At the end of the last century, malignant tumors of the oral cavity were considered a concomitant disease of wastrels due to the abuse of tobacco and alcohol. Today, experts also include the human papilloma virus among the causes of cancer in this localization, so the frequency of all head and neck tumors has increased significantly.
- What precedes cancer
- When should a malignant process be suspected?
- Stages of lip cancer
- How to treat
Head and neck cancer ranks sixth in the world among all malignant tumors and will soon be in the TOP-5, but, unlike its “brothers” in localization, the detection rate of lip cancer is not increasing, but is steadily decreasing.
The incidence of lip cancer has decreased by more than 16% over the past 5 years. In 2022, carcinoma was detected in 2,235 Russians, with men getting sick 2.7 times more often.
- Out of 100 thousand people, 29 Russians develop the disease, and at a more mature age than a decade ago.
- The average age of affected women is 75.5 years; in them, the tumor is often localized on the upper lip.
- In men, cancer is diagnosed on average 8 years earlier, in most cases on the lower lip.
- In 87.6%, the disease is detected at stages 1-2, stage 3 with metastases to the lymph nodes is diagnosed in 8%, and stage 4 in 4.6%.
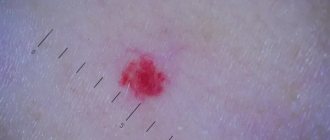
Types of acquired red moles on the body
- Simple (capillary). Proliferation of newly formed capillaries, small venous and arterial vessels. Looks like a red spot.
- Cavernous. A spongy cavity with blood - a red or bluish nodule. Often forms under the skin.
- Branched (racellose). A plexus of tortuous dilated capillary trunks. They pulsate, noise and trembling are detected. It is rare and occurs on the extremities or face. If injured, life-threatening bleeding may occur.
How to identify hemangioma? Press on top of it and it should fade or disappear.
Diagnostics
You can determine why a lump appears on your lip using diagnostic procedures:
- Inspection and palpation of the growth on the lip, detailed questioning of the patient, study of the anamnesis.
- Taking general and biochemical blood and urine tests.
- Hardware studies: ultrasound, x-ray, probing of gland ducts, sialography.
Instrumental diagnostics are used for neoplasms on the lip: cysts, tumors.
Are red moles dangerous?
In themselves, these formations are harmless and are not precancers.
If you have a lot of red moles on your body, the cause may be a serious liver or pancreas disease. Pay attention to this - this is a reason for examination.
Problems may arise in case of traumatization of hemangiomas. Even fairly small formations threaten heavy bleeding, which is not easy to stop.
Clinical case
Patient L, 26 years old, presented with a traumatized mass in the axillary region. According to her, she tore off a convex hemnagioma with the edge of a rigid corset of a wedding dress almost a few minutes before the start of the wedding ceremony. The hemangioma bled very heavily and a large blood stain appeared on her white dress. She had to wear the witness's jacket over her wedding dress. It was in such a strange outfit that the wedding took place.
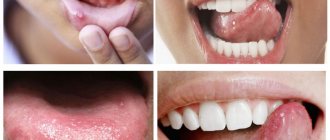
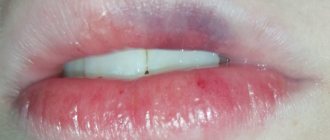
Why can a lump appear on the lip?
Lumps on the lips indicate pathological conditions in the body. They appear in diseases and injuries of various origins.
If a lump appears on your lip, the reason may be as follows:
- injury to the lip and oral cavity;
- dental infections;
- viral diseases of various body systems;
- bacterial and fungal inflammatory diseases;
- tumor and cystic neoplasms.
These causes can be divided into pathological, caused by diseases, and normal, caused by other factors.
An example of the appearance of a labial growth in the photo.
