Symptoms Causes Consequences Alveolitis Diagnosis and treatment Features of wisdom teeth Treatment at home Prevention
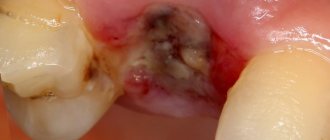
Tooth extraction is one of the most popular and simplest operations in medicine. Usually it passes without complications, but due to a number of general or subjective reasons, deviations may occur. One such postoperative complication is dry socket.
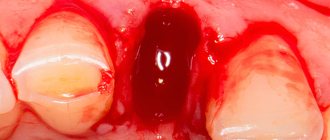
The fact is that after extraction of a tooth, a cavity forms in its place, which, in a positive scenario, is filled with a blood clot. It prevents the penetration of microbes into an open wound and promotes its speedy healing. A dry socket after tooth extraction is the absence of that same blood clot in the socket. This can happen for two reasons:
- Loss or resorption.
- Severe bleeding that prevented a clot from forming.
Whatever the reason, the healing process can take weeks and be accompanied by serious discomfort, which is not always possible to eliminate on your own.
Symptoms
Dry socket syndrome is very painful. It is quite easy to identify if the following symptoms appear within 2-3 days after tooth extraction:
- inflammation of the gums, accompanied by severe pain;
- pain in the cervical region and ears;
- the appearance of bad breath;
- taste of pus in the mouth;
- partial hearing loss;
- general malaise
Visually, a dry socket is an empty depression at the site of tooth growth, first exposing the jawbone, and then turning into a reddened, purulent wound.
Normally, the socket is a cavity that, after tooth extraction, is filled with ichor. Over the next three days, the clot thickens, and light fibrin stripes appear on it - the beginning of the formation of new gum tissue. There may be slight soreness at the wound site. From 4 to 7 days, swelling gradually subsides, and the gums acquire their usual pink color. There is no pain.
Antiseptic rinses/baths –
Remember that you should not rinse your mouth vigorously during the first few days after removal, because... you can easily rinse the blood clot out of the socket. Food will constantly accumulate in a hole without a clot and rot there, causing inflammation and pain. It is better to replace rinses with baths (pour an antiseptic solution into your mouth, hold it and spit it out, or lightly “squelch” it).
When are antiseptic baths necessary?
- if the tooth was removed due to inflammation,
- an incision was made on the gum to expose the gumboil,
- if you have teeth with untreated caries or dental plaque, infection in which can lead to suppuration of a blood clot.
Antiseptic baths are best done with an aqueous solution of Chlorhexidine 0.05-0.12%. This drug has a pronounced antiseptic effect and is slightly bitter in taste. Baths should be done 3 times a day (keep the solution in your mouth for about 1 minute each time).
Causes of dry socket
There are several causes of dry socket. Some of them can be prevented by following simple recommendations regarding personal hygiene and caution. Causes:
- smoking. In this case, there is a decrease in pressure in the oral cavity, which can lead to the loss of the formed clot;
- neglect of oral hygiene;
- low blood clotting;
- taking oral contraceptives;
- mechanical damage to the hole itself or the tissues around it.
In addition to the above reasons, a dry socket can appear as a result of an incorrectly performed tooth extraction procedure. During a complex extraction, when the tooth had to be removed from the gums in parts. All rules recommended before and after extraction must be followed.
Causes of swelling after removal
Swelling of the mucous membrane in the area of removal in the gum area, as well as swelling of the cheeks, are also considered normal after wisdom tooth extraction. This is explained by tissue injury and the body’s natural reaction to the procedure. Normally, swelling increases the next day after visiting a dental surgeon, but then, if all recommendations are followed, it should subside.
If the swelling continues to increase, you should consult a doctor. The same applies to situations where, in addition to tissue swelling, there is increased pain, discharge from the socket, and increased body temperature. The listed signs indicate inflammation, which requires initiation of treatment.
The signs will be especially pronounced if there was already purulent inflammation at the time of visiting the dentist. In this case, even a correctly performed procedure, creating an outflow of inflammatory exudate, does not exclude an increase in tissue edema. When removing the upper tooth, swelling may spread to the orbital area. During surgery on the third molar of the mandible, swelling may extend to the neck and ear area. If after a day the symptom becomes less pronounced, we can assume that there are no complications.
