- What is maxillary sinusitis?
- Symptoms
- Complications
- Types and types of maxillary sinusitis
- How is maxillary sinusitis diagnosed?
- Treatment
- Etiotropic therapy
- Puncture
- "YaMiK"-catheterization
- Treatment of symptoms of maxillary sinusitis
- Surgical intervention
- Treatment at home
- Prevention
Maxillary sinusitis (from the Latin “sinus” and “inflammation”) is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the corresponding sinuses. The causes of this disease are various: allergies, rhinitis, diseased teeth, inflammation of the tissues around the teeth, injuries. Treatment includes conservative procedures, home remedies, and surgery.
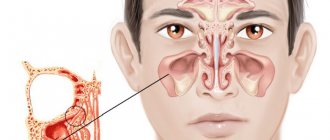
What is maxillary sinusitis?
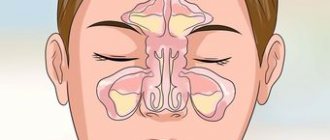
A person has several types of sinuses: frontal, sphenoid, maxillary and cells of the ethmoid labyrinth.
In each of these types, inflammation of the mucous membrane can occur. Then sinusitis will begin. Maxillary sinusitis is otherwise called sinusitis and is an inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. The maxillary sinuses were first illustrated by Leonardo da Vinci, and the disease itself was discovered by Nathaniel Highmore, a British surgeon and anatomist (he also described the maxillary sinuses in detail in his treatise of 1651). At that time, sinusitis was treated with home methods and heating.
Chronic rhinosinusitis
characterized by parietal thickenings caused by hyperplasia of the mucosa and partial fibrous changes in it. The thickness of the mucous membrane ranges from 4-5 mm.
Sinonasal polyposis, hypertrophic sinonasal rhinosinusitis. Non-tumor inflammatory swelling of the mucous membrane.
Recently, there has been an increase in the number of fungal sinusitis. Chronic forms occur under the guise of polypous recurrent sinusitis, the MRI picture is nonspecific, and laboratory diagnosis is difficult. There may be a change in the bony walls of the sinuses due to hyperostosis or destruction of the sinus wall as a result of prolonged pressure from the fungal body.
Types and types of maxillary sinusitis
Depending on the etiology (cause of occurrence) of the disease, rhinogenic, odontogenic, traumatic and allergic maxillary sinusitis are distinguished.
Rhinogenic sinusitis occurs against the background of rhinitis (when the nasal mucosa becomes inflamed). The mucous membrane is the main obstacle to infections. When bacteria gets on it, a runny nose or rhinitis develops. The causes of rhinitis are different: viruses, hyperthermia, allergies.
, decreased protective properties of the body, penetration of synthetic agents, influence of dry air, too long use of drugs with a vasodilator or vasoconstrictor effect.
Rhinitis is characterized by congestion, nasal discharge, impaired circulation in the nasal cavity, and the development of congestive blood phenomena. There are 4 types of rhinitis: allergic
, chronic, acute, vasomotor.
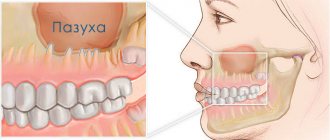
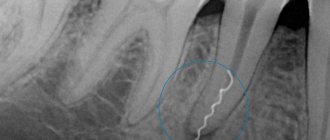
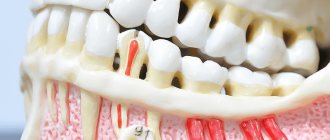
Odontogenic sinusitis occurs due to inflammation of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus due to infection from an unhealthy tooth, the tissues around it, and the communication formed between the sinus and the oral cavity after tooth extraction. Symptoms of this disease can be apathy, loss of appetite, headache, aching temples, discharge from the nose or ear, cough, runny nose and others. Depending on the course of the disease, different treatment methods are chosen: antibacterial therapy and washing of the maxillary sinuses, pumping out pus or surgery.
Injury to the maxillary sinus or jaw can also lead to sinusitis.
