September 9, 2022 Tonsillitis is an infectious disease that affects one or more tonsils.1
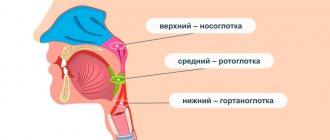
There are several tonsils: two palatine, two tubal, one lingual tonsil and one pharyngeal tonsil (aka adenoid). All these tonsils form a lymphoid-pharyngeal ring, which is responsible for local immunity. Also included in this ring are lymphoid granules located on the posterior wall of the pharynx.2
Due to immature immunity, children are more susceptible to various infections, as well as the development of tonsillitis as an independent disease. Children of preschool and school age are especially often affected. And this is quite logical, since the incidence of the disease is higher in children who visit places where children gather - kindergartens, schools, clubs, playrooms. Tonsillitis can also be contracted through airborne droplets and contact during close contact with a patient with acute tonsillitis or with toys that a sick child has played with. Tonsillitis is less common in infants.3
The development of tonsillitis in children and adults may differ not only due to different immunity, but also due to anatomical features. Children have a tonsil-adenoid. Since this is an unpaired tonsil, it is correct to call it in the singular - adenoid. Inflammation of this tonsil is called adenoiditis.4 With age, the adenoid ceases to function and, one might say, disappears, so adults do not suffer from adenoiditis.
Causes of tonsillitis in children
The disease occurs due to the ingress of bacteria or viruses. Tonsillitis is often caused by streptococcus bacteria. The disease is also caused by adenoviruses, influenza and parainfluenza viruses, herpes, etc.
Other reasons:
- staphylococcus, pneumococcus, hemophilus influenzae and other microbial associations;
- enterovirus infection;
- mushrooms;
- parasites – membrane and intracellular (mycoplasma and chlamydia);
- disruption of the process of self-cleaning of lacunae against the background of restructuring of lymphoid tissue and dysbiosis of the respiratory tract;
- a single or multiple history of tonsillitis;
- ARVI, sinusitis, adenoiditis, caries, stomatitis, periodontal disease;
- anatomical features of the pharyngeal part of the lymphatic system - deep and narrow lacunae, adhesions, multiple fissure passages;
- burdened by concomitant diseases - food allergies, perinatal pathologies, rickets, impaired breathing through the nose, intestinal infections and other factors that reduce immunity.
Reasons for appearance
Purulent tonsillitis in a child is of an infectious nature, and is provoked by the increased activity of pathogenic pathogens such as staphylococcus, streptococcus, pneumococcus, diplococcus. When identifying the causative agent of infection, one should not exclude the penetration of influenza, parainfluenza, and adenovirus viruses into the child’s body. Other provoking factors for inflammation of the tonsils are presented below:
- Treatment of sore throat with beets and vinegar
- prolonged hypothermia of the body;
- environmental factor and climate change;
- physical or emotional fatigue;
- decreased immunity;
- diseases of the ENT organs.
Types of disease
- Spicy. Most often, the acute form develops after suffering from acute respiratory viral infection, due to reduced immunity. Source: A.D. Vetrova Acute tonsillitis in children: a pediatrician’s point of view // Pediatric pharmacology, 2014, v. 11, no. 2, pp. 61-64
- Chronic. Occurs after relapses if the patient has not fully recovered. Diseases in the mouth, nose, and structural features of the tonsils contribute to the development of chronic tonsillitis. Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6248716/ Raja Kalaiarasi, Kalaivani S Subramanian, Chellappa Vijayakumar and Ramakrishnan Venkataramanan Microbiological Profile of Chronic Tonsillitis in the Pediatric Age Group // Cureus. 2022 Sep; 10(9): e3343
Classification
Acute tonsillitis, well known to us as tonsillitis. She may be
- catarrhal
- follicular
- lacunar
- fibrinous
- phlegmonous
- herpetic
- ulcerative membranous
If there is acute tonsillitis, then there is also a chronic one, which, in turn, can be simple (manifested by local symptoms) and toxic-allergic (occurs with lymphadenitis, damage to the cardiovascular system, joints, kidneys, skin). It can be compensated (no recurrent sore throats, the barrier function of the tonsils is not impaired) and decompensated (the child is bothered by frequent sore throats, complications from the sinuses, ear, kidneys, and heart are possible).
