Modern technologies, techniques and materials have made the dental implantation process one of the safest and most effective. But do not forget that this is a serious surgical intervention with its own characteristics. Therefore, situations where a patient’s dental implant falls out, although rare (a little more than 1% of all implantation operations), still occur in dental practice.
What to do if part of the rod comes out of the gums
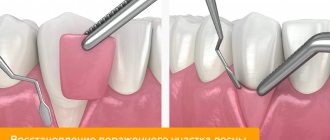
When the implant is exposed, a flap operation is performed to build up its soft tissue:
- A flap is peeled off from the palate and applied to the exposed area.
- If necessary, correction is carried out on the bone tissue.
- The edges of the wound are sutured with non-absorbable thread.
- After 10 days, the sutures are removed.
- After the artificial root has engrafted, a former is placed.
Another way to correct a defect with a lack of periodontal tissue can be the transition from a two-stage installation to a one-stage method. However, it is necessary to take into account that the one-stage technique has the main drawback - non-ideal conditions during the period of implant engraftment, high risks of developing inflammation.
What elements of implants can fall out?
The implant consists of several parts and during installation a plug, former and abutment are added to it:
- The healing abutment
fell out of the implant. The reason may be that the implant is planted too deep; it simply becomes overgrown with mucous membrane. Inflammation can also cause loss of the former; - plug
has fallen out - an error in the technology of its installation or non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations; - pin
fell out . We discussed the reasons above.
In all cases, you should urgently contact your doctor.
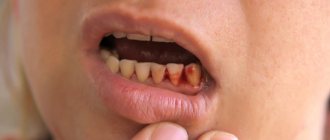
Is implant failure a sign of rejection?
If the problem of exposing the rod is accompanied by additional symptoms, it is necessary to understand their causes. Pain at the site of installation of the structure, swelling, and redness of the gums during the first week after surgery is a normal reaction to surgery, since tissue injury occurs. Signs of rejection are the following situations:
- 1-2 weeks after implantation, acute pain does not go away;
- swelling and redness of the gums do not subside after 4 days after surgery;
- discharge of ichor, bleeding lasting more than 7 days;
- the mobility of the implant is felt;
- unpleasant smell from under the plug screw;
- painful sensations when pressing on the rod;
- the appearance of purulent discharge from the gums;
- increase in body temperature.
Plastic surgery of bone tissue and gums when the implant is exposed
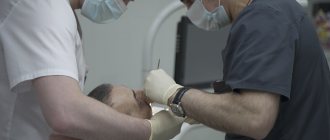
The surgical intervention is aimed at building up bone tissue and gums to completely cover the surface of the implant, which is achieved by adding bone tissue and mucous membrane to the implant area. The operation is performed by an implantologist under local anesthesia.
increase in gum volume around the implant
Before the operation, a preparatory stage is required: sanitation of the oral cavity (treatment of caries and its complications, elimination of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity), removal of tartar (professional oral hygiene).
Restoration of gum recession around the implant is carried out in the following sequence:
- the exposed area of the implant is carefully treated with antiseptics;
- perform bone grafting (bone augmentation) in this area;
- in a selected area of the oral cavity (usually on the hard palate), a flap of the mucous membrane is peeled off;
- the flap is moved to a place with tissue deficiency;
- Sutures are placed at the site of tissue collection and at the extension site.
After the operation, the graft engraftment period begins, the sutures are removed on the tenth day.
Possible complications
Gum and bone grafting, like other types of surgical interventions, has the potential to develop complications:
- the occurrence of an allergic reaction to the anesthetic;
- repeated exposure of the implant (another operation is required in six months);
- swelling in the area of the operation;
- pain;
- bleeding;
- hematomas.
Such phenomena occur due to the abundant blood supply to the tissues of the maxillofacial area, therefore even minor surgical interventions, especially on the lower jaw, are accompanied by severe swelling and hematomas. However, after a couple of days they decrease and disappear completely within 1-2 weeks.
Soreness for several hours after surgery is considered normal and can be successfully relieved by taking analgesics. If pain increases and there are no positive changes after three days, you should see a doctor, as there is a risk of developing serious complications.
Minor bleeding of the operated area is acceptable in the first few hours after the intervention, but heavy bleeding may indicate injury to a large vessel or even a blood clotting pathology. Therefore, before surgery, a laboratory blood test is required to identify possible pathologies and take them into account when planning surgical intervention.
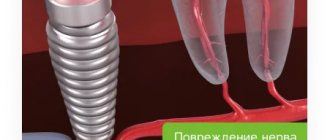
Why the design may not take root
This can happen for several reasons, related both to the course of the operation itself and to the actions of the patient in the postoperative period.
Medical error
Due to his incompetence or carelessness, an implantologist may make the following mistakes:
- choose the wrong model - the titanium root may be significantly longer or thicker than the jawbone;
- violate sterility conditions;
- incorrect installation of the implant;
- when drilling a hole for the rod, overheat the tissue;
- do not fully study information about the patient’s health status and possible contraindications.
Poor quality implant
Large dental clinics, through dealer networks, work with systems that are directly supplied from manufacturers. This eliminates the possibility of receiving a fake. In dentistry that work through intermediaries, it is risky to agree to an operation, as there is a risk of installing low-quality analogues. Therefore, you need to take the choice of a clinic and a doctor seriously, be interested in warranty conditions, survival statistics, and other important points.
