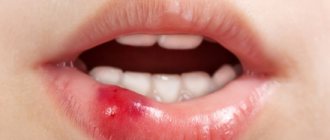
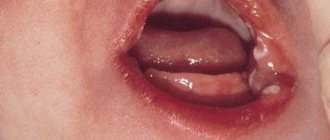
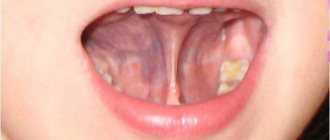
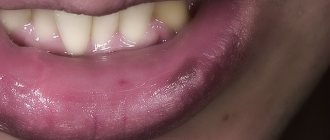
Labial frenulum tears are injuries in the mouth. They may cause bleeding but rarely require medical attention.
The labial frenulum is a thin layer of tissue that connects the lips to the gums and bones of the face. There are two different types of labial frenulum:
- the maxillary labial frenulum, which connects the upper lip to the mouth;
- the mandibular labial frenulum, which connects the lower lip to the mouth.
The frenulum of the lips helps keep them in place while the jaw and facial bones grow.
These injuries are usually treated at home, but in some cases medical attention may be required.
First aid for a ruptured upper frenulum
Upper frenulum ruptures are common in children. The main symptom is bleeding from the upper gums and lips.
These injuries rarely require treatment and heal without stitches.
First aid tips for a torn frenulum include:
- Press your outer lip against your teeth for 10 minutes to stop bleeding;
- do not pull out the lip to check the injury, as this may renew the bleeding.
Be sure to check for other signs of swelling or infection after 3 days. After this time there should be no bleeding.
Possible consequences
Often minor damage does not cause any unpleasant consequences. The same thing applies if the mucous membrane has been restored to its normal state. If medical correction has not been carried out, the tissues have grown together incorrectly, this can cause problems as a person grows and in his later adult life:
- problems with pronouncing certain sounds, especially if the injury occurred before the baby first spoke;
- susceptibility to infections of the oral cavity, if the tissues have grown together crookedly, there is no normal oral hygiene;
- Gastrointestinal problems can occur due to the fact that children do not chew food well after gum injuries.
Kids are active and curious, they require the attention and responsible attitude of adults. Childhood injuries happen everywhere; the frenulum can tear even from excessive efforts when brushing teeth or a minor bruise; only the doctor decides whether to stitch it up or not. Many speech therapists do not see a connection between such damage and poor diction. Parents should not be afraid of a protruding lip after surgery. A child can even tear the mucous membrane several times; the main thing is not to panic and maintain a reasonable approach to the treatment and prevention of injury.
The article has been verified by the editors
Can it heal on its own?
Most frenulum tears heal on their own in 3-4 days. Infections or other complications are rare.
While the injury is healing, you can apply a cold compress to it for 20 minutes to relieve pain.
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as Tylenol or ibuprofen are also helpful.
After a frenulum rupture, it is important to stay hydrated. A person should stick to soft foods to avoid chewing and avoid salty, sour or spicy foods. This may irritate the wound.
