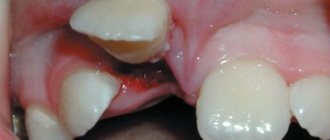
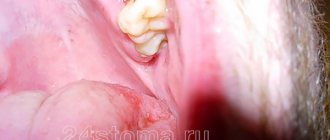
There are plenty of reasons why you can lose a completely healthy tooth in our lives. In adults, the face, and along with it the jaws, are often injured in road accidents, as a result of falls, bad habits, and sometimes attempts to sort things out by force. Even more “opportunities” open up for children who love active games on playgrounds and sports grounds. In dentistry, this situation is usually called tooth dislocation.
Practice shows that many erudite adults get lost in such situations and don’t know how to behave. Meanwhile, you can save a tooth if you get an appointment with a dentist within an hour.
Diagnosis of tooth trauma
In case of tooth injuries, timely assistance is very important to minimize the consequences of damage. It cannot be put off until later (after a day, a week, etc.) - it is important to provide yourself or your child with first aid correctly and contact a dentist as soon as possible. But first you need to figure out what damage is considered a tooth injury.
Mechanical tooth trauma is damage resulting from falls, impacts, accidents and other external influences. They violate the shape of the tooth and the integrity of dental tissues. Mechanical injuries of various types are divided into acute and chronic dental injuries. The first type includes damage to teeth as a result of a single and strong action (falling from a bicycle, swing, scooter, biting too hard food or a toy, a blow to the teeth due to an accident, etc.).
Chronic injuries are associated with bad habits (for example, chewing pencils, pens, seeds) or with a violation of the closure of teeth, due to which the dental tissues are gradually injured.
➢ The peak of injuries to permanent teeth occurs at primary school age - 8-10 years, and for milk teeth - at 2-3 years.
➢ Injury to permanent teeth is less common among professional athletes, since they wear special protection - helmets, mouth guards, and shields.
➢ Most often, injuries occur for everyday reasons: during breaks at school, during active games, at home, on the street, etc.
➢ Trauma to the front teeth, especially the incisors, is the most common occurrence (about 80% of cases).
➢ The risk of damaging teeth is 3 times higher in people with a distal bite, in which the front teeth protrude forward and the lower jaw is in a posterior position.
Complications and consequences
Knocking out teeth means acquiring a serious health problem. Even with successful and timely treatment, there is a high probability of malocclusion, speech defects, and difficulties with chewing. After the doctor has pulled out the root and implanted you, there may be problems with the implantation of the artificial tissue. Replantation of native tissues is not always completed successfully. All this is accompanied by inflammatory processes and leads to impaired quality of life, aesthetic problems, and difficulties in communication.
It is clear that after dental disorders, the bite suffers, and the teeth that fall out first are those that were previously exposed to trauma. To reduce the risk of repeated violations, they try not to overload the dentition, use protective equipment when playing sports, and avoid conflict situations that could turn into fights.
Dear readers of the 1MedHelp website, if you still have questions on this topic, we will be happy to answer them. Leave your reviews, comments, share stories of how you experienced a similar trauma and successfully dealt with the consequences! Your life experience may be useful to other readers.
Classification of dental injuries
The ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases) classification of dental injuries includes more than ten types of dental injuries. To summarize, all mechanical damage is divided into:
- for injuries to the tooth itself or fractures;
- tooth displacement or dislocation;
- damage to soft tissues and jaws.
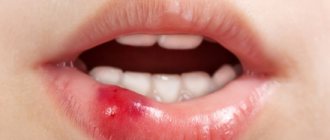
It is also worth noting a bruise - minimal damage to a tooth when it looks intact and visually no damage is visible - no chips, no cracks. But due to the impact, the blood supply to the tooth pulp may be disrupted, and subsequently the tooth may darken. Tooth bruises belong to the first class of injuries according to ICD-10. It hurts to touch, bite and chew food.
First aid for a bruise is to give pain relief if necessary, and consult a dentist as soon as possible.
But is the situation better for children in this regard?
– Here is another problem: many parents, having their own unpleasant experience of dental treatment, are afraid to take their child to specialists. They simply begin to broadcast their fears and anxiety onto them. I'll give you some tips on how not to turn a visit to the dentist into a problem.
If you are going to a reception, tell your child about the visit easily and naturally , as if you were going to meet interesting people. Call the dentist by name, show a photo on the Internet (on Instagram, for example), say that he will count your teeth, check that they are beautiful and growing correctly, and maybe clean them.
Do not say the words “treat”, “drill”, “it doesn’t hurt” - these thoughts may not have occurred to the child at all. Talk to your child a day or two in advance, then there will be less chance that he will hear “scary” stories from his peers.