Tonsillitis can be an independent disease, then it is called primary. Sometimes inflammation of the tonsils is a consequence of another infection, for example, with diphtheria, scarlet fever, measles or blood diseases.
Symptoms of the disease
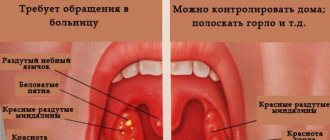
The main symptoms of tonsillitis in children that require immediate treatment are:
- pain when swallowing and yawning;
- heat;
- general intoxication of the body (weakness, decreased appetite, headaches);
- swelling and redness of the tonsils;
- formation of whitish or yellowish plaque on the tonsils;
- blisters, sores on the throat;
- loss of voice, hoarseness;
- bad breath;
- enlarged and painful lymph nodes (this sign can indicate not only tonsillitis, it accompanies many other diseases in children).
Symptoms
The symptoms are similar, but differ in intensity for each type:
Catarrhal sore throat
- starts suddenly
- sore, dry and sore throat
- general malaise, headache, pain in joints and muscles
- body temperature from 37.2 to 39 degrees
Follicular tonsillitis
- the disease begins acutely
- body temperature rises to 39-40°
- intense sore throat
- severe weakness, headache
- feeling of aching in the lumbar region and joints
- loss of appetite
Lacunar tonsillitis
- sore throat, including when swallowing food or saliva
- headache
- increase in body temperature up to 40 degrees, chills
- muscle pain (mainly in the lumbar region, calf muscles)
Fibrinous tonsillitis is similar in symptoms to lacunar tonsillitis, but has a special appearance of the tonsils. Phlegmonous and herpetic are less common.
In chronic tonsillitis, the compensated form, symptoms may not appear so acutely and intensely, but several times a year or month:
- sensation of dryness, tingling, foreign body when swallowing
- low-grade fever
- fatigue, weakness
In the decompensated form of the disease, complications may occur in the form of damage to the valve apparatus of the heart or heart muscle - myocarditis, inflammation of the joints - arthritis, kidney damage - glomerulonephritis.
Such consequences develop especially often when the causative agent is β-hemolytic streptococcus of group A, in this case they speak of rheumatism.
Rheumatism licks the joints, bites the heart
Diagnostics is based on:
- symptoms
- oral examination
- palpation of lymph nodes
- clinical blood test
To determine the type of infection and prescribe the appropriate antibiotic,
- sowing on a nutrient medium
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
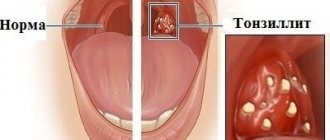
On examination, redness and swelling of the mucous membrane of the tonsils and adjacent tissues are noted. With follicular tonsillitis, numerous round, slightly raised yellowish or yellowish-white dots are visible on the surface of the tonsils. With lacunar, they merge and yellowish-gray plaques form. Fibrinous tonsillitis is characterized by the formation of a continuous film, which is easily removed.
Diagnostic methods
During the consultation, the doctor will examine the patient’s throat and palpate the lymph nodes. The examination should be carried out by a pediatrician and pediatric ENT specialist. In case of decompensation of the chronic form, the child requires consultation with a pediatric cardiologist, rheumatologist, nephrologist, because tonsillitis can cause concomitant diseases. To rule out pockets of infection in the oral cavity, the child should be examined by a dentist. Laboratory and instrumental studies are also prescribed:
- blood and urine tests;
- pharyngoscopy;
- blood test to determine C-reactive protein;
- definition of ASL-O;
- bacterial culture from the pharynx for flora.
If there are difficulties in making a diagnosis, additional studies may be required - ECG, x-ray of the sinuses, etc.
