Many parents notice with alarm that the child’s tongue is undergoing changes - it suddenly changes its normal color, begins to peel and peel. Why do such changes occur, do they represent a serious pathology, and what treatment is required?
Geographic tongue, which is also known as desquamative glossitis, is a disease of an inflammatory-dystrophic nature, accompanied by external changes in the mucous surface of the tongue. This disease does not have any “age limits” - it can occur with equal frequency in adults and newborns. Most often, geographic tongue is diagnosed completely by accident, at a regular dentist appointment.
Causes of geographic spots on the tongue
Geographic tongue is a disease manifested by dystrophic and inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane of the tongue.
The condition is characterized by alternating areas of peeling and thickening on the surface of the tongue. You should know why a child develops a geographic tongue and what parents need to do in this case. Causes of the disease:
- lack of B vitamins;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, gastroduodenitis, malabsorption syndrome, pancreatitis);
- endocrine diseases;
- autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis);
- severe forms of viral infection;
- exudative diathesis, colds;
- diseases of the oral cavity.
Blood diseases, nervous disorders and autonomic-endocrine disorders are also the causes of geographic spots on the tongue. In children, the disease is often a companion to helminthic infestation. Predisposing factors include heredity and diseases of the spleen.
Causes
Due to the fact that the causes of glossitis have not been identified for certain, it would be more correct to talk about risk groups of patients who are more susceptible to developing this disease. The following can be considered as provoking factors that can cause the onset of the disease:
- Disturbances in the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Diseases of the circulatory system.
- Disorders of the nervous system.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Weakened immunity.
- Pregnancy.
- Acute infectious diseases.
- Avitaminosis.
- Dysbacteriosis, including those caused by long-term use of antibiotics.
- Heredity.
Desquamative glossitis is a chronic disease. It is absolutely not contagious. In about half of the cases it develops together with a folded tongue and glossalgia.
Symptoms of the disease
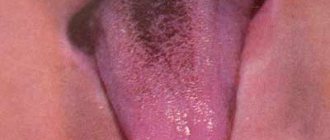
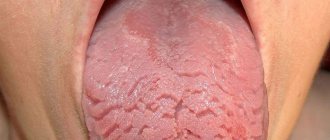
Symptoms most often appear on the back and side of the tongue. The disease is characterized by alternating areas of desquamation of the epithelium and thickening of the mucosa, resulting in whitish-gray and bright pink spots. In appearance they resemble a geographical map.
There are no obvious symptoms in this case. The condition is usually diagnosed when a patient is examined for another pathology. In rare cases (especially when eating spicy, hot and salty foods), the patient may complain of:
- change in tongue sensitivity;
- burning and tingling sensation;
- itching;
- discomfort while eating.
On our website Dobrobut.com you can make an appointment with a doctor and get answers to all your questions. If necessary, the specialist will prescribe additional diagnostics and a course of treatment after receiving the examination results.
Symptoms of geographic tongue
The main symptoms of desquamative glossitis are visible to the naked eye, so most often diagnosing the disease does not cause any particular difficulties. In the vast majority of cases, geographic tongue refers to painless pathologies - the disease is not accompanied by any complaints or painful sensations.
The appearance of the geographic tongue exactly corresponds to its name - whitish stripes, grooves and spots appear on the mucous surface of the tongue, which visually resemble a geographical map. The sizes of such spots can be very different - from several millimeters to centimeters. Most often, such lesions are multiple, and in extremely rare cases - single.
At the initial stages of the disease, the spots are small in size, but quickly begin to grow, merging with each other and creating larger spots.
The appearance of a geographic tongue in some cases may be accompanied by a feeling of discomfort, itching and tingling on the surface of the tongue, especially these unpleasant sensations intensify during meals. When eating too hot or cold, sour, spicy or salty foods, a person may experience disturbances in the sensitivity of the tongue, up to a complete loss of taste.
Diagnosis and treatment of geographic tongue in an adult
Diagnosis of the disease in most cases does not cause difficulties. The diagnosis is made after a thorough examination and history. In some cases, consultation with a dentist and gastroenterologist will be required.
When making a diagnosis in adults, an extensive examination is necessary. When collecting anamnesis, the presence of chronic diseases and allergic manifestations, as well as the state of the immune system, is taken into account. Taking all this into account, the doctor will prescribe a course of treatment for geographic tongue in an adult and monitor its implementation.
4.Treatment
In cases of asymptomatic disease, if there are no signs of underlying somatic diseases, therapy is not required and is not prescribed. The exception is the mandatory sanitation of problematic teeth and oral cavity, as well as normalization of the diet - which, however, is indicated for absolutely all people.
