Home > Laser surgery / Removal of tumors / Removal of hemangiomas > Treatment of hemangiomas of the tongue
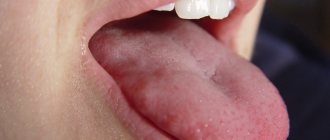
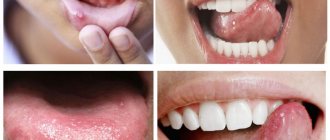
Tongue hemangioma develops in people of different ages. The appearance and symptoms of such a tumor depend on the type of tumor.
Hemangioma of the tongue is a benign formation that grows very slowly. One thing about hemangioma is that it can grow very quickly after a period of slow development. The tongue disease affects young children, adults and elderly patients. The method of treating the disease is removal.
Consultation on the day of the procedure is free
Symptoms and causes of formation
Hemangioma of the tongue can be:
- cavernous;
- capillary.
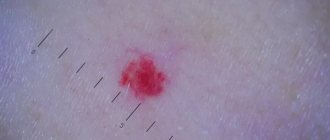
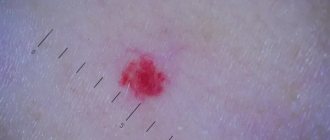
A simple capillary hemangioma grows in breadth without affecting the tissue. It consists of capillary tissue and is often affected during conversation or eating. Externally, the tumor looks like a spot or bruise. The formation must be removed - damage to the hemangioma can lead to infection.
Cavernous hemangioma of the tongue penetrates deep into the tissues; it protrudes noticeably above the surface of the tongue. This formation consists of many vessels and causes serious discomfort. The tongue may lose its mobility and increase in size due to the tumor.
The causes of hemangiomas have not been fully established. In children they occur mainly due to the growth of vascular tissue.
Types of tumor
A tumor on the roof of the mouth always indicates the onset of an inflammatory process in the human body. Tumors can be benign or malignant.
Malignant formation
Problems with the development of a malignant tumor are not limited to disturbances in speaking and eating. The lump, the cause of which is cancer, impairs articulation, complicates the ability to communicate or completely eliminates it.
Oral cancer is typical for men and is a local metastasis of other malignant tumors in the head. It is a rare cancer.
Such malignant lumps are classified as growths on the roof of the mouth. The tubercle can pop up due to a benign inflammatory process, so it is impossible to express a clear opinion about the diagnosis.
Understanding the reasons for the appearance of a tumor is important for determining the course of treatment. The causes can be accurately diagnosed by conducting clinical studies of the compaction.
Benign formation
A cyst on the roof of the mouth is not a fatal diagnosis; it is diagnosed with a number of benign tumors. Such tubercles are caused by insidious but curable diseases:
- growth of blood vessel tissue (angioma);
- cyst;
- pemphigus (erosion);
- myxoma.
Danger of hemangiomas
If a hemangioma appears on the tongue, you should urgently consult a doctor. A benign tumor can be dangerous. Capillary and cavernous types of hemangiomas are damaged during the absorption of food. With cavernous hemangiomas, bleeding is possible. This threatens the penetration of infections.
A simple capillary hemangioma may not cause discomfort. Some patients don't even feel it. But this does not mean that the disease can be ignored. The unexpected can happen at any moment. There are a lot of bacteria on the mucous membrane of the tongue, and it is only a matter of time before infection penetrates into the damaged tumor. Do not delay contacting a specialist.
At the clinic, a patient with a hemangioma will be prescribed treatment. The tumor must be removed. When removing, several methods are used:
- laser;
- surgical method;
- cryotherapy;
- removal by radio wave equipment.
Laser is the most popular method for removing hemangiomas. However, this type of treatment is not always possible. In some cases, doctors are able to solve the problem with a simpler surgical method.