Possible diseases
If a seal appears on the lip, it may be caused by the following diseases:
| Disease | Symptoms |
| Respiratory tract infections | With viral and bacterial diseases of the respiratory tract, small red and flesh-colored balls may appear on the outer surface of the mouth. They appear due to decreased immunity, and after recovery they disappear on their own. |
| Stomatitis | Stomatitis is an inflammatory disease of the mucous membranes of the mouth, most often found in children. Depending on the cause of the inflammation, the bump on the inside of the lip may be clear, red, white, blue or dark brown. |
| Candidiasis | With candidiasis, small white bumps form in the oral cavity, painless on palpation. They can be localized on the inside of the lips, gums or tongue. |
| Herpes | When infected with the herpes virus, a round, painful lump forms on the inside of a person’s lips, which is a blister with clear liquid inside. The inflamed area is itchy and may become covered with a purulent crust. |
| Human papillomavirus | A warty, white or flesh-colored growth occurs when infected with HPV. In the early stages of the disease, the tubercle appears in a single copy, after which their number increases, and the edges of the growths merge with each other. |
| Syphilis | A person infected with syphilis develops a chancre near the lip: a small hard ball resembling a subcutaneous pimple. Chancre signals the onset of the disease and disappears when syphilis enters stage 2. |
| Leukoplakia | With leukoplakia, keratinization and thickening of the epithelium on the oral mucosa occurs. Small white growths form inside the lip, on the tongue and gums. If left untreated, they develop into cancer. |
| Lip cancer | When a malignant tumor occurs, a large red or black lump appears on the oral mucosa. It can be localized on the lip, gums or throat. The lump hurts when touched and may bleed. |
Other factors
Other factors that can cause a lump on the lip include:
- Lip injuries
. A retention blood cyst occurs in wounds: when biting, after a cut or after a blow, when wounded by dental instruments during examination and treatment by a doctor. - Burn when eating hot food
. Hot food or drinks cause thermal damage to the lip tissue. Like mechanical injuries, it causes lumps to appear. - Insect bites
. Blisters caused by an insect bite in the mouth area can take a hard form and turn into a lump. - Malocclusion.
The abnormal position of the teeth causes permanent injury to the lips on the inside, leading to the formation of a pineal growth. - Orthodontic problems
. Incorrect installation of braces or dentures, as well as the retention period of orthodontic treatment, can cause mechanical injury to the lip. - Chemical burn.
When taking certain medications and consuming alkali, a burn may occur in the mouth, leading to the appearance of a lump. - Allergic reactions.
Upon contact with an allergen, the patient may experience small white growths in the oral cavity, including on the lips. - Punctures, wearing piercings.
Trauma and constant friction against the lip tissue causes cystic neoplasms with blood located next to the irritant. - Bad habits.
Smoking and drinking alcohol can cause chronic burns. Like a simple thermal burn, it provokes the appearance of neoplasms.
In case of bite pathologies, incorrect installation of braces and dentures, you should consult a specialist: a dentist or orthodontist.
The remaining reasons listed in the list do not require medical intervention.
Stages of lip cancer
Lip cancer is classified as a visual localization, because it is very easy to notice even with the naked eye. However, almost a third of patients have no complaints about the condition of their lip, and do not believe that a chronically existing crack on it could be cancer. As a rule, such patients consult a doctor for another reason, and the doctor, noticing this pathology, refers the patient for a consultation with an oncologist. This process is called “active discovery.”
In 2014, stages I–II of lip cancer were detected in 85.2% of patients, while a tumor measuring up to 2 cm is considered stage 1 cancer, stage 2 is a tumor measuring more than 2 cm and less than 4 cm. At these stages, tumors are detected without metastases to the lymph nodes and anywhere else. A lip tumor relatively rarely metastasizes to regional lymph nodes - no more than a dozen out of a hundred patients. As a rule, metastases go to the mental and submandibular lymph nodes. For infrequent tumors of the upper lip or commissure - the corner of the mouth, on the contrary, damage to the lymph nodes is rather the norm.