Prices for services
| Name of service | Service price (RUB) |
| Initial appointment, examination and consultation with a urologist | 1 000 |
| Repeated appointment, examination and consultation with a urologist | 900 |
| Initial appointment, examination and consultation with a urologist of the highest category | 1 200 |
| Repeated appointment, examination and consultation with a urologist of the highest category | 1 100 |
| Initial appointment, examination and consultation with a urologist Ph.D. | 1 400 |
| Repeated appointment, examination and consultation with a urologist Ph.D. | 1 200 |
| Appointment with treatment appointment | 1 500 |
| Appointment with treatment prescription, Ph.D. | 1 700 |
| Prescription of treatment for erectile dysfunction | 2 000 |
| Prescription of treatment for priapism | 4 000 |
| Prescription of treatment for infertility | 2 500 |
| Blockage of the spermatic cord | 1 000 |
| Collection of material for histological examination | 600 |
| Collection of prostate secretions | 700 |
| Taking a smear from the urethra | 350 |
| Ejaculate collection | 350 |
| Foley catheter replacement | 1 400 |
| Urethral instillation (introduction of medications into the urethra) | 500 |
| Bladder instillation (introduction of medications into the bladder) | 1 200 |
| Bladder catheterization (to drain urine) | 900 |
| Elimination of spermatic cord torsion (conservative) | 3 000 |
| Elimination of paraphimosis (conservative) | 1 200 |
| LOD therapy | 600 |
| Prostate massage | 700 |
| Digital rectal examination | 400 |
| Dressing | 750 |
| Scraping (imprint) from the head of the penis | 300 |
| Cystoscopy under local anesthesia | 5 750 |
| Cystoscopy under anesthesia (intravenous) | 7 800 |
| Urethroscopy under local anesthesia | 4 750 |
| Urethroscopy under anesthesia (intravenous) | 6 800 |
| Removal of a ureteral stent (or removal of a stent from the ureter) under general anesthesia (intravenous) | 12 800 |
| Dilation of the urethra, category 1 of complexity (without anesthesia) | 2 500 |
| Cystic formation of the testicle, epididymis, category I of complexity | 8 500 |
| Cystic formation of the testicle, epididymis (2 categories of complexity: with scar changes) | 11 000 |
| Cystic formation of the spermatic cord | 9 000 |
| Meatotomy (dissection of the external opening of the urethra) | 10 000 |
| Circumcision of the foreskin | 17 000 |
| Complex “Circumcision of the foreskin (circumcision)”: consultation, tests, local anesthesia*, circumcision, 3 dressings). *Intravenous anesthesia is paid additionally (intravenous combined anesthesia (anesthesia) - 6,500 rubles) | 19 900 |
| Surgical treatment for hydrocele (hydrocele) | 25 000 |
| Complex “Surgical treatment for hydrocele” (hydrocele) : appointment with a urologist, tests before surgery, surgery, dressings. *Anesthesia of your choice - paid extra | 27 900 |
| Surgical removal of spermatic cord torsion | 15 000 |
| Surgery for varicocele (Marmara operation) | 25 000 |
| Complex “Surgery for varicocele (Marmara operation)”: appointment with a urologist, clinical blood test, general urine test, 4 mandatory tests (RW, HIV, hepatitis B, C), biochemical blood test (glucose, AST, ALT, creatinine, total bilirubin ), coagulogram No. 1, blood sampling from a vein, surgery, dressings). *Anesthesia is paid additionally (intravenous combined anesthesia - 6500 rubles) | 27 900 |
| Open (operative) testicular biopsy (1 unit) | 8 000 |
| Plastic surgery of the short frenulum of the penis (laser) | 4 700 |
| Plasty of the penile velum (correction of the peno-scrotal angle) | 25 000 |
| Complex “Plasty of the penile velum (correction of the peno-scrotal angle) ”: appointment with a urologist, clinical blood test, general urine test, 4 mandatory tests (RW, HIV, hepatitis B, C), biochemical blood test (glucose, AST, ALT, creatinine, total bilirubin), coagulogram No. 1, blood sampling from a vein, surgery, dressings). *Anesthesia is paid additionally (intravenous combined anesthesia - 6500 rubles) | 27 900 |
| Vasectomy (vasoresection) | 15 000 |
| Complex “Vasectomy (vasoresection)”: appointment with a urologist, clinical blood test, general urine test, 4 mandatory tests (RW, HIV, hepatitis B, C), biochemical blood test (glucose, AST, ALT, creatinine, total bilirubin), coagulogram No. 1, blood sampling from a vein, local anesthesia*, surgery, dressings). *Anesthesia is paid additionally (intravenous combined anesthesia - 6500 rubles) | 17 900 |
| Denervation of the glans penis during early ejaculation | 30 000 |
| Testicular prosthesis – 1 unit (with local anesthesia) | 15 000 |
| Ligamentotomy (increasing the length of the penis) | 35 000 |
| Testicular puncture biopsy (1 unit) | 4 000 |
| Separation of synechiae (1 procedure) | 1 300 |
| Removal of a foreign body from the urethra | 2 500 |
| Removal of a foreign body from the penis | 6 000 |
| Removal of benign formations of the external genitalia | 3 500 |
| Removal of genital warts (1 piece up to 5 mm) | 1 200 |
| Removal of genital warts (2 - 5 pieces up to 5 mm) | 2 400 |
| Removal of genital warts (more than 5 pieces up to 5 mm) | 3 500 |
| Removal of genital warts (1 piece more than 5 mm) | 1 400 |
| Elimination of paraphimosis (operatively) | 2 500 |
| Removal of paraurethral cyst | 9 500 |
| Complex “Laser removal of angiokeratomas, Fordyce granules, pearlescent papules” : appointment with a surgeon (urologist), anesthesia, removal of all formations of one type | 9 250 |
Complications
If the labial frenulum is torn, there is a risk of infection. However, a doctor can easily treat these infections.