Cost of hemangiomas removal
| Laser tumor removal | Prices, rub. |
| Laser removal of papillomas, single warts - Cat. I. difficulties | 1200 |
| Laser removal of papillomas, multiple warts - Cat. I. difficulties | 350 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. II. difficulties | 700 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. III. difficulties | 1500 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - IV category. difficulties | 3000 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. V. difficulties | 4500 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. VI. difficulties | 6100 |
| CO2 Laser callus removal (per unit) | 6100 |
| Removal of atheroma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Cat. I. difficulties | 6 900 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Category II. difficulties | 9 400 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Cat. III. difficulties | 16 900 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - IV category. difficulties | 22 400 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Cat. V. difficulties | 33 400 |
Sign up for laser removal of tongue hemangioma
- Full name
- Telephone
Advantages of laser removal of angiomas on the body:
- Selectivity of the laser beam - only the vessels that make up the tumor are destroyed;
- Bloodlessness - the procedure for laser vaporization of a hemangioma takes place without a drop of blood, even if the formation is large;
- High cosmetic result - after laser removal of angioma there are no traces left on the skin;
- Single use - removal of angioma is carried out at one time;
- No anesthesia required.
Rice. 4. Angioma under microscopy consists of vessels
Rice. 5. Removal of angioma on the body with a laser
Removal methods
When treating a tumor, the patient is prescribed removal. The method of removal depends on the complexity of the disease. If there is no risk of damaging surrounding tissues, then a surgical method is used. This treatment is used if the tumor has not penetrated inside. In this case, the surgeon will be able to remove all the affected cells.
Surgical treatment is not suitable if the tumor has penetrated deep into the tissue. There is a risk of damaging the tongue and not removing damaged cells completely. In difficult cases, the radio wave method is prescribed. It is used to treat cavernous hemangiomas. Affected cells are removed at ultra-high temperatures.
Treatment with ultra-low temperatures - cryotherapy - is also possible. During treatment, applications are applied to the tongue, which freeze the affected cells. The tumor tissues die and separate.
Removal of angioma on the body at the Laser Surgery Center “ATLANTiK”
Our center performs removal of angiomas on the body using two types of lasers:
- Nd:YAG
- Diode-laser.
Removal of angiomas is carried out on the day of treatment, the removal session lasts no more than 5-10 minutes, anesthesia is not required for small formations up to 5 mm.
During laser removal, angioma on the skin disappears before our eyes as a result of sealing of blood vessels; large angiomas larger than 5 mm first darken and then peel off from the surface of the skin within 7-14 days, depending on the treatment area.
There are no traces left on the skin after laser removal of angiomas.
Laser treatment
The easiest way to remove a hemangioma is with a laser. This treatment method has several advantages:
- no risk of infection;
- This is a non-contact method of therapy;
- tumor cells are completely removed;
- the procedure is painless;
- It is possible to cure even cavernous tumors;
- the wound heals quickly.
Laser treatment does not take much time. The procedure uses a laser with a short beam length. Removal does not cause serious discomfort to the patient. The laser is absolutely safe, the procedure does not lead to side effects. After treatment of hemangioma of the tongue, no bleeding is observed.
Complete laser removal leads to rapid restoration of healthy tissue. The tongue heals and the patient returns to normal life. A special laser is used in clinics where they offer the procedure for removing hemangioma in this way.
Removal of tumors at Lazmed Clinic
Causes and types of lumps
Basically, growths on the upper palate are formed from:
- muscle tissue;
- epithelial tissues;
- blood vessels;
- connective tissue;
- organic liquids.
The most common cause of a lump is considered to be an inflammatory process in the oral cavity. Because of it, the flow of blood and other fluids through the vessels is disrupted.
The formation of a lump on the palate is promoted by colds and infection of the body. The main causes are cyst, angioma, myxoma, pemphigus.
Other provoking factors are fistula, epulis, exostosis.
Treatment is the use of anti-inflammatory, sclerotic, vasoconstrictor drugs. If the tumors are malignant, radiation therapy is prescribed.
