Tonsillitis is an infectious disease characterized by inflammation of the tonsils. The disease can have both acute and chronic forms. Chronic tonsillitis is diagnosed in 15% of children and 10% of adults. Another name for tonsillitis is tonsillitis, which literally translated from Latin means “squeezing”, “suffocation”. Indeed, the main symptom of a sore throat is a sore throat and discomfort when swallowing. The term "angina" is often used by both medical professionals and patients.
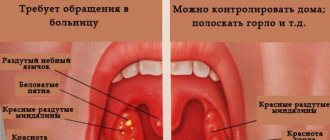
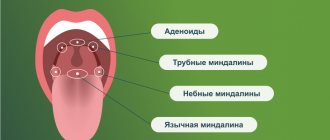
Classification of forms of tonsillitis (tonsillitis)
- I catarrhal form (the inflammatory process is manifested by redness and swelling of the tonsils).
- II follicular form (yellowish purulent dots appear on the surface of the tonsils - festering follicles).
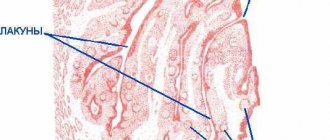
- III lacunar form (liquid pus or purulent-caseous plugs form in the lacunae).
- IV fibrinous form (characterized by the formation of a single continuous plaque of a whitish-yellow color, which can extend beyond the tonsils, often occurs in people with reduced immune system function).
- AIDS, blood diseases, hunger, old age.
- V herpetic form (most often caused by adenoviruses, herpes simplex viruses, characterized by vesicular rashes on the back of the pharynx or soft palate, predisposed to ulceration).
- VI phlegmonous form (intratonsillar abscess) is a complication of acute tonsillitis (lacunary, catarrhal, follicular) or chronic tonsillitis, which is an acute purulent inflammation of the peritonsillar tissue.
- VII ulcerative-necrotic form (gangrenous form) - characterized by the formation of yellow-white blisters (ulcers) on the tonsils, in some cases the spots spread to the entire oral cavity and throat.
- VIII mixed forms (a variant of the disease in which colonization of lymphoid tissue occurs by several pathogens at once, as a result of the addition of a secondary infection or with a severe decrease in immunity).
Norm and pathology
Language is a kind of mirror of the functioning of the body. When it is clean, pink, with visible taste buds, the person is healthy and most likely does not suffer from bad habits. But even a loose white coating, through which the surface of the tongue is visible, is considered as a variant of the norm. It can change shade depending on the time of year: in summer it can be more intense due to hot weather, in winter it becomes white-yellow, in autumn it becomes almost transparent. In addition, a yellow coating on the tongue in the morning appears in heavy smokers and those who drink too much coffee.
However, a change in the color of the tongue may be a consequence of malfunctions in the internal organs, mainly the liver, kidneys, stomach, pancreas and gall bladder. If the plaque has become dense, thick, bright yellow or brownish-yellow, and there is also bad breath, you should consult a doctor and identify the cause of the problem.
Attention!
Typically, “safe” soft deposits come off easily and, if brushed well, will not reappear. But if the plaque returns, we are dealing with pathology.
Complications of tonsillitis (tonsillitis)
Sore throat is one of those diseases that cannot be endured “on your feet”.
Indifference to your health if you have a sore throat is criminal; hoping for help from “folk remedies” and medicines from the home medicine cabinet of your friends and acquaintances is, to say the least, short-sighted. The question of treating sore throat is precisely the correct treatment. If the patient receives inadequate therapy for tonsillitis, complications may include various heart defects, kidney disease, joint damage, the transition of the inflammatory process to surrounding tissues with subsequent formation of abscesses, otitis (inflammation of the middle ear), laryngitis (inflammation and swelling of the larynx), as well as others diseases (tonsil abscess, paratonsillitis, phlegmon, meningitis, mediastinitis, purulent lymphadenitis, tonsillar sepsis, etc.).
We have all encountered more than once the problem of treating a sore throat, especially in childhood. And each of us has memories left in our memory, like a fragment of a picture from a movie, a warm bed, tea with raspberries and an anxious mother who is watching you with pain in her heart, putting a cold towel to her forehead, trying to reduce the fever, because... Typically, such infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity are accompanied by high fever. So what causes a sore throat and how can you cope with the consequences of this disease so as not to provoke complications.
According to medical statistics, infectious and inflammatory diseases of the mouth and throat account for an average of 30% of the total number of diseases of the ENT organs. The main causative agents of this kind of throat infection are bacteria, the so-called pathogenic microorganisms staphylococci and streptococci, which can easily get on the mucous membrane of the throat and provoke inflammation, especially in children, who are traditionally included in the “risk group”. But in addition to pathogens of a bacterial nature, yeast-like fungi of the Candida albicans group and mold fungi of the genus Aspirgillius can also complicate the course of throat diseases, which are difficult to treat and require, first of all, diagnostic measures to identify the causative agent of the infection, both bacterial and infectious in nature, that provoked inflammation, and selection of a treatment regimen that can suppress two pathogens at the same time. And diseases such as pharyngomycosis and laryngomycosis are among the socially significant diseases, because require an individual approach to therapy.
