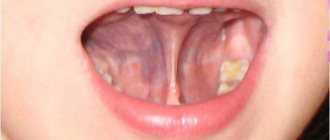
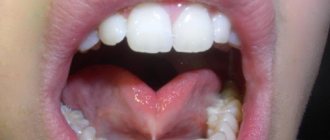
Impact of frenulum pathology
Problems with speaking
But sometimes a child has a congenital pathology - shortened frenulum .
Such a diagnosis means that the frenulum is not attached in the middle of the tongue, but much closer, at the tip. Sometimes it lasts until the very tip, and the tongue even slightly bifurcates from its pressure. A serious pathology is diagnosed after the birth of a child by a neonatologist, and minor deviations in the length of the frenulum can be detected in preschool age, when the child begins to have problems pronouncing certain sounds.
Problems with breastfeeding
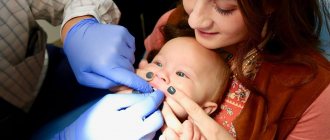
In infancy, a shortened frenulum can interfere with breastfeeding, as the baby cannot grasp the nipple comfortably, often loses it, and may even experience pain when sucking. This negatively affects the child’s weight gain and causes a lot of unpleasant moments for the whole family.
Indications and contraindications
Cutting the frenulum in children is resorted to in cases where:
- there are difficulties with breastfeeding;
- Speech defects and dental problems are observed.
Trimming the upper lip frenulum in children is recommended by dentists at the age of 6-8 years, when all four front incisors have fully erupted. But a short frenulum of the tongue can be operated on even in a newborn.
Among the contraindications:
- increased body temperature;
- decreased hemoglobin;
- purulent-inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
If you have a polyvalent allergy to anesthetic drugs, surgery is contraindicated.
Tongue frenulum surgery
At what age should a tongue tie be operated on?
In infancy, the frenulum looks like a thin membrane and has no blood vessels or nerve endings. Plastic surgery is performed with one movement of a scalpel without anesthesia and subsequent treatment. After this simple procedure, the mother just needs to give the baby the breast; mother's milk will prevent any hygienic problems in the incision area. But this procedure may negatively affect future tongue movements due to the resulting scar. Therefore, if it is possible to avoid such a procedure, it is better to postpone the resolution of the issue to a later date.
For the mother, the main thing in this situation is to establish the process of breastfeeding.
With age, the membrane becomes stronger, blood vessels appear in it, and it is no longer possible to correct this as simply as in infancy. Usually, at a later age, a shortened frenulum is discovered during an appointment with a speech therapist, pediatrician or dentist. Signs of this phenomenon may include problems with speech, since the baby cannot make sounds that require touching the tip of the tongue to the palate or teeth. He begins to burr or lisp. Parents may also notice that the child has problems sticking his tongue out of the mouth.
Doctors recommend waiting until surgery
If a slightly shortened frenulum is detected, even at an early age, doctors recommend waiting until surgery. It can lengthen on its own as it grows.
Plastic surgery – frenuloplasty
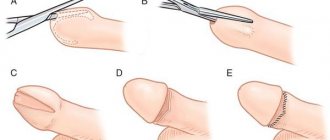
But if this did not happen before primary school, a full-fledged plastic surgery called frenuloplasty is required. It is done under general or local anesthesia, depending on the perseverance and age of the child. The operation itself is extremely simple and does not take long, so if possible it is better to limit yourself to local anesthesia. The frenulum is cut at the tongue and moved a little further, and then sutured to functional size.
Postoperative period
The postoperative period at this age, unfortunately, requires special oral care, sometimes even taking antibiotics. The stitches are removed within a week. Once the incision and suture sites have completely healed, a long period of exercise with a speech therapist is required to ensure that the child develops proper language skills.
If a child is diagnosed with a shortened frenulum of the tongue, do not rush into action.
Early excision, although seemingly simpler, may cause speech problems later. Therefore, first, find a good pediatrician and consult to choose the optimal age of the small patient. And remember, such a problem can be solved in any case, it is only important to choose the method you need.
If you have any doubts about your child’s tongue frenulum, come to the A.Dent children’s clinic, here you will receive a comprehensive consultation and, if necessary, a course of treatment will be prescribed.
Table of contents
- For what reason does a frenulum defect form?
- Symptoms of congenital frenulum pathology
- Types of frenulum pathology
- Complications with frenulum defects
- How is a frenulum defect treated?
It is due to the presence of the lingual frenulum that a person has the ability to consume food, influence breathing and even control the tongue to speak. It is worth noting that problems often arise with the lingual ligament, since its structure is of considerable importance.
- Ideally, the membrane in the oral cavity should be approximately 3 cm in an adult, and at least 8 mm in children, which will be considered normal.
- The frenulum may vary from person to person in length, density, and degree of elasticity.
