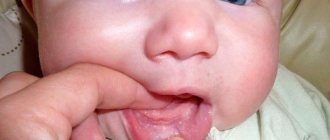
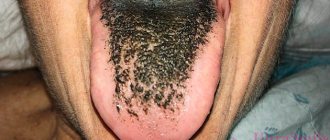
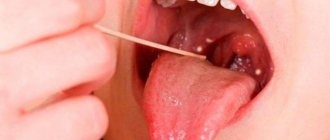
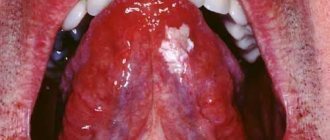
We are used to the fact that we need to go to the dentist if we have problems with our teeth or gums. What to do if you have inflammation of the tongue or glossitis? Dentists identify more than 10 types and subtypes of infection. The infection can be caused by both fungus and bacteria. Viral infection is less common. Inflammation can be caused by a lack of certain vitamins and minerals, or hormonal changes. There are many reasons for the disease, so it is important to identify what exactly caused the inflammatory process.
Causes of glossitis
- improper oral hygiene;
- bacterial infection;
- fungal infection;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- congenital pathologies of the tongue (folded tongue);
- allergic reaction;
- tongue injury (often caused by malocclusion);
- oral infections;
- lack of iron in the body;
- burn of the mucous membrane (hot food or drinks);
- infectious diseases (AIDS, tuberculosis, scarlet fever, measles).
Causes of pimples in the mouth
70% of red, white or pinkish rashes in the oral cavity, including on the tongue, indicate the presence of a serious dental disease. The asymptomatic course of the disease does not mean that the “trouble” will go away on its own. However, prescribing treatment on your own, guided by the advice of friends or recommendations from the Internet, is dangerous.
Important!
In principle, there cannot be acne on the tongue. Purulent skin rashes develop due to inflammation of the sebaceous glands, which are not present in the mouth. Accordingly, we call those pimples that appear in the oral cavity “pimples” by analogy. Just by external similarity.
There are several reasons for the appearance of irritations that visually resemble pimples:
- mechanical damage. A prick with a fish bone, a scratch, a burn from hot coffee can provoke a similar pathology;
- allergy. Not necessarily to foods; a seasonal allergic reaction is possible, manifesting itself in such an unusual way;
- viral and infectious diseases. Herpes, rubella, scarlet fever and ARVI sometimes manifest themselves as rashes in the mouth;
- fungal infection (candidiasis);
- stomatitis. Usually, with stomatitis, pimples first appear on the gums, but sometimes red spots with a whitish halo, which react sharply to touch or spicy/hot food, form over the entire lingual surface.
There is no point in waiting until diseases become chronic. In 98% of cases, such pathologies are treated quickly and inexpensively, if you do not neglect the condition and do not self-medicate.
The most common types of glossitis
The most common occurrences in dental practice are:
- acute catarrhal glossitis;
- tongue abscess;
- desquamative glossitis.
Acute catarrhal glossitis is the most common type of inflammation. Inflammation can be caused by microbes or mechanical damage to the tongue. The predominant symptoms are pain, redness and swelling.
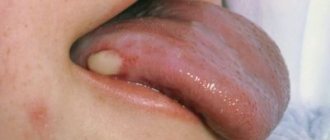
A tongue abscess is the appearance of an abscess in the tongue. The abscess can be superficial, under the mucous membrane, or maybe in the thickness of the tongue. Abscesses in the thickness of the tongue, in addition to pain in the tongue, can cause a disturbance in the general condition. A person develops a fever, a headache, and weakness. Most often occurs due to injury to the tongue.
Desquamative glossitis, also known as “geographic tongue,” most often appears in children. It appears in the form of various spots on the tongue, which look like a white coating, alternating with areas of pink mucous membrane. There are no changes other than appearance. Scientists have identified a clear reason for it. The main factors are believed to be bacteria, allergic reactions and hormonal imbalances.
