearance of a cyst implies the formation of a cavity, which gradually grows while simultaneously filling with pus. This condition can last for a long time, and the patient does not experience pain. A sign suggesting the presence of a cyst is slight pain that occurs when pressing on the gum. Such a symptom only in rare cases becomes a reason to visit a dentist. Basically, it occurs in later stages, when the pain intensifies and becomes nagging, continuous, cannot be relieved with analgesics, and inflammation begins to additionally manifest itself in the form of swelling and swelling of the gums in combination with a persistent unpleasant odor in the oral cavity. Finally, a situation cannot be ruled out in which a fistula occurs - that is, a channel through which the contents of the cavity independently come out.
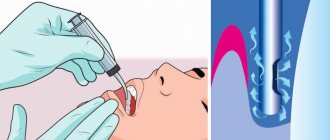
An effective way to detect a cyst in a timely manner is to conduct an X-ray examination followed by its opening and removal.
It should be noted that at the very beginning the disease poses minimal danger to surrounding tissues, since the cavity itself is reliably isolated by thick walls. However, as pus accumulates, the pressure on the walls increases, creating the possibility of a breakthrough, which can lead to blood poisoning and, in the long term, damage to the structure of the jaw bones. At the same time, the dynamics of cyst development are unpredictable and strictly individual. However, in the presence of other inflammatory processes or infections, in a weakened body the transition to the acute stage can occur quickly.
Particular attention should be paid to early diagnosis of the disease in pregnant women. This is due to the complexity of treatment: during pregnancy, only stabilization of the cyst is possible. If the inflammatory process worsens, the choice of treatment methods is strictly limited. That is why, at the planning stage of pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo a full examination by a dentist.
Postoperative period
Despite precautions, the operation is complex and requires time for rehabilitation. Gum healing occurs within a week, bone tissue restoration takes 1-2 months, depending on the volume of the removed cyst.
Accelerated rehabilitation
Patients who want to reduce recovery time after surgery to 1 day, prevent possible swelling, and get rid of pain 100% can take advantage of the unique accelerated rehabilitation program developed in our Center. The complex includes:
Surgeon's advice
In the first 2-3 days after surgery it is recommended:
- Avoid any thermal procedures (hot bath, steam bath, sauna, compresses)
- Limit physical activity
- Do not use straws for drinks
- Do not chew on the side of the extracted tooth
- Perform antiseptic mouth baths (never rinse)
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor
Tooth root cyst in children
The disease has features and varieties that are characteristic strictly for children. First of all, we are talking about formations that arise and go away on their own, without complications: in the form of a rash that appears on the gums, as well as the so-called “Epstein’s pearl”. Both varieties do not pose a danger due to the absence of purulent masses, which means that the cavity is infected. In addition, they may not occur at all, being only some of the phenomena accompanying the development of the child.
The situation is different with the appearance of a cyst during the growth of teeth (both milk and molars). In this case, the resulting cavities are infected, and given the previously described asymptomatic nature of the disease in the early stages, the most reliable method of determining its presence is regular visits to the doctor. This allows for successful treatment at the very beginning of the development of the cyst, saving the tooth in almost 100 percent of cases.
What do patients say about apex resection? Reviews are usually only positive!
“Resection of the top of the tooth took about an hour, the operation was performed under pain relief. It didn’t hurt very much near the tooth for about a month. A few months later I had to take an x-ray, the doctor showed that all the tissues had been restored."
“The cyst grew, they told me to remove it, it was a little unpleasant, but quite tolerable - the doctor quickly and accurately carried out the procedure. Everything was restored soon, now it’s completely unnoticeable that there was anything there.”
At Ritsa Dentistry, cyst removal operations are performed by experienced surgeons with extensive experience in performing such procedures. Therefore, you can rely on our professionalism and entrust the treatment of the cyst to our doctors.
Methods for treating dental cysts
As mentioned earlier, the only reliable and error-free method for diagnosing a cyst on the root of a tooth is an x-ray. In most cases, one x-ray is sufficient; however, due to individual tooth growth patterns, an additional x-ray of the root portion may be required.
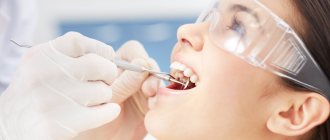
Based on the analysis of X-ray data, the dentist determines and prescribes the type of treatment. Due to the difficulty of accessing the cavity, the process of getting rid of the cyst can take several sessions - however, only this method allows you to eliminate the pathology while keeping the tooth itself healthy.
There are two main directions of treatment: therapeutic and surgical.
