Quick transition Treatment of a short frenulum of the tongue
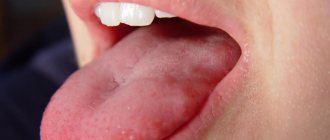
A short frenulum of the tongue (ankyloglossia) is one of the most common minor anomalies in the development of the oral cavity.
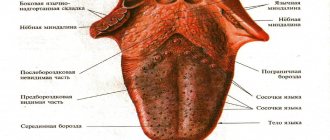
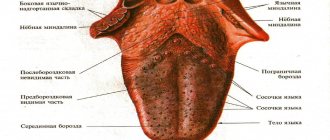
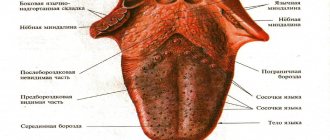
The frenulum of the tongue is a fold of the oral mucosa that runs along the midline and connects the floor of the mouth with the lower surface of the tongue.
The function of the tongue frenulum is to fix the tongue to the soft tissues of the oral cavity, preventing tongue retraction (glossoptosis), especially during the neonatal period.
Symptoms
When crying, the tip of the baby's tongue bifurcates in the shape of a stylized heart.
The baby cannot stick his tongue out of his mouth. To test this reflex, you can run your finger over the baby's lips. Normally, the baby sticks his tongue out quite far, moving it around his lips in search of mother's milk.
Breastfeeding takes a lot of time, the baby is capricious, nervous, and clicking sounds are heard when sucking.
The baby is not gaining weight well.
A child with a short frenulum cannot reach the palate with his tongue.
There is a noticeable disturbance in the pronunciation of certain sounds during speech formation.
With a short frenulum (less than 1.5 cm), if it is attached to the soft tissues of the floor of the mouth, functional disorders do not always occur. These include difficulty sucking during breastfeeding and disturbances in sound pronunciation during the formation of phrasal speech.
Cracks in the tongue
Causes
The causes of cracked tongue are:
- Glossitis is an inflammation of the tongue that occurs either as an independent disease or as a symptom of systemic pathologies.
- Viral and bacterial infections, especially often glossitis is caused by the herpes simplex virus type 1.
- Mechanical injuries of the tongue, serving as an entry gate for infectious agents. Provoking factors leading to damage to the tongue are low-quality elements of orthopedic structures (prostheses, braces), sharp edges of damaged teeth.
- Constant consumption of hot, hot, spicy food, strong alcoholic drinks, having an irritating effect on the mucous membrane of the tongue, violates its integrity, which leads to the penetration of pathogenic microflora into cracks with the development of inflammation.
Other reasons - why is the tongue cracked?
- An allergic reaction to various food and drug allergens, to denture material, to components included in toothpaste or hygienic mouth rinses.
- Deficiency of vitamins (especially groups B, A) and microelements (iron, zinc) increases the sensitivity of the tongue mucosa to adverse external influences.
- Failure to comply with hygienic rules for oral care.
- Severe dryness of the mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue, caused by disruption of the salivary glands, dehydration or elevated body temperature.
- Diseases of the digestive system, cardiovascular, endocrine system, collagenosis, metabolic disorders.
- Helminthic infestation leads to the fact that some nutrients are not absorbed in the body, local immunity decreases, and the condition of the mucous membranes, including the tongue, worsens.
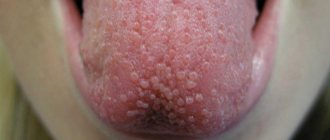
Folded glossitis is a congenital abnormality of tongue development. It is characterized by an increase in the size of the tongue and the appearance of grooves, cracks and folds on its surface. As a rule, a folded tongue does not cause discomfort, but with poor oral hygiene, food debris can accumulate in the deep folds, which serve as a favorable environment for the proliferation of bacterial or fungal microflora. As a result, inflammation develops: redness, swelling. The patient experiences pain, burning of the tongue, and bad breath.
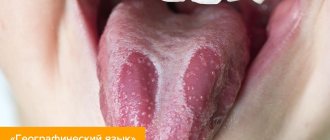
Desquamative glossitis is called “geographic tongue” due to the presence on the surface of the tongue of numerous red, smooth lesions surrounded by a whitish border, which create a bizarre pattern reminiscent of a geographical map. In places where the epithelium peels off unevenly, furrows and cracks appear on the tongue. In areas of desquamation (desquamation) of the epithelium, there is increased sensitivity of the tongue to thermal and food irritants (hot, cold, sour, salty), burning and tingling, and impaired taste sensations.
The appearance of desquamative glossitis is most often associated with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as endocrine disorders, and pathologies of the hematopoietic system.
