Acute toothache is often a consequence of advanced caries and pulpitis. If the nerve is inflamed, the tooth may hurt even in the absence of external irritants: mechanical stress, applying paste, eating cold or hot food. You can relieve pain syndromes with pills, but it is impossible to cure such a disease on your own. If the inflammatory process is started, serious complications of the health of the dental system will arise, which in the future can only be cured with the help of long-term, painful and expensive treatment.
What is a dental nerve
Under the coronal part in the root canals there is soft connective tissue penetrated by nerve endings, capillaries, and lymphatic vessels. It is called the pulp, colloquially the nerve. It performs a plastic, sensory, protective, trophic function.
If inflammatory processes occur and untimely therapy occurs, it may die. If it is impossible to preserve the pulp, amputation is performed. Removing the nerve of a tooth leads to fragility of hard tissues, but with correct treatment it will retain its functionality for many years.
Wisdom teeth - difference from other teeth
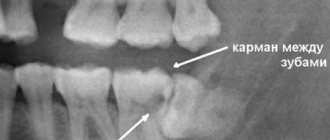
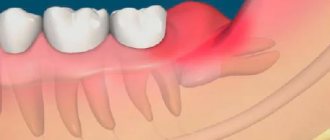
This tooth is no different from other molars in its structure. If it erupts without pain, does not cause discomfort to the person and has normal roots, then they do not get rid of it. Its cutting is often accompanied by acute or dull pain, lack of comfort when eating food and other unpleasant symptoms. The upper teeth can cause food stuck and damage to the mucous membrane, and the lower teeth can lead to the formation of a purulent hood, caries, etc.
The main differences are two factors:
- excessively curved or fused roots;
- the same curved root canals.
The first factor is reflected in the difficulty of extraction: the roots grow together and can have the most bizarre shapes. This is what causes the main difficulties for painless elimination. The second factor provokes difficulties with further treatment: canals of this shape are very difficult to subject to filling and mechanical stress.
Indications and contraindications for removal
Pulpitis is treated conservatively and surgically. If it is possible to preserve the pulp, the dentist tries to cure the disease with medications and physiotherapy.
The nerve must be removed in the following cases:
- if the carious lesion has spread to the canals and pulp;
- there is a concomitant disease of periodontitis (inflammation of the periodontium, which holds the tooth unit in the socket);
- severe damage to dentin by caries (large area, presence of several carious cavities);
- mechanical damage;
- the presence of concrements in the canals - hard deposits that cause irritation and inflammation of soft, sensitive tissues;
- lack of positive results from therapy;
- unbearable pain that cannot be relieved by medications.
Depulpation can also be carried out if the orthopedist indicates prosthetics.
The procedure is not performed if:
- stomatitis, acute infections, since pathogenic microorganisms can penetrate deep into the jaw and cause the development of serious diseases;
- poor blood clotting due to the risk of heavy bleeding;
- pregnancy due to the inability to provide the necessary anesthesia.
Modern techniques
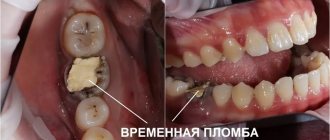
Until recently, the procedure was very painful and was divided into 2 stages. At the first visit, the canal was expanded with a drill, arsenic was placed into the cavity and a temporary filling was placed. A few days later they carried out cleaning, and only after that the filling began. During the interval between procedures, the patient experienced severe pain, which could not always be relieved with medications. Today, depulpation is done in one visit, and the session time does not exceed 30 - 40 minutes.
If during diagnosis it turns out that the pulp needs to be removed (or its partial extraction is required) or the treatment did not give the desired effect, then the doctor chooses the method that is best suited for the particular case.
During vital amputation, a small part of the nerve that is located under the crown is removed, after which the tooth is filled. Thus, the dental unit continues to receive nutrition, which means it is alive and fully functional.
Devital amputation is done if complete removal of the tooth nerve is necessary. It becomes “dead”, fragile, but can still perform its function for a long time.
Procedure steps:
- anesthesia;
- isolation from saliva getting inside;
- drilling out a carious cavity;
- antiseptic treatment;
- depulpation;
- cleaning, obturation and filling of canals;
- application of a light-curing composite.
The work is very difficult and can only be performed by a professional doctor. If you miss even minimal cavities, lateral tubules, then the dental tissues react and begin to collapse. In our clinic, a panoramic photograph of both jaws is taken, and treatment is carried out under a dental microscope. It allows you to perform dental operations with high precision, protects against injuries, as well as the development of complications and relapses.