The cause of allergic sinusitis is the body's hypersensitivity to one of the irritants. The disease begins in the nasal cavity and then spreads to the maxillary sinuses. What usually serves as an allergen? This is pollen during the flowering period, fur and excrement of pets, dust mites, medicines, household chemicals, perfumes, cosmetics, chemicals, dirty city air.
According to the duration of the disease, sinusitis is divided into:
- acute (less than 3 months);
- recurrent acute (can repeat up to four times a year);
- chronic (more than 3 months);
- exacerbation of chronic sinusitis (adding new symptoms to existing ones).
According to the severity of symptoms, sinusitis is:
- lungs
- moderate severity
- heavy.
Diagnostics
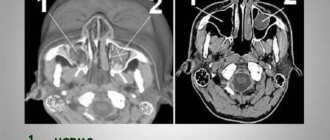
Physical and instrumental examinations together with radiation diagnostics (computer and magnetic resonance imaging) and a thorough analysis of the patient’s ENT complaints allow us to make the correct diagnosis. It is necessary to distinguish maxillary sinusitis first of all from trigeminal neuralgia, in which pain appears suddenly and is “burning” in nature. Sinusitis is indicated by the appearance of a strip of pus under the middle concha, after the introduction of vasoconstrictor drugs on the probe, or by the predominance of pain in the sinus area without nasal discharge.
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
How is maxillary sinusitis diagnosed?
When diagnosing a disease, it is necessary to collect a number of indications: find out about complaints, write down symptoms, analyze the patient’s medical history and conduct an examination (computed tomography, x-ray).
Possible symptoms: headache, temporal pain, nasal and ear discharge, accumulation of mucus in the back of the throat, intoxication (in severe cases).
The medical history should contain information about past illnesses, injuries, hypothermia, etc.
The examination usually consists of palpation and percussion in the area of the paranasal sinuses, and also includes pharyngoscopy and rhinoscopy.
Mycetoma
non-invasive fungal sinusitis of the left maxillary sinus
The hypointense MR signal of a mycetoma may be mistaken for air in the paranasal sinus; Non-invasive fungal sinusitis does not look the same in different sequences.
If they are large, they cause headaches due to the pressure of the cyst shell on the walls of the sinus.
Often combined with allergic rhinitis, hypertrophy of the nasal turbinates and deviated nasal septum
Large cysts located in the lower parts of the maxillary sinus may be asymptomatic, while a small cyst located on the upper wall, in the area of the 2nd branch of the trigeminal nerve, can cause headaches.
Mucocele of the ethmoid labyrinth and frontal sinus on the right
This is a large formation of the paranasal sinus, lined with epithelium and filled with mucus, which is formed as a result of obstruction of the main sinus canal.
The most typical symptom: expansion of the paranasal sinus with smooth, clear contours with thinning and remodeling of the adjacent bone plate.
Treatment
Etiotropic therapy
Prescribing antibacterial agents (the main causative agents of acute sinusitis) helps to achieve rapid results in therapy:
- β-lactams: amoxicillin, clavulanate, cefaclor, cefuroxime axetil, sulbactam;
- fluoroquinolones: levofloxacin, gatifloxacin, moxifloxacin;
- macrolides: azithromycin, clarithromycin.
Puncture
This method is used if the disease cannot be cured with medication. It is the most famous method for removing pus from the maxillary sinuses. Quite painful, unlike other procedures.
"YaMiK"-catheterization
A fairly effective remedy in the fight against maxillary sinusitis, it does not cause complications. The procedure is quite painful, like puncture; patients cannot always tolerate it well.
Important: the operation is not advisable for isolated lesions of one paranasal sinus, since infection can be introduced into healthy paranasal sinuses.
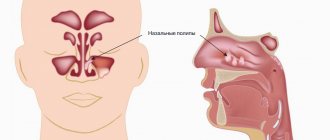
Why are polyps of the maxillary sinuses dangerous?