Diamond-shaped glossitis is characterized by the appearance on the back of the tongue of an atrophic area of red, sometimes bluish color, on the surface of which filiform papillae are completely absent. Diamond-shaped, oval lesions are flat or protruding above the surface of the tongue (tubercular, papillomatous form). In the tubercular form, the affected area consists of tubercles separated by folds and cracks.
The disease is asymptomatic and is discovered by chance at a dentist's appointment. In rare cases, the patient is bothered by a burning sensation and sometimes pain on the back of the tongue if inflammation develops.
Symptoms
Cracks in the tongue can be combined with other symptoms of glossitis.
- Glossitis, caused by bacterial microflora, is manifested by symptoms of acute inflammation: swelling, hyperemia, local pain, local fever.
- With glossitis of a viral nature, bubbles appear on the surface of the tongue, which, after opening, leave behind painful erosions.
- When affected by fungi, the tongue is covered with a cheesy coating, under which the hyperemic mucosa is visible.
- Unpleasant sensations in the mouth: itching, burning.
- Change in color of the mucous membrane of the tongue.
- The appearance of cracks, erosions, ulcers.
- Taste sensations become dull and sometimes disappear completely.
- Swelling of the tongue interferes with correct sound pronunciation, speech becomes slurred.
In the absence of treatment, glossitis becomes chronic with a persistent change in the structure of the tongue in the form of the development of hyperplastic processes.
Treatment
If cracks appear in the tongue that cause discomfort to the patient, this is a reason to consult a dentist.
For pathologies of the dental system, the following is prescribed:
- Sanitation of the oral cavity: treatment of caries, professional teeth cleaning (removal of plaque and tartar), correction of malocclusions, installation of new fillings to replace outdated ones, replacement of dentures.
- Thorough oral hygiene - proper brushing of teeth, tongue, use of an irrigator, rinsing the mouth after meals.
- Maintaining a mechanically and chemically gentle diet during inflammation means excluding hot, spicy, sour, salty foods and strong alcoholic drinks from the diet.
- Treating the tongue with antiseptic solutions.
- For pain, local anesthetics are used.
- Prescription of wound-healing, softening agents for the mucous membrane of the tongue.
If dental reasons for the development of pathology are not confirmed, you should consult a therapist. When identifying the causes of cracks in the tongue, the patient undergoes treatment from specialized specialists: gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, hematologist and others.
Published: 11/25/2021 Updated: 12/02/2021
Information verified by an expert:
Rykova
Tatyana Viktorovna,
expert doctor, co-founder of the VitaDent clinic, dentist-therapist
Back to the list of articles
Consequences of frenulum anomaly
Hypotrophy due to impaired sucking, poor weight gain in infants.
Malocclusion, the first signs of which during the period of temporary occlusion is the rotation of the central lower incisors to the lingual side.
Impaired development of the lower jaw, as a result, the formation of a distal bite.
Local gingivitis, periodontitis up to exposure of the roots of the teeth in the area of the lower jaw incisors.
Violation of the pronunciation of sounds that require raising the tongue upward: “sh”, “zh”, “sch”.
Impaired language development due to asymmetrical growth. Low mobility of the tongue impairs the articulation of some sounds. Violation of diction (clarity, intelligibility of pronunciation).
Treatment
Pre-hospital assistance
It is recommended to avoid foods that are too hot, cold, hot or spicy. You should eat soft foods that do not injure the tongue, preferably stewed, boiled, steamed. The best option is a diet that includes purees, slimy porridges, pureed soups. Before and after meals, you need to rinse your mouth with weak solutions of chlorhexidine and potassium permanganate or a solution of furatsilin. For severe pain, the surface of the tongue can be lubricated with local anesthetics.