In addition to increased swelling and pain, the following signs will be an indication for an emergency visit to the dentist:
- Discharge of pus from the socket.
- Bleeding.
- Pain when swallowing.
- Pain when trying to open your mouth.
- Swelling of the face, accompanied by redness of the skin.
It is unlikely that tissue swelling will be completely avoided, but the risk of complications can be reduced. It is enough to follow the doctor’s instructions, take prescribed medications and monitor oral hygiene.
Consequences
If during the first two days after tooth extraction pain appears, swelling does not subside and the temperature rises, then most likely these are signs of inflammation. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor, as dry socket syndrome can lead to serious complications. Such as:
- flux.
It begins to form when an infection gets into the hole. Characterized by severe swelling and pain. Requires immediate specialist intervention. - alveolitis
This is a deeper penetration of the infection - deep into the gums. Bacteria spread quickly and, if this process is not stopped in time, there is a risk of tissue necrosis. In this case, the losses can be very serious.
Attention!
The consequences of untimely or incorrect treatment can be irreversible. Do not neglect your doctor's advice. A wound on the mucous membrane is always a vulnerable area, subject to attack by bacteria and their rapid spread.
What to do if a tooth is removed
Stop the bleeding.
If you have had a tooth removed, your doctor will tell you in detail what to do in the first hours after the operation. For some time after the procedure, blood may flow from the hole. To stop bleeding, you need to place a cotton swab on the empty alveolus, bite it firmly and hold it there for 45 minutes. If bleeding continues, you should contact your dentist to prescribe a course of treatment after tooth extraction.
Do not injure the blood clot.
The blood clot that forms at the site where the tooth was is important for healing, so care must be taken to avoid traumatizing it.
The clot can be damaged by hard food, a toothbrush or a toothpick. Brushing your teeth is a must, but it should be done carefully. If oral hygiene is not maintained, the infection accumulates in the oral cavity and can cause pain and inflammation of the alveoli, which requires the doctor to prescribe treatment after tooth extraction.
Do not eat hot or cold food.
During the day you should not take very cold or hot food or drinks. Temperature changes lead to narrowing and dilation of blood vessels, which can cause bleeding from the socket. For the same reason, doctors do not recommend going to the bathhouse, taking a hot bath or shower. It is also not advisable to drink alcoholic beverages on the first day after a dental procedure.
Up to contents
Forms of alveolitis
Depending on the course of the complication, three stages are distinguished:
- Serous.
It makes itself felt
2-3 days
after tooth extraction. At this stage, pain occurs when eating, headache. Lymph nodes increase in size. - Purulent.
This is the next form that occurs after the serous one, if timely treatment is not carried out. Diagnosed a week after the tooth was removed. The pain becomes unbearable and is also felt in the head or ear. The hole becomes covered with a purulent, dirty yellow coating. There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth. Swelling and lymph nodes enlarge and become painful. Opening your mouth and eating food is extremely difficult due to pain. - Hypertrophic.
At this stage, it seems that the symptoms are subside: the condition is normalized, the temperature decreases. However, atrophied tissue grows, and when pressure is applied, pus is released from the inflamed wound.
If you notice any of the above symptoms, you should not self-medicate, but rather consult a dentist.
Types of inflammation
The most common types of inflammation that occur after tooth extraction are:
- Alveolitis is an inflammation of the walls of the empty socket of an extracted tooth. The patient suffers from swelling, redness, and “tugging” pain. Weakness, malaise appear, and body temperature rises.
- Gingivitis is inflammation caused by tooth extraction. The tissues turn red, begin to swell and bleed.
- Periostitis is an inflammation of the jaw bone (periosteum). The disease is characterized by severe toothache, swelling of the gums, gumboil, and distortion of the facial contour. Pathological mobility of the tooth appears, lymph nodes are palpated in the face and neck.
- Periodontitis is inflammation of the periodontium, the area around the root of the tooth. The disease is characterized by aching or sharp pain in the tooth, which intensifies when biting. Without treatment, the pain gradually turns into throbbing, tearing pain. The patient complains of severe weakness, fever, and sleep disturbances.
- Trauma to the gums from dental fragments. With mechanical damage to tissues, swelling, redness appear, and spontaneous pain begins, intensifying when touched. If the injury persists for a long time, a dark pressure ulcer with purulent and serous discharge may form at the site of injury.