The development of neoplasms in the oral cavity can be provoked by:
- congenital predisposition;
- smoking and drinking alcohol;
- damage to the mucous membrane;
- dental errors (installation of unsuitable dentures, untreated fillings, etc.);
- viral infection;
- diseases of internal organs and other factors.
The nature of the clinical picture depends on the type of growth.
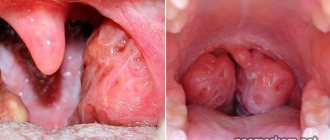
Angioma
Angioma is a benign tumor that appears due to dilation of blood vessels. Less commonly, the tumor is formed from the lymphatic ducts. This tumor is called lymphangioma, and when pressed it causes pain.
Sometimes a lump on the roof of the mouth indicates trauma: burns, damage to the mucous membrane during eating (cutlery, solid food, fish, poultry or fruit bones), rubbing with the base of a removable denture.
In this case, it is enough to eliminate the root cause factor, as well as carry out antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and reparative treatment.
Dentist
Novikova Olga Alexandrovna
8 years of experience
The growth formed due to the proliferation of blood vessels is of two types:
- Simple angioma. Externally it has a reddish-blue surface. A simple angioma is formed due to the coagulation of blood vessels.
- Cavernous angioma. Has a dark burgundy tint. Formed in the cavernous cavities of the mouth.
The first type of tumor occurs due to disruption of the capillaries running along the palate. Cavernous angiomas are formed due to the proliferation of venous vessels. The endothelium grows around such compactions, due to which the neoplasms have a hard shell to the touch.
Cyst
Cystic cavities rarely occur on the palate. They usually do not exceed 1 cm in diameter. The appearance of a cyst is caused by a malfunction of the salivary gland, which is caused by:
- mucosal injuries
- narrowing of the salivary ducts;
- inflammation of the gland;
- congenital anomalies.
Cystic cavities do not cause pain. Without treatment, pus forms in them, which leads to an abscess.
Pemphigus
Pemphigus, or epidermolysis, is a benign white neoplasm. The tumor first appears in childhood. The main cause of pemphigus is congenital predisposition.
The development of epidermolysis triggers carious processes in the oral cavity. Having reached a certain size, pemphigus opens up on its own, and painful erosions remain in its place. The latter eventually turn into ulcers. This transformation is explained by the fact that in pemphigus the connection between epithelial cells is disrupted.
Myxoma
Myxoma is a type of cystic cavity that is formed due to the proliferation of capillaries. Growths of this type are characterized by a bumpy surface. The main cause of myxoma development is considered to be inflammation of local tissues.
Diagnosis of the neoplasm is carried out through hypoxia and x-ray examination. Additionally, a biopsy is prescribed to rule out a malignant tumor.
Other neoplasms on the palate
The most common neoplasms on the palate also include:
- Fistula. A characteristic sign of this neoplasm is the presence of a small hole through which pus comes out.
- Exostosis. Formed due to protruding bone tissue.
- Epulis. It is a small ball that is attached to the base by means of a thin stem. Epulis is more often detected in women.
Almost all growths on the palate interfere with chewing and swallowing food. Less commonly, the formation of cones is accompanied by pain. Sometimes they bleed when pressed.
Due to the fact that some of the cones are formed due to the proliferation of lymphatic or blood vessels, the development of growths on the palate causes swelling of the oral mucosa. At the same time, the lymph nodes located near the jaw enlarge.
Our specialists
- Kiani Ali
Candidate of Medical Sciences, laser medicine specialist, dermatocosmetologist.
Sign up
- Stepanova Inna Igorevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, maxillofacial surgeon, specialist in laser medicine.
Sign up
- Fedotova Marina Andreevna
Surgeon, dermatocosmetologist, laser medicine specialist
Sign up
- Popovkin Pavel Sergeevich
Surgeon, oncologist, laser medicine specialist.
Sign up