If there are symptoms of a particular disease that may be the cause or basis for the development of desquamative glossitis, the patient is referred to a specialist of the appropriate profile, where he receives etiopathogenetic treatment.
Treatment of pathology
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause. Geographic tongue is not an independent disease, but a condition that signals serious problems in the body.
Additional events:
- sanitation of the oral cavity;
- exclusion of salty, spicy and hot foods from the diet;
- alkaline rinses, local applications with anesthetic;
- prescription of antihistamines;
- prescription of multivitamin complexes.
If you strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations, the prognosis for the disease is favorable.
Traditional medicine recommends using oak bark decoction, calendula or chamomile decoction as rinses. You can also use propolis (applied to the affected areas), vegetable oil (oral baths) and honey.
Treatment of desquamative glossitis
Desquamative glossitis does not belong to the category of dangerous diseases with serious consequences. Many parents, seeing that their son or daughter’s tongue is peeling off, panic, fearing that such changes in the mucous membrane could develop into oncological tumors. These fears are completely unfounded. Desquamative glossitis never develops into cancer.
If geographic tongue is a secondary symptom of another, underlying disease, treatment should be comprehensive.
To eliminate discomfort, itching and burning on the mucous surface of the tongue, painkillers can be used. In order to save yourself from discomfort, you must definitely exclude from your diet all spicy, salty, sour, too hot and cold foods.
Antiseptic rinsing of the mouth is necessary several times a day. For this purpose, special disinfectant medications are used, which are prescribed by the doctor.- An oil bath gives an excellent effect. You can take sunflower, corn or olive oil, which is heated in a water bath for 20-25 minutes.
- A thorough sanitation of the oral cavity is carried out - timely treatment of carious teeth, gum diseases, systematic cleaning.
- Taking multivitamin complexes will be an effective addition to the course of treatment. But in no case should you choose them yourself - you should definitely consult with a specialist.
Adult men and women are recommended to give up many bad habits - smoking, frequent consumption of strong alcoholic drinks, as well as sweets and other foods with a lot of sugar.
Complications and prevention
Geographic tongue is not an independent disease, but its appearance signals serious disturbances in the functioning of the body. The sooner you contact a specialist, the sooner adequate treatment will be prescribed. Timely therapy is a guarantee of a high-quality cure for the disease.
In childhood, complications are very rare.
Preventive actions. Fighting bad habits, taking vitamins in the spring and autumn, adequate treatment of gastrointestinal diseases and timely sanitation of the oral cavity will help avoid this condition.
Book a consultation with our specialists and find out how to treat geographic tongue disease.
1.General information
The apt, albeit somewhat frivolous name “geographic tongue” refers to the inflammatory-dystrophic process in the mucous membrane of the tongue, also known as “wandering glossitis”, “migratory oral erythema”, “exfoliative glossitis” (formulation in ICD-10), “desquamative glossitis”, etc. Exfoliative in translation means “flaky”, desquamative means “deprived of scales”, glossitis is inflammation of the tongue. Peeling of the epithelium in combination with inflammation and dystrophic changes together form red and white patterns on the tongue, which in many cases really resemble a fragment of a geographical map.
In different historical periods in medicine, there were different views on the essence and pathogenesis of desquamative glossitis (the term and concept were introduced into the medical paradigm in 1831), and the discussion continues to this day. Thus, some authors consider this process to be neurodegenerative, others to be purely inflammatory, and others generally consider it as a non-pathological variant of the norm.
The prevalence of “geographic language” varies significantly depending on the age, gender, and clinical composition of the studied samples; in terms of the general population, it is estimated at 2-5% of the population. There is a slight predominance of women, children and adolescents.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
How to treat ulcers at home - traditional methods
As an additional treatment for ulcers on the tongue, you can use traditional medicine recipes:
- It is effective to use mouth rinses with home-prepared decoctions of plants that have antiseptic properties (calendula, sage, St. John's wort, viburnum berries, rose hips, chamomile, linden flowers). The brewing technology is simple - a tablespoon of dry plant is poured with 250 ml of boiling water. The container with the lid closed is left for 30-40 minutes. After filtering, you can carry out procedures. The oral cavity should be treated at least 5 times throughout the day. Keep the liquid in your mouth for about a minute each time you rinse.
- Ulcers will heal faster if they are treated with wound healing agents. These are mainly essential oils: sea buckthorn, calendula, rose hips, as well as aloe and Kalanchoe juices. They need to be applied pointwise, capturing only the affected tissue.
