An acute inflammatory process, which, usually starting from the labia minora or majora, gradually spreads to the clitoris and vagina, is called vulvitis in medical practice. This pathological condition is accompanied by acute symptoms, which can manifest in the fair sex, regardless of age.
Vulvitis requires immediate consultation with a specialist, as it can lead to adhesions in the mucous membranes of the external genitalia, which subsequently causes serious problems in the intimate area, and in the case of the disease in young women, becomes a cause of infertility.
Causes of inflammation of the clitoris and labia
Most often, the pathology is of an infectious-inflammatory nature. Depending on the cause of the development of vulvitis, there are two main forms of the disease.
- Primary vulvitis. This inflammation is somewhat less common than secondary inflammation, and usually affects either patients of a younger age category or women in the postmenopausal period. The cause of the development of primary inflammation of the labia and clitoris is the following factors: failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene, too tight synthetic underwear, allergic reactions to shower gel or other hygiene products, mechanical damage to the external genitalia and hormonal imbalances. Little girls may experience similar inflammation if they have helminthiasis - infestation with worms.
- Secondary vulvitis . The most common form of inflammatory processes of the clitoris and labia resulting from infectious infection. Nonspecific pathogens of vulvitis include all representatives of opportunistic flora, which are normally natural inhabitants of female microflora - Escherichia coli, staphylococci, streptococci, yeasts, etc. Specific infections include sexually transmitted infections. Secondary vulvitis occurs more often in young patients of childbearing age, as they are sexually active.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Scanty, white, odorless vaginal discharge is considered physiological and does not require drug therapy. Women need to carefully monitor their hygiene, avoid hypothermia and wearing tight synthetic underwear. If there is heavy foul-smelling white discharge, the patient should contact a gynecologist as soon as possible to find the cause of the symptom and select the optimal treatment. Before the diagnosis is verified, the use of any medications is undesirable.
Conservative therapy
Effective treatment of diseases accompanied by vaginal discharge includes medications and physical therapy. To cleanse the genitals and relieve inflammation, baths with decoctions of oak bark and chamomile are prescribed. Antihistamines are used to relieve itching and swelling. Etiotropic and pathogenetic therapy is carried out using such groups of drugs as:
- Antifungal agents
. Medicines in the form of vaginal suppositories can quickly and effectively destroy the causative agents of mycotic infections. For extensive candidal lesions, therapy is supplemented with systemic drugs. - Antiseptics
. Suppositories with chlorhexidine and drugs of similar action help cleanse the vagina of pathogenic microorganisms. Douching with antiseptic solutions and herbal decoctions is prescribed. - Lactobacilli
. In order to influence the pathogenetic mechanisms of the appearance of discharge, special vaginal suppositories with beneficial bacteria are included in the treatment regimen. The suppositories are designed to restore microflora. - Anti-tuberculosis drugs
. In case of damage to the genital tract caused by Koch's bacillus, specific etiotropic treatment is necessary. Antibacterial agents from several pharmaceutical groups are commonly used.
In most cases, careful adherence to the recommendations of the attending physician allows you to quickly eliminate white vaginal discharge; treatment of genital tuberculosis takes longer. In the future, to prevent the resumption of pathological secretion, it is important to take medications that disrupt the composition of the vaginal flora with caution. You should take care of maintaining your immune system - get enough rest, eat well, and avoid stressful situations.
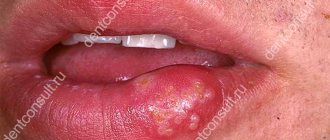
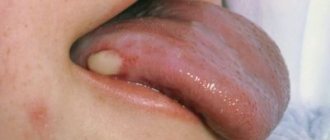
Symptoms of inflammation of the clitoris and labia
The symptoms of the pathological process are vivid, so it is impossible not to notice it, and includes the following signs:
- itching, burning and soreness of the affected area;
- tissue swelling;
- hyperemia (change in color) of the skin;
- development of small ulcerative lesions;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse.
All of the above symptoms usually intensify during urination and during intensive walking. Lack of rational and timely treatment can lead to the spread of an infectious and inflammatory process to the tissue of the inner thighs and vagina.
Prevention
In order for life to be fulfilling, without various discomforts in the intimate area, a woman needs to adhere to simple rules:
- wear high-quality underwear made from natural materials;
- outerwear should not be too tight;
- avoid casual unprotected sex;
- strict adherence to personal hygiene, use intimate gels (have high acidity);
- Lead a healthy lifestyle: eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, dairy products, reduce your consumption of sweets;
- try to avoid stressful situations;
- every 6 months a preventive examination by a gynecologist is required;
- Do not constantly use panty liners, they prevent the skin from breathing.
Remember that only a specialist in his field can provide quality assistance. For any discomfort in the intimate area, consult a gynecologist.
You can ask your question to our author:
Diagnosis and treatment of inflammation of the external genitalia
The diagnosis can only be made by a gynecologist. At the same time, no special diagnostics are needed at the first stage. The doctor will immediately notice inflammation during a routine gynecological examination. Next, the doctor determines the cause of the inflammation, after which a treatment regimen is selected.
Depending on the cause of the development of the pathology - an allergic factor, injury, incorrectly selected underwear - it is enough to simply limit the direct contact of the provoking agent with the organs and apply symptomatic therapy (local treatment that relieves unpleasant symptoms). You can easily identify this cause by donating blood for allergies. The analysis will show the cause due to the presence in the blood of special antibodies that are formed only during allergic reactions.