Tell us what will happen: the doctor will ride on a chair, shine the sun in your mouth, blow the wind on your teeth and look with a mirror. Be there for your child, put down your phone, instill confidence in him.
Depending on the age of the child and on the recommendation of the doctor, you can:
- sit in the dental chair and put the child on you with his back to you, hugging him with his arms, taking his palms in your hands (at the same time, you should not tremble or be nervous);
- sit next to a chair and take the child by the hand;
- sit within sight. You need to be close with little ones (up to about 4 years old) and those who are trying out for the first time.
And I would really like to remind parents that the foundation of prevention is a proper, balanced diet and its regimen: “clean” intervals between meals are very important for teeth. We remember that until the age of two, there should be no sugar in a child’s diet.
Indeed, today it is believed that caries is a behavioral, controllable disease that begins due to a disruption of the oral microbiome. Due to excess consumption of carbohydrates (simple sugars), the amount of cariogenic microflora increases: it produces a lot of acid, which dissolves tooth enamel.
Oral hygiene is the second important aspect of prevention. Ideally, you should discuss the choice of hygiene products (paste, brushes, threads, irrigator) with your dentist.
Dental injuries in the form of fractures
Chips of enamel, fractures of the coronal part with damage to the pulp, fractures of the roots - all these injuries fall into the category of “tooth fracture”. There are 3 options for fractures of primary teeth:
- if the baby tooth is slightly injured, then the doctor usually monitors its condition;
- In case of significant damage, the baby tooth is removed in order to preserve the permanent tooth germ, since the injured baby tooth becomes a source of infection. This often happens with longitudinal fractures - when the tooth cracks in half lengthwise, and it is no longer possible to save it;
- in other cases, the tooth can be saved through restoration and canal treatment. In young children, treatment is often carried out during sleep.
First aid for a tooth fracture: It is very important to collect all the tooth fragments and put them in water or milk. If you collect all the parts of the tooth and quickly, within half an hour, get to the dentist, the tooth can be restored and it will be successfully fixed in the socket. If it was not possible to collect the tooth particles, then treatment of the tooth injury is carried out:
- In case of minor damage to the enamel (chips, cracks), tooth polishing is not performed - the dentist restores the tooth by installing a filling.
- If there is severe damage to the crown of the tooth, endodontic treatment may be required to preserve the pulp and then the installation of an inlay and/or crown.
- If the root is fractured, the tooth is rigidly splinted for 3-4 months, and the dentist monitors the condition of the pulp. Sometimes it is necessary to treat the canal of a coronal fragment, but there is no need to connect the fragments with pins. The tooth can almost always be saved, since this is a sterile injury, and the treatment prognosis is favorable, and therefore it is not necessary to remove teeth with a broken root.
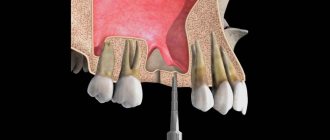
The peculiarities of dental prosthetics in children are the impossibility of using implants, so a lost tooth is replaced with a removable plate, an artificial tooth is fixed with fiberglass to adjacent teeth, or orthodontic mini-screws are used to fix the prosthesis with a temporary screw. Tooth replantation is also used - transplantation of a lateral tooth in place of a missing one.
Treatment
Oral injuries can vary in nature and severity. No matter how painful a tooth bruise seems, treatment must be carried out in a specialized dental clinic. We at Natadent often encounter such cases. After the initial diagnosis, visual examination, interviewing the patient and collecting anamnesis, an x-ray is taken - this is the only way to clearly determine which tissues are damaged and prescribe the correct treatment.
By studying an x-ray, the doctor can determine what kind of damage the tooth has received (this could be a fracture, dislocation, crack, various deformations and other pathologies).
Only after a correct diagnosis can treatment be prescribed. If a tooth injury has caused serious damage, electrodiagnostics is prescribed - a special procedure that allows you to determine the condition of the pulp, detect hemorrhages and necrotic areas in it. If diagnostic actions show that the damage is not very serious, a set of preventive measures is prescribed, which includes:
- application of compresses;
- use of decoctions for mouth rinsing;
- exclusion from the diet of hot dishes and foods that require chewing; exclusion of this area of the dentition from the chewing process by applying a bandage or protective splint.
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs.
If a more serious tooth injury is diagnosed, treatment may include surgery to the structure of the tooth and surrounding tissue. The sequence of actions is determined by the complexity of the injury, but in most cases includes the following steps:
- ;
- Local anesthesia is performed (or general if complex and painful treatment is involved).
- If the pulp sac is damaged, even if the tooth enamel has retained its structure, the doctor drills a hole in it and removes the nerve.
- The canals and cavity are cleaned, treated and filled, as in conventional caries treatment.