Diagnosis and treatment methods
Diagnostics at a dentist's appointment will help confirm the symptoms of a dry socket. After an examination, the doctor will prescribe treatment. As a rule, it depends on the stage of inflammation. In the case of a mild form, drug treatment with antiseptics and anti-inflammatory drugs is possible. At the middle stage, you will need antibacterial therapy, as well as cleaning the hole from pus and filling it with an anti-inflammatory drug. All actions are performed under anesthesia. If necessary, antibiotics are prescribed.
At the third stage, the most advanced stage, the patient may need hospitalization and even surgical intervention. With proper care and no complications, the hole heals within seven days. And a month later there is no trace left of her.
What do doctors recommend?
For several days, it is necessary to rinse the oral cavity with an antiseptic solution, which will prevent the entry of microbes from the external environment through the wound surfaces of the gums. The number and duration of rinses is determined by the attending physician. Rinse solutions should be no cooler than room temperature and no hotter than 37 degrees. The simplest and most inexpensive option is a solution of baking soda (1 teaspoon per glass of water). In addition, rinsing can be done using pharmaceutical products.
Rinses from the pharmacy
| Iodine-containing products | Iodinol, yox (spray) |
| Chlorine-containing | Chlorhexidine, miramistin, eludril, |
| Nitrofuran | Furacillin |
| Based on hexetidine | Stomatidin, hexoral |
| Vegetable | Chlorophyllipt, calendula tincture, |
| Antiseptic lozenges | Faringosept, septolete, grammidin |
| Means to accelerate the healing of mucous membranes | Rotocan, dental paste solcoseryl, stomatophyte, propolis spray, sea buckthorn oil. |
| Infection Control Products | Antibiotics, bacteriophages (staphylococcal bacteriophage, pyobacteriophage) |
Features of wisdom tooth removal
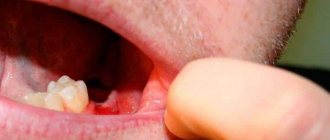
Dry socket after wisdom tooth removal is not uncommon. This syndrome occurs especially often in the lower jaw due to the fact that as a result of swallowing and opening the mouth, the muscles tense, aggravating the appearance of a dry socket and, as a result, alveolitis. Dry socket occurs in approximately 50% of cases
. Due to the anatomical features of the jaw, the blood clot often falls out.
When extracting a wisdom tooth, you must carefully observe precautions and resort to this procedure only in cases of extreme necessity. After all, the inaccessibility of the place complicates treatment.
Oral hygiene
It is not carried out on the first day to exclude infection and accidental injury. Chlorhexidine can be used almost immediately after tooth extraction, as it does not cause side effects; the main thing is to rinse carefully and according to the instructions. Further hygienic cleaning can be performed once a day with a soft brush, carefully avoiding the surgical area.
Floss is also used to remove food debris from between teeth and a warm saline solution is used to rinse the mouth after each meal. Do not forget about cleansing your tongue, as plaque also accumulates on it, in which bacteria actively multiply.
Removal of sutures after tooth extraction occurs on the 7th - 10th day. By this time, the wounds have already healed and restrictions on hygiene procedures are lifted. Cleaning is carried out twice: in the morning and in the evening.
Treatment of dry tooth socket at home
If the pain from dry socket inflammation is too severe, you can take painkillers. In the first two days, apply cold compresses to the inflamed side at intervals of 20 minutes, then change to warm ones.
Drink more fluids, especially water. It removes harmful substances from the body. Avoid alcohol.
Rinse your mouth with a salt water solution. This clears the wound of dead cells and relieves inflammation. But you should not apply pressure in the area of the hole - you can provoke the displacement of the blood clot. You should rinse your mouth after every meal and before going to bed.
You can also apply a drop of clove oil to the wound to relieve pain. Rinsing with sage and chamomile flowers, a decoction of burdock leaves and aspen bark, and anise infusion will also have a positive effect.
If after all the treatments the pain has not subsided, the swelling has not subsided, and your health has only worsened, then you should urgently consult a doctor. There is a high probability that the process of rotting has begun.
