The prevalence of food allergies in infants, according to WHO, is about 10%. This is a fairly large percentage and recently there has been a tendency towards its growth. It’s not uncommon to encounter a mother in the pediatrician’s office complaining of food allergy symptoms in her baby. To effectively treat food allergies in infants, the doctor must try not only to prescribe medications, but also to explain the rules for caring for the baby and explain the intricacies of diet therapy.
In the development of allergies, hereditary predisposition is of great importance. Therefore, if mom or dad have allergic reactions, then the baby’s risk of developing food intolerance becomes higher.
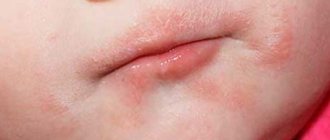
Causes of rashes around the mouth in children
A rash around the mouth in a child of different ages occurs for several reasons:
- excessive salivation;
- violation of hygiene;
- infectious diseases;
- dermatitis;
- helminthic infestation;
- influence of external factors.
A rash around a child’s mouth can be caused by many factors that are important to identify for proper treatment.
Many of these causes are associated with vitamin deficiency and the use of hormonal drugs to treat certain diseases. The impetus for the spread of the rash can be a disruption of the digestive tract. This is both an imperfection of the enzymatic system and functional disorders.
Children of different ages go through several growth spurts. These are the stages of maturation of internal and endocrine organs. Therefore, a rash may appear for some period of time and go away on its own.
Environmental factors
Rash and irritation around a child's mouth often occurs if the skin is exposed to:
- wind;
- ultraviolet radiation;
- humid hot climate.
A baby's skin is very delicate, so it needs to be protected from open sunlight. The result of insolation is the appearance of red spots and rashes. If a child has increased salivation and is outdoors, then when there are gusts of wind, the skin may become chapped, reddened, and covered with dermatological elements.
The increase in symptoms occurs gradually: from the first hours, dry skin appears, then it turns red, and blisters with watery contents appear. When the climate changes or vacations in hot countries, the elements appear due to the onset of excessive work of the sebaceous glands.
Consequences of acne
Acne can cause more than just rashes. Some people believe that acne is a skin condition that eventually outgrows, but it can have a profound and lasting impact on one's life. Many people experience one or more of the following after acne appears.
Acne scars: When the breakout goes away, it leaves behind a permanent scar. Some scars cause indentations in the skin. The rest are gradually disappearing. It's impossible to predict who will develop scars after their acne goes away, but the following factors increase your risk:
- acne has been present for a long time because the teenager does not treat it or the treatment does not work;
- One or more close blood relatives have had acne in the family.
Dark spots on the skin: As acne breakouts fade, some people see the area where acne once was. This completely flat spot can be pink, red, purple, black or brown, and is often mistaken for a permanent acne scar. Source: Modern Treatments and Rehabilitation of Acne Vulgaris. Barinova A.N. Russian family doctor, 2022. p. 5-18.
Neonatal acne in newborns
Newborns include children up to 28 days of life. Some mothers notice irritation on the baby's skin during this period, which makes them worry. This condition is typical for 20-30% of children and refers to physiological phenomena.
A rash around a child’s mouth is a consequence of hormonal changes in the body, which begins to live independently.
The second reason for the phenomenon is the proliferation of yeast-like fungi on the surface of the body, which need sebum for nutrition. Externally, it is not difficult to determine that this is acne of the perinatal period. The elements are pointed, with a white shaft in the center. The contents of the vesicle are viscous, which distinguishes clear discharge from herpes infection or dermatitis.
Unlike other causes of its appearance, newborn acne migrates over the face and neck and is not typical for other parts of the body, as with urticaria and miliaria. In addition, there are no signs of intoxication, which would indicate an infectious process.
Types of acne, formation mechanism and what they look like
Teenage acne on the face of adolescents can be of several types (or a combination of them). Source: Pathogenetic rationale for local acne therapy in adolescence. Mazitova L.P., Aslamazyan L.K., Kvachakhiya L.L., Namazova L.S. Pediatric pharmacology, 2008. pp. 94-97):
- whiteheads;
- black dots;
- acne;
- nodules, cysts, or both (deep and painful).
- Whiteheads . Removing whiteheads can lead to more whiteheads and acne scars, which is why dermatologists recommend treating whiteheads with an acne treatment rather than picking at them. Whiteheads form when excess oil and dead skin cells clog the pores. This causes white or flesh-colored pimples to appear. Medical name: closed comedon, which means “closed pore.”
- Black dots . Dermatologists recommend treating this type of acne with a retinoid, since squeezing the blackheads can cause infection or permanent scarring. This type of acne also develops when excess sebum and dead skin cells accumulate inside the pore. As the secretion accumulates, it expands the pores and you see blackheads. Many people mistakenly believe that a black spot is dirt. What you are actually seeing is a chemical reaction. When deposits inside the pore react with oxygen in the air, a black color appears. Medical name: open comedo, which means “open pore.”
- Sometimes excess oil, dead skin cells and bacteria get trapped in the pores. Bacteria, which are usually found on our skin, can multiply quickly in excess oil. As the pores become filled with bacteria, inflammation (swelling) develops and a pimple appears. Medical name: If a pimple contains pus, it is called a pustule . A pimple without pus is called a papule .