Radiation diagnostics
Of course, CBCT of the area of the impacted tooth provides the most complete three-dimensional picture of the position of the nerve and tooth. It is important to note here that any such examination must be supported by a written description from the radiologist. In this case, the surgeon has legal protection in case of a conflict situation and a lawsuit. The description must indicate the likelihood of such an injury: “the root of the tooth is adjacent to the wall of the mandibular canal,” “damage to the joint canal is possible when the tooth is removed,” “a narrowing of the canal at the level of the impacted tooth is detected.” OPTG is a more outdated research method; in the image it is not always possible to assess the location of the mandibular canal, especially in the buccolingual aspect. However, this classical diagnostic method is still widely used. A radiological sign of the contact location of the nerve and tooth is the following criteria: absence of the mandibular cortical plate at the level of the impacted tooth, narrowing of the lumen of the mandibular canal at the level of the tooth (Fig. 3,4). From a practical point of view, CBCT does not provide significant advantages and does not reduce the risk of developing paresthesia when removing an impacted tooth, since the extraction process is not computer-guided.
Prevention of complications. Before surgery to remove an impacted tooth, it is necessary to inform the patient about the possible risks of damage to the inferior alveolar nerve. It is important to convey to the patient that the timing of restoration of sensitivity of the lower lip depends on many factors and it is impossible to indicate the exact recovery time. The patient must be informed for what reasons the tooth is being removed; it is important to have a written description of the position of the tooth by the radiologist and a written opinion from the orthodontist. All this data must be attached to the patient’s medical record, and only after reviewing and signing the voluntary medical intervention can you begin to work with the patient.
Rice. 3. Narrowing of the lumen of the mandibular canal on OPTG is a sign of the anatomical proximity of the tooth root and the lower alveolar nerve.
Rice. 4. Darkening of the cortical pattern of the mandibular canal on OPTG is a sign of the anatomical proximity of the tooth root and the inferior alveolar nerve. After the tooth was removed, an open vascular nerve bundle was visible in the wound.
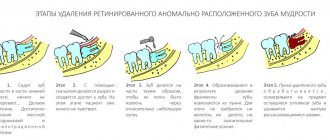
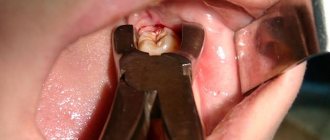
The technique of removing an impacted tooth requires sufficient lighting and good visualization of the surgical field. It is necessary to carry out a wide opening of the wound with skeletonized alveolar part at the level of the second molar and retromolar fossa and partially the branch. Small access significantly complicates the view of the wound. In most cases, tooth extraction begins with freeing the crown from the adjacent bone, then sawing the tooth along the dentino-enamel junction with a drill. After removing the crown and tooth, work is carried out on the roots. Based on the shape of the tooth cavity and the position of the orifices, the bifurcation of the roots is determined, and the roots are separated using a drill. When removing a single-rooted third molar, the socket is expanded on the side opposite to the position of the nerve (in most cases, on the buccal side). Root luxation with an elevator must be carried out without strong pressure, because a root fracture in the apical third with its subsequent removal increases the risk of nerve injury. In some cases, it is advisable to leave the tooth root in the wound as a “foreign body” in order to prevent nerve injury. The root fragment does not complicate wound healing, since the tooth does not have an apical infection. It is important to inform the patient that the tooth root “must be left” in order to preserve the integrity of the surrounding structures. Abroad, there is a generally accepted method for preventing nerve injury during tooth extraction - coronectomy, in which only the crown part of the tooth is removed. In fact, this removal can be considered incomplete. The root of an impacted tooth moves coronally over time, and bone tissue forms between the tooth and the mandibular canal. The second stage involves removing the roots of the tooth. This technique is not prescribed in domestic standards for the treatment of pericoronitis and is not described in the national guidelines, therefore it cannot be recommended for use in the Russian Federation.
Advantages of contacting FamilySmile
In our clinic, tooth nerve removal is performed by doctors with extensive experience. We provide dental services of any complexity, including implantation, prosthetics, treatment of baby teeth, teeth with thinned enamel, loose gums with increased sensitivity and much more. We carry out diagnostics and dental treatment under a microscope, which magnifies the image 30 times. The doctor can see all the defects in the root part and eliminate them accurately and painlessly.
We use only safe drugs, high-quality injections and filling materials. At the patient's request, we treat under anesthesia or sedation.
How painful is the surgery?
The use of modern equipment and special surgical equipment makes the task of removal easier for both the doctor and the patient. Painful sensations are eliminated by anesthesia. The injection is made by the dentist into the gum area. The injection itself is almost imperceptible and does not cause discomfort.
Wisdom tooth extraction can be sensitive for patients who have been taking pain medications for a long time. For particularly sensitive people, it is suggested to use either a repeat injection or a stronger anesthetic. More pronounced sensations can be observed in isolated cases in patients with an advanced abscess.
Painless surgery - complex or simple - is already a reality. The specialists of the Zuub clinic, thanks to the use of modern equipment and their accumulated experience, carry out operations efficiently and quickly. In such conditions, the patient can not only count on the absence of pain, but also complete comfort during removal.