Stage III includes lip tumors larger than 4 cm or smaller cancer, but with metastases to the lymph node. The size of the lymph node should not exceed 3 cm. In 2014, stage III was diagnosed in 9.7% of patients. A lip tumor of any size, but with metastases to one or more lymph nodes larger than 3 cm, is already considered stage IV. Systemic metastasis to other organs in lip cancer is very rare, occurring only in every seventh patient diagnosed with stage IV cancer. The last stage was detected in 4%. Within a year after the diagnosis of a malignant neoplasm, 4.5% die, which is 120 people.
| More information about treatment at Euroonco: | |
| ENT oncologists | from 5,100 rub. |
| Chemotherapy appointment | RUB 6,900 |
| Emergency oncology care | from 12,100 rub. |
| Palliative care in Moscow | from 44,300 rubles per day |
| Radiologist consultation | RUB 11,500 |
Treatment options for tumors
- Surgical technique (excision of the tumor, suturing it, ligation of the afferent and efferent vessels, ligation of the vessels with excision of the hemangioma, embolization of the vessels).
- Electrocoagulation by introducing electrodes into the formation or along its perimeter).
- Cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen is carried out for small tumor sizes and when it is superficial.
- Laser removal that minimizes damage to surrounding healthy tissue. The procedure is carried out quickly, there are no stitches, scars or blood loss, almost complete painlessness, low risk of relapse.
- Conservative methods are used for small lesions. They consist of sclerosing the tumor with alcohol.
- According to indications, a combination of surgical and conservative methods is used (preliminary ligation of the vessels and sclerosis in the center).
Classification
To classify the disease, the international TNM system is used, where:
- T (tumor) stands for tumor;
- N (nodulus) are lymph nodes that are affected by a tumor;
- M (metastasis) – metastases outside the lymph nodes.
T symbol gradation:
- Tx – there is no data to evaluate the primary neoplasm;
- Тis – preinvasive carcinoma (invasion of the lamina propria or intraepithelial invasion);
- T1 – tumor size up to 2 cm in greatest dimension;
- T2 – tumor size in greatest dimension is 2-4 cm;
- T3 – neoplasm in greatest dimension – more than 4 cm;
- T4a – the neoplasm spreads to neighboring tissues and organs (inferior alveolar nerve, skin of the nose or chin, floor of the mouth, etc.);
- T4b – the neoplasm affects the pterygoid processes, the masticatory zone, the base of the skull, and the carotid artery.
Gradation of the N symbol, which indicates metastases (or lack thereof) in regional lymph nodes (L/N):
- NХ – there is no data for assessing regional l / y;
- N0 – regional lymph nodes are not affected;
- N1 – in one lymph node on the affected side there are metastases up to 3 cm in size in the greatest dimension;
- N2 – in one lymph node on the affected side there are metastases 3-6 cm in greatest dimension; in several lymph nodes on the affected side in the greatest dimension there are metastases up to 6 cm; contralateral or bilateral involvement of lymph nodes with metastases up to 6 cm in greatest dimension;
- N2a – in one lymph node on the affected side there are metastases 3-6 cm in greatest dimension;
- N2b – on the affected side there are metastases in several lymph nodes up to 6 cm in the greatest dimension;
- N2c – contralateral or bilateral involvement of lymph node metastases up to 6 cm in greatest dimension;
- N3 – there are metastases in the lymph nodes more than 6 cm in greatest dimension.
M symbol gradation (distant metastases):
- M0 – no distant metastasis;
- M1 – distant metastases are present.
Stage according to TNM classification
| Stage | T | N | M |
| I | T1 | N0 | M0 |
| II | T2 | N0 | M0 |
| III | T3 | N0 | M0 |
| T1-T3 | N1 | M0 | |
| IV | T4 | N0 | M0 |
| Any T | N2,3 | M0 | |
| Any T | Any N | M1 |
Links[edit]
- ^ a b c
Rajendran A;
Sundaram S. (February 10, 2014). Schafer's Textbook of Oral Pathology
(7th ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences APAC. pp. 16–17. ISBN 978-81-312-3800-4. - ^ a b c
Rapini, Ronald P.;
Bologna, Jean L.; Iorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-volume set
. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0. - McKusik, Victor Alexandrovich (May 27, 2009). "Commissural pits of the lips". Internet-Mendelian Inheritance in Man
. Retrieved May 22, 2022.
