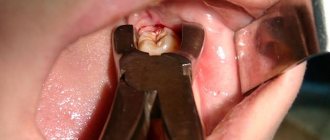
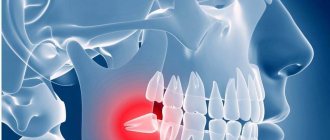
Quite often, wisdom teeth cause problems to a person. They erupt at approximately the age of 20-25 years, when the dentition has already formed and in most cases their appearance is accompanied by complications. The extreme molars do not serve any useful function, so dentists often recommend that patients have them removed.
It should be understood that wisdom tooth extraction is a rather complicated procedure for both the doctor and the patient, especially the removal of molars on the lower jaw.
When you need to remove the bottom "eight". Indications
Wisdom teeth are distinguished by late eruption, which occurs at 20-30 years of age. During this period, the dental system is practically formed and the third molars often do not have enough space in the dentition. Eruption causes various complications and in most cases requires removal of the molar. In addition, in humans, with evolution, a decrease in the size of the jaws occurs, since, due to the nature of nutrition, the chewing load is constantly decreasing.
Most people do not take good hygienic care of their last teeth. They are located at the end of the dentition, and it is often technically impossible to clean them well. This leads to the accumulation of plaque, damage to the enamel by the carious process and its complications (pulpitis, periodontitis). Root canal treatment is very difficult due to difficult access. Therefore, eights must be removed in 90% of cases.
Removal of a fully erupted wisdom tooth
Removal of the lower wisdom tooth is indicated in the following cases:
- Excessive pressure on neighboring teeth, which can lead to their destruction;
- Injury to surrounding tissues;
- Constant biting of the mucous membrane of the cheek;
- Carious lesion that cannot be eliminated due to difficult access;
- Complications of caries: pulpitis, periodontitis, periostitis;
- Dystopia – location of the molar outside the dentition;
- A tooth that is a chronic source of infection;
- Formation of perihilar cysts, granulomas;
- Malocclusion and displacement of other teeth.
Method for removing a horizontally lying figure eight
Any position of a wisdom tooth identified as a deviation from the norm implies an unambiguous recommendation for complex removal. The operation falls into this category because it requires a series of traumatic actions for the patient to extract the tooth completely.
The intervention can be complicated by various unpleasant consequences, so before the operation the surgeon carefully prepares and calculates possible options for the development of the situation. An X-ray is mandatory.
Most dentists vote for early removal of the impacted figure eight. Over the years, the molar roots grow strongly and the jaw bones become denser, which prevents the tooth from being quickly removed from the socket. In youth, tissues are restored faster, and discomfort is experienced more easily.
However, the complexity of the operation is quite surmountable, and it occurs under strong anesthesia. The patient does not experience pain during removal.
Can you put a crown on a wisdom tooth?
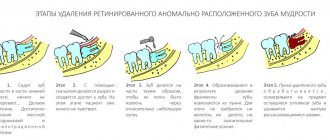
Step-by-step method for extracting a horizontally located wisdom tooth:
- The use of an anesthetic, the drug “Ultracaine” is mainly used;
- Making an incision in the gum to expose an impacted wisdom tooth;
- If access to the roots is difficult, sawing the bone is necessary. The manipulation is performed extremely carefully, without the risk of damaging the adjacent tooth;
- Application of forceps and removal of the figure eight using loosening technology;
- When the third molar is in a recumbent position, the dentist first saws the tooth into pieces and removes them piece by piece;
- Suturing the incision on soft tissues with the application of a cotton-gauze swab. If self-absorbable suture material is used, no further treatment of the wound is required. In case of direct suturing, the sutures are removed at a doctor’s appointment in the clinic.
At the last stage of the operation, ice is applied to the extraction area, thus preventing the formation of severe swelling of the gums. The doctor discusses the possible consequences of the intervention: increased temperature, tissue soreness due to injury, bleeding. In this case, the normal limits are indicated, if exceeded, you should immediately contact the clinic.
Removal of the lower impacted figure eight
A common complication is wisdom tooth retention, which is incomplete eruption. It can erupt above the gum as part of the crown or as one or two bumps. In this case, the second part of the crown will be covered with a gingival hood. With insufficient hygienic care, food accumulation, gum inflammation, and pericoronitis (inflammation of the hood) occur. In the case of pericoronitis, the dentist excises or cuts the gingival hood. But if the situation is constantly repeated and bothers you, then it is better to remove such a tooth. Chronic inflammation of the gums is a source of infection that spreads throughout the body and can provoke an exacerbation of other diseases.