Development mechanisms
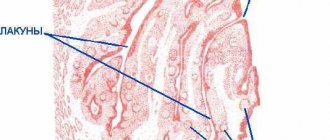
The palatine tonsils are an important organ of the immune system; they form a barrier against foreign microorganisms and dust particles entering the respiratory tract. This must be remembered when deciding on surgical treatment of tonsillitis. In the thickness of the organ there are crypts, which are convoluted canals; they open to the surface with an exit hole called a lacuna. The wider the lacuna, the better microorganisms and dust particles are removed from the tonsils and the less likely it is to develop inflammation.
On the surface of the organ there is always a non-pathogenic, conditionally pathogenic flora; immunoglobulins and interferon are produced in the tissues. When the balance shifts towards the former, the tonsils turn from protectors into a source of constant infection. In this case, a sore throat develops, and with untreated acute tonsillitis, the disease becomes chronic. Based on the above, it is easy to conclude that careful and complete treatment of acute tonsillitis is necessary.
Treatment of tonsillitis in children
With properly selected medications, treatment of tonsillitis in a child takes about a week. The patient is prescribed bed rest, plenty of fluids and a gentle diet, excluding spicy and fatty foods. Medicines are selected according to the type of tonsillitis, accompanying symptoms, and the age of the child. Medicines should only be prescribed by a doctor.
The treatment program includes:
- painkillers;
- washing and rinsing;
- sprays and lozenges;
- physiotherapy. Source: T.V. Spichak Diagnosis and treatment of tonsillitis in children from the perspective of evidence-based medicine // Issues of modern pediatrics, 2010, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 130-135
Antibiotics are prescribed to children only in severe cases, as they cause side effects (abdominal pain, diarrhea, etc.).
Removal of the tonsils (tonsillectomy) is used in exceptional cases, if frequent relapses of the disease are observed, conservative treatment is ineffective, and complications from internal organs are identified.
In case of exacerbation of the chronic form of tonsillitis, the child requires bed rest, diet correction with the exception of fatty, fried, smoked, sweet foods, as well as drug therapy, which includes antibiotics, vitamins, desensitizing drugs, and immunomodulators.
Necessary:
- wash the lacunae of the palatine tonsils with antiseptics;
- treat the back wall of the pharynx and tonsils with solutions of fucorcin, Lugol;
- the child should regularly gargle with antiseptics and herbal decoctions.
You also need to do inhalations, use antiseptic aerosols, and take antimicrobial lozenges.
Physiotherapy may be prescribed :
- Ural Federal District;
- UHF;
- microwave;
- ultraphonophoresis;
- laser therapy.
Complications of the disease:
- descent of purulent infection into the heart sac;
- abscess;
- bleeding from the tonsils;
- eustacheitis;
- otitis;
- purulent inflammation;
- swelling of the larynx with the development of asphyxia, which can be fatal.
Treatment for sore throat
Treatment is carried out mainly at home. Moreover, it is necessary to adhere to bed rest. A sick child is hospitalized when he is less than 3 years old, his high fever (39°-40°) does not subside, he has difficulty breathing, swallowing food and liquids, an abscess is detected on the tonsils, and there is a real threat of complications.
Drug treatment
In order to prevent complications of purulent tonsillitis in a child, treatment is carried out with antibiotics, local agents for the inflamed tonsils, and drugs to eliminate painful symptoms.
Treatment with antibiotics
Penicillin-based drugs (phenoxymethylpenicillin, amoxicillin) are used. If you are allergic to penicillin or need re-treatment with antibiotics due to recurrent sore throat, use antibacterial agents of a different group (macrolides), such as sumamed, azithromycin, erythromycin.
In severe forms of the disease or when complications occur, even stronger antibiotics (cephalosporins) are used for treatment.
Treatment with topical drugs
To speed up the cleansing of the surface of the tonsils from pus, gargle with antiseptic solutions of miramistin or chlorhexidine. Sprays that have an antiseptic effect and contain an antibiotic are used: for example, hexoral, bioparox.