- Nodule or cyst . When the pores become filled with excess oil, dead skin cells and bacteria, causing inflammation (swelling) that penetrates deep into the skin, a lump or cyst forms. Because these rashes penetrate deep into the skin, they can be painful. The main difference between a nodule and a cyst is that the cyst contains pus. Because nodules do not contain pus, they feel firmer to the touch than cysts.
Irritation from drooling in infants
Starting at approximately 4 months, the baby begins a period of hypersalivation. Parents notice that the child has a lot of saliva, which hangs like ropes from his mouth. This is due to the start of the salivary glands, although it often coincides with the period of teething.
Physiologists believe that this is a protective mechanism that allows you to get rid of microorganisms that get into your mouth with your hands. Due to the constant damp environment, redness and irritation appear on the chin. Mechanical removal of viscous secretion does not produce results.
Hypersalivation can be caused by pathological conditions:
- oral candidiasis;
- helminthic infestation;
- otitis;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- intoxication as a result of exposure to heavy metal salts.
If a large amount of saliva appears, pathology must be excluded. You need to blot the skin with a disposable or reusable clean scarf.
Atopic dermatitis or infantile eczema
Atopic dermatitis is a reaction to hazardous foods. Redness can occur on the body in the chest area, arms and neck. If the allergen is not excluded, the elements open up, begin to get wet, and the skin becomes very itchy.
Five foods that cause atopic dermatitis
Genes responsible for predisposition to the development of the disease have been identified. But it can be realized only with an initially low state of immunity. Often, manifestations of pathology begin under the influence of a stress factor. If there are inflammatory skin diseases, traumatic injuries, then this is the entrance gate for infection and allergens.
The cause of the development of dermatitis can be food, respiratory antigens, or the body’s reaction to long-term use of antibiotics.
Tips for proper treatment of atopic dermatitis:
Treatment methods for molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum should be treated by a doctor. You should not try to remove papules yourself - this can lead to bacterial infection.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum depends on a number of factors, primarily on the stage of development of the disease, the severity of symptoms and the state of the patient’s immunity. The following methods can be used:
Instrumental removal
Papules can be removed instrumentally, followed by treating the wound with antibacterial agents.
Credestruction
Cryodestruction is the removal of papules using exposure to low temperatures. Papules are treated with liquid nitrogen. Tissues treated in this way freeze and die.
Radio wave removal
Molluscum contagiosum papules can be removed using the radio wave method (using the Surgitron apparatus) and using a laser.
Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is the effect of high-frequency current on papules. It is popularly described as “cauterization with electricity.” At the moment of discharge, a local strong thermal effect occurs, the tissues coagulate, which virtually eliminates the risk of infection at the treatment site.
Conservative treatment
The course of treatment for molluscum contagiosum may include conservative treatment with ointments and creams, as well as taking antiviral drugs (if the affected area is large).
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Worms
If a child or parents do not follow hygiene rules and allow contact with street animals, then there is a high probability of worms appearing. This phenomenon is typical not only for children from the category of dysfunctional families, due to their activity and great desire to learn about the world around them. This period usually occurs after 1 year.
You can suspect that the rash is associated specifically with worms by the long-lasting rash, which does not decrease even under the influence of medicinal drugs. After therapy, the phenomena disappear on their own, without additional help. As worms multiply, they cause intoxication. It manifests itself as local allergic reactions.
Children are most often characterized by the appearance of 3 types of helminths:
- pinworms;
- roundworm;
- whipworms.
All these parasites belong to the category of nematodes. With helminthiasis, the rash most often has the appearance of acne.
How long do food allergies last in infants?
Children with food allergies have an increased risk of other allergic reactions or illnesses in the future. There is also a chance that intolerance to the product will remain with the baby for life. However, up to 50% of allergic reactions in babies go away by the age of one year. And up to 90% by 5 years. Most of the patients I have worked with at 3 years old go to kindergarten without any manifestations of the disease.
It is possible to protect your child from food allergies by paying close attention to his diet and the mother’s diet during breastfeeding. And if allergies cannot be avoided, contact a specialist and be healthy.
Allergy
Inflammation of the skin around the mouth often appears as a result of allergies. You can suspect this cause if the child has moved from infancy to the junior preschool group, teeth have already erupted, and the rashes are periodic. This means that the body reacts to certain foods , the rest of the time the immune system functions quietly.
Allergens are divided into several categories, depending on the route of entry. Often with this form of the disorder other symptoms appear: lacrimation, runny nose, swelling of the mucous membranes. The use of anti-cold medications has no effect.
Dermatitis in a child and psychosomatics
Skin health directly depends on a person’s mental well-being. Stress changes hormonal levels and metabolism, causing disruptions in the functioning of the immune system. Therefore, a calm emotional state will prevent exacerbation of the disease and delay the first appearance of symptoms.
When faced with contact dermatitis, analyze the causes and identify the allergen that caused it.
