From this article you will learn:
- what is curettage of gums and teeth (video),
- methods of its implementation, reviews,
- What is flap surgery for periodontitis?
The article was written by a practicing periodontist surgeon.
Curettage is a surgical technique for the treatment of chronic periodontitis, which involves scraping out the contents of periodontal pockets. Its goal is to remove granulations, subgingival dental deposits, the epithelial lining of the pockets, as well as a layer of necrotic “cement” on the surface of the tooth root from the pockets. This is a fairly complex intervention that requires surgical skills and should ideally be performed only by a periodontal surgeon (oral surgeon).
There are 2 methods of this operation in dentistry. Closed curettage is a technique that is preferred for shallow periodontal pockets up to 4.0 mm (which corresponds to mild periodontitis). Open curettage is a more complex surgical technique, which is indicated in the presence of periodontal pockets with a depth of more than 4.0 mm, i.e. carried out for moderate to severe periodontitis. The open technique requires good surgical skills, because... During the operation, the gums will peel away from the bone tissue around the teeth.
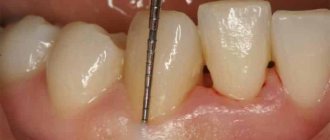
Closed curettage technique –
There is also an even more radical option for open curettage, which is called the term “flap operation” (we will also talk about this in more detail below). The following is a very important point. If the closed curettage technique has the right to be performed by ordinary dental therapists with advanced training in periodontics, then open curettage and flap operations can only be performed by dental surgeons or maxillofacial surgeons.
How to do curettage
Curettage is a surgical operation.
Plaque, stone, and pathological tissue are removed from the periodontal pocket. If necessary, osteoplastic surgery is performed. This is necessary if bone resorption has already begun. Curettage must be carried out in the treatment of periodontitis and periodontal disease, as this is one of the most effective methods for eliminating inflammation in the gums. According to the technology of the procedure, there are two types of it:
- Open;
- Closed.
General information about periodontal diseases
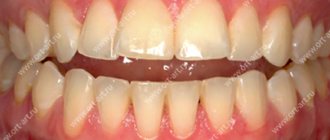
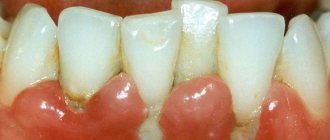
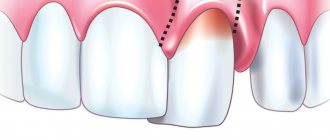
A brief excursion about periodontal disease and its diseases is necessary to understand why curettage is prescribed for certain problems with the gums. So, the tissues that surround the tooth and hold it in the alveolus are called periodontium. For a number of reasons, a pathological process may begin in them, which is a manifestation of gingivitis, periodontitis or periodontal disease (as an aggressive form of periodontitis). With gingivitis, the edge of the gum becomes inflamed, affecting only its mucous membrane. Without treatment, inflammation spreads to the deeper layers of the periodontium, causing deepening of the periodontal (gum) pockets (the gums peel away from the tooth). As a result, the dental unit becomes loose and its neck is exposed. This disease is classified as periodontitis.
Closed curettage
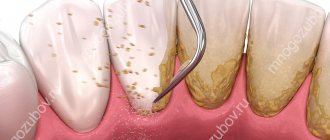
Can be used if the depth of the periodontal pocket does not exceed 5 mm, and pathological changes in the bones have not yet begun. When performing closed curettage, pathological tissues are exposed to ultrasound and hand instruments in the form of hooks, with the help of which granules are removed from under the gums. There is no cutting of the gums, so the procedure can be considered more gentle.
Flaws:
- The doctor performs the operation almost blindly; he does not see the subgingival space. Therefore, it is not possible to thoroughly clean the periodontal pocket in all cases.
- There is a risk of incomplete cleaning. Success largely depends on the experience of the dentist performing the procedure.
Due to its characteristics, closed curettage is suitable for mild to moderate periodontitis and periodontal disease. Sometimes it becomes the only possible method, since others cannot be used for some reason.