The insidiousness of the disease is that small polyps do not cause any inconvenience. They grow slowly, without arousing suspicion for years. In our practice, there are situations when they are discovered by chance on a computer tomogram during preparation for treatment, extraction or implantation of teeth. And this is a great success for the patient; timely treatment can be undertaken at the initial stage without radical methods.
Otherwise, the polyps gradually grow, causing inconvenience to the point of blocking breathing . A worried patient runs from one ENT doctor to another. But the hope for a high-quality, timely examination in the clinic is weak; an appointment for a computed tomography scan of the sinuses can be waited for months. And standard drug treatment prescribed without the necessary diagnostics does not help. It is good when a doctor refers a patient to a specialized institution, even at the expense of his own reputation.
Initially, polyps are benign formations, but they are prone to degeneration into malignant ones . Sometimes there is a decrease in size, but these are rare cases. Therefore, when they are detected, you need to keep the situation under control. The best solution to the problem is removal of polyps to eliminate oncological problems.
Treatment of symptoms of maxillary sinusitis
Symptomatic treatment of sinusitis includes topical decongestants (such as xylometazoline and oxymetazoline) that improve sinus ventilation, mucolytics (such as carbocysteine) that improve mucus secretion, topical antiseptics (miramistin and others) and irrigation therapy (such as nasal douches). , before using which you need to use vasoconstrictor drugs), which flush out mucus and kill microbes in the sinus cavity, topical glucocorticosteroids, combined drugs (non-steroidal and anti-inflammatory drugs - paracetamol, ibuprofen).
Among the most effective drugs for treating the symptoms of sinusitis are
Sialor based on silver ions . It has an anti-inflammatory effect and prevents the proliferation of bacteria. Thanks to the mild action of the drug, the balance of microflora is maintained and favorable conditions are created for the regeneration of the nasal mucosa.
Surgical intervention
Drug treatments are not always effective; sometimes it is necessary to resort to surgery. At the same time, both approaches to diseased sinuses (extranasal, endonasal, combined), surgical technologies (magnifying devices and lighting devices), and surgical methods differ.
Important: after sinusitis, patients should be periodically (at least once every 3 months) observed by an otolaryngologist.
Treatment at home
An option for treating maxillary sinusitis at home is steam inhalation, which improves blood circulation, thins mucus accumulations, and also improves the flow of medications from the blood. But in acute cases of maxillary sinusitis, this method is dangerous; it can provoke generalization of the infectious process.
You can do inhalations with a decoction of herbs (calendula, celandine, bay leaf, string of sage, chamomile). Add alcohol tincture of propolis (1 teaspoon per 0.5 liter of decoction) and a couple of drops of iodine to boiling water.
In addition to such inhalations, you can also breathe over boiled potatoes. Important: you need to breathe for 10 minutes every day, the course is a week.
Warm the nose with table salt in a bag, boiled with an egg, and a blue lamp. Rinse the nose with the following solution: 1 teaspoon per glass, furatsilin (2 tablets), herbal decoctions (sage, celandine, chamomile). The procedure can be repeated up to 10 times a day.
The most common (58-90%) is squamous cell carcinoma.
1. are asymptomatic for a long time, under the guise of inflammatory changes, especially in the absence of destruction of the walls 2. quickly spread to neighboring structures and by the time of recognition, infiltrate several areas 3. it is difficult or impossible to establish the original site of tumor origin 4. extremely rarely metastasizes to distant organs and tissue 5. it is not possible to clearly define the boundaries of the lesion 6. MR semiotics: tissue formation, spread to surrounding tissues, bone destruction
If bone structures are damaged - the hard palate and the alveolar process of the upper jaw, it is necessary to undergo an additional radiological examination - X-ray CT, which clarifies the presence or absence of bone destruction.
Detection of tumor tissue against the background of soft tissue structures - the pterygopalatine and infratemporal fossa, masticatory muscles, soft tissues of the cheek, as well as the spread of the tumor to the frontal and sphenoid sinuses, the ethmoidal labyrinth intracranially requires MRI (with contrast enhancement). In addition, MR imaging is indispensable in the differential diagnosis of postoperative or post-radiation changes with relapse or continued growth.