Are bumps on the lips dangerous?
The danger of bumps on the lips depends on the cause of their occurrence. Small blisters that appear after eating hot food or an insect bite will not harm the body.
Complications can result from:
- retention cyst caused by trauma;
- inflammation due to infections;
- herpes and papilloma on the lip.
Important!
New growths that appear due to smoking or drinking alcohol are also dangerous. If you don't change your lifestyle and give up bad habits, they can develop into lip cancer. A lump on the lip is a neoplasm caused by injury or disease. To prevent the pathology from developing into cancer and causing further complications, consult a specialist.
Diagnostic procedures
When the first signs of lip cancer are detected, the patient should contact an oncologist. The doctor will examine the affected area and palpate the lips, gums, cheeks, and regional lymph nodes. The condition of the outer covers of the red border of the lips will allow the oncologist to make a preliminary diagnosis. If signs of a malignant process are detected in the neoplasm, the patient receives a referral for an ultrasound examination of the lips, radiography of the lower jaw, and panoramic tomography. The oncologist will collect biomaterials (smear-imprint) from the tumor for laboratory tests. Histological analysis is performed after a biopsy of the primary cancer site.
If the patient has symptoms of lymphatic metastasis, the doctor takes a biopsy sample from the lymph nodes. The search for hematogenous metastases is performed using chest x-ray or ultrasound.
Prevention
It is important to follow some prevention rules to reduce the risk of developing the disease.
Primary prevention includes the following measures:
- Stop smoking pipes and cigarettes.
- Avoid exposure to carcinogens.
- Take care of oral hygiene.
- Protect your face from exposure to ultraviolet rays.
- Do not abuse alcohol.
- People prone to lip diseases need to undergo annual preventive examinations.
The rules of secondary prevention are as follows:
- Treat all dental diseases, as well as dyskeratosis and cheilitis, .
- Those who work in enterprises where carcinogenic exposures are possible should undergo medical examinations more often and, if necessary, treat pre-cancer.
Causes
There are a number of factors that increase the likelihood of developing this disease:
- Mechanical – constant injury from the edges of teeth or poor-quality dentures.
- Temperature - addiction to too hot drinks and food, smoking.
- Chemical - smoking, contact with certain carcinogens, chewing certain mixtures.
- Meteorological - the influence of wind, frost, humidity, excessive ultraviolet radiation.
In addition, some viruses can be provoking factors, in particular the herpes . Among these factors are also called malocclusions.
A malignant tumor of the lip always develops as a consequence of the transformation of other pathologies. Precancerous conditions are:
- limited precancerous hyperkeratosis ;
- warty precancer;
- cheilitis Manganotti.
In addition, the following diseases can develop into a malignant tumor:
- keratoacanthoma;
- leukoplakia;
- chronic cheilitis ;
- post-radiation stomatitis ;
- ulcerative and hyperkeratotic forms of lichen planus ;
- papilloma.
According to observations, this disease often develops in rural residents of the southern regions. The risk of its development is increased by poor oral hygiene, deficiency of vitamins A, E, C and beta-carotene, and gastrointestinal diseases.
What to do if a hemangioma hurts
Typically, the formation of such a formation does not cause physical discomfort. It appears when its surface begins to ooze. This phenomenon poses a threat to human life: any ulcer on the mucous membrane or skin is an open gate for infection. It can cause blood poisoning and death. Therefore, if any pain occurs, you should immediately consult a dermatologist.
- Some aspects of the diagnosis of renal cell and transitional cell carcinoma of the kidney
A hemangioma growing on the lower lip may be accompanied by swelling. It causes nagging pain. Discomfort also occurs when the formation grows deep and begins to compress the nerve endings. It intensifies during physical activity, under the influence of high and low temperatures, often becomes unbearable and forces a person to take drastic measures.