Alternative methods of performing the procedure
Removal of hard dental deposits in the pocket cavity can be done in various ways. A significant part of them can be classified as a closed type of operation, because their use does not involve any incisions in the gums.
Vacuum curettage in dentistry
The periodontal cavity is cleaned here with special curettes, which are connected to a vacuum suction device for separated particles from the treatment area. Fewer injuries and instant removal of tissue particles and plaque reduce the risk of complications and shorten the rehabilitation period.
Chemical
This technique uses various chemicals (particularly citric acid) to soften and then remove hard plaque particles. The solution has not only a cleansing and softening effect, but also an antiseptic, making it easier and with less damage to remove all excess from the gum pocket, while simultaneously disinfecting the cavity and reducing the likelihood of infection.
Ultrasonic
The method of destroying hard dental deposits using ultrasound requires the use of special equipment, for example, the Vector apparatus. Using ultrasound, as well as a water-air jet under pressure, it allows you to successfully remove hard plaque, although ordinary hand tools are also used for curettage.
Cryo method
The use of liquid nitrogen to remove various deposits and affected tissues is also practiced when treating periodontal pockets. Freezing also kills pathogens, reduces the risk of complications and makes the entire operation completely bloodless.
Laser
The most frequently asked question from patients is what is laser curettage of periodontal pockets? We answer: laser curettage is one of the most modern methods of cleaning gum pockets, its essence is that the laser beam heats the area of action to a high temperature, instantly burning out foreign inclusions and bacteria, while simultaneously closing the blood capillaries, preventing bleeding. This method causes less tissue trauma, does not require sutures, and shortens the recovery period.
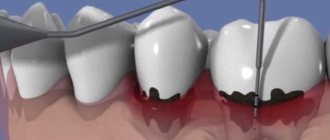
Open curettage
Used if the depth of periodontal pockets is more than 5 mm. This is a surgical intervention, but compared to a closed one, the effectiveness is much higher. Since open curettage requires cutting into the gums, the operation is performed under anesthesia.
Stages:
- The doctor cuts the gum and peels it away from the tooth. After exfoliation, the tooth root is completely exposed. The dentist gets full access to the bone tissue.
- Cleaning and antiseptic treatment. The roots are cleaned of accumulated plaque and stone and polished using a burr and special pastes. After this, the tissues are treated with an antiseptic.
- Osteoplasty. This stage is not always necessary. With advanced periodontal disease, bone resorption gradually begins around the teeth, which will lead to loosening and tooth loss. In order to restore the bone, osteoplastic material is implanted.
- Suturing. After plaque removal, the gingival flap is returned to its place and sutured. A bandage with an antiseptic solution is applied on top.
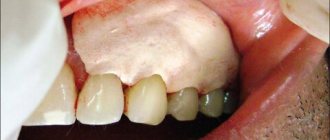
Open curettage is a more complex procedure, but more effective than closed curettage. The surgeon sees the entire subgingival space and has access to bone tissue. Therefore, the quality is very high; both plaque and granulation tissue are completely removed from under the gums.
If necessary, open curettage can be performed simultaneously with flap surgery. It is indicated if the gum tissue is loose and the gum contour is disturbed. Very often, with periodontal disease, the gums begin to overhang the teeth. This violates the aesthetics of a smile. During flap surgery, the dentist removes excess mucous membrane and then sutures the gum.
Indications and contraindications
Curettage of periodontal pockets is performed if the gum pockets (normally having a depth of no more than 2 mm) have deepened to 4 mm or more. In this case, other methods will no longer give the necessary effect and will not stop periodontal destruction and exposure of tooth roots.
Signs indicating the development of periodontitis and the need for this procedure can be considered:
- gum inflammation, bleeding,
- bad breath, discharge of pus from gum pockets,
- change in the appearance of the gums (swelling, darkening),
- tooth mobility.