Thus, in order to exclude a pathological process and begin treatment on time, it is necessary to undergo a complete radiation examination.
Folk remedies
Subtotal darkening of the maxillary sinuses can be treated using traditional methods. Medicines based on medicinal plants are also used in the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract. For this purpose, saline solutions, drops, and compresses are used.
The only contraindication is an allergic reaction to the components of the drug.
For young children under 1 year of age, traditional treatment methods should be used with caution so as not to provoke the development of an allergic reaction.
Mustard oil
Rhinitis and sinusitis can be treated with mustard oil. To do this, the oil must be slightly heated, but the temperature must be comfortable so that when the oil is instilled into the nose, the mucous membrane does not burn.
Place 3-4 drops of oil into each nasal passage 2 times a day. The oil has anti-inflammatory and antiviral effects, and also reduces swelling of the nasal mucosa.
Garlic
Garlic has antibacterial properties and can be used to make drops for the common cold. To do this, you need to take 2 cloves of garlic, pass through a press, place in gauze (folded in several layers) and squeeze out the resulting juice.
Then add 3-4 tbsp to the garlic juice. l. water or 2 tbsp. l. olive oil. This must be done so that garlic juice does not lead to a burn of the mucous membrane.
For the first use, 1 drop is instilled into each nasal passage. If no allergic reaction subsequently occurs, then you can instill 2-3 drops into each nasal passage for 7 days.
Such drops are prohibited for use by children. Since the mucous membrane in children has a more immature structure compared to adults. Instillation of such drops may cause burns.
In addition to drops, garlic can be used as an air disinfectant. To do this, the garlic is first peeled and cut into small pieces. Garlic is laid out on plates and placed at different ends of the room. Since garlic is a natural antiseptic, its action will deactivate viruses and bacteria that are released by a sick person.
Propolis solution
To treat sinusitis, use a propolis solution. To do this, take a 10% alcohol solution of propolis. Before use, dilute a small amount with water so as not to irritate the mucous membrane. You need to instill 1-2 drops into each nasal passage for 7 days.
Due to the alcohol content, this method of treatment is contraindicated for children.
Aloe juice
Aloe is used not only to treat inflammatory diseases, but also to prevent viral infections.
For this purpose, drops can be prepared from aloe juice. To do this, take aloe juice and mix it with water in a 3:1 ratio. If such drops are indicated for a small child, then the proportion is 5:1. You need to instill 2-3 drops into each nasal passage for 10 days.
Black radish
Any compresses are prohibited in the phase of acute inflammation, as well as at elevated body temperature. A black radish compress is effective in reducing swelling of the mucous membrane.
To prepare such a compress, you need to take one radish, peel it and grate it. Then you need to mix with vegetable oil and heat slightly. Apply the prepared pulp to the sinus area for 10 minutes. You can use thin cloth or gauze for this purpose. The course of treatment with this remedy is no more than 7 days.
Sea salt
A hypertonic sea salt solution can be purchased at a pharmacy, or you can prepare it yourself at home.
For this purpose, you need to take ½ teaspoon of sea salt and dissolve its contents in a glass of warm water. Then you need to draw the required amount of solution into a sterile syringe and rinse each nasal passage one by one. It is recommended to rinse your nose with saline solution up to 5 times a day.
Children need to rinse their nasal passages by instillation. Until the age of 3, the nasal passages should not be washed with sprays or a syringe. Since a strong stream of solution can promote the advancement of microorganisms to the auditory tube. Since the auditory tube in children is short, this can cause otitis media.
If a subtotal darkening is observed on the x-ray of the maxillary sinuses, this means that a pathological process has begun in them. In some cases, a number of additional diagnostic procedures may be required to clarify the diagnosis.