It's not always easy. To be sure of the correct diagnosis, conduct the necessary tests and receive treatment, come for a consultation at our center. In addition to treatment, you will learn how to properly prevent this disease. December 3, 2020
Author of the article: dermatologist Mak Vladimir Fedorovich
Perioral dermatitis
Perioral dermatitis occurs mainly in young people, under 20 years of age. People who use hormonal-based cosmetics are at risk. In children, the disorder appears in no more than 5% of all cases, followed by peeling and the appearance of small dotted elements with a white dot in the center. Localization of manifestations is the chin, nasolabial triangle.
As the elements spread, they merge with each other and infection occurs. The rash does not cause significant discomfort or itching. If treatment is not started at an early stage, the skin becomes rough and may change color to brown. Subsequently, the restoration of the normal pale pink color of the cover does not occur.
This type of irritation occurs for several reasons:
- decreased immunity;
- the use of hormonal agents to combat dermatitis;
- allergy;
- hormonal changes;
- skin damage from bacteria;
- vitamin deficiency;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- use of fluoride-containing paste;
- disruption of the nervous system;
- prolonged exposure to the sun.
The border between diseased and healthy skin is defined as a thin white film.
Treatment of facial acne in teenagers
The appropriate acne treatment plan depends on many factors, including:
- type of acne;
- where acne appears on the skin;
- what treatments have already been tried;
- when the rash started;
- age;
- whether acne left dark spots or scars Source: Modern methods of treating acne in children. Nosacheva O.A., Torshkhoeva R.M., Namazova-Baranova L.S. Pediatric pharmacology, 2013. p. 23-30.
Your treatment plan may vary. But there are a number of drugs that are included in clinical guidelines for the treatment of acne. Effective treatment for facial acne in a teen may include retinoid medications, benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid, or salicylic acid. An antibiotic may be prescribed and applied to the skin.
Nodules and cysts are more difficult to treat. Treatment may consist of prescription medications applied to the skin, antibiotics, and isotretinoin (a medication approved for the treatment of severe acne).
Sometimes additional laser or light therapy is needed: Research shows that laser and light devices can help clear up acne. This type of treatment works best in combination with other acne treatments.
Healthy Diet: Some studies show that eating a healthy diet can also help give you clearer skin.
Skin care is so important that without it you won't get the results you want. Even if you use an acne treatment correctly, if teens are too rough on their skin, new breakouts may appearSource: Combination Acne Therapy. Mamarasulov D.I., Yuldashev M.A., Moon A.V., Ismoilov B.B. Medicine: theory and practice, 2019. p. 342-343.
Herpes
Decreased immunity can be caused by viral and bacterial infections. Often a sign of unstable functioning of the protective system is a herpetic rash. These are small elements with watery contents. The appearance of herpetic elements in an infant is a very unfavorable sign.
As a rule, infection occurs through direct contact with close relatives during an exacerbation period.
Since immunity is just being formed, innate immunity and protective factors contained in breast milk protect for up to 6 months, herpetic eruptions may indicate congenital pathologies with an immunosuppressive effect.
An exacerbation of the infection is typical after the age of 3 years , when the child begins to visit kindergartens, come into contact with various bacteria and viruses, and enters the social sphere.
Causes of food allergies in newborns
Food allergies in babies who have just been born are very rare. The baby receives only mother's milk. This is food that nature created for your baby and nothing can be better than it. Therefore, the peak age of food allergies in breastfed infants can be considered around 4–5 months, when the baby begins to receive complementary foods - products added to breast milk: vegetables, fruits, cereals, meat, dairy products and others. The situation is somewhat different with bottle-fed babies. The formula itself can cause food intolerances. Therefore, when choosing a mixture, it is better to consult a specialist.
Other causes of rash around a child's mouth
If there are no signs of allergies, dermatitis or enterovirus infection, then the appearance of irritation may be associated with individual characteristics of digestion. In this case, the child has unstable stools, a tendency to constipation, and particles of undigested food in the stool. This may occur due to inappropriate nutrition for the child's age.
The most common cause of the disorder is infection. The aggressive factor is staphylococcus, an element of normal microflora. With hypothermia and decreased immunity, it begins to multiply on the skin, causing a pustular rash on the face and other parts of the body.
Fungal flora also reacts to decreased immunity. If the mother had thrush during pregnancy, which was not completely cured at the time of birth, then candida remains on the surface of the body and can appear at any time. A sign of a fungal infection is the presence of white or yellowish patches that peel off when rubbed.
If there is a strong wind outside and the face is not protected, then foci of peeling appear on the chin and in the perioral area. This is caused by chapping of the surface of the skin.
Violation of personal hygiene rules is an additional factor in changes in the condition of the protective cover. If you touch your mouth with unwashed hands, bacteria begin to multiply on the mucous membrane.
Other reasons may be:
- allergy to the latex from which the pacifier is made;
- consequence of vaccination;
- insect bite
The main sign indicating the category of rash is the nature of the rash and the presence of auxiliary symptoms.
What is the most common allergen in infants?
