With a wide variety of offers from dental clinics about a full range of services, it is worth knowing which doctor can perform tooth extraction and visiting only such specialists.
Every person at any age needs dental treatment, and sooner or later it becomes necessary to have a tooth removed. Our price in Dolgoprudny for this type of service is optimal, taking into account the availability of many drugs for pain relief and the work of real professionals. Often, in search of a specialist who can perform this manipulation, patients end up with inexperienced doctors. This can lead to complications. And only then, having understood the issue, it turns out that not every dentist actually has the right to carry out such manipulations. Therefore, if it is necessary to remove a tooth, price should not be a fundamental factor in choosing a doctor; it is important to know who exactly you need to contact.
Specializations in dentistry
There are different areas in dentistry, but they are all united by one task - maintaining the health and proper functionality of the dental system. The basic area is therapeutic dentistry, but there are other highly specialized areas.
For example, the tasks of a dental therapist include primary diagnosis, treatment of teeth and gums without the need to use highly specialized skills. Most often this is the prevention and treatment of caries and pulpitis, gum inflammation or, for example, tongue diseases. Along with the therapist, other specialists also work on the health and beauty of our smile:
- periodontist – works with diseases of gum tissue, periodontal and periodontal tissues,
- orthodontist – helps to correct the correct bite and straighten teeth,
- orthopedist – restores damaged and missing teeth by using various prosthetic methods,
- hygienist – specializes in the prevention of dental diseases, carries out comprehensive oral hygiene with the removal of plaque, supra- and subgingival deposits,
- a surgeon, including an implant surgeon, performs complex operations on the mucous membrane and jaw bone, implants implants, etc.
There are different directions in dentistry
. Important! Separately, we can distinguish a pediatric dentist who specializes in the treatment of temporary baby teeth and diseases of the oral mucosa in children.
A dental surgeon is a doctor who removes teeth. However, if a simple extraction is required, a general practitioner can successfully cope with this task. Many people also confuse an orthodontist and an orthopedist, but these are two completely different specializations. As mentioned above, the first one works with anomalies of the dental system - it is he who supervises the correction using orthodontic plates, braces and other corrective systems. As for the orthopedist, he is engaged in the restoration of teeth using removable and non-removable prosthetic devices - starting with crowns and ending with the installation of complete dentures on the entire jaw, including implants.
So, the surgeon is the same doctor who pulls out teeth. To understand the issue in more detail, we will consider possible indications for extraction and features of the procedure.
What does an orthodontist treat in children?
The list of orthodontic diseases, pathologies and anomalies is extensive. These are not only bite defects, but also many other deviations - congenital, hereditary, acquired. The most common problems people come to dentistry for are:
- teeth;
- dentofacial rows;
- bite
Pathologies and dental anomalies
When assessing individual units of a child’s jaws, a pediatric dentist or orthodontist will pay attention to the developmental features of each individual tooth:
- shape - classic or spiky, screwdriver-shaped, barrel-shaped, with deformations of the cutting edge line;
- dimensions - reduced or increased compared to neighboring units;
- tissue structure - normal teeth, underdeveloped condition, excess tissue volume;
- timing of appearance - according to the age of the child, early eruption or late;
- position in the jaw row - rotated, tooth growth from the side of the lip or from the side of the palate, excessive protrusion from the gums, growth in place of another tooth.
Also, the pediatric orthodontist will note the number of teeth in a row - edentulism or the presence of supernumerary teeth.
Almost all of the problems listed are solvable. Modern dental methods can quickly and painlessly change the positions of teeth, reverse pathologically located units, help quickly remove excess teeth and perform prosthetics in the absence.
Anomalies of the dentition
What does the pediatric orthodontist treat in this case? Problems of the dentition are more serious for dental health than single anomalies of growing units. Incorrect position of the jaws affects the quality of speech, creates difficulties in nutrition, and worsens the aesthetics of the face.
The most common problems relate to:
- The size of the jaw rows is excessive growth of one of the jaws compared to the second or a delay in development in both rows.
- The position of the jaw relative to the base of the skull is asymmetry, forward or backward displacement.
- Consistency and symmetry of the arrangement of teeth - poor contact when closing, crowding, rare position, large gaps between units.
Anomalies of bite, occlusion
Pathological bite is the most common problem among young patients. The orthodontist will successfully correct the bite
- distal - the upper dental row is highly developed and protrudes forward;
- mesial - excessive development of the lower jaw is observed;
- cross - when the teeth are closed, the upper dental row intersects with the lower one;
- deep - the upper incisors completely cover the lower ones;
- open - the teeth are only partially connected.
There are many pathologies, and the doctor’s task is to make the correct diagnosis and select the correct treatment.
In what cases is tooth extraction prescribed?
