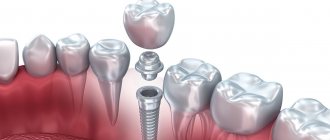
After the installation of a titanium implant is completed, it is necessary that it be completely covered with bone tissue and mucous membrane: this ensures the conditions for its successful engraftment into the bone. But situations arise when the edge of the implant becomes visible due to bone and gum deficiency. Such defects are eliminated by performing bone grafting and gingivoplasty - operations to increase the volume of tissue around the implant.
In order not to trigger a pathology that significantly impairs aesthetics, it is important to notice the initial manifestations of this complication in time.
Why is the gum exposed under the implant?
Implant exposure is a fairly common occurrence. More common with two-stage implantation. A characteristic sign is the exposure of the metal rim of the abutment under the prosthesis, resulting in the formation of a black stripe . Usually the defect makes itself felt some time after the operation.
Common causes of complications:
- using an implant with a polished neck that remains above the bone surface after screwing in;
- too thin mucous membrane;
- overtension of the gingival flap;
- temporary crown pressure;
- poor quality oral care after implantation;
- mechanical trauma to the gums (toothbrush, hard food);
- improper formation of the gingival margin;
- subsidence of the bone as a result of long-term use of artificial teeth.
What shouldn't you worry about?
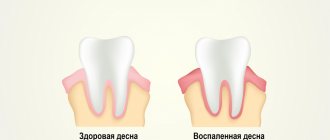
Normally, after implantation you may notice:
- Minor bleeding, in which the amount of blood is insignificant, and the blood itself stops flowing within 1 day.
- Pain that gradually goes away. Usually, even with severe pain, it becomes easier on the third day. Although pain also depends on the extent of the procedure, it is obvious that when installing 10 implants you may experience pain longer than when installing one. Typically, the doctor writes a prescription for a painkiller that completely relieves pain after implantation.
- Edema.
- A slight increase in temperature to 38 degrees is considered normal.
- Numbness in the implantation area.
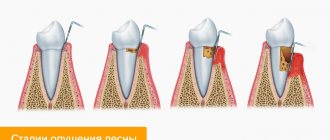
What methods are used to treat recession?
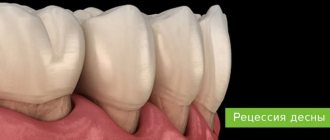
Gum recession is manifested by exposure of the root system. The problem negatively affects the appearance and is fraught with the development of pathologies.
In dental practice, there are two ways to treat recession:
- Elimination of the defect using soft tissue plastic surgery . This allows you to adhere to the two-step technique, as well as prevent the development of the infectious process. However, surgery cannot be avoided. Plastic surgery is performed by augmenting the gums.
- Transition to a one-stage operation protocol. The plug is removed and an abutment is placed in its place. This option does not guarantee the possibility of infection and loosening of the implant, since a two-stage implantation method was initially chosen.
Existing correction options
The choice of method for correcting the slipped gum margin is determined by the clinical situation. There are three variants of pathology:
- Apical edge migration. The bone volume is maintained in sufficient quantity. The implant is stable.
- Migration with bone deficiency. Stability has been maintained.
- Loss of gum tissue, bone resorption, implant mobility.
The first two clinical situations require periodontal plastic surgery. In the third case, the implant is replaced and tissue deficiency is filled.
Plastic surgery of soft tissues if a dental implant has come out of the gum
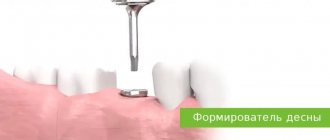
The procedure for correcting the gingival contour and improving the structural and functional state of the periodontium is called gingivoplasty . Allows you to restore the aesthetic appearance of the jaw when implants are exposed in case of recession.
When and in what cases is it carried out?
After implantation, the patient may experience mucosal deficiency and incomplete coverage of the surface of the titanium rod. It looks ugly and causes a deep feeling of discomfort. Plastic surgery of soft tissues is a reasonable way out of this situation. It is indicated if:
- there is a strong tension on the flap;
- the installed crown puts pressure on the gum, blocking its growth around the implant;
- The patient suffered an injury during hygiene procedures or eating food that requires surgical correction.
The procedure has certain risks. Sometimes the doctor has to put a plug on the artificial root. This does not guarantee that infection cannot enter the bone bed. When the rod is exposed, the development of resorption of bone structures is possible.
How is surgery performed if the implant is visible from the gums?