1. The first place is occupied by intolerance to cow's milk protein. It should be noted that most modern formulas for feeding infants are based on cow's milk proteins. This is the reason why the baby is allergic to the formula. In addition, a breastfed baby can also have a reaction to cow's milk protein if the mother has an excess of dairy products in her diet. We are not talking about a specific component of milk or formula. Cow's milk contains many different proteins: albumins, globulins, casein. Some of them cause an allergic reaction more often, others less often. Casein makes up about 80% of all milk proteins. Its composition in cow's milk is identical to that of goat's. This explains the cross-reaction in babies to cow's and goat's milk. Therefore, if you are intolerant to cow's milk, it is not recommended to replace it with goat's milk, or mixtures based on goat's milk, in the child's diet. Some proteins are destroyed by heat treatment. This is due to the lower reactogenicity (ability to cause reactions) of boiled milk. There is a protein similar in composition to the protein of beef or veal meat. If the baby is intolerant to this type of protein, there will be a cross-reaction to milk and meat products.
2. The next most common cause of allergies in an infant is a chicken egg. The egg also contains a protein called ovalbumin that is an allergen. Therefore, it is recommended to start introducing eggs into the diet with the yolk and in small portions. Watch your baby's reaction to this product carefully. When feeding eggs and protein for the first time, you should also carefully monitor the reaction. Don't forget that eggs are found in some pasta and baked goods.
3. Gluten is a common cause of food intolerance. This is a protein found in some grains. In order to prevent an undesirable reaction, it is recommended to start complementary feeding with gluten-free cereals. These include: buckwheat, corn, rice. Cereals rich in gluten, such as semolina, millet, and oatmeal, should be introduced closer to the age of one. In the first year, a reaction to gluten is less common than intolerance to cow's milk protein or egg white.
4. In addition, brightly colored fruits and vegetables can cause food reactions. Such as carrots, beets, pumpkin, peach. It is better to postpone their introduction into the diet and give preference to green and white vegetables - such as zucchini, cauliflower and broccoli. It’s best to start introducing your baby to fruits with green apples and pears. It is also better not to rush with exotic fruits such as mango or kiwi.
Do not forget that an allergic reaction is possible to any product. When giving a treat to a baby for the first time, a mother should remember the risk of intolerance. Try not to rush, especially with the introduction of the very first complementary foods. Give unfamiliar foods to the child in small portions in the morning so that it is possible to control the reaction to them throughout the day.
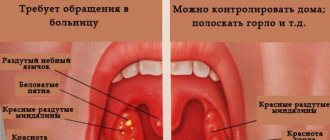
What does the color and type of rash indicate?
All types of rash are different. Therefore, the external manifestations of the elements can tell the doctor a lot. A pinpoint rash often indicates an infectious process and intoxication. If it is filled with fluid, it is caused by the herpes virus.
When the rash is detected only in one place, the cause is most often local in nature . If elements appear on the back, arms, neck, then the matter is in internal processes.
Based on the appearance of the manifestations, one can suspect the cause of the phenomenon:
| Disease | Appearance of the rash |
| Perinatal acne | Small elements with a white rod inside. Contents viscous |
| Atopic dermatitis | The elements merge with each other, the surface of the skin is red and peeling |
| Herpes | Bubbles of different sizes, filled with clear liquid |
| Allergy | Elements rise above the surface of the skin, the skin around is red, there is no content inside |
| Weathering | Characterized by redness of the skin, areas of peeling and itching |
| Worm infestation | The rash is pinpoint, elements without content, appear in the area of the nasolabial triangle, neck |
| Perioral dermatitis | At first, the elements are located separately, then merge with each other, pus appears, wet areas appear, the surface peels off |
When redness and peeling are observed, this is a sign of the allergic nature of the disorder. If the affected area is large, the specialist suspects toxic erythema. The purulent contents of the vesicle indicate infection, a bacterial complication.
Regardless of the type of rash, they occur on initially intact skin. The intensity and location of the process determine the type of elements. Each characterizes a disruption in the functioning of the entire organism.
Acne classification
When classified by age group, there are mainly two types of acne:
- In newborns and young children. The belief that acne only affects teenagers and adults is wrong. Infants, children of preschool and early school age, although not often, also suffer from acne. Newborns face this problem because their mothers transfer hormones to them shortly before birth. Acne also occurs when the stress of childbirth causes the baby's body to release these hormones.
- Teenagers and adults. Acne affects 80% of people aged 11 to 30 years. Usually occur during pubertal changes in hormonal levels. Increased production of sex hormones during puberty makes the sebaceous glands more active.
Table - Classification of childhood acne by age
| Form | Child's age |
| Neonatal | from birth to 6 weeks |
| Infantile (early childhood) | from 6 weeks to 12 months |
| Middle childhood | from one to 7 years |
| Pre-adolescent | from 7 to 12 years (for girls before menarche) |
Neonatal acne develops during a period of hormonal changes. In all forms of acne, additional provoking exogenous factors play a significant role.
Diagnostic methods
A rash around a child’s mouth is classified as belonging to a specific type using the same type of research according to the algorithm:
- general blood analysis;
- immunological study for antibodies to the suspected infection;
- general urine analysis;
- prick allergy test;
- stool analysis for worm eggs.