A planned operation to remove lower teeth is performed:
- When dental tissues are destroyed below the gum level. Such a dental unit cannot be used as a support for orthopedic treatment.
- Impenetrable root canals. In this case, conservative treatment becomes impossible.
- Tooth mobility in all planes.
- If, in the case of a jaw bone fracture, a dental unit is found in the fracture line. In this case, without removing the tooth, it is not possible to correctly compare the fragments.
- Dystopian teeth.
- "Eights" covered with a hood of mucous membrane. With frequent exacerbation of pericoronoritis.
Contraindications
Like any dental procedure, extraction surgery sometimes requires a delay. When is this operation contraindicated?
Local contraindications:
- Inflammatory diseases of the soft tissues of the oral cavity (stomatitis, gingivitis, etc.).
- If the dental unit is in the projection of a malignant tumor.
- Damage to the mucous membrane caused by an allergic response (medicinal stomatitis, cheilitis, etc.).
- Manifestation of specific infections in the oral cavity: tuberculosis, syphilis, actinomycosis.
- Radiation therapy or radiation sickness.
- If there is no permanent tooth germ in the jawbone, then removing the temporary unit should be delayed as long as possible.
General contraindications:
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
- Chronic diseases of internal organs in the acute stage.
- Acute degree of mental disorder.
- Infectious disease: measles, chickenpox, scarlet fever, diphtheria, dysentery, influenza.
- Pathology of the nervous system.
- Blood diseases.
- The beginning of pregnancy and the last trimester of pregnancy.
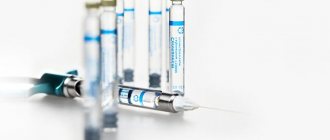
Anesthesia
Before the operation, complete anesthesia of the required area of the jaw is carried out. The most commonly used is local anesthesia, which is carried out using a carpule syringe and an anesthetic. Anesthesia of the lower jaw occurs 8-10 minutes after the injection. The duration of the analgesic effect depends on the drug used and is 2-4 hours. The operation itself is completely painless, but after the anesthetic wears off, the patient begins to feel pain. Therefore, after the procedure, the specialist gives prescriptions about the need to use medications (painkillers, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial agents).
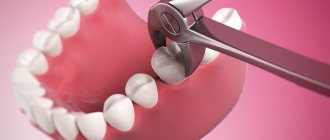
Easy removal
Simple extraction is the extraction of a tooth without the use of additional tools or techniques. A simple operation is observed after complete eruption, correct positioning of the molar, and the absence of serious pathologies. The doctor applies forceps and, after rocking movements, removes the molar from the jaw
The following stages of the procedure can be distinguished:
- Anesthesia;
- Selection and preparation of tools;
- Tooth ligament separation;
- Application and fixation of forceps;
- Luxation of a molar;
- Extraction from bone;
- Checking the hole;
- Stop bleeding;
- Recommendations for the patient.
Difficult removal
Removing a wisdom tooth in the lower jaw is often difficult. The operation differs in its duration, the use of a special instrument, and the use of a drill. Often the tooth is sawed and removed in parts. In this case, the figure eight is incorrectly positioned or impacted. Removal consists of the following steps:
- High-quality pain relief;
- Preparation of tools and auxiliary materials;
- Separating the tooth ligament or creating access;
- Application and fixation of forceps;
- Extraction of a molar in whole or in parts;
- Inspection of the bone socket, cleaning it if necessary;
- Stop bleeding;
- Stitching;
- Prescriptions and recommendations for the patient.
What is complex wisdom tooth extraction?
Tooth extraction is called complex if the tooth has several roots, and the operation will require an incision into the soft tissue of the gums and, possibly, the periosteum. Another difference from classic removal is the need to use additional tools (except for forceps and an elevator). The difficulty of performing surgical intervention is due to the difficulty of accessing the extreme elements of the dentition, the root features of the “eights” and the specifics of the clinical case (they are often dystopic or impacted).
Important: you cannot postpone the removal of the defective “eight”. This can lead to suppuration and, as a consequence, to the formation of an abscess and the development of sepsis.
Possible consequences after removal
Complications can occur after any surgical procedure. These include: bleeding from the wound, suture dehiscence, inflammation of the socket (alveolitis), increased body temperature over 38 degrees, numbness of the jaw, bone fragments or tooth remains in the socket.