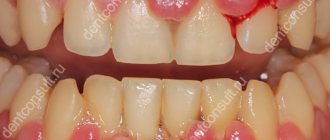
Such a radical measure is usually resorted to in cases where it is no longer possible to save the causal element. As part of the procedure, the doctor carefully removes the tooth along with the root. Moreover, it is important that this is done extremely carefully, with minimal trauma to the surrounding bone tissue and mucous membrane. Thus, the procedure is prescribed if the following indications exist:
- pronounced mobility with destruction of periodontal bonds as a result of the development of periodontitis, periodontitis or the formation of an extensive cystic formation,
- serious injury with root fracture,
- complete destruction of the crown with inflammation of the root,
- problematic eruption of eights (wisdom teeth),
- the need to correct the bite in case of severe crowding - in such a situation, it is sometimes necessary to remove one or more healthy elements in order to restore the aesthetics and functionality of the entire jaw apparatus.
Extraction may be prescribed for a severely damaged tooth.
Timely extraction saves from the uncontrolled spread of the inflammatory process to healthy mucosal tissue and neighboring teeth. To avoid the development of complications after the procedure, it is important to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations. In the future, it will be possible to fill the gap in the series with the help of a bridge or prosthetics on an implant - the second option is more preferable.
Dentistry
The phrase dentist appeared in Russia in 1710. Before this, no one had treated the teeth; they were gradually destroyed . If a tooth started to hurt badly, it was simply pulled out. Thanks to Tsar Peter I, dental schools appeared. Only a hundred years later a decree was issued prohibiting practicing medicine without a diploma.
Gradually, dental faculties began to appear at universities. Dentistry began to develop rapidly as a science. There is a need to pay more attention to diseases of the oral cavity. Already at that time, people needed specialists with extensive knowledge in this field of medicine. Over time, the phrase dentist has become less common. It has been replaced by the word dentist. What's the difference?
In a modern college you can get an education and become a dentist after 3 years if you have a diploma. Such a specialist can work and treat teeth, but with some restrictions. For example, he will not be able to treat:
- pulpitis;
- correct bite;
- engage in complex prosthetics;
- do anesthesia.
In fact, many people do this in practice. Mainly in small settlements where there are no necessary specialists, the dentist is forced to provide assistance to people without having the right to do so by law. Essentially, he performs the functions of a dentist.
Abroad, a dentist is called a dentist . They receive education in secondary medical educational institutions. Few specialists abroad have a diploma of higher medical dental education. Mostly such specialists are found in large cities, and not in small towns.
How the procedure is performed - extraction options
First, the specialist must examine the oral cavity, select the appropriate anesthesia method and extraction method. In some cases, due to an acute inflammatory process, removal is postponed until the next appointment. In the meantime, the doctor prescribes the patient a course of antibiotics to relieve acute symptoms and normalize the condition.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia. If a patient has a strong, overwhelming fear of dental treatment (dental phobia), deep sedation may be offered to relieve anxiety. In rare cases, the procedure is performed under general anesthesia, but recently experts are more often giving preference to deep sedation as a safer and no less effective alternative.
To extract a tooth from its socket, the doctor may use one of the following techniques:
- simple extraction: using special forceps, the surgeon grabs the crown and then carefully removes it along with the root. Incisors, canines and molars are first rotated, double-rooted molars are swung,
- complex – if the tooth needs to be extracted in parts or the remaining root must be removed. The doctor has to saw the crown and root system, cut out the root using different attachments for a drill, make incisions on the gum if the element is impacted,
- atypical - first, the specialist makes a trapezoidal incision on the surface of the gum and peels off a flap of the mucous membrane to open access to the alveolar socket. Next, he saws the crown and roots with a bur and then carefully pulls them out piece by piece. By the way, the same technique is relevant for cases of fracture of the root apex1.
For simple removal, the doctor uses special forceps.
After removing the tooth from the socket, the specialist carefully cleans the wound from small fragments, treats the tissue with antiseptics and places a sterile swab in the socket. If necessary, applies sutures or fixes the drainage system to ensure the outflow of purulent masses. Finally, the patient receives explanations on how to care for the socket after removal. You can read more about them in our special article.
Postoperative care
Dentists at the Granova Clinic recommend adhering to the following rules:
- After tooth extraction, you should not eat for the first 2 hours. After this, you can only eat warm, not hot, food for 24 hours, because hot foods can cause bleeding.
- After tooth extraction, the mouth should not be rinsed. For difficult removal, rinsing can be useful, but not on the first day, and the rinsing agent should be selected by a doctor.
- For a week after removal, it is recommended to refrain from physical activity and stop drinking alcoholic beverages and cigarettes.
- The postoperative wound should not be touched.
Features of complex extraction
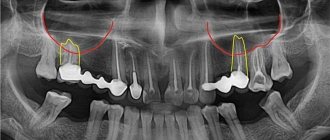
First, the doctor conducts a visual examination and palpation, studies x-rays and uses them to assess the condition of the bone tissue and periodontal tissue. Only after a thorough examination of all aspects of the clinical picture can a specialist make a final verdict. Based on the same X-ray image, he determines the number of roots, the shape and depth of their occurrence, and assesses the complexity of the work ahead.