- If the structure of the ligament is correct, then it will not affect the mobility of the baby’s tongue.
For what reason does a frenulum defect form?
Dentists call frenulum pathology a congenital defect, which depends on several factors.
- Genetic inheritance. According to statistics, if one parent had a similar problem, then the probability of it occurring in the child is 50%.
- Violation of fetal development during the perinatal period. In other words, a congenital defect of the frenulum appears, which leads to abnormal cords, or in other words, the formation of connective tissues well supplied with blood fluid, which prevents the child from properly controlling the tongue.
There are a number of predisposing factors that can lead to such a defect.
- The emergence of the virus in the mother’s body during pregnancy, especially before childbirth.
- Impact of bad environment.
- Pregnancy after 35 years of age.
- Presence of intrauterine infection of the fetus.
- Presence of chronic somatic diseases.
- The occurrence of traumatic injury to the abdominal cavity before pregnancy.
Symptoms of congenital frenulum pathology
In order to diagnose pathology in the development of the frenulum and give indications for correction, you will need not only an examination by a dentist, but also the presence of obvious signs of such a problem. Namely:
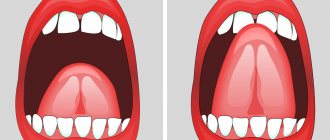
- inability to move the tongue outside of the abnormal location;
- the presence of a bifurcation of the tip of the tongue, as well as the shape of the tongue in the form of a cup or groove, due to the fact that its base is tightly pressed to the bottom of the mouth;
- inability to lift and extend the tongue forward;
- touching the lips with the tongue only with its tip;
- the presence of a thin thread between the tongue and the base of the oral cavity when examining a baby.
Types of frenulum pathology
The frenulum defect can be partial or complete. The differences lie in the symptomatic picture.
In the first case, the ligament under the tongue is partially attached to the edge of the bone bed of the dental structure, and in appearance resembles an avascular transparent thin film. In this case, incomplete mobility of the tongue is diagnosed.
In the second case, the tongue is completely immobilized, since its entire length is chained to the base of the mouth. The lips are pressed very tightly against the teeth, and when examined by a specialist, the baby can roll his tongue into a tube, but inside the mouth, without pulling it out.
Complications with frenulum defects
Important: If the pathology of the frenulum is not corrected, then serious consequences are quite possible, which are much more difficult to eliminate.
- A slowdown in the development of the lower jaw and all adjacent bones becomes noticeable.
- An abnormal bite often occurs, in other words, an uneven dentition. There are two options - either too large gaps will form between the teeth, or vice versa - they will begin to move too tightly, which will cause distortion of their location.
Infants who have this pathology often have problems with breastfeeding.
- Due to the lack of full control of the tongue, a child from birth cannot consume breast milk, since he physically cannot grasp the nipple.
- During the feeding process, milk production in the mother's breast will not be stimulated.
- Due to a violation of the sucking function, feeding can be carried out for a long time, but this does not allow obtaining the required amount of milk and, as a result, the child has to be supplemented with artificial nutrition.
- Due to all of the above points, the child begins to develop a fear of feeding and manifests itself in the form of anxiety when hunger occurs. That is why experts recommend switching children completely to artificial nutrition.
If there are problems with the frenulum, nutrition is disrupted because:
- difficulty chewing food;
- difficulty swallowing foods;
- Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity can often occur, which occurs due to increased sensitivity of the mucous membrane.
The most serious consequence is considered to be speech impairment.
- When the time comes for gradual speech training, minor defects may be observed.
- Diction and word formation may be impaired, and even a lisp may be present.
- The child is unable to pronounce the upper lingual sound correctly.
- Problems appear at the age of 2-3 years.
- Maybe personal discomfort when talking, which leads to more silence from the child rather than communication.
Important: If you find such problems, you should immediately contact a specialist to eliminate it as early as possible.
How is a frenulum defect treated?
Doctors may use conservative treatment, which requires the use of articulation exercises. In some cases, this helps avoid surgery. The technique consists of stretching and training the articulatory apparatus.
In extreme cases, surgical correction or, in other words, frenulotomy is performed. This method is used if the defect causes serious problems for the baby. If the frenulum defect is partial, then it is simply trimmed a little, and if you have to deal with complete fusion of the tongue and oral cavity, then a serious operation is needed. During the procedure, the gums and lips are separated from each other, just like the lips are separated from the tongue.
Correction of the ligament under the tongue in newborns is required when:
- identifying problems with breastfeeding, for which plastic surgery of the congenital anomaly is performed by slightly cutting the frenulum;
- the absence of blood vessels and nerve endings in the frenulum under the tongue, which requires cutting the lingual ligament, and if the ligament has partially grown in, then the procedure will not cause problems and does not take much time to carry out;
- If a defect is identified immediately after birth, the procedure is carried out through the use of special dental scissors, which are used to trim the ligament in the first minutes of life, and to stop bleeding it is enough to simply apply it to the chest;
- detecting a problem in the first year of life, for which dental scissors or a radio wave scalpel are also used, with the additional use of local anesthesia.
