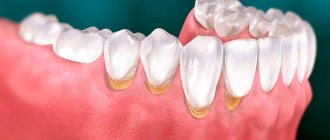
A purulent formation on the gum is popularly called gumboil. Very often it is not taken seriously, but it is not just a small swelling that will go away on its own. Flux is an ontogenic periostitis, a complex infectious disease that affects the periosteum and jaw bone. Periostitis occurs quite often, but without adequate treatment it is fraught with serious complications, including blood poisoning.
It is almost impossible to cure gumboil without the help of a dentist. The treatment program includes therapeutic, physiotherapeutic, and surgical methods.
Have you noticed purulent formations on your gums and swelling of your cheeks? Do you have acute pain in your tooth or gum? Come for a consultation with a dentist at our clinic. Timely treatment of flux allows you to get rid of the problem within about 7 days.
Why does flux form?
Dental diseases are always the precursor to gumboil. Most often lead to suppuration:
- Untreated caries. If caries is not treated, the inflammatory process begins to spread to other tissues. Pulpitis and periodontitis gradually develop.
- Mechanical injury. Injury can lead to more than just crown destruction. Very often, an inflammatory process develops in injured tooth or gum tissues. Without treatment, purulent processes develop and gumboil forms.
- Periodontitis. In more than half of the cases, gumboil develops precisely against the background of periodontitis, as its complication. This is due to the fact that purulent processes from periodontal pockets can spread to the neck of the tooth.
- Poorly sealed canals. Before filling, the canals must be completely cleaned and the filling material must completely fill the cavity. If at least one of the conditions is violated, the infection from the canal spreads to other tissues.
Types of gingivitis
Gingivitis differs in the nature of its course:
- Acute gingivitis is a disease whose symptoms appear suddenly and progress quite quickly.
- Chronic gingivitis is a sluggish process, the symptoms of which increase gradually.
- Aggravated gingivitis (recurrent stage of a chronic process) is an increase in the symptoms of a chronic disease.
- Gingivitis in remission is the moment of complete relief of all symptoms.
The form is:
- catarrhal gingivitis, which is manifested by swelling and redness;
- ulcerative (ulcerative-necrotic) gingivitis, with necrotic (dead) areas of the gums;
- hypertrophic gingivitis, in which there is a significant increase in the volume of gum tissue and its bleeding;
- atrophic gingivitis, on the contrary, is characterized by a decrease in the volume of gingival tissue;
- desquamative (geographic) gingivitis, which is manifested by intense redness and abundant desquamation of the epithelium of the mucous membrane.
According to its distribution in the oral cavity, gingivitis can also be local (affects some areas of the teeth) and generalized (the process affects the gums of the entire jaw or both jaws). And according to severity - mild, moderate and severe gingivitis.
When do you need dental help?
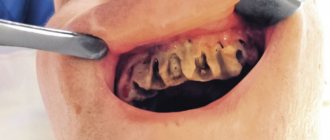
Flux has pronounced symptoms. The main one is the appearance of an abscess on the gum next to the diseased tooth. The abscess develops gradually. At first, the gums swell a little and a small red or whitish bump is noticeable on it. After some time, a noticeable fistulous tract forms on the lump, from which pus flows. The development of periostitis is accompanied by other symptoms:
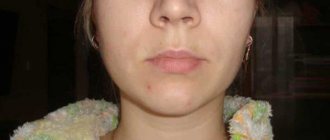
- Swelling and swelling of the gums, lips, cheeks. Sometimes they can be so large that facial features are distorted.
- Severe cutting pain in the tooth area. Innervates the temporal region, orbits.
- The diseased tooth begins to become very loose, even if there was no mobility before or it was insignificant.
Since flux is caused by infection, it is characterized by symptoms that appear during any infectious process. The patient feels unwell, his temperature rises, his head hurts, and weakness appears. Lymph nodes on the head and neck become enlarged.
Any of these symptoms is a reason to consult a doctor. The more advanced the case, the higher the risk of complications. This disease is often accompanied by other pathological processes. For example, a cyst may form in tissues affected by infection.