A normal reaction of the body in response to surgery is the appearance of pain, discomfort, unpleasant sensations in the surgical area, a slight increase in temperature, swelling of the angle of the jaw, and facial asymmetry. These symptoms occur due to soft tissue injury, damage to blood vessels and nerve endings. The pain should subside over time and disappear after 5-10 days.
If after 3-4 days the pain does not decrease and the symptoms of inflammation increase, you should consult a dentist. The most unpleasant complication is alveolitis - inflammation of the socket of an extracted tooth. It manifests itself as acute pain, redness and swelling of the gum tissue, a significant increase in temperature, and general symptoms. The wound may discharge purulent contents or necrotic plaque. In this case, treatment by a dentist is necessary.
Indications for removal
The dentist decides whether or not to remove a tooth, adequately assessing the situation in the mouth.
Direct indications are:
- advanced caries that cannot be treated;
- lack of a crown, with roots not suitable for implantation;
- crown fracture exposing the pulp;
- the dental unit is a source of infection, as a result of which complications develop (tonsillitis, periostitis, sinusitis, osteomyelitis of the jaw, abscess and phlegmon of the cheek);
- unsuccessful treatment of periodontitis;
- unerupted or incompletely erupted teeth are the cause of frequent inflammation, damage to nearby tissues and teeth;
- severe mobility with an extreme degree of periodontal damage that cannot be treated;
- purulent periodontitis, which is not relieved by conservative methods;
- crowding of teeth.
Prevention after surgery
After the last molar is removed, the specialist gives instructions that must be strictly adhered to. This is done to prevent complications, speed up wound healing and restore the body. The doctor recommends:
- Do not eat food for several hours after surgery;
- On the first day, you can apply a cold compress to reduce swelling and inflammation;
- For the first two days, you should not rinse your mouth, so as not to remove the blood clot from the hole from which healing will occur;
- Hygienic care can be carried out as usual; teeth in the surgical area should be brushed very carefully;
- Take painkillers and other medications prescribed by your doctor;
- From the second day, the mouth can be rinsed with antiseptic solutions, decoctions of medicinal herbs, and mouth rinse;
- It is recommended to eat soft foods, avoid too hard, spicy, hot foods;
- Bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol) should be eliminated;
- During the week you cannot visit the sauna, bathhouse, or gym.
Bleeding
If bloody discharge appears from the socket of an extracted wisdom tooth, you should call your doctor and report the situation. Minor gum bleeding can occur due to tissue injury, high blood pressure, or problems with blood clotting. In most cases, this does not threaten health and goes away on its own. If bleeding is severe or frequently repeated, you should inform your doctor and come for an examination. To prevent complications, you should rest more for several days, avoid physical activity, and monitor your blood pressure.
Pain in the socket
Everyone experiences pain after removal surgery and worries for several days. The intensity of pain will depend on the traumatic nature of the operation and the complexity of the surgical interventions. During the postoperative period, the dentist recommends using painkillers. If the pain does not disappear, but intensifies after 3-4 days, this may indicate complications. A professional examination and consultation with a doctor are required.
When should a wisdom tooth in the lower jaw not be removed?
There are no absolute contraindications to removal, but there are relative ones:
- The figure eight does not need to be removed if it is correctly positioned, functions and does not injure surrounding organs;
- The operation cannot be performed without preliminary preparation if the tooth is located in the area of the tumor or puts pressure on a large vessel or nerve;
- For some diseases, it is necessary to prepare the body for surgery (rheumatism, diabetes, blood diseases, etc.)
You can carry out high-quality removal of a wisdom tooth of any complexity at the Berezka dental clinic. Specialists perform various surgical procedures effectively, safely and painlessly. All manipulations are carried out professionally and taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient.
When is surgery indicated?
Indications can be called urgent and planned. The difference between them is that with an urgent operation, the clinical picture in the oral cavity and the general condition of the patient does not require delay. Delay may result in complications not only in the maxillofacial area, but the patient’s general condition may worsen.
Urgent indications include:
- A situation where dental tissues are severely destroyed and do not provide any functional benefit, but only aggravate purulent inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and soft tissues of the face. Usually these processes come from this jaw structure, due to the constant accumulation of pathogenic microflora there. Untimely treatment can cause the following purulent-inflammatory processes: periodontitis, periostitis, sinusitis, phlegmon or abscess.
- Diagnosed osteomyelitis in the projection of a destroyed, diseased dental unit.
- Longitudinal dental fracture.
- Transverse fracture of the dental crown with opening of the pulp chamber, but due to curvature or resorption of the roots, the tooth cannot be treated endodontically.