Since a number of conditions are caused by contact with an allergen, conducting a test reduces the time to search for the type of pathogen. An important type of diagnosis is to examine the nature and color of the rash. He tells you what microorganisms it is caused by.
Diagnostics
If your teen has acne, a dermatologist can diagnose acne by looking at the breakouts. During your appointment, your dermatologist will also note what types of acne they are and where the breakouts appear on the skin. This will help your dermatologist create an effective treatment plan. Sometimes what looks like pimples is another problem. For example, some people mistake hidradenitis suppurativa, also called acneinversa, for everyday acne. Treatment for this condition is different from that for acne. Another disease that can be mistaken for acne is perioral dermatitis. This often causes rashes that look like pimples around the mouth. Whether your teen has stubborn acne or another condition, a dermatologist can accurately diagnose acne vulgaris and create a treatment plan tailored to your teen's needs.
Treatment with drugs depends on the cause of the rash
A rash around a child’s mouth is treated taking into account the cause that caused it. There is no universal remedy that would help in all cases.
Some measures help prevent the development of the disorder:
- compliance with hygiene rules;
- early contact with a doctor;
- for dry skin, you need to use nourishing creams;
- before going outside during the cold period, you need to apply a protective cream;
- use only children's clothing and body care products;
- reduce the time a child spends outdoors in the open sun in summer.
Therapy for the disorder must be comprehensive. These are local and systemic remedies. At all stages of treatment, it is necessary to monitor whether the patient’s condition improves. Once the type of pathogen is determined, etiological treatment is prescribed. It involves antibacterial or antiviral treatment that is active against this pathogen.
In most cases, physiotherapy methods are included in therapy. They help improve local blood flow and have an anti-inflammatory effect. The possibility of using alternative medicine should be checked with a doctor.
Prevention measures
To ensure that your child is not bothered by any pimples around the mouth, it is necessary to follow some preventive recommendations. In early childhood, it is worth monitoring the baby, not allowing him to put foreign objects in his mouth. Equally important is skin care, which uses high-quality baby products. To prevent a rash from occurring during teething, it is recommended to always keep a napkin with you and wipe the skin. Careful monitoring of your baby's oral hygiene helps prevent acne. It is important to feed your child proper and healthy food so that the immune system does not weaken. During cold weather, a special protective cream is applied to the epidermis.
Folk remedies for treating rashes around a child’s mouth
Traditional medicine has proven itself to be a simple, inexpensive and safe way to cope with various types of problems. It is not always acceptable for young children, due to the high likelihood of allergies to herbs. When a rash appears around the mouth, products with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects help.
For example, the following can cope with perioral dermatitis:
- a decoction of string, St. John's wort, chamomile or sage in the form of lotions on the affected areas every 4-5 hours.
- lubricating the elements with propolis boiled in a water bath;
- using a mixture of honey, flax and onion juice, taken in equal volumes, boiled for 10 minutes. and cooled to room temperature;
- using lotions with soda solution (1 tsp per 1 cup of warm water);
- lotions with pulp or juice of fresh pumpkin;
- application of oak bark decoction topically.
Before using any product for the first time, you need to do a sensitivity test. To do this, apply a decoction to an inconspicuous area of skin and wait for 2 hours for the appearance of inflammation.
The following remedies can also help with atopic dermatitis:
- A mixture of rice starch, glycerin and milk, taken in equal proportions and mixed until smooth. Use as an ointment at night and store in the refrigerator.
- Raw, finely grated potatoes, used as a lotion.
- Mix 2 parts of crushed Kalanchoe leaves with 1 honey and stir. The paste is applied 2-3 times a day to the affected areas of the body. This method is effective, but is used with caution due to the high allergenic properties of honey.
- Celery root juice with salt and a few drops of vinegar is applied as a lotion to the skin 3-4 times a day. After 3 years, it is allowed to take 20 ml orally 2 times daily.
- Cucumber juice is applied every 2-3 hours, which helps moisturize the area and relieve inflammation.
- If 1 tsp. Boil chamomile in a water bath with the addition of 100 g of vegetable oil, then the resulting composition can be lubricated on the rash areas up to 3 times a day.
Tar, celandine, mash, potatoes are folk remedies that are used in the fight against atopic dermatitis
If your child has chapped lips and the skin around them, you can try to relieve the pain by using vitamin masks. They are used for shallow damage to the epidermis.
The available means are:
- chamomile ointment prepared at home;
- a mixture of liquid honey, vitamin A and E;
- mask made from sour cream or cream with a high degree of fat;
- Vaseline oil mixed with sea buckthorn and apricot oil.
A rash around the mouth, in the area of the nasolabial triangle in a child often occurs as a result of a combination of several factors. Monitoring the child helps to quickly determine the cause of the disorder, which helps avoid unpleasant consequences and complications.
Author: V.L. Dyleiko
Design: Anna Fleyman
The most common dermatitis in children: features of diagnosis and therapy
According to foreign researchers, approximately 25% of all visits to doctors are complaints about skin pathology [1]. Among them, the most common dermatitis in children is seborrheic, contact (diaper) and atopic. In recent years, scientists have noted an increase in the incidence of these skin diseases in general practice. Thus, in the Netherlands, during the period 1987–2001, doctors most often diagnosed fungal (dermatophytoses), atopic, bacterial (impetigo) and contact dermatitis in children aged 0–17 years, which accounted for 57% of all cases of skin diseases [2].