Conservative therapy
An important part of the treatment is the sanitation of the oral cavity, and, if necessary, the replacement of dentures and orthodontic structures. The list of therapeutic measures is determined by the nature of the pathology:
- Glossitis
. Rinses and applications with anesthetics are indicated. For intense pain, lubrication with a mixture of glycerin and anesthesin is effective. Plaque is removed with a swab containing proteolytic enzymes. Treat with antiseptics. Local healing drugs are used. - Phlegmon and tongue abscess
. For superficial abscesses, rinse with antiseptic solutions, prescribe antibacterial agents, and if ineffective, surgical interventions are performed. For deep abscesses and phlegmons, conservative therapy is an auxiliary treatment method, carried out against the background of operations, and includes antibiotics, analgesics, antihistamines, and anti-inflammatory drugs. - Candidiasis
. Alkalinizing rinsing solutions are used as local remedies. The oral cavity is lubricated with antifungal ointment and treated with solutions of iodinol, lugol, fucorcin. The therapeutic regimen also includes general antifungal drugs and, in severe cases, immunotherapy. - Glossalgia
. It is recommended to take light tranquilizers, motherwort, and valerian. A good result is achieved with trimecaine blockades of the lingual nerve and injections of B vitamins. Unpleasant sensations are eliminated through oral baths and applications with anesthetics. The main pathology and neurotic disorders are treated. - Xerostomia
. It is recommended to stop smoking and drinking alcohol, use soft-bristled toothbrushes, drink frequently to moisturize the mouth, and suck on sugar-free lollipops to stimulate saliva production. The oral cavity is lubricated with a solution of vitamin A. Novocaine blockade of the salivary glands is performed, vibration massage, medicinal electrophoresis, and galvanotherapy are prescribed. - Neuralgia
. Anticonvulsants, non-narcotic analgesics, and vitamin complexes are used. For severe pain, antidepressants, sleeping pills, sedatives, and antipsychotics are recommended. Therapeutic blockades are carried out. Lubricate the tongue with a solution of cocaine. Patients are given a referral for SMT, galvanization, and diadynamic therapy. - Anemia
. In case of iron deficiency anemia, treatment of the underlying disease, nutritious nutrition with a high content of heme iron, and ferrous preparations are required. In case of pernicious anemia, the provoking pathology is corrected and vitamin B12 is prescribed.
Short frenulum of the tongue - how to determine?
Symptoms of a tongue frenulum are usually identified by a speech therapist during a myofunctional examination. Most often, specialists (this can be attentive parents or the patient himself) observe the following symptoms:
- Limitation of tongue mobility; it is difficult for the patient to move the tongue out of the mouth and raise the tip of the tongue to the upper lip.
- The tip of the tongue bifurcates when you try to push it forward.
- The patient pronounces the sound L incorrectly, making it sound like V.
- Sometimes a short frenulum of the tongue brings purely everyday discomfort, as in the clinical case described above.
Medical assistance
If the tongue is cracked and hurts, is swollen on the sides, or there are other signs of the progressive development of the disease, then treatment must be started immediately . A protracted process can progress to a more complex stage, up to necrosis or oncology.
Constant inflammation causes intoxication of the body and is fraught with the entry of pus into the gastrointestinal tract.
Only a doctor can give a qualified answer to the question of why the tongue cracks. Due to the variety of possible causes of cracks in the tongue, the problem arises of which doctor to contact in order to establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment. First of all, you need to get examined by a dentist. This is necessary to identify prerequisites associated with problems in the oral cavity, or to exclude such a scenario.
If, as a result of a dental examination, the cause of cracks in the tongue was not identified, this means that the problem may be caused by diseases of the internal organs. Usually the patient knows or guesses from how he feels about its existence. Depending on the type of possible pathology, you need to contact a specialized specialist.
If there are no obvious signs of illness, you need to consult a therapist or pediatrician. You can first take a general blood test and do an ultrasound of the internal organs.
Localization of cracks
The position of the cracks is not random. Localization is divided into three types, each of which is caused by specific problems. You can independently identify the type of localization by assessing the position of the cracks in the tongue: in the center, on the sides or at the tip.
The presence of cracks only at the tip of the tongue indicates the following causes of the problem:
- Thermal damage. Hot food first comes into contact with the tip of the tongue and causes major damage to it. Often the problem is contact with a hot metal spoon.
- Chemical damage. Occurs from contact with spicy, sour foods or corrosive substances.
- Physical impact. The tip can crack due to an incorrect bite or a cut on the sharp protruding parts of the incisors and canines.
Photo: cracks on the sides of the tongue
The formation of cracks in the tongue in the middle has a different reason, since it is almost impossible to injure this area without touching the periphery. This means that inflammation is an indicator of pathology or disease of internal organs. In addition, the formation of cracks in the center is possible when the middle area dries out, local circulation is impaired, or the immune system is weakened. There may be only one crack; upon examination, it appears as if the tongue has split into two parts.
The presence of cracks on the sides of the tongue can be caused by various reasons. If the inflammatory process is present on the side on one side, then this means physical damage from the sharp edges of small and large molars or dentures. If the tongue is cracked on both sides, it means that there are serious malfunctions in the functioning of the body , where glossitis acts only as an indicator of pathology.
Types of glossitis
In total, there are more than ten types of glossitis, three of which are accompanied by the appearance of cracks in the tongue. They have quite pronounced visible differences. To independently diagnose the type, you can compare the current state of the tongue with photos of classic manifestations of the disease.
Folded glossitis takes its name from the main external manifestation - the presence of folds. Sometimes, with this type of disease, a cracked tongue is present from birth. If it does not hurt, is not loose and there are no other unpleasant sensations, then the condition is considered normal. However, with deep cracks in the tongue, treatment is still necessary.
The problem of a folded tongue is often only of an aesthetic nature, although people with this feature are recommended to have constant monitoring by a dentist.
