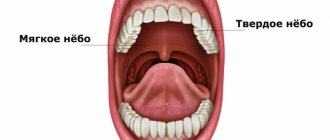
Metallic taste when coughing: causes and symptoms
The following conditions can cause a person to have a metallic taste when coughing:
Gum disease
Gum disease or periodontal disease is an infection of the gum tissue in the mouth.
The accumulation of bacteria in the mouth can cause gum disease. Maintaining good oral hygiene is usually sufficient to prevent bacterial buildup. Smoking is another possible cause of gum disease.
Some other symptoms of gum disease include:
- bad breath
- swollen and inflamed gums
- bleeding gums
- difficulty chewing
- increased sensitivity in teeth
In more severe cases, the disease can cause gums to recede and teeth to weaken or fall out.
Cold
A cold is the result of an infection in the nose, throat and lungs. Rhinovirus infections cause colds and can easily spread to others.
Most people with a cold experience mild symptoms, such as a sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, and cough. Some people also experience fever.
A cold can affect your sense of smell, which then affects your taste, potentially causing a metallic taste in your mouth.
Sinus infection
Sinus infections can cause loss of smell, which can cause a lack of smell and a metallic taste in the mouth.
The maxillary sinuses are the empty spaces behind the cheeks and forehead that connect to the nose. A sinus infection, or sinusitis, can cause inflammation in the sinuses. This inflammation causes a number of symptoms:
- green, liquid substance coming from the nose
- stuffy nose
- cough
- fatigue
- fever
- a sore throat
- bad breath
- tooth pain
- headache
The symptoms of a sinus infection are different from a runny nose, which only affects the nasal passages.
Some types of medicines
Some medications may cause a metallic taste in the mouth. For example, some antibiotics and lithium have this side effect.
If the side effects of your medications affect your daily life or make it difficult to eat or drink, you may want to contact your doctor. It is important not to stop taking these medications without first consulting your doctor.
Stomach upset
Indigestion refers to a group of symptoms that affect the gastrointestinal system, including the respiratory tract, stomach and intestines. Stomach upset can be caused by:
- abdominal pain
- unpleasant feeling of fullness after eating
An upset stomach is not a disease. But it can be a consequence of certain diseases, such as gastritis, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or irritable bowel syndrome.
In other cases, food, drinks, or stress can cause stomach upset.
Cancer treatment
Cancer treatment can affect the way your senses work and change the normal flow of saliva. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy can also cause a metallic taste in the mouth.
About 80% of people undergoing cancer treatment experience changes in the taste of food. In particular, cancer treatment may cause certain foods—such as salty, bitter, or sweet foods—to taste bad.
Meat in particular may taste metallic, while other foods may taste milder than usual.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy hormones can cause dysgeusia. Some pregnant women experience a metallic taste in the mouth due to dysgeusia, a distortion of a person's sense of taste.
People with dysgeusia experience changes in their taste. The taste tends to be salty, rancid, or metallic. Sometimes foods may have no taste at all.
Dysgeusia is most common in the first trimester, and taste usually returns to normal in the second trimester.
Mechanisms of development of pleurisy in cancer
The mechanisms of formation of pleural effusion in cancer are different and are associated with the influence of a malignant tumor:
- With
direct We are talking about the penetration of metastases into the pleura, which leads to an increase in capillary permeability and is fraught with obstruction of the lymph nodes. This leads to a decrease in the outflow of lymph from the pleura and to blockage of the thoracic duct or bronchus. - Indirectly
. Hypoproteinemia (decreased protein in the blood plasma), tumor pneumonia and pulmonary embolism develops.
The cause of exudation (fluid release) into the pleura may also be previous radiation therapy. Due to the variety of predisposing factors and mechanisms for the development of pleurisy in cancer, it is necessary to distinguish between malignant effusion and pleural carcinomatosis, which is associated with the involvement of the pleura in the tumor process in lung cancer.
Most often, pleurisy of the lungs in oncology develops for a combination of reasons:
- metastasis to the pleura, leading to excessive capillary permeability and causing effusion;
- damage to the mediastinal lymph nodes (located in the chest between the lungs), which can impair the outflow of lymph;
- development of chylothorax (accumulation of lymph with a high fat content in the pleural cavity) due to damage to the lymphatic duct;
- bronchial obstruction, which occurs when the bronchial lumen is blocked by a tumor, which leads to a decrease in pressure in the pleural cavity, promoting the influx of fluid.
In cancer, pleurisy develops against the background of a violation of the body's protective functions. The inflammatory process is also always associated with autoimmune disorders and injuries. Oncological processes in the body are most often accompanied by the development of an exudative form of pleurisy - hydrothorax (fluid accumulation in the pleural cavity).
Metallic taste when coughing: treatment
Treatment for metallic taste in cough will depend on the cause. Some of its causes are easy to remove, while others can persist for a long time.