Seborrheic dermatitis. The fungus Malassezia furfur is considered a possible etiological factor for seborrheic dermatitis. These microorganisms usually colonize healthy skin, but they also play an important role in the etiology and/or exacerbation of folliculitis, seborrheic and atopic dermatitis.
There are two clinical forms of the disease: seborrheic dermatitis of infants and seborrheic dermatitis of adults.
Seborrheic dermatitis affects 10% of boys and 9.5% of girls; more often - children aged the first 3 months of life, then the incidence decreases slightly (by 2 years it usually goes away or persists until 4 years of age). In adults, seborrheic dermatitis is diagnosed at any age: the rash is represented by red itchy papules covered with scales, on the scalp it resembles dandruff.
In infants suffering from seborrheic dermatitis, already at the 2-3rd week of life, accumulations of fatty, sebaceous scales (gneiss) appear on the skin of the scalp (to a lesser extent on the forehead, cheeks, in the folds behind the ears), and in cases of damage to large folds of the skin of the body and extremities - a maculopapular rash, also covered with scales on the periphery. The rash can also be localized in the area of the external auditory canal and sternum, on the neck, in the axillary and groin areas. Itching is moderate or absent [3]. When the rash is localized in the diaper area, a bacterial infection may occur, which sometimes makes treatment very difficult. If left untreated, the rash may spread to other areas of the body, becoming generalized. Against the background of seborrheic dermatitis or after its disappearance, some children develop another dermatitis - atopic, in the etiopathogenesis of which (especially the severe form of the disease) Malassezia furfur also plays a very significant role.
Important distinguishing signs of seborrheic dermatitis are the absence of itching of the skin, as well as the predominant lesion of the scalp and diaper area in children suffering from seborrheic dermatitis. Atopic dermatitis is characterized by skin exudation, while seborrheic dermatitis is characterized by an earlier onset and the absence of a hereditary burden of atopy (Table 1).
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis is not particularly difficult. Manifestations of the disease in the scalp in newborns (milk crusts) can spontaneously go away by the 6-8th week of life (or for such children it is enough to prescribe daily washing of the hair with a special shampoo, followed by the application of mineral or olive oils). They also cleanse irritated skin with areas of hyperseborrhea, especially in problem areas. For this purpose, the use of cleansing gel “Bioderma Sensibio DS”, “Saforel” is recommended, “Topicrem” is also recommended, shower gel foam is for skin prone to mycoses, “Friderm Zinc” (for flaking of the scalp).
After preliminary cleansing, the skin is dried and a dermatological cream (for example, Bioderma Sensibio DS) is applied to problem areas (in newborns and children - scalp, forehead, buttocks; in adults - wings of the nose, eyebrows, chin).
Of the dermatological shampoos specially designed for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in children and adults, Nizoral shampoo containing 2% ketoconazole is widely used. However, the same clinical improvement in a comparative study was noted with the use of Kelual DS shampoo, which has fungicidal, fungistatic, anti-inflammatory and keratoregulating effects due to the content of the non-imidazole antifungal drug ciclopiroxolamine (D. Shuttleworth et al., 1998). Cyclopiroxolamine has a high coefficient of fungistatic action (suppression of proliferation of Malassezia fungi); in addition, it has a unique anti-inflammatory effect, comparable even to the effect of a mild corticosteroid (K. Gupta, 1998). The composition of the Kelual DS shampoo also includes another antifungal drug - zinc pyrithione 1%, which has a fungistatic and kerator-reducing effect. The combination of two antifungal active components has a synergistic effect in suppressing the proliferation of Malassezia fungi, which is reflected in the high coefficient of fungistatic action in the Kelual DS shampoo, which, as the study has shown, is superior to the inhibitory activity of ketoconazole. Additionally, the Kelual DS shampoo contains keluamide, which has a mechanical dispersive effect, ensuring rapid elimination of squams (keratolytic effect).
In case of the formation of seborrheic crusts on the head and severe peeling of the skin, you can also use the Friederm Tar shampoo, Mustela Stelaker Cream (apply it to seborrheic crusts in children, leave it overnight and then wash it off with Mustela Bebe Foam Shampoo for newborns).
Typically, medicated shampoos are used 2 times a week, the course of treatment is 6 weeks.
Other nonpharmacologic approaches (eg, limiting the use of hair sprays and gels, exposure to sunlight) may also be helpful in older children and adolescents.
For seborrheic dermatitis, topical corticosteroids should be avoided as first-line treatment [4]. Recently, a report appeared on the high therapeutic activity of the combined use of antifungal shampoo (ketoconazole) and the topical calcineurin inhibitor tacrolimus (currently in Russia this series of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is represented only by Elidel cream (pimecrolimus 1%)) [5].