Desquamative glossitis is characterized by focal damage to the surface with almost imperceptible shallow cracks. The papillae desquamate and a whitish heterogeneous layer forms. The affected areas quickly recover, acquiring a natural color, and those adjacent to them become inflamed. The geometry of white areas (plaque) on the surface often changes. In advanced cases, due to the large number of cracks, a person feels the tongue is loose.
Diamond-shaped glossitis is characterized by the presence of a rhombic or oval-shaped area of red-blue color. It is located in the middle of the tongue, in the region of the posterior third. The tongue cracks in the center, so that the entire affected area seems to be divided into two parts. This type can be chronic, and during exacerbations, pain and burning begin.
Main symptoms
Sometimes the presence of cracks and grooves in the tongue is not accompanied by unnatural or painful sensations and can only be detected during examination by a dentist, ENT specialist or therapist. But this doesn't always happen. Patients often complain of the following related problems:
- pain;
- burning sensation;
- feeling that the tongue is loose;
- there is blood and ichor;
- elevated temperature;
- swelling and itching appeared;
- it becomes painful to chew;
- there is a problem with speech;
- increased salivation appeared;
- change in natural color;
- taste disturbance;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor.
If cracks appear on the tongue, and the phenomenon is accompanied by one of the listed symptoms, then they speak of a progressive disease. This inflammatory process is referred to as glossitis; the prognosis for recovery from it is usually favorable. The appearance of erosions, furrows and ulcers indicates damage to the deep parts of the tongue. In this case, you should definitely contact a specialist.
Sometimes the tongue cracks and becomes covered with ulcers due to general damage to the ENT organs. Thus, tonsillitis or fungal pharyngitis can cause swelling and the appearance of white grooves. This condition is not isolated as an independent disease. Treatment in such cases begins with eliminating the underlying problem.
Methods for eliminating a short frenulum of the tongue
A short frenulum of the tongue is corrected surgically. The most modern method is cutting the frenulum of the tongue with a laser, since there is less pain, the operation is almost bloodless, the wound is sterile and heals quickly.
Operations can be different:
- Frenuloplasty of the tongue is plastic surgery of the frenulum of the tongue with mobilization. Mobilization is the preparation of the edges of the wound for a screed by pulling the tongue forward and upward; flap formation is often used in plastic surgery. In most cases, frenuloplasty of the tongue is the most favorable way to lengthen the frenulum for both healing and restoration of the tongue.
- Frenulotomy is a dissection of the frenulum, usually done in the maternity hospital by simply cutting the frenulum without sutures.
- Frenulectomy - excision of the frenulum. During this operation, the doctor cuts the tissue wedge-shaped in several places, then applies sutures, but does not mobilize the tongue. This is a disadvantage of the method.
Obviously, each case is individual and the choice of method should be made by a specialist.
Impact of frenulum pathology
Problems with speaking
But sometimes a child has a congenital pathology - shortened frenulum .
Such a diagnosis means that the frenulum is not attached in the middle of the tongue, but much closer, at the tip. Sometimes it lasts until the very tip, and the tongue even slightly bifurcates from its pressure. A serious pathology is diagnosed after the birth of a child by a neonatologist, and minor deviations in the length of the frenulum can be detected in preschool age, when the child begins to have problems pronouncing certain sounds.
Problems with breastfeeding
In infancy, a shortened frenulum can interfere with breastfeeding, as the baby cannot grasp the nipple comfortably, often loses it, and may even experience pain when sucking. This negatively affects the child’s weight gain and causes a lot of unpleasant moments for the whole family.
Use of traditional medicine
At home, you can use well-known methods to help heal wounds in the mouth, eliminate pain, relieve swelling and other symptoms. However, before treating cracked tongue with folk remedies, you need to ensure their compatibility with the prescribed medications.
The most effective are the following recipes:
Herbal infusion of chamomile, celandine, sage and calendula. For adults, you can add St. John's wort. Take after meals in the form of baths or lotions. Promotes wound healing and relieves swelling.- Compresses from fermented milk products. Soften scars and scabs. The procedure should be done in the morning for 15 minutes.
- Sea buckthorn or olive oil. In the morning you need to drop a few drops on the mucous membrane and in the middle of the tongue, then do not drink or eat for 15 minutes. Softens dry formations on the tongue and mucous membranes.
- Honey. Has wound-healing and antimicrobial effects. A piece of the product can be placed in the middle of the tongue and dissolved. Gives a good effect if cracks bleed.
- Propolis tincture (for adults only). The strongest disinfectant: has antimicrobial, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. Since alcohol tincture cannot be used in its pure form if there are open wounds, you need to dilute 1 teaspoon in 100 grams of warm tea. Drink after meals.