The goal of gingivoplasty is to build up the mucosa to completely cover the surface of the implant. This is done by adding your own tissues from other parts of the oral cavity. The operation is performed by a periodontist under local or general anesthesia, at the patient’s choice.
Before the procedure, a preparatory stage must be carried out, including the elimination of caries, relief of existing inflammatory processes, and removal of tartar.
Extension is carried out:
- in a selected area, usually the palate, a flap of mucous membrane is peeled off;
- applied to the exposed area;
- bone correction is performed if necessary;
- stitches are placed.
Afterwards the graft engraftment stage begins. After 10 days, the sutures are removed, and when tissue fusion is complete, the gum is incised to gain access to the structure and change the former to the abutment.
Possible complications
Gingivoplasty, like any surgical procedure, has its risks. Complications include:
- development of an allergic reaction to the administered anesthetic;
- recurrence of gum recession (requires re-building after 5-6 months);
- swelling of the operated area;
- painful sensations;
- bleeding;
- hematomas.
This is due to the abundant blood circulation of the tissues of the maxillofacial area. Therefore, with the slightest surgical intervention, especially on the lower dentition, severe swelling and bruising appear, which are not as dangerous as they look. After a couple of days their severity decreases, and after a week or two there is no trace left of them.
The appearance of pain in the first hours after the procedure is considered normal. It can be easily managed with analgesics. If the painful sensations increase and do not go away three days after gum growth, then you need to consult a doctor. Perhaps we are talking about the development of a serious pathological process.
Minor bleeding is acceptable in the first hours after the intervention. Intense hemorrhage, in addition to injury to a large vessel, may indicate a blood clotting disorder, which is dangerous. Preoperative examination, including this indicator, is important.
Numbness of the face after the anesthesia wears off is a rare but unpleasant phenomenon. This is a sign of serious nerve damage. Restoring its functions usually takes at least 4 months and requires treatment.
Patient management after surgery
The first days after implantation play a decisive role for healing, so it is extremely important to comply with all conditions that promote osseointegration of the implant.
- Applying pressure packs immediately after suturing the wound. This helps stop bleeding and avoid hematoma.
- Provide hypothermia for two days. To prevent severe swelling of the soft tissues of the face from developing, cold compresses - ice cubes wrapped in cloth - should be applied to the outside of the cheek near the operated area.
- Gently brush with a soft-bristled toothbrush without touching the seams.
- Refusal of solid foods, which creates an increased load on the implant. It is strictly forbidden to drink hot drinks and alcohol.
- Limiting physical activity.
- Refusal to visit baths and saunas.
- Daily dental examinations for a week.
- Rinse with antiseptic solutions. They destroy harmful bacteria that can cause inflammation.
- In the case of a complex operation, the doctor may prescribe drug treatment: antibiotics, antihistamines, drugs to optimize osteogenesis.
- Removal of sutures, usually within 7-10 days. In difficult cases, two-stage removal is practiced: on the 10-12th day, the sutures are removed after one and after another 4-5 days the remaining ones are removed [1, 2, 3]
It is recommended to eat soft foods - liquid or pureed (soups, sour cream, curdled milk, milk, etc.).
The diet is followed during the treatment period and for two weeks after fixation of the permanent prosthesis. Nutrient mixtures made from liquid proteins can be very useful Mirsaeva F.Z., Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Surgical Dentistry of BSMU [3]
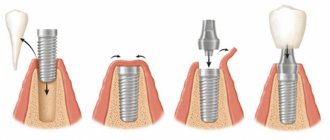
Implantation using a one-stage installation method - solving the problems of implant exposure
The one-stage method of installing an artificial tooth is popular due to the immediate aesthetic result. The procedure is carried out in one stage, including the following actions of the doctor:
- examination of the patient for contraindications;
- sanitation of the oral cavity, elimination of existing problematic issues;
- removal of the desired tooth;
- preparing a bone bed for a titanium root;
- screwing in the implant;
- installation of abutment and temporary crown.
Once healing is complete, the temporary prosthesis will be replaced with a permanent one.
What parts does the implant consist of, and what part of it can fall out?
The implant consists of several parts and is used to replace a tooth. The most important stage of implantation is fusion with bone tissue. At this moment, bonds are created at the molecular level between the implant and the bone. Thus, the implant is firmly fixed in the bone tissue and it is extremely rare that mobility or rejection and loss of the implant may occur.
When it comes to the loss of a dental implant, it most often means that one of the components of the implant has fallen out:
- The implant itself. A titanium artificial root that was installed into the bone.