A labial frenulum tear is unlikely to cause serious complications. However, people with abnormal labial frenulum structure may experience:
- receding gums around teeth;
- large gap between the upper front teeth;
- Difficulty moving lips.
The surgeon can correct these problems through medical procedures, including frenulum removal.
Predisposing factors for the development of seizures
There are many factors for the development of inflammation. And with a detailed study of the medical history, at least one of the predisposing factors is discovered in patients suffering from seizures. And diabetes comes first. Therefore, if symptoms appear frequently, an examination is prescribed to exclude or confirm diabetes mellitus.
This disease undermines the immune system, activates yeast-like fungi and, as a result, causes inflammation. Diabetes predisposes to the development of numerous oral diseases: multiple forms of caries, periodontal diseases, etc.
There are other predisposing factors, including:
- bad habits, namely lip licking;
- anatomical features: it is known that people whose upper lip hangs over their lower lip most often experience pockets in the corners of the mouth. By the way, the lip can hang over due to bite pathologies;
- immunodeficiencies, for example, due to HIV infection, chemotherapy for the treatment of cancer pathologies, as well as other diseases;
- some genetic diseases, for example, Down syndrome, etc.;
- deficiency states. With poor nutrition, hypovitaminosis often forms due to which the body becomes more prone to infections and other diseases;
- diseases of the oral cavity, for example, multiple forms of caries, the presence of dentures/crowns, leading to chronic irritation of the mucous membrane, overbite;
- herpetic infection;
- dry red border of the lips, which can be explained by many reasons, including vitamin deficiency. Dry crusts and the formation of cracks predispose to the penetration of viruses, bacteria and fungi, which leads to inflammation.
When to see a doctor?
Most people can treat a frenulum tear at home. However, in some situations a doctor may be required.
A person should see a doctor within 24 hours if the injury appears infected but there is no fever.
You should consult a doctor immediately if the following symptoms appear:
- a deep tear that may require stitches;
- severe pain that lasts for several hours;
- difficulty swallowing liquids, including saliva;
- problems with fully opening or closing the mouth;
- increased pain or swelling after 48 hours;
- heat.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
How long does it take for the frenulum to heal after surgery?
When using a scalpel or scissors, silk sutures are placed at the end of the procedure. They are removed on days 5-7. But there are times when you need to walk around with the strings longer. It all depends on the characteristics of the body and the care of the postoperative wound. After the laser there are no stitches, but the care is the same. It consists:
- in maintaining oral hygiene,
- in optimizing the diet - food should be homogeneous and at the optimal temperature,
- in performing special gymnastics, which is prescribed by the doctor to develop the muscles involved in chewing and facial expressions.
What to do and how to remove the defect?
Medicine does not stand still. Nowadays, doctors offer several ways to correct the frenulum. The baby who tore it will undergo appropriate plastic surgery. There is plastic surgery using a scalpel, gum scissors, and a new method of removal - laser. The doctor decides which method is best to resort to. Any procedure has its own indications and contraindications. This is discussed with a specialist.
Laser frenulum removal is an innovative method. It has a lot of positive reviews not only from doctors, but also from patients.
There are methods that have proven themselves to be positive over the years:
Procedure
| Description | |
| Frenotomy | The frenulum is cut vertically and sutured horizontally. |
| Frenectomy | The method is most suitable for large strands. It is cut along its entire length, and then the interdental papilla and all excess tissue are removed. |
| Frenuloplasty I | The frenulum is cut with a scalpel or scissors. A diamond-shaped defect remains. For mobilization, the edges close to the incision of the mucous membrane are excised and, using a raspator, brought closer to the periosteum, closer to the formed vestibule. Then everything is sutured. |
| Frenuloplasty II (according to Limberg) | A vertical incision and two oblique ones are made in the center of the frenulum. Triangular flaps are formed and mobilized. Then they are fixed taking into account that the central cut is located horizontally. It is sutured with interrupted sutures. |