Causes of gingivitis
Most often, gingivitis develops as an independent disease, but sometimes the causes of its occurrence are acute and chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system, hematopoietic organs, infectious diseases, and changes in hormonal levels. In this case, gingivitis is one of the symptoms of the underlying pathology. The causes of gingivitis can be internal or external.
Internal reasons include:
- tooth growth that injures the gums - the eruption of wisdom teeth;
- vitamin deficiency, hypovitaminosis (most often lack of vitamin C and zinc);
- weakened immune system;
- metabolic disease;
- allergic diseases;
- diabetes;
- stress, mental illness;
- anomalies and various deformations of the gums;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
External reasons are a number of factors:
- physical (injuries, burns);
- chemical (the influence of aggressive substances);
- medical (incorrectly applied fillings, incorrectly installed veneers, traumatic wearing of braces);
- bad habits (smoking, mouth breathing);
- biological (infectious process);
- hygienic (insufficiently thorough hygienic procedures).
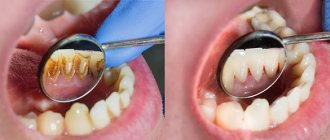
Toxins from microorganisms that enter the oral cavity with food and water, as well as those that live there permanently, form dental plaque (plaques) due to insufficient hygiene measures. They are the most common cause of the inflammatory process.
Inflammation can develop differently depending on the cause. Chronic catarrhal gingivitis occurs most often due to unsatisfactory hygiene measures or as a result of gum injury or burns. Hypertrophic gingivitis is caused by crowded teeth, incorrectly installed fillings or dental crowns, as well as changes in hormonal levels, for example, during pregnancy (pregnant gingivitis) or puberty (adolescent or juvenile gingivitis). Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (Vincent gingivitis) is usually caused by an infectious process. It occurs due to the activation of two microorganisms (Vincent spirochete and spindle bacillus) against a background of weakened immunity, hypothermia, stress or malnutrition.
Flux treatment methods
Treatment should be started as early as possible. If an abscess on the gum opens spontaneously, there is a risk of infection entering the bloodstream. With such an infection, blood poisoning develops, and such a complication can lead to serious consequences, including the death of the patient.
Flux treatment is always complex. The treatment program depends on the degree of tooth decay and the spread of infection.
Dentistry for those who love to smile
+7
Make an appointment
Additional measures to prevent hematomas
To reduce the risk of blood balloons swelling on the oral mucosa, patients are advised to follow a few simple rules:
- avoid salty and spicy foods that irritate the mucous membranes;
- adjust the design of prostheses and orthopedic systems for the jaw apparatus;
- increase the amount of medium-temperature liquid and semi-liquid foods in the diet
We should also not forget about the need to regularly visit the dentist for the timely detection and elimination of diseases of the teeth and gums. This solution will help maintain oral health and avoid a number of serious pathologies with unpleasant symptoms.
Opening an abscess on the gum
The abscess is always opened. This reduces the risk of spontaneous opening, which can cause complications. The flux is opened under local anesthesia. If the patient has panic or other indications, the doctor may choose a different method of anesthesia.
A small incision is made on the anesthetized gum in the area of the gumboil, no more than 2 cm in length. After the dissection, the doctor completely cleans and sterilizes the purulent cavity and treats it with antiseptics. A crust should not be allowed to form in the area of the incision, as it will interfere with the outflow of ichor and purulent contents. To do this, a drainage is inserted into the incision. After the cavity is cleared of pus, you can begin general treatment, the purpose of which is to eliminate the causes that caused periostitis.
Epulis
Treatment
The lump on the root of the tooth is attached to a stalk and is either red or gum-colored. It affects the lower jaw and occurs as a result of malocclusion, permanent mechanical damage, and poor quality dentures. Often observed in women with hormonal imbalance.
Treatment
It is removed by one of three methods: scalpel, diathermocoagulation or cryodestruction. The manipulation is performed under local anesthesia.