Usually, the presence of an acceptable amount of opportunistic microorganisms produced on the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, larynx and throat serves as a natural barrier against external infection entering the body, but as a result of exposure to external and internal factors, their volume may increase, and due to additional infection by bacteria and pathogenic microorganisms , diseases of an infectious and bacterial nature can develop, including those aggravated by a fungal infection, such as mycosis of the throat or candidiasis.
It should be noted that fungi of the genus Candida are quite widespread and, as a result, the possibility of getting this infection in public places through shared objects, food, including by airborne droplets is quite high. In addition, the development of this type of infection can be caused by such reasons as uncontrolled and long-term use of antibiotics without special indications, less often, disruption of hormonal levels and the endocrine system, reduced immunity, frequent diseases of a viral nature, childhood, incl. and incorrectly selected therapy for ENT diseases.
Fungal infections of the throat differ from the symptoms of ordinary sore throat of a bacterial nature in the appearance of plaque, which resembles cottage cheese. It is easy to remove, but underneath there is an inflamed mucous membrane, with redness and ulcers. And if a fungal throat infection is caused by fungi of the genus Aspirgillius, then such plaque is quite difficult to remove and has a yellowish tint. It should be noted that the localization of a fungal infection in the mouth and throat is also characterized by the manifestation of symptoms of a common sore throat.
It is quite difficult to detect fungus in the mouth and throat at an early stage, because... at the beginning of infection it usually does not appear, only as the colonies increase. Characteristic symptoms begin to appear gradually, in the form of discomfort, soreness, burning and dryness in the throat, and pain during swallowing. In addition, there is a presence of white plaque in the larynx, tonsils, tonsils and tongue, as well as the appearance of erosive surfaces in the form of ulcers and cracks in the mucous membrane of the throat. Traditionally, the temperature rises, headaches appear, swelling of the nasopharyngeal mucosa occurs, as well as characteristic symptoms of general poisoning and intoxication.
In children, the course of fungal tonsillitis is much more severe than in adults, because In childhood, the phenomena of intoxication in the body and pain syndrome are especially pronounced. The child becomes weakened, more capricious, and refuses to eat. In addition, when removing plaque from the mucous membranes of children, the delicate skin may be injured, and sometimes minor bleeding may occur. Also, in children there is a high probability of dysbiosis and diarrhea, due to the fact that yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida can move into the intestinal tract and provoke intoxication and characteristic symptoms of poisoning.
The initial diagnosis for the presence of fungi in the throat can first be carried out independently by examining the mouth and throat for the presence of white plaque. But it is important to remember that only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis, because... Only with the help of laboratory diagnostics can one identify the pathogen that has caused infectious and inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx and oral cavity and select the necessary treatment regimen for this disease.
Instrumental research or laboratory diagnostics includes the following studies:
1. Laboratory mycological research - analysis of biomaterial (smear from the throat), provides the most accurate determination of the pathogens that caused a fungal infection of the throat.
2. A skin test with fungal allergens is carried out by introducing a fungal allegory test under the skin. This research method is necessary to establish the most accurate diagnosis and also to identify the chronic stage of the disease.
3. An immunological test is carried out to detect antibodies to the fungus in the blood.
These studies are the most informative and will allow the specialist to choose the right tactics for treating emerging lesions of the throat mucosa with fungal colonies.
After the doctor has made the correct diagnosis and identified the causative agent of the infection, the next step towards recovery is treatment of the fungal infection. The main goal is to get rid of a large number of pathogens in the throat, restore microflora, the integrity of the mucous membranes and strengthen the immune system. Treatment of fungal tonsillitis is carried out comprehensively, combining traditional medicinal methods in conjunction with a balanced diet. First of all, antifungal agents are prescribed, and if this therapy does not give the desired effect, antibiotics are prescribed. The course of treatment can last up to 2 weeks, but in acute forms of the disease it is necessary to prescribe additional therapy in the form of vitamins, antiallergic agents and probiotics containing bifidobacteria and lactobacilli to restore normal gastrointestinal microflora. In addition, local antiseptics are additionally prescribed.
One of these drugs, which has proven itself in the treatment of ENT diseases, including purulent-inflammatory infections of the oral cavity, nasopharynx and throat, is the modern anti-inflammatory drug of plant origin Abisil, created on the basis of natural terpenoids of Siberian fir. The drug has pronounced anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, analgesic, wound-healing, and anti-exudative effects. It should be especially noted that microbiological studies of the drug Abisil revealed a wide range of antibacterial activity against gram-positive and gram-negative strains and various types of pathogenic microbes, often causing purulent-inflammatory diseases. Abisil is especially sensitive to staphylococci and streptococci, which are the main pathogens for throat diseases, in particular purulent sore throat. In addition, the drug was found to have antifungal activity against yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida and mold fungi Aspirgillus. But the most valuable thing about it is that microorganisms do not become resistant to the drug, and therefore it can also be used in complex cases when inflammation is caused by antibiotic-resistant microflora. Possessing a complex and multidirectional effect, Abisil helps to get rid of purulent sore throat in a short time, including sore throat aggravated by a fungal infection. And in most cases, when traditional therapy for the treatment of fungal tonsillitis, including the simultaneous use of antibiotics and antimycotics, does not give the desired effect, Abisil therapy acts as an alternative to antibiotic therapy and shows a positive effect in the treatment of these pathologies. In addition, Abisil helps restore the activation of the protective functions of the mucous membrane and restores the balance of the microflora of the nasopharynx, in contrast to local synthetic antiseptics, which suppress both pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microflora of the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and throat.