In general, under the age of one year, the procedure will not take more than a few minutes, and complications do not arise after it. As a rule, after cutting the frenulum immediately after birth, improvements in breastfeeding are noticeable.
Correction of the lingual ligament during the period before school is carried out in a special way and with the presence of specific indicators
- At 2-3 years, a change occurs in the structure of the frenulum, as vessels begin to form in it. The ligament thickens and becomes fleshy. That is why frenuloplasty is performed under anesthesia, in a hospital, and it is necessary to apply sutures that will dissolve on their own.
- If a shortened frenulum is detected in a preschooler due to incorrect sound pronunciation, then this is organic dilalia, and not undergoing correction will lead to inaccurate diction in the future.
Important: In any case, if defects occur with the frenulum under the tongue, you should consult a dentist and speech therapist. This will help solve the problem at an early stage and avoid the serious consequences described earlier. The treatment is carried out without difficulty, quickly and efficiently, which eliminates the occurrence of stress in the child, regardless of his age category.
There is a type of correction through bloodless plastic surgery of the lingual ligament. The method appeared relatively recently, but is already very popular. The essence of the correction is:
- the absence of a detrimental effect on the general condition of the child during frenolotomy;
- carrying out the operation using a special laser device that does not cause discomfort;
- using not anesthesia, but an anesthetic in the form of a gel;
- easier postoperative period, unlike other methods of cutting the ligament, regardless of age and complexity of the problem.
Important: remember that the sooner the procedure is performed, the greater the likelihood of avoiding speech defects and other problems that can cause a lot of harm in adult life. The presence of incorrect diction and incorrect pronunciation of sounds has a very negative impact on learning, communication and even finding a suitable job.
For school-age children who have identified a problem such as pathology of the frenulum under the tongue, radical measures must be taken.
- In advanced cases, after the age of 5 years, frenuplasty must be performed as prescribed by the dentist, or in other words, a serious surgical intervention under general anesthesia, with sutures. If there are severe restrictions in the excursion of the tongue, as well as pronounced complications, for example, advanced pathology, the orthodontist or speech therapist will refer the child to a dental surgeon. The result of the procedure is the release of the tongue, but a properly observed rehabilitation period is required to eliminate the possibility of complications. In some cases, it may be necessary to correct uneven teeth.
- Surgery may be required for an adult with severe periodontal disease and speech defects.
- It is mandatory for children to visit a speech therapist so that speech can be corrected directly, since after the intervention of a doctor, speech normalization does not occur on its own.
Important: The presence of a short frenulum in a child is a serious problem that must be dealt with immediately, not by independent actions, but with the help of qualified specialists. According to statistics, those children whose frenulum was corrected in infancy are the best at restoring speech and getting rid of speech defects. Proper classes with a speech therapist help to completely eliminate the defect, but the participation of parents in the development of the child and, especially, correctional procedures is imperative.
How to determine
How to recognize any frenulum deviations? What consequences can this pathology have for a child? - such questions are often asked to mothers at a doctor’s appointment.
Identifying a short frenulum in a baby is not difficult even for a non-specialist; it can be seen immediately.
Parents just need to lift the baby’s lip a little and they will be able to see where the frenulum is woven. Compare with the level of the incisor neck. In a normal state, the bridle should be woven slightly above this level - approximately half a centimeter. If the reading is lower, this may directly indicate a short frenulum.
But the final diagnosis, of course, must be made by a doctor. If a pathology is detected, you should contact a medical facility. The consequences of a short frenulum can be found in the list below:
- sucking function is impaired. In most cases, the baby is not able to properly attach to the mother's nipple - to clasp it well and completely;
- changes external data, the face takes on a not entirely aesthetic appearance;
- Tremas are formed, diastemas are gaps located between the front teeth. The latter can be provoked by physiological reasons, for example, this is observed at the stage of development of baby teeth. During this period, the child’s body prepares the jaws for the natural process of replacing teeth with permanent ones. But there are gaps that are caused by pathological reasons - one of which is a short frenulum. In this case, both surgical and orthodontic treatment are recommended;
- be a provoking factor in the manifestation of bite pathology. This occurs as a result of the constant tension of the frenulum causing the incisors to protrude forward. A similar disorder usually occurs in children who already have permanent incisors. The pathology is treated, as in the previous case, with the help of a surgeon and an orthodontist;
- due to the pressure that is constantly exerted on the mucous membrane of the upper jaw, prerequisites are created for the development of inflammatory processes and dental diseases - gingivitis and periodontitis. As a result of the gums exposing the necks of the teeth, they acquire increased sensitivity, which opens the way for caries.