Gum disease can usually be treated with proper oral hygiene measures. These include brushing your teeth every day, flossing, and using mouthwash if necessary. Quitting smoking may also help.
Antibiotics are the first line of treatment for many bacterial infections. For example, to treat a sinus infection, your doctor will prescribe an antibiotic. Your doctor may also suggest other medications to relieve symptoms, such as a decongestant or antihistamine.
Over-the-counter medications are very effective in treating most cases of indigestion. For example, antacids help neutralize excess stomach acid that causes heartburn.
More severe cases may require prescription medications. For example, proton pump inhibitors are especially effective in people who also have heartburn.
If a metallic taste is a result of cancer treatment, it is important not to self-medicate. Avoid taking any vitamins, supplements, or other products without first consulting your doctor. This may interfere with treatment.
Also, to eliminate the metallic taste, people can try using plastic or glass utensils instead of metal ones. Citrus fruits, sugar and salt can also help cover up the metallic taste in your mouth.
You may want to consult your doctor before adding extra sugar or salt to your food.
Do not stop taking medications that cause a metallic taste without talking to your doctor first.
What gives the yellow-green color to purulent sputum?
The respiratory organs are an open system of tubes devoid of valves, membranes, sphincters, etc. The air we breathe contains microorganisms in addition to organic and inorganic dust. These are viruses, bacteria, fungi. Once inside the respiratory system, they can be removed from it with the help of mucus and villi. In this case, a person will not even feel the presence of foreign objects in the bronchi. But during illness, microbes gain an advantage, multiply quickly, and come into conflict with the human immune system. They die, the protective cells die, and the surrounding tissue is damaged. Complex cytotoxic reactions occur. All these “military” actions lead to a change in the color of sputum. The more pronounced the inflammation process, the more purulent the sputum will become. In chronic long-term processes, sputum acquires a green-brown character and becomes viscous. In this case, the patient may cough up sputum in the form of casts of the bronchi. Green color.
The purulent nature of sputum can occur in acute and chronic lung diseases. In any case, this symptom cannot be ignored. Treatment measures must be carried out quickly and effectively.
Sputum interspersed with dark gray lumps may indicate mold growth or a tuberculosis infection.
The canary-colored sputum is characteristic of pulmonary aspergillosis.
Klebsiella pneumoniae causes a cough with sputum the color and consistency of “raspberry jelly.”
Yellow sputum is characteristic of acute diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus, streptococci S. pneumoniae, S. pyogenes. Such sputum can occur in any pulmonary disease from acute bronchitis to pneumonia.
Green sputum is more typical for chronic lung diseases; this may be bacterial associations of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Such as Haemophilus influenzae + Staphylococcus aureus. Or Pseudomonas aeruginosa P. aeruginosa in combination with streptococci. Occurs in patients with bronchiectasis, COPD, and cystic fibrosis.
Thick green sputum with an odor indicates a lung abscess, abscess pneumonia. Pathogens can be S. aureus, K. pneumoniae, gram-negative bacilli, Streptococcus pyogenes Haemophilus influenzae.
The presence of blood in the sputum may indicate a pulmonary embolism, cancer, or problems with the larynx.
What to do?
In acute diseases, purulent sputum does not appear immediately, but usually on the 4th day of the disease. If coughing up such sputum is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, then the help of a doctor is necessary. No need to self-medicate!
In COPD, bronchiectasis, and obstructive bronchitis, sputum may become purulent within one to two days. Often green-yellow color of sputum is constantly present in a person suffering from chronic pulmonary diseases. During exacerbations, it becomes intensely green and coughs up large quantities. Patients with chronic lung diseases should have an individual plan prescribed by a pulmonologist for preventive and urgent action in connection with the appearance of purulent sputum. If you do not have such a plan, remind your doctor that you need one. If your active actions do not help within 5-7 days, contact a pulmonologist.
Diseases characterized by purulent sputum
- COPD,
- Bronchiectasis,
- Pneumonia,
- Chronic purulent obstructive bronchitis,
- Lung abscess, abscess pneumonia,
- Pulmonary tuberculosis,
- Cystic fibrosis,
- Purulent processes in the nasopharynx,
- Pulmonary aspergillosis,
- Non-tuberculous mycobacteriosis.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of diseases of the respiratory organs leading to expectoration of purulent sputum is a set of measures that includes examination, auscultation, and percussion of the chest.
Mandatory x-ray examination. Computed tomography of the chest organs (CT CT) is considered more informative.
Functional breathing tests - respiratory function, body plethysmography and diffusion tests are often necessary.
Sputum examination is an important stage for prescribing treatment and assessing the prognosis of the disease. Routine sputum tests are important to assess the severity of inflammation (by counting the number of leukocytes in the sputum) and eosinophils. A general sputum test can help identify Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Fragments of mycelium or pseudomycelium of fungi.