General treatment
Methods depend on the reasons that caused the flux. The only exception is periostitis, which develops against the background of periodontitis. In this case, immediately after opening the abscess, the doctor begins periodontal treatment. No medical manipulations with the tooth are required. In other cases of dental disease you need to treat:
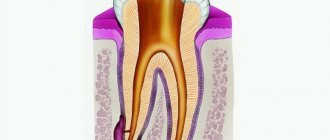
- Pulpitis. First, the dentist drills out carious cavities and performs pulp removal. After this, endodontic canal treatment is performed.
- Periodontitis. Treatment depends on whether depulpation and canal filling have been previously performed. If periodontitis has developed for the first time, the doctor will remove the pulp, clean and fill the canals. If filling of the canals has already been performed previously, they need to be unfilled and treated again. Since it is very important that the pus comes out of the flux completely, when treating complicated pulpitis and periodontitis, a temporary filling is not placed.
- Tooth after restoration. At the first stage, the doctor is faced with the task of completely removing inflammation. After this, the damaged tissue of the root apex is removed. If the condition of the root allows, the tooth is restored again using a core tab or pin and an artificial crown. When the damage is very severe, it is more advisable to remove the tooth.
Symptoms of hematomas in the oral cavity
The most noticeable sign is the spread of vesicles with bloody contents throughout the mucosa. Often there are no other symptoms of pathology. Sometimes patients complain of itching and tingling in the area of damaged tissue. Doctors say that this is a reaction to additional chemical and mechanical irritation of the inflamed mucous membrane under the influence of saliva, contact with teeth, etc. When hematomas form on the oral mucosa during tooth eruption, there are sensations of bursting and pressure from within the gum tissue. If inflammation has become a complication of a burn, pain is a logical consequence of mechanical irritation of the mucous membrane.
Signs of the appearance of blood balls on the cheeks in the mouth, requiring immediate examination and diagnosis, are included in a separate group. Among them:
- relatively frequent appearance of a large number of points of inflammation;
- the duration of wound healing, despite the measures taken to treat them;
- hematomas that are too large, interfering with eating and full communication;
- formation of bloody balls on the lips.
Each of these signs can be a symptom of serious disorders in the body. Therefore, the optimal solution would be to refuse self-medication and schedule a consultation with a qualified dentist.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods are used as additional ones. They allow you to quickly cope with the infection and stop the inflammatory process. The following methods can achieve good results:
- Fluctuarization. The inflamed tissues are exposed to low voltage current.
- Electrophoresis with lidase. Electrical current is applied to the tissue, allowing the drug to be effectively distributed.
- Ultrahigh frequency therapy. The method is based on the influence of an electromagnetic field.
- Ultrasound therapy. The effect of ultrasound on infected tissues accelerates their regeneration.
- Laser therapy. Damaged tooth tissue is treated with a laser beam.
Cyst
Description
A hard, bone-like compaction of gums under a tooth, up to 1 cm in diameter. Occurs in people with weakened immunity, genetic predisposition, as well as due to acute infectious diseases, mechanical damage to the soft tissue of the oral cavity.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out in the same way as for fibroma - by excision. After surgery, mouth rinses and baths are necessary, as well as repeated visits to the doctor to monitor recovery.
Rinse
They are used as an additional treatment in order to completely remove pus and ichor from an opened abscess and prevent the infection from spreading to healthy areas. Soda-salt baths and rinsing with antiseptic solutions help make treatment more effective and speed up gum healing. When rinsing, you must adhere to the following rules:
- During the day, do 4-5 gentle rinses or baths. To do this, just take the solution into your mouth and hold it for about 30 seconds.
- During the day, do 4-5 gentle rinses or baths. To do this, just take the solution into your mouth and hold it for about 30 seconds.
Forms of gingivitis and symptoms
Signs of gingivitis directly depend on the nature of the disease and its form. Let's look at each form of gingivitis separately. So, complaints and visual inspection.
Catarrhal gingivitis
This form of the disease usually occurs without obvious pain. Its immediate symptom is bleeding gums when brushing teeth, eating solid foods and other mechanical effects on the dental system.
Ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis
This is one of the most unpleasant forms of gingivitis, which is characterized by a feeling of itching of the gingival papillae, severe pain, copious flow of saliva, fever, inflammation of the lymph nodes and the formation of necrotic areas of the gums.
Hypertrophic gingivitis
Patients suffering from this form of gingivitis complain of severe pain, constant bleeding of the gums and a significant increase in the volume of the gums, which can partially cover the crowns of the teeth from the outside (not from the tongue). At the same time, the patient’s gum remains quite hard and under it, on the teeth, tartar forms, which creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of microorganisms. With hypertrophic gingivitis, teeth may move slightly.
Atrophic gingivitis
The last and most advanced stage of gingivitis, often leading to periodontitis, is atrophic gingivitis. With it, the gum tissue becomes thinner, decreases in size, the necks of the teeth, and sometimes their roots, are exposed. Teeth become more sensitive to temperature changes (cold or hot drinks, frosty air), to sour or sweet foods, to the mechanical impact of a toothbrush.
Desquamative (geographic) gingivitis
The symptoms of this form of gingivitis differ from others by pronounced red spots on the gums, desquamation of the upper layer of the epithelium, the appearance of blisters on the gums and the formation of mouth ulcers and erosions.
How to avoid complications
To avoid missing a cyst in the early stages, check with your dentist at least once every six months, especially if your child has chronic pulpitis or periodontitis. The occurrence of cysts is most likely between the ages of 6 and 12 years, especially during the formation of the first molars in the lower jaw.
Teach your child proper and regular oral hygiene. This will reduce the likelihood of inflammation and caries in both milk and permanent teeth. For this, use high-quality children's toothpaste for a specific age. Asepta has developed Baby, Kids and Teens pastes that take into account the dental needs of children of different ages. For the little ones, specialized Asepta wet wipes designed in the form of finger pads are suitable - wipe the gums after each feeding.
It is necessary to treat infections and caries in a timely manner so that they do not lead to the formation of a cyst in the future.
When to see a doctor
Complications after implantation normally last 5-7 days. An alarming signal should be the persistence of unpleasant symptoms longer than this period. In this case, there is no need to postpone going to the doctor. Timely treatment will help avoid serious consequences.
You need to contact a specialist when you have:
- undiminished or growing swelling (normally, a decrease in the severity of edema, hematomas occur in the first days after implantation);
- acute, pulsating pain at the site of swelling;
- persistence of low-grade fever for 3 days, its increase;
- loss of sensitivity, numbness;
- the appearance of bad breath.
Opinion of an implant surgeon : “Although serious complications as a result of implantation do not occur often, the patient should carefully monitor his well-being. You can prevent the development of unpleasant consequences by timely and competently assessing the scale of the problem. If there is no positive dynamics, you should contact your dentist.”
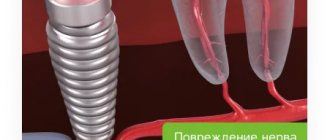
Why do bruises appear after implant placement?
Bruises are formed due to damage to small blood vessels, hematomas are the result of deep damage to soft tissues followed by muscle hemorrhage. Such reactions are located in the gums, but sometimes, due to inflammation in the area where the titanium structure is implanted, they move outward.
Reasons for development:
- An insufficiently experienced implantologist - due to inexperience, the facial nerve or artery may be affected.
- Intolerance to materials and medications used during implantation.
- Anatomical features of the patient’s body (rate of blood clotting, tissue regeneration).
- Violations at the stage of preparation for implant installation.
- Failure by the patient to follow medical recommendations at the postoperative stage.
Gum cancer
Description
A rare dangerous disease. It is characterized by the formation of a dense lump on the gum at the root of the tooth; it can develop asymptomatically for several months.
Treatment
Requires serious medical intervention, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, long-term recovery and follow-up.
Gum cancer, if detected early, is curable, otherwise it ends in death. Red and white bumps on the gums appear in both adults and children. Only a doctor can correctly identify the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment. The sooner you see a dentist, the greater the chances of a quick recovery.