— the sequence of actions during therapeutic treatment is as follows: the dentist gains access to the intradental canals (to do this, the tooth tissue is opened), expands them, cleans the cavity from pus, then disinfects it and installs a temporary filling. In the absence of relapse and a favorable outcome, the temporary filling is replaced with a permanent one. An alternative option may be the depophoresis method. Its difference is that the cleaning of the canals occurs due to the sequential introduction of a special substance into them, which, under the influence of an electric current, disinfects them. The common property of both methods is their applicability in the early stages of the disease;
— surgical intervention is used in most cases due to its reliability and high efficiency. There are three types of surgical treatment: cystectomy, hemisection and cystotomy. The first option involves opening the gum from the side and removing the cyst, followed by suturing. Rehabilitation takes place while taking antibiotics. Hemisection requires additional removal of the affected tooth root and crown fragment. If a cystotomy is prescribed, penetration into the cavity is carried out through the near wall. This method has a significant rehabilitation period.
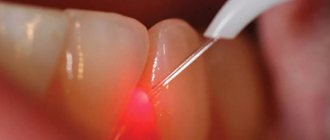
In addition to the above methods, laser therapy is used. Its principle of operation is to insert a thin tube into the cyst, allowing complete disinfection using a laser, followed by vacuum cleaning. This progressive method is painless and effective, since it is guaranteed to preserve the tooth and protect against recurrence of pathology.
3D tomography - to eliminate risks
Accurate diagnosis is the key to successful surgical treatment without risks and complications. The Center uses a dental tomograph Sirona Galileos (Germany)
- Assessment of the anatomical features of the tooth
- Determination of the location and size of the cyst
- Diagnostics of the nasal sinuses in ENT mode
Rehabilitation period and prevention of dental cysts
Due to the fact that the cyst is an inflammatory infectious process, drug therapy necessarily includes taking antibiotics, which are selected by the attending physician. Vitamin complexes and immunomodulators act as compensating medications. Treatment of dental cysts with medications is carried out simultaneously with removal of the cyst.
The main ways to avoid the disease are to regularly visit the dentist and carefully monitor oral hygiene. For preventive purposes, you can periodically rinse with infusions and decoctions - for example, aloe, calendula, sage. Combined with strict adherence to the dentist’s recommendations and timely relief from chronic nasopharyngeal diseases, this will ensure dental health for years to come.
You also need to clearly understand that a cyst on the root of a tooth is one of the serious and complex diseases, the treatment of which requires time and highly qualified surgeons. Only this guarantees the absence of complications: re-infection, the occurrence of an abscess, pulpitis or fistula, damage to adjacent tissues and teeth.
Popular questions
The pathology is dangerous, and the operation and recovery period are painful, so patients are interested in many questions about the tumor:
- How long does swelling last after removal of a dental cyst?
Surgery always leads to soft tissue swelling. A large wound remains at the site of the removed tumor, so the swelling lasts for several days. If the cheek is very swollen, then doctors recommend applying a cold compress to the projection of the operated area several times a day. - What should you do if your tooth hurts after removing a cyst?
The pain spreads to neighboring tissues and can radiate to the temples, throat, and neck. To relieve acute symptoms, you need to take analgesics. After one or two days, the pain will become less intense and the medication can be stopped. - What are the complications after removing a tooth with a cyst?
Possible wound inflammation, bleeding, suture divergence. The most unpleasant consequence is a relapse of the disease. - How long does it take for a wound to heal after removing a tooth with a cyst?
The wound heals in about one week, and complete tissue restoration will take 4 to 6 weeks.
When can an implant be placed?
Implantation is allowed after complete tissue healing. The recovery time depends on how carefully the removal was carried out and the size of the tumor:
- When eliminating small tumors along with the tooth - 2-3 months .
- When removing large tumors - up to six months .
In any case, implantation is recommended no later than 6 months, since without chewing load the bone decreases.
BobrovnitskyOleg Igorevich
Implant surgeon, 9 years of experience
Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category. Clinical expert and leading implant surgeon at Nobel Biocare. All types of implantation and bone grafting, surgical preparation before installation of implants.
More about the doctor
How to speed up the time before implant installation
It is impossible to reduce the time from removal to implant installation. However, the patient cannot prolong it. You must follow your doctor's recommendations to prevent the inflammation from spreading. Rules for caring for the oral cavity after removal of a cystic tooth:
- do not drink or eat food for 4 hours;
- do not injure the wound with a toothbrush;
- rinse your mouth regularly with an antiseptic;
- take antibiotics (as prescribed by a doctor);
- use dental gel or paste to accelerate regeneration (as prescribed by a doctor);
- give up smoking and alcohol.
Superficial healing occurs in 10-14 days. It takes 1-6 months to restore bone tissue.
The issue of implantation should not be rushed, since careful and systematic preparation minimizes the risk of early and late complications.