The microbiological method (sputum culture) answers the question of what is the name of the microorganism that causes purulent, mucopurulent inflammation in the lung tissue. The sputum is sown on special nutrient media, the colony is counted and the name of the pathogen is determined. Detection of H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis and S. Pneumoniae.
For example, risk factors for Pseudomonas infection include recent hospitalization (2 days within the past 90 days), frequent use of antibiotics (4 courses within the past year), severe COPD, isolation of P. aeruginosa during a previous exacerbation, stable period of Pseudomonas colonization, and systemic use of glucocorticoids.
It will require the prescription of antibiotics aimed at destroying these particular microorganisms.
How can we help?
First, it is necessary to treat the disease leading to cough with purulent sputum. Be it an acute or chronic disease. The presence of hemoptysis is an urgent reason to consult a doctor.
- If the disease is caused by bacterial flora, then antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
- If we are dealing with influenza and bacterial pneumonia that has developed against it, a combination of antiviral drugs and antibiotics is needed
- If the cause of purulent sputum is a fungal infection, then it is necessary to treat with antifungal drugs
- If tuberculosis is detected, then use anti-tuberculosis drugs.
For a rapid response to treatment, bronchoscopy may be effective. These are manipulations in which a flexible endoscope is inserted into the bronchus, which sucks out purulent sputum from the bronchi, and with the help of it you can pour an antiseptic and antibiotic into the bronchus. But the method is traumatic, unpleasant and dangerous with complications.
An alternative to bronchoscopy can be considered hardware coughing technologies - intra-alveolar percussion devices, vibration vests, exercise therapy sets, breathing simulators and coughers for home use.
When to see a doctor
A metallic taste when coughing may be a symptom of a condition that requires medical attention. For example, accompanying feverish symptoms may indicate an infection that should be treated only with prescription medications.
Most people do not need medical care for minor conditions such as the common cold. However, older adults should see a doctor if their symptoms keep getting worse or persist for more than a few days.
If a medicine or cancer treatment is causing a problem, call your doctor first before making any changes. Your doctor may prescribe a different medicine or recommend other possible changes.
Symptoms of malignant pleurisy
The clinical picture of malignant pleurisy is different. In 25% of cases there are no symptoms. The disease is diagnosed during an examination. Pathology begins to manifest itself mainly only when the volume of liquid reaches 300 ml.
When a malignant tumor is localized in internal organs, characteristic signs develop. Pleurisy in lung cancer is accompanied by:
- Chest pain
. A chronic symptom is observed mainly in mesothelioma (primary soft tissue neoplasm). Severe pain occurs when the ribs and vertebrae are affected by metastases. The symptom is characteristic of the growth of a cancerous tumor into the chest wall. - Cough
. In isolated form, pleurisy is usually dry. If a respiratory infection occurs, sputum begins to be produced. If there is a malignant neoplasm in the lumen of the bronchus, blood and pus are present in the sputum. - Shortness of breath
. In the case of the exudative form of pleurisy, it develops against the background of fluid accumulation around the lung. The effusion compresses the organ, preventing its full expansion, which leads to limited movement of the diaphragm. Shortness of breath may have varying degrees of severity, depending on the increase in the amount of free fluid. - Paleness of the skin
. With the accumulation of pleural effusion, there is a disturbance in the outflow of blood in the area of the neck veins, which swell and become noticeable during a visual examination.
In addition to the listed symptoms, metastatic pleurisy in cancer is accompanied by fever, weight loss and loss of appetite. Increased sweating, excessive fatigue and lethargy are also observed. The movement of the affected side of the chest lags behind when breathing, compared to the healthy lung.
A characteristic sign of tumor pleurisy is a gradual increase in shortness of breath, which is accompanied by characteristic heaviness in the chest area. The patient constantly lies down on the sore side, which contributes to a temporary improvement in the condition, since the healthy lung is completely expanded.
What types of cancer most often lead to pleurisy?
The prognosis of pleurisy in oncology depends on the organ affected by cancer. The highest survival rate has been established for malignant tumors of the breast and ovaries. The prognosis for pulmonary pleurisy in oncology is much worse. To determine the outcome, the LENT scale is used, which takes into account not only the condition, but also the patient’s functional capabilities.
Most often, pleurisy develops with cancer:
- lung (24-50% of patients);
- ovaries (up to 10%);
- breast (48%).
Less commonly, a complication occurs in the presence of a malignant process in the colon, stomach and pancreas - from 1 to 6% of cases. The prognosis and therapeutic options are determined by the prevalence and nature of the tumor process. The degree of sensitivity to drug therapy matters.
If a malignant tumor is sensitive to cytostatics, as in ovarian, breast and lung cancer, then with timely adoption of therapeutic measures it is possible to prevent relapses of exudation. If systemic therapy is ineffective, pleurodesis is performed to improve the prognosis.