The drug does not accumulate in the body, does not have teratogenic or embryotoxic effects and therefore can be used in all age groups, incl. and in children, and is indicated for use in the treatment of purulent-inflammatory throat infections. But in any case, to provide effective assistance and prescribe therapy for fungal infections of the throat, it is necessary to consult a doctor and his observation during the treatment. It should be noted that treatment with Abisil is simple and accessible. For tonsillitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis, it is recommended to irrigate the mucous membranes of the mouth with the drug 2-3 times a day after meals. This can be done using a pipette or a syringe through a special nozzle, distributing Abisil in an amount of 1-2 ml to the area of the palatine tonsils and adjacent palatine arches, larynx and pharynx. In this case, it is additionally necessary to drip 2-3 drops of the drug into the nose. The duration of treatment is 1-3 weeks. In case of chronic disease, the course of treatment can be repeated after 1-2 months. After the procedure, it is not recommended to eat, drink or rinse your mouth for 3-4 hours. For fungal infections of the oral cavity, it is recommended to treat the affected areas of the oral mucosa 3-4 times a day with a cotton swab moistened with the drug. In addition, rubbing the drug Abisil into the front of the neck, into the area of the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes is also effective. In rare cases, a short-term burning sensation may occur at the site of application of the drug, but it quickly passes. Combining the drug with other external agents is not recommended.
Another component of a full fight against fungal infections of the mouth and throat is a balanced diet, which additionally helps to get rid of mycosis. The fact is that fungi can feed on the foods that we eat and therefore, when forming a diet for the treatment of fungal sore throat, we should exclude foods that can provoke the growth of fungi, thus depriving them of additional nutrition. First of all, you should exclude alcohol, sugar, baked goods, baked goods, sweets, condensed milk, jams and preserves, dairy products, as well as canned foods containing vinegar. And the following foods must be included in the diet: meat, fish, eggs, cereals, legumes, fresh vegetables and herbs, garlic, spices, mineral water and tea.
You should pay attention to the fact that with improper therapy or neglect of the prescribed treatment by a doctor, complications of the disease can be provoked, in which the mucous membrane of the throat is destroyed and open wounds and ulcers appear on it, into which infection can re-enter and provoke secondary infection in the form of bacterial inflammation . Repeated inflammation is characterized by the appearance of abscesses and abscesses of the larynx. In addition, the development of fungi in the body can also cause a reaction in the form of an allergy, and most often, mycotic eczema can occur, which manifests itself in the form of peeling and the occurrence of inflammation and wounds on the skin. Another complication may be the occurrence of recurrent tonsillitis, which can occur frequently, once every 1-1.5 months, up to 10-12 times a year, and this is associated with the life cycle of the fungus.
What preventive measures must be taken so that the fungus in the throat does not develop further and does not develop into a chronic disease with frequent relapses. First of all, it is necessary to monitor hygiene and cleanliness of the oral cavity, and avoid contact with infected people. Take antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor, do not self-medicate and do not take antibiotics longer than the prescribed course. Make it a rule to visit the dentist for a preventative examination of the oral cavity and begin treating the disease immediately, without delaying it for later, and do not forget to strengthen your immune system. The most important rule in the treatment of fungal infections of the oral cavity and larynx is to identify the cause of the disease, eliminate the pathogen and adhere to the therapy prescribed by the doctor and a set of preventive measures so that possible relapses and complications do not arise in the future.
Treatment of sore throat at GUTA CLINIC
Treatment of tonsillitis in our clinic is carried out comprehensively, drug therapy is prescribed individually, both antibacterial and immunomodulating, decongestants, antihistamines are used, as well as physiotherapy (rinsing, washing, irrigating the tonsils with various medications).
Treatment of abscesses is only surgical followed by rehabilitation therapy. Otorhinolaryngologists at GUTA CLINICS recommend that at the first symptoms of tonsillitis - difficulty swallowing, pain and discomfort in the throat, redness of the tonsils, fever, changes in sense of smell, taste, voice - contact a specialist. Don't let your sore throat progress and stay healthy!
Yellow coating on the tongue: how to treat
Treatment of pathology should begin with clarification of the diagnosis. To do this, you need to consult a therapist and specialists, take the necessary tests and undergo appropriate diagnostics. Treatment may include not only taking medications, but also a special diet, rinsing with medicinal solutions, careful oral hygiene, etc.
To prevent the formation of a yellow coating on the tongue, experts recommend not to overuse coffee, fried and spicy foods, and to include more vegetables and fruits.