Symptoms of a maxillary sinus cyst
A cyst of the maxillary sinus does not have specific symptoms in the early stages; the first complaints appear when the tumor grows significantly (15 mm or more). The intensity of growth is an individual indicator for each patient, as is the severity of symptoms.
The main signs of a cystic formation in the maxillary sinus:
- Chronic nasal congestion on the affected side;
- Bursting sensations in the cheek area (closer to the eye);
- Persistent headaches, poorly controlled by analgesics;
- Accumulation of mucus at the back of the throat (especially in the morning);
- Intermittent mucous or clear nasal discharge;
- Frequent sinusitis with purulent discharge from the nasal passages;
- Pain when pressing on the causative tooth, redness and swelling of the gums;
- Facial asymmetry with pain in the anterior wall of the sinus.
Infection of the sinus by the odontogenic (that is, through the tooth) route most often develops in sinuses with a wide bottom and deep protrusions of the alveolar process into the jaw. The filling of the sinus with air is important - with moderate pneumatization, the risk of cyst formation is less.
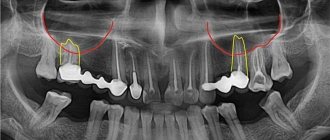
During a diagnostic examination, the doctor identifies a hole in the bottom of the sinus. With an exacerbation of odontogenic sinusitis, sharp-smelling purulent masses are released from the nose, and upon rinsing, crumbly-granular white inclusions are found. An x-ray, as a rule, confirms the diagnosis of a maxillary sinus cyst, after which the doctor draws up a treatment plan.
Make an appointment
Types of operations
If a cyst of the maxillary sinus is detected, it will not be possible to limit oneself to therapeutic measures alone, but there is still a prospect of saving the tooth. The treatment of cysts is carried out by a dentist surgeon, who, based on the clinical picture and instrumental examination data, selects a surgical intervention technique:
- Cystectomy is an operation involving excision and curettage of the entire cyst cavity, followed by suturing;
- Cystotomy is an operation to excise the anterior wall of the tumor, and the doctor communicates the posterior wall with the oral cavity.
Indications for a specific technique are determined individually and depend on the type of cyst, the size of the neoplasm, and the number of teeth involved in the pathological process. Conservative treatment is possible only in the absence of obvious inflammation, it takes 3-4 months, but during this time the tumor can grow with the appearance of complications. That is why surgical opening of the sinus is considered the most reliable method of treating maxillary and other types of cysts.
Treatment of maxillary sinus cyst
Surgical activities carried out by a dentist in the clinic are aimed at:
- Relief of the inflammatory process;
- Elimination of the source of infection in the oral cavity;
- Removal of the root of a tooth with a cyst or extraction of the entire tooth;
- Sinus scraping, antiseptic treatment;
- Closing the communication between the oral cavity and the sinus;
- Creation of drainage for the outflow of liquid contents through the nasal passage.
First, the doctor determines which tooth caused the inflammatory process in the sinus, and the roots of several teeth may be affected. Using radiographs, the size of the sinus and the location of the cyst are analyzed, and the type of anesthesia is selected (usually local anesthesia with the latest generation of drugs). The surgeon will make every effort to save the tooth if possible. With shallow immersion into the cyst cavity, tooth-preserving operations (for example, root resection) show a good effect. When a tooth is immersed more than 1/3 of its length inside the tumor, it is recommended to remove it in order to prevent relapses of the disease.
The “Smile Factor” uses biocompatible modern materials to fill the cavity of the maxillary cyst, ensuring accelerated tissue regeneration. This tactic allows you to restore the jaw bone in a safe way; the prognosis for the intervention is favorable.
The protocol for working with the paranasal sinuses also includes a consultation with an ENT doctor. Treatment is considered successful when clinical symptoms of the disease disappear and there are no pathological changes in bone tissue on control radiographs.