When diagnosing the infectious nature of the disease, microbiological culture is carried out on nutrient media in order to identify the causative agent and the correct selection of antibiotic therapy. To do this, the gynecologist takes swabs from the genital tract and sends them to the laboratory.
There, they first determine the type of infection, and then test different drugs on the samples. Since almost all pathogens of sexual diseases easily adapt to medications, choosing pills that will help you completely recover is not easy. Sometimes specialists go through up to a dozen different medications.
Unfortunately, inflammation is rarely caused by a single pathogen; more often, the cause is a whole bunch of infections, starting with thrush and ending with gonorrhea. In such cases, it will not be enough to simply take smears - the examination will continue further. You will have to donate blood for syphilis, hepatitis and undergo a pelvic ultrasound, as the process quickly spreads through the genital tract, affecting internal organs.
Diagnostics
The presence of a woman with copious white secretions coming from the vagina, especially with a noticeable sour odor, is an indication for visiting an obstetrician-gynecologist. A diagnostic search involves a comprehensive physical and instrumental examination of the genital tract to determine the cause that provoked the white discharge, as well as clarifying laboratory methods. The most informative ones are:
- Gynecological examination.
The technique is aimed at studying the condition of the mucous membrane of the reproductive organs; during the examination, areas of hyperemia or destruction of the epithelium, a dense cheesy coating surrounded by an inflammatory border are determined. The speculum examination is necessarily complemented by a digital vaginal examination. - Endoscopic methods
. Detailed visualization of the epithelium of the cervical mucosa during colposcopy makes it possible to detect erosions and other suspicious changes. To clarify the cause of the discharge, it is necessary to conduct a Schiller test and a vinegar test. If there is possible damage to the uterus, hysteroscopy is required. - Sonography
. Ultrasound of the pelvic organs is a standard non-invasive method that effectively detects signs of inflammation of the uterus and appendages, and large tumors. In doubtful cases, diagnostic laparoscopy may be prescribed. - Lab tests
. As a screening, an analysis of vaginal microflora and bacteriological culture of discharge is recommended. If there is a cheesy discharge with a distinct acidic odor, the smear is examined under a microscope to detect candida. If there is a probable tuberculosis infection, specific tests for mycobacteria are done.
A comprehensive gynecological examination includes determining the level of estrogen and progesterone in the blood on different days of the menstrual cycle. If there are difficulties in diagnosis, X-ray visualization of the internal organs of the reproductive system with contrast is performed - hysterosalpingography. According to indications, consultations with other specialized specialists are prescribed.
When can white discharge be a symptom of pathology?
The main symptom of the pathological process is a change in the normal color of the discharge. They may take on a green tint, become gray, pink, or even bloody. At the same time, an unusual pungent odor is felt. Such symptoms indicate inflammation or other pathological processes in the woman’s reproductive system. In addition, the following can provoke such a reaction in the body:
- microtrauma and perineal rupture;
- douching with disinfectant solutions;
- prolapse of the vaginal walls.
Often atypical discharge is accompanied by unbearable itching. This is a clear sign of illness that should force a woman to see a doctor. Often itching and burning of the genitals accompanies thrush, in which the leucorrhoea acquires a cheesy consistency and a creamy hue, with a specific smell of yeast.
During trichomoniasis (an infectious disease of the genitourinary system), the mucus becomes foamy, gray or yellow-green in color. There is also discomfort caused by severe itching in the genitals.
White plaque on the penis: possible diseases
White plaque on the penis accompanies balanitis, provoked by an exacerbation of psoriasis. Skin pathology has no clear cause and is considered irreversible. When relapsed, psoriatic plaques can affect the genitals, causing inflammation.
White plaque on the penis and itching of the genitals are not uncommon with diabetes. The disease is characterized by metabolic disorders, failure of the production of the hormone insulin or insulin resistance. A diabetic's urine contains glucose, which irritates the head of the penis when urinating. As a result, balanoposthitis develops.
Curdled discharge on the penis occurs due to candidiasis (thrush) of non-infectious origin - increased activity of fungi of the genus Candida. Disturbance of microflora balance occurs against the background of:
- weakened immune status;
- prolonged psycho-emotional overload;
- incorrect antibiotic therapy;
- intoxication (including alcohol);
- systematic contact of the genitals with synthetic fabrics;
- unbalanced diet;
- failure of metabolic processes.
Candidiasis is transmitted sexually if a woman has progressive thrush.
A separate category consists of sexually transmitted diseases. Infection occurs through unprotected intimate contact with an infected partner. Redness of the penis and a white coating are among the symptoms of most sexually transmitted infections.
STDs and pathogens
| bacteria | |
| syphilis | treponema pallidum |
| gardnerellosis (in men) | gardnerella |
| gonorrhea | gonococci |
| ureplasmosis | ureplasma |
| viruses | |
| papillomatosis | human papillomavirus |
| cytomegalovirus infection (CMVI) | cytomegalovirus |
| genital herpes | herpes virus type 2 |
| prokaryotes | |
| mycoplasmosis | mycoplasma |
| protozoan parasites | |
| chlamydia | chlamydia |
| trichomoniasis | trichomonas |
What is leucorrhoea?
The content of the article
Leucorrhoea is a vaginal discharge similar in consistency to egg white, which a woman usually notices on her underwear. Regular mucous discharge, which changes its consistency during the menstrual cycle, is not in itself considered a dangerous symptom. It is bad if the leucorrhoea is yellow, gray or red in color, has an unpleasant odor, or is released in large quantities. These are symptoms that indicate serious changes in the body that cannot be ignored.