- Among the effective recipes, a solution based on soda , salt, iodine stands out (3 drops of iodine and a teaspoon of bulk ingredients per 200 ml of water). Applications and rinsing should be carried out at least 3-4 times a day for a week.
It is difficult to carry out medical procedures for babies less than a year old, and not all traditional methods can be used.
Therefore, the following treatment options for tongue ulcers have long been used for them:
- treatment of lesions with hydrogen peroxide;
- wiping the oral cavity, including the tongue, with a mixture of milk (100 ml), one yolk and honey (1 tsp);
- taking yarrow juice with honey (1 spoon 3 times a day for 3 weeks);
- processing with a mixture of egg white and water.
In what cases is it necessary to consult a doctor?
If you use folk recipes when identifying ulcers, you can get rid of them without the help of a doctor. But at the same time, the child’s condition must be stable.
If after a week’s treatment the lesions do not dry out or, in addition to them, other alarming symptoms appear (temperature, fever), then you should not hesitate to visit the clinic.
Associated symptoms and what they indicate
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out taking into account the accompanying symptoms.
- Small sores on the tongue and lips may indicate a viral infection - herpes
Temperature indicates an inflammatory process. This is typical for candidiasis, herpes, allergies, and aphthous stomatitis.
- Ulcers located under the tongue appear due to injury, candidiasis, and somatic diseases.
- On the tip of the tongue, sores most often form due to mechanical damage to tissue.
- Accompanied by plaque ulcers due to candidiasis and problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
- Small sores on the tongue and lips may indicate a viral infection - herpes. Thrush ulcers often spread to the lips.
- On the tongue and throat, ulcers are formed as a result of mechanical trauma, malocclusion, dehydration, vitamin deficiency, and the use of medications with a high concentration of active substances.
- Ulcers in a baby indicate possible problems with the internal systems of the body. May indicate an allergic reaction, vitamin deficiency, mechanical damage to the tongue, fungal or viral infection.
Possible causes of ulcers on a child’s tongue
Ulcers on the tongue are a symptomatic manifestation characteristic of several diseases. It makes no sense to treat a symptom without eliminating the provoking factor.
Therefore, the primary task is to determine the cause, which is achieved by analyzing a set of signs:
| Causes of ulcers on the tongue | ||
| Name | Description | Associated symptoms |
| Aphthous stomatitis | The disease is characterized by the formation of ulcers on the tongue with a diameter of 1 to 5 mm. The wounds hurt a lot, which is why the child becomes restless and irritable. When there is mechanical impact on the aphthae, they begin to bleed. | Initially, redness appears on the tongue; if left untreated, it turns into gray or white ulcers. Due to the burning and pain from aphthae, eating is difficult. There is also a spreading white coating on the surface of the tongue. |
| Herpes stomatitis | Herpes stomatitis is contagious, caused by the Herpes virus. Many ulcers appear in the child's mouth, which is similar to a rash. The formed bubbles quickly burst, leaving wounds in their place. The lesion is often transferred to the skin of the face, lips and nose. | Blisters on the tongue contain a clear or slightly yellowish liquid. After a breakthrough, painful gray-white ulcers with a narrow scarlet rim are formed. There is also an increased body temperature and an increase in the size of the lymph nodes. |
| Thrush (candidiasis) | The causative agent of the disease is Candida fungi, transmitted through toys, dishes and other household items. The disease can also develop under the influence of infections, hormonal fluctuations (adolescence), and also as a result of hypothermia. | In the absence of treatment, in addition to yellowish and white ulcers, the following are observed: swelling, dry mouth, tightness of the mucous membrane, increased body temperature, cracks in the corners of the mouth. The sores emit an unpleasant odor due to suppuration. |
| Allergy | Formations on the tongue are caused by the body's reaction to an allergen. | The disease manifests itself in the form of red spots and ulcers with blurred outlines. Over time they merge. Other symptoms are: swelling of the lip, face. |
| Gastrointestinal problems | The tongue reflects any problems in the body. If there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract, white ulcers form. | In addition to ulcers on the white tongue, there are: disturbances in the microflora of the oral cavity, discomfort when chewing food and swallowing. The outbreaks are located in small clusters. |
| Tongue injuries | Injury to the tongue or mucous membrane occurs frequently. Ulcers appear in the area of tissue damage. | The ulcers are usually painless and are recognized by their pink or reddish color. If the wounds become infected, yellowish pus may form. Apart from pain at the site of injury, no other symptoms are noted. |