To eliminate pain and sore throat with purulent sore throat in children, you can use lozenges (strepsils, falimint). They contain components with analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects.
Warning: If the child does not yet know how to gargle and suck tablets, treatment can only be carried out with sprays. It is recommended to give him slightly warm tea to disinfect the oral cavity.
Clinical recommendations for disease prevention
The main methods of preventing tonsillitis in children are compliance with sanitary and hygienic measures (avoiding contact with patients and their things, washing hands, using a scarf and hand sanitizers) and strengthening the immune system (hardening, playing sports, etc.).
Tonsillitis is a common disease in children and adults, which without proper treatment can become chronic. If you notice symptoms of illness in your child, immediately contact the children's medical department.
Sources:
- HELL. Vetrova. Acute tonsillitis in children: a pediatrician’s point of view // Pediatric pharmacology, 2014, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 61-64.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6248716/ Raja Kalaiarasi, Kalaivani S Subramanian, Chellappa Vijayakumar and Ramakrishnan Venkataramanan. Microbiological Profile of Chronic Tonsillitis in the Pediatric Age Group // Cureus. 2022 Sep; 10(9): e3343.
- T.V. Spichak. Diagnosis and treatment of tonsillitis in children from the standpoint of evidence-based medicine // Issues of modern pediatrics, 2010, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 130-135.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Lacunar tonsillitis
Regional lymphadenitis develops. On palpation, the submandibular, anterior ear, and cervical lymph nodes are enlarged, painful, dense, and not fused to each other.
A clinical blood test is characterized by leukocytosis - an increase in the level of leukocytes to 15*109/l and higher, the appearance of a large number of immature forms of leukocytes and an increase in ESR to 40-50 mm/hour.
Treatment
As in most cases, treatment can be conservative or surgical.
Surgical treatment includes tonsillectomy (complete removal of the tonsils) and tonsillotomy (partial removal of the tonsils).
Conservative therapy
- antibacterial, protected aminopenicillins are more often used because many bacterial strains have β-lactamase activity. Antibiotics must be taken in full, despite the reduction in symptoms; ignoring this rule often leads to the development of chronic tonsillitis
- desensitizing, relieves swelling of the tonsils
- immunostimulating, it is very important to help the immune system fight infection
- painkiller
- diet therapy, spicy, fried foods must be avoided. Stop using spices
- physiotherapy (KUF)
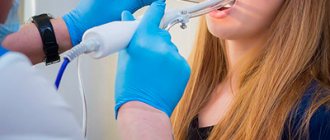
A necessary remedy for combating chronic tonsillitis is local rinsing of the tonsils with both antiseptic solutions and antibiotics. Miramistin and Dioxidin are more often used as solutions. You can do this at home, but not all “plugs” can be washed out, and it is these deep-seated accumulations of microorganisms that cause tonsillitis to become chronic. To clean the lacunae of the palatine tonsils as completely as possible, the ENT specialist performs rinsing of the tonsils.
This method allows you to:
- effectively bring chronic tonsillitis into stable remission
- avoid the development of dysbiosis and fungal infection on the surface of the tonsils
- reduce the risk of needing surgery
- exclude trauma to the tonsils
- treat tonsillitis painlessly
Rinsing is performed using a syringe or a vacuum rinsing apparatus. In the first case, the antiseptic solution is drawn into a syringe and flowed through a special nozzle to the tonsils. In the second case, the solution is supplied and sucked out using the device, and the contents of the lacunae are removed along a pressure gradient. This allows you to penetrate deep into the tissues of the tonsils. In our clinic, your baby will have tonsils washed and a course of physiotherapy, which will allow you to forget about tonsillitis for a long time and avoid surgery. Washing is usually carried out in a course of 5-10 procedures, twice a year or as needed.
To prevent tonsillitis, it is necessary to harden the baby and avoid excessively salty, spicy or hot foods. Follow the rules of home hygiene. It is important to treat acute tonsillitis on time, and most importantly, in full.