Failure to comply with operating and maintenance rules
Even if the doctor performs the operation correctly, observing all the norms, problems with implant healing may arise due to the patient’s fault. Among its possible errors:
- providing the doctor with incomplete information about your well-being and health status. Even minor facts must be stated;
- excessive load on the implant during the healing period;
- failure to follow the rules of oral hygiene - even artificial teeth require careful care;
- hypothermia or overheating in the first days after surgery (visiting a sauna, diving into ice water);
- undisciplined use of medications prescribed by a doctor.
Deterioration of health
Rejection may occur several years after implantation. In addition to mechanical damage, the cause may be the development or exacerbation of:
- cardiovascular diseases;
- diabetes;
- AIDS;
- tuberculosis;
- oncological diseases.
The risk of rejection increases significantly if the patient smokes . Nicotine and tar disrupt the nutrition of mucosal cells, which has a negative effect on the condition of the tissues around the installed rod.
Possible reasons
Any implant is a foreign body for the body. In order for it to take root well, it is necessary to follow the doctor’s recommendations after the operation. If you ignore the dentist's instructions, inflammation may occur, causing the structure to become unstable.
The main reasons for implant failure also include:
- installation of an unsuitable design - a product with a small diameter or length, made of metal alloys to which there is an allergy;
- mistakes made by the doctor during the operation - overheating of the bone tissue, violation of asepsis, tightening the rod too much;
- malocclusion - crowding of teeth, midline displacement, retrusion and protrusion, transposition, rotation;
- mechanical damage - bruises and fractures, causing displacement of the implant;
- chronic diseases - diabetes, immunodeficiency, blood clotting disorders.
Before installing an implant, the doctor must collect an anamnesis, conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and select a suitable design taking into account the clinical picture.
How is inflammation treated?
If signs of inflammation appear, you should immediately consult a doctor . He will conduct an examination and order an x-ray. If necessary, temporarily unscrew the implant plug and clean its outer surface.
Signs of advanced peri-implantitis are eliminated by removing the structure, since an advanced inflammatory process will lead to the spread of infection. At the initial stage, surgical sanitation of the focus of gingival inflammation is carried out:
- They make an incision.
- Granulation tissue is removed.
- The surface of the titanium root is cleaned with a Prohy-Jet apparatus or special curettes.
- Rinse the pocket.
- After the operation is completed, the patient is prescribed antibiotics and antiseptic rinses.
The conservative phase of treatment includes procedures:
- Professional oral hygiene.
- Irrigation with ozonated solution.
- Laser therapy.
- Oral applications and baths are prescribed.
Rejection of titanium dental implants after healing: when does it happen?
The main causes of delayed rejection and instability of implants:
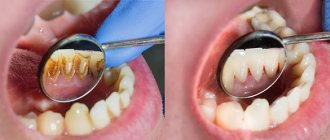
- Peri-implantitis. This inflammation of the surrounding tissues may be a consequence of non-compliance with the protocol or the development of initially undetected weak infectious processes, caries, or the initial stage of periodontal disease.
- Features of bone structure. A small amount of tissue will not hold the embedded pin.
- Pathologies during osseointegration. When choosing a cheap implant from the “no name” series, the pin does not integrate; only scar tissue grows. Fibrosis begins and the structure falls out.
Sometimes the cause of trouble is the treatment of emerging oncological diseases, the use of potent drugs that affect the regeneration of tissue cells.
How much does it cost on average in Moscow?
Treatment of complications
| Name of service | Cost, rub. |
| Periodontal applications in the area of 1 tooth | 370 |
| Application of a protective periodontal bandage | 400 |
| Laser therapy of the gum mucosa | 490 |
| Implant removal | 6900 |
| Implantation of osteoconductive material in the area of 1 tooth | 10900 |
| Implantation of a protective membrane (1 tooth) | 12900 |
Gum plastic surgery
| Name of service | Cost, rub. |
| Plastic surgery of marginal gums | 1200 |
| Gingivoplasty (1 tooth) | 1500 |
| Plastic surgery of marginal gums (segment) | 3500 |
| Plasty of gingival margin recession | 3500 |
| Flap surgery in the area of one tooth | 3500 |
| Smile line plastic surgery | 4000 |
| Gingivoplasty (1 tooth) using laser | 4000 |
| Gingivoplasty (segment) | 4500 |
| Flap surgery (three teeth) | 7000 |
| Gingivoplasty (segment) using laser | 10000 |
| Flap surgery (segment) | 10000 |
| Flap surgery (whole mouth) | 30000 |
What we do to speed up the survival of dental implants and prevent unpleasant consequences
Our clinics have the latest diagnostic equipment, so the doctor will not miss an alarming symptom and will prescribe treatment before implantation. During preparation for surgery, if necessary, doctors of related specialties - periodontists, therapists - are invited for consultation.
When dental implants have already been installed, rehabilitation takes place under the supervision of the attending physician, who will pay attention to oddities even when you have not yet discovered them. But when using our equipment and dental implants from world-famous companies, such problems practically do not happen. Personal customer service will help you not to get confused: there is always someone to turn to and ask an exciting question. Our patients are never left alone with a problem.
Solution
If the neck or root of a tooth located next to the implant is exposed, gum plastic surgery may be required. Flap operations are common in dental surgery. To cover exposed areas, soft tissue flaps taken from the hard palate are used. This is a fairly simple operation, the contraindications for which may include:
- allergy to anesthetics,
- malignant tumors of the jaw,
- poor blood clotting,
- uncompensated diabetes mellitus.