Further, the procedure in most cases is carried out according to the following scheme:
- the surgeon makes an incision on the mucosa to provide direct access to the cervical area,
- if it is necessary to separate the teeth, the doctor saws the crown and root system, after which he literally saws it out of the bone tissue in order to remove the tooth in parts,
- then he lowers special forceps to the very edge of the alveolus, clamps the instrument, fixes it and, carefully twisting or rocking the tooth, removes it from the socket,
- the flap of tissue is returned to its place and sutures are applied.
Complex tooth extraction is a full-fledged operation.
As mentioned above, the procedure can be performed both under local anesthesia and with additional deep sedation. And only in exceptional cases is the use of general anesthesia allowed.
Indications for visiting a dentist
If something hurts or bothers you in your mouth, this is a direct indication for visiting a dental office or dental clinic. The primary examination will be carried out by a therapist, and then, depending on the clinical picture and symptoms, he will either conduct treatment himself or refer the patient to the appropriate specialist.
Treatment with a therapist will be required if the following symptoms occur:
- Sensitivity of teeth to thermal effects, to sour and sweet foods has arisen.
- Spots or depressions, so-called carious cavities, appear on the enamel.
- Uncomfortable sensations appeared in the process of chewing food, closing the jaws, sudden “shots” of pain or constant pain.
Indications for visiting a hygienist:
- Visually noticeable hard yellowish formations are tartar at the border where the gum adheres to the tooth.
- Changes in enamel color - darkening, yellowing, appearance of spots of different colors.
Indications for visiting an orthopedist:
- Destruction of the tooth crown by more than 40%.
- Congenital or acquired disorders of the appearance of teeth, their shape, size, structure.
- Injuries to teeth due to the formation of cracks and chips.
- Wide interdental gaps.
- Pigmentation of dentin due to age-related changes or hemorrhage.
- The absence of one tooth, several or complete edentia.
- Impaired diction, the cause of which is some kind of dentofacial anomaly.
Indications for visiting an orthodontist:
- Curvature of the teeth, their incorrect position in the dentition, especially in combination with non-closure of the lips.
- Incorrect closure of the dentition.
- The lower jaw protrudes forward and overlaps the upper jaw.
- Crossbite.
Indications for visiting a surgeon:
- Destruction of the crown due to advanced caries, fracture, dislocation of a tooth without the possibility of its preservation and restoration due to injury or accident.
- Severe toothache that does not subside even after taking painkillers.
- If your wisdom teeth are bothering you.
- Irregularly positioned or difficult to erupt teeth.
- Injuries, damage, diseases of the soft tissues of the oral cavity or jaw bones.
Indications for visiting a periodontist:
- Any disturbances in the structure and function of the gums - bleeding, looseness, pallor, redness or cyanosis, swelling, pain, hypertrophy. The appearance of a whitish, serous plaque on the gums. Ulceration of the gum edge, its detachment from the tooth enamel (exposure of the parts of the tooth that are under the crown - neck and root), necrosis of periodontal tissue.
- A feeling as if the tooth has become taller or a visual lengthening of the tooth without mobility.
- Unpleasant, putrid odor from the mouth.
- Lack of periodontal and gum pockets.
- The formation of first spaces, then gaps between the teeth.
- Mobility, displacement, loss of healthy teeth.
- The above symptoms are accompanied by general malaise and enlarged lymph nodes in the neck.
Important! You should also contact a dentist if there is absolutely nothing bothering you. Preventative examination 1 or 2 times a year in combination with professional hygienic teeth cleaning at the same frequency are the best methods for preventing any oral diseases.
to contents ^
Treatment of complications with the growth of figure eights
The most common complication with the growth of figure eights is pericoronitis
(formation of a gum hood). When a molar erupts, it is forced to overcome many obstacles: the jaw bone, periosteum, and periodontal tissue. During long, complex eruption, a specific mucous canopy (hood) is formed over the molar. Bacteria and food particles penetrate under it, which causes inflammation.
If coronary artery disease is not treated, the consequences will be serious, the inflammation will spread to the periosteum and jaw bone. This is fraught with the development of periostitis, osteomyelitis, tissue suppuration with the formation of phlegmon, cysts, and fistula tracts. Nearby tissues may be affected, and inflammatory ENT pathologies (otitis media, sinusitis) may occur.
Treatment of pericoronitis is surgical and involves excision of the mucous hood. The operation opens access to the growing eight. The doctor removes the affected tissue, carefully treats the surgical area, and evaluates the clinical picture. According to the situation, he decides whether to remove the eights or help the molar to erupt completely, taking the correct place in the row.