;
;
A tooth bruise is a dangerous injury that can lead to undesirable consequences and complications. Even if pulp removal and filling have been performed, it is advisable that the patient undergo a course of therapeutic treatment, and after some time come for additional examination. Only after this can it be said that the consequences of the injury have been completely eliminated and there will be no complications.
Dislocation
When a tooth is dislocated, sometimes it is impossible to completely close the mouth, or the tooth becomes loose and changes its position relative to other teeth. How to distinguish a tooth dislocation from a fracture? If the appearance of the teeth has changed - they have become shorter, tilted, etc., and the gums are bleeding, then you are dealing with a dislocation.
First aid for dislocation is the most correct tactic: do not let the child close the teeth, do not touch them and do not try to set them back on their own, because such displacements can be accompanied by injuries to the bone and gums. It is best to immediately contact a dentist, who will take a three-dimensional photograph, return the teeth to the correct position, and apply dental plaster for several weeks. The sooner you do this, the better.
Experts distinguish between many types of dislocations, including partial, complete and impacted.
Partial dislocation
With such damage, the tooth partially falls out of the socket. Often the alveolar wall is damaged, there is a tear in the periodontal fibers, and therefore the tooth becomes loose, bleeding occurs, and severe pain occurs when pressing and chewing. However, the anatomical structure is not disturbed, so the main task is to fix the tooth in the correct position in the socket until healing. In case of partial dislocation, this is achieved using special caps or splinting. The key point is to get the victim to the dentist as quickly as possible.
Complete dislocation
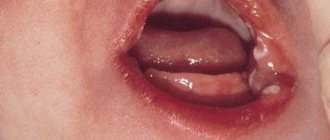
The tooth completely falls out of the socket, which is accompanied by heavy bleeding. When a baby tooth falls out, it is not reinserted, since placing the baby tooth in the socket can damage the germ of the permanent one. But if a permanent tooth falls out, then the necessary first aid is to find the tooth, wash it with water, but do not rub it or treat it with alcohol, since there are still living cells on it. Then the tooth needs to be inserted into the socket or, if this is not possible, put the tooth in milk and call the clinic to get instructions on how to do this.
If the tooth is placed back into the socket within 5 minutes, the prognosis is favorable - the tooth will successfully take root. Over a period of 5 to 10 minutes, the chances decrease as the number of living cells decreases. If the tooth has been exposed to air for a long time and has dried out, it will not take root for long, just a few years.
In any case, you need to get to the clinic as soon as possible - preferably within half an hour. If this is not possible, then contacting a dentist is still necessary. It is necessary to carry out root canal treatment, since when a tooth is severely displaced or falls out completely, the blood supply to it stops.
Impacted dislocation
Milk teeth are very often driven deep into the socket, since when they fall, the impact force is directed from bottom to top. This is very dangerous for the buds of permanent teeth, which are located behind the roots of baby teeth. Due to such trauma, various disturbances in the formation of the enamel of permanent teeth can occur, which manifest themselves in the form of yellow and white spots or defects in the shape of the tooth. It is necessary to take a targeted picture on a visiograph to assess the risks for permanent teeth. If a baby tooth is impacted too deeply, it is removed to reduce the risk of developing defects in permanent teeth. Sometimes tooth reduction is performed, in which the dentist very carefully returns the impacted tooth to its correct position and then splints it.
Tooth injuries are often accompanied by damage to soft tissues - cheeks, gums, lips. In this case, the dentist prescribes mild antiseptics - most often chlorhexidine preparations, as well as a gentle diet without harsh foods.
Where to go with a dental injury
But if you have already provided first aid to a child or adult for a tooth injury, then why also contact a dentist? The fact is that there are damages that cannot be seen with the naked eye - for example, a fracture of the tooth root inside the bone, fractures of the jaw bones and the walls of the tooth socket. Even after successfully placing the tooth back into the socket, splinting is necessary - this is the temporary stabilization of the tooth using a wire that is attached to adjacent teeth. In some cases, it is necessary to suture the edges of the wound or prescribe antibiotics.
If you ignore the problem and do not consult a doctor on time (or do not visit the clinic at all), complications will arise. The tooth may darken, become mobile, and the most common complication after a tooth injury is pulp necrosis, in which the neurovascular bundle inside the tooth dies. The dentist uses special tests to determine the vitality and condition of the pulp. Leaving dead tissue inside a tooth can lead to tooth root resorption as the body begins to perceive it as a foreign body due to infection. This leads to tooth loss in a fairly short time. This is why it is very important to have your teeth examined by specialists after an injury.
Symptoms
There are no problems in making a diagnosis if teeth are knocked out during a fight. Knocked out teeth with fragments and blood fall out completely or remain in contact with the gums, but are removed with the slightest effort. Bleeding can be profuse, especially when painters are damaged. Additionally, there may be concomitant non-dental disorders that are not visible to the naked eye.