At the same time, there are often cases when the gum looks normal at first glance, but a deep pocket has formed under it, requiring mandatory intervention. In order to determine this, an X-ray of the tooth is taken, which shows the formed pockets and periodontal destruction. After a comprehensive examination and exhaustion of other treatment options, the doctor may decide to perform a curettage. Contraindications to curettage in dentistry are relative. These are, as a rule, inflammatory processes in the acute stage, accompanied by copious discharge of pus, fibrous formations (scars) inside the pocket, a very large pocket depth (more than 6 mm), and severe loosening of the teeth. Some of these problems can be solved - for example, suppressing severe inflammation, splinting mobile teeth, etc. And after this it becomes possible to carry out curettage.
Rehabilitation
Curettage of periodontal pockets is a surgical operation, after which there will be a period of rehabilitation. Following the recommendations will speed up gum healing, make it less uncomfortable, and avoid complications.
Oral care rules depend on the method:
- Closed curettage. Immediately after surgery, you should not eat for several hours. On the first day, it is better to refrain from brushing your teeth with a brush and toothpaste, replacing it with rinsing. During the entire rehabilitation period, you need to monitor your diet - exclude solid foods and foods containing dyes. After curettage, there may be increased sensitivity of the teeth and gums. A special paste that your doctor will recommend will help you remove it. It is imperative to rinse your mouth with solutions of strengthening and anti-inflammatory medications.
- Open curettage. Since this surgery requires cutting into the gum, recovery takes longer. Recommendations for the first 1-2 days after surgery are the same as for closed curettage. It is very important to minimize the possible stress on the gums and teeth. It is advisable to reduce physical activity at first. Until the stitches heal, your mouth should be rinsed with solutions of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents. This will help speed up healing and tissue regeneration.
Possible complications
Complications can be caused by the individual characteristics of the body or violation of the doctor’s requirements. Increased tooth sensitivity can last up to two months. In order to speed up its regression, you will need to use special pastes and gels prescribed by your doctor. Swelling and hematoma at the surgical site may persist for up to 14 days. This is not dangerous and goes away on its own. In some cases, tightness and difficulty opening the mouth may occur, but this problem usually disappears within a few days. Teeth can remain mobile for up to 3 weeks. You must wait until the end of this period before returning to solid foods.
Flaws
Gum curettage is a simple dental operation with good results. However, it is not without its drawbacks:
- Traumaticity. Like any surgical intervention, curettage injures soft tissue.
- The need for anesthesia. Normally, the operation is performed under local anesthesia. Sedation or general anesthesia is used in extreme cases or when the patient is in panic.
- Rehabilitation. The gums heal quickly, but at this time it is necessary to follow the recommendations and take care of the oral cavity. Infection of the wound can lead to complications.
Curettage of gums in Krasnodar
In Krasnodar, you can undergo the gum curettage procedure at our Symmetry dental clinic. Our specialists have extensive experience and high qualifications, confirmed by many specialized diplomas and positive reviews from our patients. We have all the necessary modern, high-quality dental equipment.
Alternatives to curettage
Alternative technologies are suitable as prevention or in the early stages of pathology development. At the Zuub clinic they use:
- Comprehensive teeth cleaning. This is good prevention. It can be used as one of the stages of complex therapy, but not as an independent treatment. During cleaning, using ultrasound and a mixture of water, air and soda, tartar and plaque are removed from the surface of the teeth. You won't be able to empty your pockets this way.
- Treatment with the “Vector” device. A method for cleaning and disinfecting shallow periodontal pockets. In mild stages of periodontal disease, it can be used as an alternative to closed gum curettage, but it cannot replace open vector therapy. "Vector" is more effective than classic complex cleaning. It is based on a combination of exposure to an ultrasonic wave and a special suspension with abrasive particles. Since the ultrasonic wave is applied vertically, it penetrates deeply under the gum. In addition, ultrasound has a good disinfecting effect. Thanks to this, with a small depth of periodontal pockets and an undeveloped pathological process, it can give a good result.
The periodontist selects the gum treatment technology based on the clinical picture.
Come for a consultation with a dentist at the Zuub clinic.
What do oral care experts advise after the procedure?