In recent years, Malassezia furfur has been considered not only as a trigger factor for atopic dermatitis in children and adults, but also as one of the causes of severe recurrent course of the disease, refractory to traditional therapy. Also, these microorganisms are more often detected in this variant of atopic dermatitis, when the skin process is localized on the head, neck and chest area (in the English literature, the so-called head and neck dermatitis - “dermatitis of the neck and head”).
Atopic dermatitis. Spergel and Paller provide the following clinical criteria for atopic dermatitis [6].
Mandatory criteria:
- itching;
- eczematous changes: chronic or recurrent; the most age-specific patterns involve the face, neck, and extensor surfaces of the extremities in infants and children; Damage to the flexor surfaces, especially in older children and adults, is less pronounced in the groin and axillae.
Important features in favor of this diagnosis (not found in all patients):
- onset of the disease at an early age;
- xerosis;
- atopy (IgE reactivity).
The diagnosis of atopic dermatitis can be made after excluding diseases such as scabies, allergic contact dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis and ichthyosis.
As practice shows, atopic dermatitis is characterized by clinical polymorphism. Suffice it to say that the literature describes more than 26 separate locations of the skin process on parts of the body and nine typical signs of the disease, the main of which, in combination with dry skin, are three: itching, erythema, papules. However, the location of skin lesions often depends on age. Thus, in infancy (the onset of the disease before 2 years of age) the cheeks, face, neck, and outer surface of the limbs are affected. In the age period from 2 to 10 years, rashes are usually localized in the elbow and popliteal folds, on the back, back of the neck, and lateral surfaces of the torso. Adolescents and adults are characterized by damage to the face (mainly periorbital or atopic cheilitis), the dorsum of the hands, and in the area of the elbows and knees. Itchy papules are located against the background of lichenized and dry skin, often with pronounced peeling.
Today, external therapy is recognized as the most important, pathogenetically substantiated and absolutely necessary for every patient with atopic dermatitis, which includes proper skin care (cleansing/moisturizing/softening) followed by the application of anti-inflammatory drugs to it. According to the American prof. D. Leung, “moisturizing and softening the skin are key in the treatment of atopic dermatitis” [7]. Moreover, due to impaired barrier function and dry skin, moisturizers/emollients should be used even during periods of the disease when there are no symptoms [7, 8]. This approach is based on scientific data: in particular, in patients with atopic dermatitis, the same inflammatory cells that infiltrate the lesions are found in unaffected areas of the skin; in addition, the manifestations of skin hyperreactivity and xerosis in different areas of the skin are no different [7, 8]. Because of its hyperreactivity, atopic skin has the ability to change depending on fluctuations in air temperature, stressful situations, after eating certain foods, or for other unknown reasons. The condition of the skin also changes after applying external medications; Sometimes patients or doctors themselves can associate symptoms such as burning, increased itching, hyperemia with the external agent used, which often leads to discontinuation of the drug. In fact, the cause may be the above exogenous factors. If necessary, the doctor conducts a drug tolerance test on the patient. Rare cases of the development of allergic contact dermatitis even to the main anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of atopic dermatitis (topical corticosteroids or topical calcineurin inhibitors) have been described. Another feature of atopic skin is that its dryness, accompanied by transepidermal water loss, increases the systemic absorption of external hormonal agents and, consequently, their side effects [9].
Accordingly, effective treatment of dry and itchy skin may improve treatment outcomes for atopic dermatitis. However, it is impossible to influence such causes of dry skin as changes in the stratum corneum, disturbances in keratinization, the composition of the balance and amount of intracellular lipids, metabolism of transepidermal water, changes in skin pH, etc. simply by applying moisturizers and/or emollients to the skin. These are very complex physicochemical, biochemical and pathophysiological processes that occur differently in skin diseases. Recently, scientists have been considering dry skin in atopy from the point of view of a unified pathophysiological concept “atopy, dry skin and the environment” [10, 11]. Recognizing the importance of this approach, the dermatocosmetic lines “A-Derma”, “Dardi Lipo Line” were created, as well as a new unique emollient, which is used with great success in the treatment of atopic dermatitis abroad - “MAS063D” (Atopiclair) [12, 13]. Thus, according to Abramovits et al., in 94% of patients with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis, the need for topical corticosteroids completely disappeared within 50 days after using the non-steroidal hydrolipidic cream “MAS063D” (Atopiclair) [13].
The unique line of products “A-Derma” (“Egzomega”) uses the exceptional qualities of the oat extract of the Realba variety: amylose, amylopectin and β-glycans included in “Egzomega”, coming into contact with water, form a moisturizing and protective film on the surface of the epidermis . In addition, they promote the retention of lipids, polyphenols and proteins, forming a micelle “reservoir” that releases active substances as needed and provides prolonged action; proteins have an anti-inflammatory effect; phospholipids and glycolipids nourish and moisturize the skin; polyphenols have antiradical and anti-inflammatory effects; magnesium, iron, copper, zinc, manganese are protein cofactors. Egzomega products also contain essential omega-6 fatty acids and vitamin B3, which ensures the restoration of the structure and barrier function of the skin.
To care for the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis, other products from the medical and cosmetic series such as “Aven”, “Mustela Stelatopia”, “Uriage”, “Vichy”, etc. are also widely used.