- Shaper. This is a special part of the structure that is installed to preserve the volume of the gum and its correct outline.
- Abutment. This is a special adapter, which is fixed at one end into the implant and at the other into the crown.
- Prosthesis. This is the part that directly replaces the crown of the tooth, that is, its visible part.
What to do to prevent receding gums after implant placement
You can avoid unpleasant situations by following simple rules:
- take medications prescribed by the doctor in a timely manner;
- rinse your mouth regularly with antiseptic solutions;
- treat the operated area with care;
- stop smoking;
- do not eat hard, sour, hot, cold foods;
- avoid thermal procedures, such as baths, saunas, hot baths;
- treat sutures with a special ointment prescribed by a doctor;
- brush your teeth twice a day (in the morning - after breakfast, in the evening - before bed);
- use an irrigator, floss.
To identify problem areas in a timely manner, you should visit your dentist periodically.
Aftercare and hygiene
Recommendations after implant installation include, first of all, careful oral hygiene.
- Brush your teeth with a toothbrush and toothpaste twice a day for 2-3 minutes.
- Clean the gingival parts of the structure with floss. This allows you to remove plaque from places where its deposits are critical for the functioning of the implant.
- Use dental brushes. Their individual selection in size and shape is required, taking into account the characteristics of the prosthesis.
- Use a single-tuft toothbrush or irrigator to clean hard-to-reach areas of the structure.
- Use mouth rinses containing alcohol-free extracts of medicinal plants - for example, Colgate® Plax Altai Herbs.
- Avoid toothpicks because they are traumatic and can damage the structure.
- At least twice a year, consult a doctor for a preventive examination and professional hygiene of the prosthesis on implants [4].
If the patient follows all the recommendations after dental implantation, then the risk of any complications is extremely low. In this case, the dentures serve for years and even decades without losing their properties and appearance.
List of sources
- Minina A. N. Basics of dental implantation. Vitebsk: VSMU, 2013. // URL: https://elib.vsmu.by/bitstream/123/11042/1/Minina-AN_Osnovy%20dental%27noj%20implantatsii_2013.pdf (accessed March 16, 2021).
- Paraskevich V. L. Dental implantology: Fundamentals of theory and practice. Minsk: Unipress, 2002. // URL: https://dental-ss.org.ua/load/kniga_stomatologia/implantologija/dentalnaja_implantologija_osnovy_teorii_i_praktiki/9-1-0-22 (access date 03/16/2021).
- Mirsaeva F.Z. Dental implantology. Ufa: State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education BSMU of the Ministry of Health of Russia, 2015. // URL: https://library.bashgmu.ru/elibdoc/elib624.pdf (access date 03/16/2021).
- Naumovich S. A. Technologies of dental prosthetics on dental implants. Minsk: BSMU, 2011. // URL: https://rep.bsmu.by/bitstream/handle/BSMU/2079/%D0%A2%D0%B5%D1%85%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0 %BB%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%B8%D0%B8%20%D0%B7%D1%83%D0%B1%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%20 %D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D1%82%D0%B5%D0%B7%D0%B8%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0 %B8%D1%8F%20%D0%BD%D0%B0%20%D0%B4%D0%B5%D0%BD%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%BB%D1%8C%D0%BD %D1%8B%D1%85%20%D0%B8%D0%BC%D0%BF%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%BD%D1%82%D0%B0%D1%82%D0%B0 %D1%85.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed 03/16/2021).
Expert opinion
Emir Romanovich Omerelli
Maxillofacial surgeon, implantologist
Experience: more than 13 years
Two main points that minimize the risk of complications are high-quality preparation for implantation, including detailed diagnostics, and following the doctor’s recommendations in the postoperative period. It is also necessary to be attentive to any symptoms - if there are alarming signs - the pain does not go away for several days, the temperature rises, swelling of the mucous membrane - do not wait until the pathological process develops more strongly, come to the clinic immediately and give the doctor the opportunity to correctly “react” to any abnormal symptoms.
What to do if a tooth-implant does fall out?
The most important thing is to come to see our doctor.
Because often by implant loss, patients mean not just the loss of the implant itself, but, for example, the decementing of the crown or gum former. If, nevertheless, the dental implant falls out, then we must take into account that this happens quite rarely and mainly against the background of inflammation - peri-imlantitis. It should also be noted that in the first stages of inflammation of the tissue around the implant, the process can still be stopped, and in this case the prognosis for the implant will be quite favorable.