In the dental office, the doctor, under anesthesia, will clean the hole or prepare the gums - depending on the degree of neglect of the case. Fill it with antiseptic gel.
About the medicine
The medicine that is placed in the hole can be applied to a piece of gauze, which is subsequently inserted into the hole. In this case, after a certain amount of time indicated by the doctor, it needs to be taken out. This can be done either independently or during your next visit to the dentist. If this is not done in time, the process of putrefaction may begin, which will greatly complicate the situation. It is also not recommended to take out the gauze ahead of time, since food particles can get into the hole and the tongue can touch it, which will interrupt the healing process and also cause complications.
A hemostatic sponge with medication can be installed in the hole.
There is another way to install the medicine - in a hemostatic sponge. It already contains a medicine that helps disinfect the socket cavity and helps stop bleeding. You cannot take this sponge out - it will dissolve on its own. Most often this happens within 1-2 days, but in some cases the sponge may remain in the hole for 5-6 days. There is no need to be afraid of this. As a last resort, you can consult a doctor who will examine the wound and determine whether healing is proceeding normally.
Often the medicine in the sponge is very bitter, and this causes severe discomfort to the person. Unfortunately, nothing can be done about this, since getting rid of the sponge ahead of time is strictly contraindicated. To eliminate bitterness, you can drink sweet tea or juice.
- Why do my gums hurt after tooth extraction?
Remember ! No circumstances can influence the ability to remove the medicine from the hole ahead of time. After 3-4 days, the surface of the hole will heal, and you will no longer have to experience discomfort.
You cannot take out gauze or sponge with medicine on your own - this can cause complications.
People often wonder what kind of medicine is used for these purposes. Sometimes the gauze that is placed in the hole is treated with iodine - this will both disinfect the wound and prevent bleeding. The hemostatic sponge is already treated with a special substance consisting of boric acid, collagen and nitrofural, which helps stop the bleeding and protect the hole from various influences. But most often dentists use Alvozhil.
"Alvogil"
No other means are used for inserting into the hole.
Prevention
Preventing dry socket is always easier and cheaper than treating dry socket. To do this, you need to follow a number of preventive measures. Namely:
- If possible, limit physical activity for several days after tooth extraction;
- do not touch the removal site with your hands or tongue;
- do not chew on this side;
- eliminate the use of tobacco and alcohol;
- do not eat too hot, cold or spicy foods;
- It is advisable to grind food into puree.
Expert of the article Bolshakova Evgenia Vladimirovna Dentist-hygienist
More than 11 years of experience
How is the affected tooth removed?
The procedure itself should only be performed by an experienced surgeon and only when other treatment methods can no longer help. There are a number of reasons that can trigger the removal of an affected tooth:
- if the crown of the tooth is completely destroyed;
- when the patient is indicated for prosthetics;
- if complications arise during the eruption of a wisdom tooth;
- if filling requires perforation of the root canal.
A tooth can be removed for many reasons
Important ! There are cases when there is every reason to remove a tooth, but the patient has contraindications to this. In such cases, most often the intervention is carried out within the walls of a hospital with subsequent monitoring of the patient’s condition.
There are a number of main contraindications to surgical tooth extraction. These include:
- previous heart attacks;
- high blood pressure;
- arrhythmia;
- blood diseases;
- mental problems or neurological diseases.
There is a certain scheme for tooth extraction
If no contraindications have been identified in a patient who needs surgical removal of the affected tooth, then he is referred to the procedure itself, which should be carried out according to the following scheme.