Don't self-medicate! If a ball is inflated on your gum and you don’t know what to do, contact a dentist in Odintsovo. The doctor will conduct a full examination of the oral cavity, accurately diagnose the disease, and prescribe effective treatment.
You can make an appointment for a consultation, as well as find out the cost of admission and treatment by calling the clinic in Odintsovo.
What can cause your gums to turn blue?
So, why can individual areas of the gums change their color, and where do such blue spots appear on the mucous membrane? This could be due to many different factors. So, for example, if we are talking about a child, the reason may be the eruption or change of baby teeth. In adults, a similar symptom is sometimes provoked by certain diseases of periodontal tissue or the oral mucosa as a whole. Also, the area near the tooth may turn blue due to unsuccessful prosthetics or malfunctions in the internal systems of the body. Let's look at possible provoking factors in more detail.
Why do my gums turn blue?
Causes of blue gums in a child
The time when a baby's first teeth emerge varies in each situation individually. When an already formed rudiment erupts, inevitable injury to soft tissues occurs, and, as is known, a large number of vessels are concentrated in them. Due to a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane, blood enters the soft tissues, and a hematoma forms. If the child is one year old and a bruise appears on his gum, namely in the place where the tooth should appear, there is nothing to worry about.
“And sometimes the teeth start to break through with a bruise. We had the same thing with the side ones. I remember looking in the morning and a blue spot appeared on my daughter’s gum. I thought that she had hit herself somewhere, so I decided to observe. And after a while a white stripe appeared.”
Marina7, Irkutsk, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
Among the pathological causes of the formation of blue areas in the mouth in children, experts in the field of pediatric dentistry and pediatrics identify the following conditions:
- inflammation of gum and periodontal tissues: the most common cause of blue discoloration is gingivitis - inflammatory processes that spread in the gums without disrupting the periodontal attachment. Redness turning blue is observed in localized areas, mainly in the cervical area. At the same time, the child becomes whiny and capricious, and his appetite is impaired. If left untreated, the next stage may be periodontitis,
Gingivitis in a child can cause blue gums - diseases of the mucous membrane: often stomatitis leads to blue gums - an inflammatory disease, the development of which is accompanied by the appearance of painful rashes on the gums, the inside of the cheeks, lips, palate and tongue. In this case, a change in the color of the soft tissues is noted around the tumors. Associated symptoms include severe pain in the oral cavity, as well as a sharp increase in body temperature.
Stomatitis is common in infants
It is worth noting that most often the diseases described above are diagnosed in children with weakened immune defenses. However, the main enemy of oral health is poor oral hygiene. Plaque and dental deposits are the key cause of most dental ailments.
Why does the mucous membrane turn blue in adults?
In adults, the gums most often turn blue after poor-quality dental intervention, as well as against the background of periodontal diseases and systemic pathologies of the body as a whole. Thus, the most common cause of hematoma is unsuccessful prosthetics. A small blue spot may appear above the crown if it is pushed too far under the gum. As a result, microcirculation will be disrupted, a blood clot will form, swelling and hypoxia of the mucosa will appear. Much less often, a similar situation occurs during restoration with filling materials, when the composite is carelessly applied to the gum1.
On a note! There is an opinion that the soft tissues surrounding the structure may turn blue due to metal-ceramics. This is a common misconception based on the assumption that the metal is oxidizing. In fact, changes in the gums around the crown only indicate its incorrect installation. The metal in the crown does not oxidize and certainly does not rust. To create such orthopedic structures, a special alloy is used, which fully meets all the necessary requirements.
In some cases, darkening of gum areas may indicate the development of certain pathological conditions of internal organs and systems. These include the following factors:
- thin blood vessel walls or blood clotting problems,
- violation of microcirculation,
- gingivitis and periodontitis,
- deficiency of vitamins and microelements in the body,
- anemia.
Blue gums in adults may occur after the installation of crowns.
In the case of anemia, a lack of iron, vitamin B12 and other vital substances in the body leads to a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in red blood cells. As a result, the patient experiences pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, including the appearance of cyanosis.