Symptoms and mechanisms of development of urticaria
The appearance of the main symptoms of urticaria - blisters and redness - is associated with the mechanism of development of the disease. This is an increase in vascular permeability and acute swelling in the tissues that surround the vessels.
The mast cell plays a leading role in the development of urticaria. These are special immune cells, the granules of which contain special biologically active substances (mediators). The most studied of them is histamine. It is because of its action that the symptoms of urticaria arise - rashes, redness, swelling, itching.
A blistering rash appears suddenly on any part of the body, disappears quickly and without a trace within 24 hours, and then appears elsewhere. When you press on the center of the redness, a white spot is visible.
The itching begins at the same time as the rash. This is how histamine acts on nerve endings.
Depending on the factor that activated the release of histamine from mast cell granules, different types of urticaria are distinguished.
In children with urticaria, there may be a deterioration in their general condition: increased body temperature, disruption of the digestive system (diarrhea).
Symptoms of glossitis
- increased salivation;
- swelling and redness;
- pain and burning when eating;
- plaque on the tongue in the form of spots;
- bad breath;
- papillomas or warts on the tongue;
- speech disorder;
- foreign body sensation.
Prevention of glossitis - high-quality oral hygiene and no bad habits. It is important to undergo timely preventive examinations and also eat well. All these factors actively contribute to the development of the disease and bring a number of problems.
Diagnostic procedures for urticaria
Diagnosis of acute urticaria is usually quite simple. An examination and questioning of the patient about his medical history is sufficient. Finding out the reason is not so easy, and for this purpose additional research is carried out:
1. Laboratory tests:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- blood biochemistry (liver tests - ALT, AST, bilirubin, rheumatic tests, blood glucose);
- stool examination (coprogram);
- bacterial cultures from the nasal and pharyngeal mucosa.
2. Instrumental research:
- chest x-ray;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- endoscopic examinations of the upper and lower gastrointestinal tract (gastroscopy, colonoscopy).
3. Allergy tests:
- intradermal tests with allergens;
- cold and heat tests;
- physical stress tests, line drawing, tourniquet application.
4. Immunological methods.
5. Consultations of related specialists:
- gastroenterologist;
- endocrinologist;
- rheumatologist;
- gynecologist and others as necessary.
First of all, it is important for a specialist to establish what nature the urticaria is – allergic or non-allergic. In the allergic form, one can clearly trace the connection between the symptoms and the introduction of the allergen. It is confirmed by skin, allergy and immunological tests.
Treatment of glossitis
A specialist must make an accurate diagnosis and identify the cause of the disease. If you suspect that you have glossitis , and all symptoms indicate this, contact your dental clinic. This is the only way to create the right treatment plan and provide timely assistance. Quite often in such cases, doctors prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and rinsing the mouth with special antiseptic solutions. In advanced stages, glossitis is treated surgically. Deep abscesses must be opened in the maxillofacial department. Under no circumstances should you take medications without a doctor’s recommendation.
You can cure glossitis, caries or any other diseases of the oral cavity right in your sleep. Family Dentistry Center "Medexpert" provides dental treatment under medicinal sedation. Thanks to this approach, the patient falls into a healthy sleep, ceases to feel pain and discomfort, while the vital functions of the body remain unchanged. Sedation is widely used in pediatric dentistry and even helps fight dental phobia. Dental treatment can be comfortable and painless - tested for yourself.
When and which doctor to contact
Usually a doctor is consulted:
- if the rash spreads over a large area;
- when symptoms increase;
- when signs of general intoxication occur;
- if the urticaria does not go away on its own after eliminating the factor that caused it;
- if the disease becomes chronic or often recurs,
It is advisable not to delay your visit to the doctor and come when the first manifestations of the disease occur. Then it will be easier to establish the cause, and treatment will take less time. In addition, the doctor will recommend what to do to prevent hives.
A therapist or pediatrician, a dermatologist can provide assistance with urticaria, and an allergist is involved in targeted diagnosis and treatment.
4.How to treat urticaria and Quincke's edema?