Despite the fact that the closed curettage cleaning procedure does not require a gum incision, some rules of postoperative care must still be followed. Firstly, after the procedure you cannot eat for 2-3 hours, and you can brush your teeth only the next day. If there is swelling (in the first day), cold compresses should be applied (on the outside of the cheek). In the first week after the procedure, you need to exclude hot, spicy, and sour foods from your diet. If possible, stop (reduce) smoking. Secondly, you must carefully follow the recommendations of your doctor. He can prescribe medications, rinse the gums, perform applications and physical procedures.
Periodontist's note: only complex treatment can be effective in the fight against periodontal diseases. Performing curettage without subsequent treatment will bring short-term relief, then the pathological process will resume.
The dental network offers services for the treatment of periodontitis, including closed curettage. Contacting our branches has significant advantages:
- treatment by highly qualified doctors;
- compliance with treatment protocols and procedures that meet international standards;
- providing family and cumulative discounts;
- stable cost of services;
- Convenient daily work schedule.
You can contact any of the branches of our clinic in Moscow, located within walking distance from metro stations:
- Alekseevskaya (VDNKh district, etc. Mira), address: st. 3rd Mytishchiskaya house 3, building 2;
- Shelepikha, address: Shelepikhinskaya embankment, building 34, building 1.
Modern technologies help our doctors effectively perform closed gum curettage, and reliable anesthetics help make it painless. The high qualifications of our specialists serve as a guarantee of quality and safety. The health of your gums is in good hands!
What is a periodontal pocket?
Normally, the depth of the gingival groove - the depression between the surface of the tooth and the gum - should not exceed 2 mm. As soft plaque, consisting of food debris and gradually turning into hard deposits, is concentrated in it, a pathological focus is formed. This leads to deepening of the grooves and the formation of periodontal pockets, the presence of which provokes inflammatory processes and the development of caries.
In addition to solid deposits, the formation of pockets can be caused by:
- inflammation of periodontal tissues;
- bite defects;
- Gastrointestinal diseases, metabolic disorders;
- lack of solid food in the diet;
- hormonal imbalances and other factors.
Why do you need deep teeth cleaning?
The procedure for hygienic teeth cleaning with simultaneous root cleaning involves the removal of plaque, dental deposits and hard tartar not only from the visible part of the surface of the teeth, but also from the periodontal pockets and soft tissues surrounding the tooth. Deep teeth cleaning is an effective way to combat inflammatory diseases such as gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, plus a non-surgical, least traumatic and highly effective method of treating severe stages of gum pathology.
If you neglect the rules of oral hygiene and do not have your teeth and periodontal pockets professionally cleaned by a dentist, the periodontal pockets will deepen over time, resulting in the destruction of the bone tissue that holds the tooth and tooth loss. Learn more about the benefits of teeth whitening and teeth cleaning
Differences between methods
| Closed curettage | Open curettage |
| Trauma is low | Traumaticity high |
| Depth of gum pockets up to 5 mm | Depth of gum pockets from 5 mm |
| Duration (in a segment of 6-7 teeth) 1-2 hours | Duration (in a segment of 6-7 teeth) 2-3 hours |
| Efficiency high, subject to correct diagnosis and experience of the doctor | Efficiency very high |
| Recovery 3-4 days | Recovery 2-3 weeks |
| Price low | Price high |
Note! Closed curettage is effective only for shallow gum pockets at the initial stage of periodontitis. For moderate and severe stage disease, only the open method is indicated! But in the absence of a periodontist surgeon in the clinic, even with deep pockets, they can offer a closed technique, which is performed by a dentist-therapist who does not have proper knowledge in the field of periodontology. The procedure may improve the condition for a short time, but the disease will progress in any case, since the infection is not completely eliminated. Subsequently, you will get an aggravation, suppuration from the gum pockets and accelerated resorption of bone tissue.
We recommend that you carefully choose a clinic and doctor. Only an experienced periodontist can assess how affected the tissue is, make a correct diagnosis and select an effective method.
Medvedeva Tatyana Alexandrovna
Dentist-periodontist, 6 years of experience
Specialist in the diagnosis and treatment of gum diseases. Conservative, surgical, regenerative treatment. Microsurgical operations without pain under sedation.
More about the doctor