| Stage | Description |
| Visit doctor | Before performing the procedure, the doctor must find out whether the patient has allergic reactions to any anesthetics, cardiovascular pathologies, or whether the patient suffers from hypertension. |
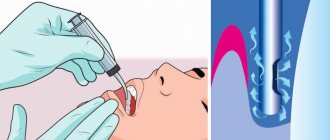
| Anesthesia | After all the necessary information has been obtained, the patient is sent for anesthesia. A fairly large number of different means are currently used to remove teeth. Their duration of action is from forty minutes to three hours. |
| Preparation | Next comes preparation for the intervention itself: in order not to injure the gum during manipulation, it first peels off from the tooth bone by at least five millimeters. This procedure is carried out using a special tool. The surgeon places special forceps on the tooth, and then begins to swing the tooth itself with them in order to destroy the ligaments attached to the jaw bone. |
| Removal | The affected tooth itself is pulled out, that is, extraction. After the affected tooth has been removed, the resulting hole must be thoroughly examined. This is necessary so as not to leave tooth fragments or a cyst in the wound cavity. If the extraction of the affected tooth took place in the presence of flux, then after its removal the gums are cut in the right place and the pus is released. After this manipulation, a drainage is inserted into the wound cavity. |
| Treatment | After the procedure is completed, you need to treat the wound itself. If pus is found at the site of the lesion, then in this case the hole must be washed with an antiseptic solution, and then an anti-inflammatory agent should be placed in the wound. If the hole itself is too large after extracting the tooth, then a suture is necessary. |
| Consultation | After the procedure has been completely completed, before discharge, the doctor must instruct the patient in detail on how to care for the hole during the healing period, and also prescribe any medications if necessary. |
After the tooth is removed and before the patient goes home, the doctor inserts a special medicine into the tooth socket. It is necessary to protect the wound from various influences, as well as for faster and more proper healing. Some patients complain that the turunda with the medicine interferes greatly, but this will have to be endured.
Important ! If you remove the turunda ahead of time, serious complications may develop, which will have to be dealt with not only by the dentist, but also by other doctors.
A special medicine is placed in the hole
The doctor prescribes exactly the medicine that is safe for every person. True, it does not have the most pleasant taste, but a person will have to ignore this factor if he wants the wound to heal as quickly as possible.
There are exceptional cases when it is simply impossible to remove the affected tooth according to the scheme above. The reason for this may be the following factors:
- How long does it take for drugs to leave the body?
- if the tooth root is crooked;
- if the bone tissue of the tooth is too fragile;
- if the crown of the affected tooth is already completely destroyed;
- if the figure eight is in a position of incomplete eruption or in a horizontal position.
If a patient who needs tooth extraction has any of these characteristics, then the intervention is performed in a different way. First, the gum is cut and peeled away from the bone. After this, the specialist drills out the desired area using a drill, which creates access to the root of the required tooth.
Important ! In some cases, the partitions between the roots of the tooth are sawed, after which each root is removed one by one.
In some cases, the tooth is removed differently
After such procedures, healing is more difficult and longer. Such an intervention may cause the patient to develop stomatitis. In many cases of such intervention, a secondary infection is attached to the affected area.
However, no matter which tooth is removed, medicine must be placed in the hole. This procedure is required.
Treatment in the clinic
The optimal solution for treating a diagnosis of dry socket or alveolitis is a visit to the dentist. It is better to go to the same doctor who performed the tooth extraction, since he already knows the course of the operation, did the diagnostics and remembers the characteristics of your body.
Whatever clinic you choose to contact, study its website, the doctors who work there and reviews.
At the RUTT dental center we use the latest equipment and advanced materials. The experience of our doctors is confirmed by numerous diplomas, certificates and awards. You can be sure that you will be in the hands of a reliable specialist.
Taking antibiotics after the procedure
Dentists quite often resort to antibiotics in the postoperative period, especially after tooth extraction. But not every patient who has undergone tooth extraction requires antibiotics. They are prescribed only in the following cases:
- Ear hurts after wisdom tooth removal
- if the patient experiences inflammatory processes in the gum area;
- if the patient is elderly;
- if complications arise during the operation or features of the anatomy of the teeth are revealed, which contributes to more extensive trauma;
- if the patient has a reduced immune system or suffers from any blood diseases.
Sometimes antibiotics are necessary
This list is not all the reasons for prescribing antibiotics in the postoperative period, because each individual case has its own characteristics. An experienced dentist will be able to easily determine which patient needs to take medications after tooth extraction. The doctor must determine the duration of administration and dose individually for each case. Most often, the course of taking the drug after tooth extraction lasts from five to seven days. In rare complicated cases, treatment can last up to fifteen days. It is simply impossible to determine the average dose of antibiotics that is needed, since each individual drug has its own individual characteristics.
Important ! It is strongly recommended not to take antibiotics unless prescribed by a doctor.
In addition to antibiotics, your doctor may also prescribe medications to normalize the microflora after taking antibiotics. The most commonly prescribed drug is Linex, but sometimes other drugs from the group of probiotics are also prescribed.
"Linex"