The easiest way to deal with urticaria and angioedema is if you can identify and eliminate the factor that caused the problem. But this is not always possible. Typically, antihistamines are used to treat hives. They will help relieve the symptoms of the disease. Sometimes antihistamine medications need to be taken regularly to prevent the rash and associated swelling.
Chronic urticaria is treated with antihistamines or a combination of them. But if this does not give the desired result, sometimes the doctor prescribes corticosteroids.
In severe cases of urticaria and angioedema, an injection of adrenaline or steroid medications may be necessary.
What else can be done to treat hives?
While the course of treatment is ongoing and you are waiting for the redness and swelling to disappear, follow these simple recommendations.
- Do not use hot water. Let it just be warm.
- Wash with mild soap.
- You can apply cold compresses or apply a damp cloth to the affected areas.
- Be in a cool room.
- Wear loose, lightweight clothing.
Complications of urticaria
It is important to know what hives look like and to be able to provide first aid correctly.
This will help prevent the development of severe complications that can lead to death. Often urticaria is accompanied by Quincke's edema, which is also called angioedema. Its development in the larynx area is especially dangerous, as it can compress the trachea and impair breathing.
Another serious complication is anaphylactic shock. This is a life-threatening immediate allergic reaction that occurs when the human body is hypersensitive to a particular allergen. Usually develops upon repeated contact with the allergen and requires immediate medical attention.
Treatment of urticaria
The only way to get rid of the disease is to avoid contact with the allergen, which is previously detected by laboratory tests.
If testing does not reveal a provoking factor, and the urticaria is episodic, then taking antihistamines will quickly eliminate the symptoms. During treatment, it is recommended to follow a diet that, in case of urticaria, will help prevent the recurrence of the disease. The menu should include only hypoallergenic products: lean boiled meat, soups with recycled meat broth or vegetarian. It is better to choose rice, buckwheat, and oatmeal from cereals. Low-fat cottage cheese, natural yogurt, apples, dried fruit compote, excluding raisins, and whole grain bread are recommended.
Citrus fruits, nuts, fish and all seafood, chocolate products, smoked meats, coffee, eggs, honey, and store-bought baked goods should be excluded from the menu during treatment.
Treatment is carried out by a dermatologist and an allergist-immunologist. For topical application, ointments for urticaria are effective; they not only relieve itching, but also eliminate swelling, redness and a burning sensation on the skin. One of the most effective is Dimetinden gel, which must be applied in a thin layer to the affected area of the skin up to 4 times a day.
A course of antihistamines is prescribed in the form of tablets. Your doctor may also prescribe calcium gluconate or calcium chloride for urticaria. They help reduce the symptoms of allergies, but they should only be administered under the supervision of a doctor in the treatment room.
If antihistamines do not provide the desired effect quickly, or for severe forms of hives, corticosteroids are used, which can be applied to the skin or taken in the form of tablets or injections.
Diagnosis of urticaria
Before starting treatment, it is important to understand what exactly a person has such a strong allergic reaction to.
Only by removing this provoking factor from your usual life can you not be afraid that the symptoms of urticaria will appear again, and this is possible even after proper therapy. Most often, this type of allergy appears to food. It is possible to determine what exactly caused the rash by a blood test: the level of IgE antibodies to a mixture of food allergens is detected. First of all, you need to diagnose the presence of an allergic reaction to:
- nuts;
- vegetables and legumes;
- citrus fruits and fruits;
- seafood;
- cereal and sesame flour;
- fruits and melons;
- baby formula;
- fish;
- meat;
- mushrooms;
- loose leaf tea;
- goat milk.
In addition to food, allergic manifestations can also occur to other substances that surround us almost everywhere in life:
- mold fungi;
- pollen from early flowering trees;
- pollen of late-flowering trees;
- weed pollen;
- epithelium of domestic animals;
- house dust;
- house dust mite;
- poultry feather.
To identify the exact type of allergen, allergy tests are performed on certain foods.