Rehabilitation, features of care
After surgery, slight discomfort persists for 10-14 days. The turundas are removed from the nasal passages on the third day, and the sutures are removed after a week. Swelling, pain, difficulty breathing are temporary phenomena due to the specifics of the operation and do not require separate therapeutic measures. After removing the tampons from the nose, you should carefully follow the doctor’s instructions regarding rinsing the passages with antiseptics. Antibiotic therapy and instillation of vasoconstrictor drugs are prescribed.
During the first month after surgery it is recommended:
- Sneeze and cough gently with your mouth open;
- Follow a gentle diet with a predominance of soft foods;
- Limit intensive nose blowing;
- Avoid active facial movements;
- Postpone visiting the bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool;
- Do not go under water (even in the bathroom);
- Temporarily limit sports training;
- Sleep with the head of the bed raised on a comfortable pillow.
After treatment, you should visit the dental clinic once every 3-4 months throughout the year. During examinations, the attending physician monitors the progress of recovery, preventing relapses.
Possible complications
Treatment of a maxillary cyst should be carried out exclusively in a properly equipped clinic. Home measures to “resolve” the tumor are ineffective, and in many cases they contribute to the accelerated growth of the cyst due to improper actions by the patient.
Failure to contact a dental surgeon in a timely manner can result in serious consequences:
- Spread of the pathological process to healthy teeth followed by their loss;
- Penetration of infection into other air sinuses of the skull;
- Melting of the bone by purulent masses with the occurrence of osteomyelitis;
- Visual impairment, “double vision” due to compression of the eyeball by the cyst;
- Pronounced facial asymmetry with very large sinus tumors;
- Pathological fracture of the maxillary bone due to tissue thinning;
- Exhausting headaches, respiratory dysfunction, chronic malaise.
The most serious complication of a maxillary sinus cyst is considered to be the spread of inflammation to the membranes of the brain and the brain itself, which is extremely dangerous for the patient’s life.
Preventive actions
The following measures will help prevent the occurrence of a maxillary cyst and minimize the risk of complications with existing tumors:
- Sanitation of the oral cavity with competent treatment of teeth and gums;
- Timely treatment of ENT diseases (rhinitis, etc.);
- Correction of a deformed nasal septum;
- Treatment of allergic rhinitis;
- Early seeking medical help at the first symptoms of the disease.
Smile Factor doctors have modern techniques for treating jaw cysts of any size. Particular emphasis is placed on the painlessness and safety of the intervention, which is achieved by using proven drugs and consumables.
The patient receives competent advice during the rehabilitation period, so that recovery proceeds with maximum comfort. The exact price of treatment for a dental cyst is determined by the amount of work, type of surgery and other factors.
Diagnosis of polyps in the maxillary sinuses
During the examination, the main thing is to carry out a differentiated diagnosis to exclude other ENT diseases accompanied by similar symptoms
Upon visual examination, an increase in regional lymph nodes and swelling of the tissues in the area of the maxillary sinuses are observed.
X-ray examination in our Center is performed
on a computed tomograph in ENT mode .
Allows you to assess in detail the condition of the paranasal sinuses, determine the location and size of polyps. In difficult or controversial situations, the following may additionally be required:
- Videoendoscopy for examination of the nasopharynx and nasal cavity
- MRI to detect purulent fluid in the nasal appendages
- Bacteriological culture
How is recovery going?
Rest assured that we will not keep you at the Center unnecessarily
No hospitalization
Even in advanced cases with complex localization of polyps, the operation takes no more than 2-4 hours. Waking up after medicated sleep is not accompanied by deterioration of the condition and pain. The use of low-traumatic treatment protocols and the accumulated experience of doctors allow us to perform the operation as carefully as possible in relation to you. Hospitalization with an overnight stay at the clinic is not required .
For elderly patients with chronic cardiovascular diseases, a postoperative recovery service is provided in a day hospital for several hours under the supervision of an anesthesiologist. In any case, you will spend the night at home, in a familiar environment.
Inpatient recovery is necessary if general anesthesia was used, which often leads to complications, weakness and exacerbation of chronic pathologies. If a patient is offered a hospital stay for several days, this means that the clinic does not have modern equipment and qualified surgeons, or they are “squeezing” money out of you.