Before using emollients/moisturizers, a patient with atopic dermatitis should comply with certain skin care conditions (cleansing with special hygiene detergents, using dechlorinated water, etc.). Moisturizers/emollients are applied after preliminary cleansing of the skin using medicated skin care products - usually the same line of medicinal cosmetics (Topicrem Bodygel, BioEcolie; Mustela Stelatopia, washing cream; Egzomega - cleansing shower oil for atopic skin, etc.).
In case of persistently recurrent course, as well as moderate and severe forms of atopic dermatitis, patients are advised to use medicinal cosmetics containing additional anti-inflammatory (for example, alphabisabolol, allantoin, dexpanthenol, etc.) or antifungal substances (for example, “Topicrem” gel - foam for body skin prone to mycoses, which contains piroctone olamine 1%).
In particular, the use of the Topicrem cosmetic line is recommended (Table 2).
The Dardia Lipo Line treatment products include natural hydrophilic substances - lactate, urea and glycerin, while cetearylethyl hexanoate and a mixture of medium chain triglycerides maintain the lipid balance of the skin. The combination of these components leads to the achievement of the best results in the maintenance therapy of allergic dermatoses, preventive skin care after the use of topical corticosteroids, chemotherapy and radiation, as well as in daily skin care. The water-fat and anhydrous forms of the products in this line are ideal for dry and very dry skin, are easily absorbed and evenly distributed over the skin (Table 3).
It has been proven that the effectiveness of moisturizers/emollients depends on the dose (they should be used regularly in sufficient quantities), skin pH, and also on patient compliance [7, 8, 12, 13]. It is especially important to use them before applying anti-inflammatory drugs to the skin (topical corticosteroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors). There are even cases in the literature of equivalent effectiveness of moisturizers and topical corticosteroids in patients with atopic dermatitis. In general, skin hydration and moisturizers significantly increase the effectiveness of complex therapy for atopic dermatitis and the quality of life of such patients. In addition, moisturizing preparations have a kind of preventive effect even before the appearance of pronounced symptoms of exacerbation of the disease and can significantly reduce the amount of drug therapy. At the same time, they do not replace topical drugs that have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Modern practice shows that the importance of using moisturizers in the treatment of atopic dermatitis is significantly underestimated throughout the world. Thus, a recent survey showed that of 77% of children suffering from atopic dermatitis to whom specialists prescribed emollient ointments, only 21% used them immediately after washing [14].
The goal of the treating physician and nurses is to instruct patients with atopic dermatitis and their caregivers to regularly cleanse and hydrate the skin, followed by the application of an anti-inflammatory drug if necessary.
Sometimes in children under one year of age, the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis presents certain difficulties, especially if the skin manifestations are localized in the diaper area. Diaper dermatitis almost always occurs in the buttocks area. The disease is associated with factors such as the immaturity of the protective mechanisms of the child’s skin, its mechanical damage (friction from diapers) and chemical irritation from urine and feces. Depending on the severity, the clinical manifestations of diaper dermatitis can vary from mild skin erythema of varying prevalence to the appearance of papules, erosions and infiltrates in the skin folds. Severe diaper dermatitis is characterized by the appearance of conflicts, then erosions and crusts on the surface of the papules.
In some children suffering from diaper dermatitis or seborrheic dermatitis, signs of atopic dermatitis can also be detected at the same time.
In the treatment of diaper dermatitis, the use of medicinal hygiene products is justified (Bepanten, Topicrem ultra-moisturizing emulsion, Mustela Stelkactive diaper cream, etc.), which are applied only after preliminary cleansing of the skin with special hygiene products. Air baths are important. The use of topical corticosteroids in the treatment of diaper dermatitis is unjustified. In addition, when prescribing a topical combination drug, the doctor must be sure of its necessity, i.e., correctly determine the indications for its use. Thus, according to American researchers, if a child has diaper dermatitis, most doctors considered it more appropriate to use a combination drug consisting of a strong class topical corticosteroid (Betamethasone valerate) and an antifungicide (clotrimazole), explaining this by the fact that the basis of diaper dermatitis is candidiasis and inflammatory mechanisms [15]. At the same time, doctors forgot that this topical corticosteroid is contraindicated for use in children under 12 years of age. Moreover, as another study showed, every second pediatrician (56%) prescribed a similar drug to children aged 0 to 4 years [16].
The International Expert Group on Atopic Dermatitis (2006) recalls that in adult patients with atopic dermatitis, a combination of atopic, contact and irritative dermatitis may be observed, and atopic dermatitis involving the hands and feet should be differentiated from psoriasis of the palms and soles and fungal skin lesions [8 ]. It is also necessary to remember about such rare pathologies in children as genodermatosis - Neferton syndrome; in adults and children - vitamin deficiency, malignant skin tumors. Thus, mycosis fungoides, by the nature of the skin lesions and the presence of intense itching, may be similar to the common form of atopic dermatitis, however, mycosis fungoides appears in adolescence and adulthood [7, 8].
For questions regarding literature, please contact the editor.
D. Sh. Macharadze , Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of RUDN University, Moscow