It often happens that rashes appear due to seasonings and herbs used in cooking: paprika, cumin, cloves, basil, ginger, tarragon, thyme, marjoram, dill, bay leaf, black pepper, vanilla. Some types of fish may also be allergenic: cod, halibut, mackerel, and squid meat. But sometimes an allergic reaction in the form of urticaria develops to such familiar products as:
- cucumber;
- apricot;
- cherry;
- tomato;
- plum;
- grape;
- persimmon;
- carrot;
- beet;
- watermelon.
All tests are carried out only by a specialist laboratory technician. You cannot independently determine the presence of an allergy in the form of urticaria to a particular food product or substance. This can be life-threatening, since it is possible to develop not only Quincke's edema, but also anaphylactic shock.
Symptoms of urticaria
The main manifestation is the appearance on the skin of red or pink spots of various shapes, and blisters, the size of which can reach several centimeters.
A slight swelling may appear, which gradually disappears over the course of a day, rarely two. If the swelling affects the deeper layers of the skin or mucous membranes, angioedema may result - a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical intervention.
The rash of allergic urticaria is always accompanied by unbearable itching, and some patients describe it as an unbearable burning sensation. Violent scratching of such areas can lead to infection of the epidermis with further complications in the form of pustules and wounds.
Minor manifestations of urticaria include:
- headache;
- elevated temperature;
- sleep disorder;
- anxiety;
- loss of appetite.
According to the nature of the course, allergic diseases are divided into two types.
Acute urticaria is diagnosed most often. Blisters and swelling of the skin in this form appear completely suddenly, sometimes against the background of a person’s excellent health. Most often caused by some external reasons, food. It also happens after using medications, especially when self-medicating. Symptoms go away on their own within a few days to several weeks.
Chronic urticaria is a condition in which symptoms continue to persist for more than 6 weeks after the first rash on the skin. This variant is characterized by a wave-like course, when periods of complete absence of symptoms (recovery) are abruptly replaced by exacerbations with the appearance of a new portion of spots and blisters. This is accompanied by unbearable itching and rapid development of Quincke's edema. The emerging elements of the rash can merge with each other, covering more and more new areas of the skin.
Sometimes periods of complete well-being without symptoms can last for a long time - up to 10 years.
Children's urticaria is an allergic skin disease, which most often develops against the background of an existing exudative diathesis and appears due to food products introduced as complementary foods.
It has been noticed that this type of allergy mainly develops in babies who are bottle-fed or eat foods that are not appropriate for their age.
3.Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis of urticaria or Quincke's edema is made after examination. Your doctor will ask you a few questions to find out the possible cause of your hives or angioedema and examine your skin. Depending on your health condition, you may need to consult an allergist, immunologist or dermatologist.
Skin tests may be done to determine which substance is causing your allergy. And routine blood tests are needed to determine the presence of some systemic disease.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Our doctors
Orlova Tatyana Vladimirovna
Doctor - allergist-immunologist, pulmonologist, doctor of the highest category
Experience 38 years
Make an appointment
Shundeva Oksana Veniaminovna
Allergist, doctor of the highest category
Experience 39 years
Make an appointment
Treatment of the disease
If the allergen is known, then the main recommendation is to avoid, if possible, contact with the substance that provokes hives. That is why accurate diagnosis is important - it is necessary to understand which group of chemical compounds can lead to the development of urticaria. It often happens that the same substance is found in different foods or in different pharmaceuticals. And an allergy to pets can affect only one breed or spread to almost all pets, from cats to hamsters.
Therapy is needed if the disease has become a recurrent form - this happens if it is impossible to stop contact with the provocateur. In a situation where test results show the presence of an infectious focus, it is necessary to determine the infectious disease. It is likely that the urticaria will go away after healing.
If a patient is diagnosed with an allergy to dust, food or plants, then lifestyle changes are required: frequent wet cleaning, following a proper diet and avoiding walking during the flowering period of plants. Concomitant treatment is designed to alleviate symptoms when they reappear.