Branded rehabilitation on the day of treatment
The author's accelerated rehabilitation program ensures complete elimination of unpleasant consequences in the form of swelling, hematomas, muscle spasms, and pain.
Medicines to take home
After the operation, you will receive a free set of necessary medications to avoid purchasing counterfeit products. You don't have to run around pharmacies looking for the right medication in your postoperative condition.
The package with medications contains instructions with recommendations in the postoperative period. Please follow them to avoid complications.
The mechanism of changes in the structure of the mucosa
Thickening of the mucous membrane develops gradually, especially in patients whose immunity is not weakened. When the maxillary sinuses are affected, the damage begins with the development of swelling of the mucous membrane, as well as blocking of the ducts through which mucus is excreted.
Thickening of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses
These secretions cannot be removed through the ducts, so the swelling intensifies, which worsens the patient’s condition. Pressure increases in the sinuses, which leads to the formation of cysts and polyps. If, before the development of edema, pathogenic microorganisms enter the sinus cavity, pus is formed when the ducts are blocked and the mucous membranes swell.
This development mechanism is observed in most cases. When the pathological process is mild, there are no microorganisms in the cavity, which reduces the likelihood of complications.
Symptoms of the disease
Often small polyps do not cause discomfort to patients. But, large or multiple, they can block the nasal passages, leading to breathing problems, decreased sense of smell, and recurring respiratory infections.
Most common symptoms:
- chronic runny nose;
- persistent deterioration in breathing through the nose;
- decreased or absent sense of smell;
- violation of taste sensitivity;
- facial pain, pain in other parts of the head;
- a feeling of heaviness, discomfort in the eyes, facial walls of the sinuses, head;
- snore.
Operation stages
Complex treatment is carried out in 1 day, we strive to combine all activities in one visit
- Preparation The operation is performed only after professional hygiene and sanitation of the oral cavity, and re-treatment of compromised dental roots. Sterility ensures there is no risk of infection.
- Removal Surgery according to the selected protocol for accessing the sinus with putting the patient to sleep with the simultaneous administration of an analgesic. Performed in a sterile operating room.
- Control X-ray examination CT after surgery is mandatory - to assess the quality of the operation performed and the condition of the maxillary sinus.
If a tooth with an inflamed root was removed, which provoked the growth of a polyp, after the operation the orthopedist will install a temporary orthopedic structure. You will never leave our Center without teeth.
On days 10-14, the sutures are removed and a control CT scan is performed. The patient is invited for a preventive examination and a convenient date for the visit is agreed upon.
Interpretation of the radiograph
The presence of exudate in the nasal sinuses indicates the presence of an acute inflammatory process, and thickening of the walls of the nasal sinuses and narrowing of their lumen may indicate chronic inflammation.
Subtotal darkening of the maxillary sinuses
A horizontal fluid level may indicate inflammatory diseases of the maxillary sinuses (sinusitis).
Subtotal darkening with an upper horizontal level in the area of the maxillary sinuses may indicate sinusitis.
If the darkening is localized in the frontal sinuses, then this indicates the development of frontal sinusitis.
To diagnose tumors, radiography with a contrast agent is performed. This helps to better see the location of the tumor and its size. When contrast is introduced, tumor formations “absorb” the pigment and become more visible.
Why you should entrust treatment to the ENT department of dentistry
70% of patients who turned to us for help were previously treated in city clinics with many drug courses and traumatic operations in the form of sinus punctures. But, unfortunately, such methods are not able to get rid of polyps. A tumor in the paranasal sinuses can only be eliminated through surgery.
ENT dentistry is a comprehensive approach to the treatment of tumors in the maxillary sinuses. It combines two areas - otolaryngology and dentistry, allowing you to combine options for dental and ENT treatment .
Intervention in the maxillary sinuses requires highly qualified and trained physicians. Only a maxillofacial surgeon with ENT training can cope with such a task without complications . In addition, special high-tech equipment is required.