Periostitis is a purulent inflammation of the periosteum, the tissue covering the bone of the upper or lower jaw. Over time, the inflammation spreads to other tissues of the oral cavity , and a painful and unpleasant abscess can grow on the gum.
Periostitis is of two types: acute and chronic . the acute one , it goes on very quickly. Inflammation is manifested by asymmetric swelling of the cheek on the side of the diseased tooth and enlargement of the lymph nodes, and an increase in temperature is observed. Chronic periostitis can pass without obvious symptoms, while negatively affecting the condition of the child’s teeth, destroying them from the inside. The chronic form often occurs due to untreated acute periodontitis, pulpitis or due to injury.
Why is periostitis dangerous?
It is impossible to delay the treatment of periostitis , as this can lead to very dangerous consequences:
• acute purulent periostitis – it is manifested by swelling and hardening of the gums, tooth mobility, and increased body temperature. The child's appetite and sleep deteriorate. In this situation, the baby urgently needs medical attention and hospitalization;
• and dentia - the inflammatory process can quickly spread into the bone tissue, damage the rudiments of permanent teeth and destroy them. In the future, because of this, a tooth will not be able to grow .
• f legmon – inflammation of the tissues located under the skin, accompanied by severe swelling, thickening and suppuration. If not treated in time, it can cause blood poisoning.
Symptoms of the disease
The reaction develops rapidly; signs of angioedema in children are swollen lips, neck, and face. The upper torso, hands, feet, and genital area are often affected. Quincke's edema is visible in the eyes of a child - the eyelids swell on one or both sides.
- When the tonsils are affected, the picture is similar to a sore throat.
- Edema of the larynx is indicated by a hoarse voice, difficulty breathing, a gusty cough, blue discoloration and then gradual paleness of the skin.
- Swelling that appears in one area may occur in another. This mainly applies to large-scale swelling.
- When the mouth and tongue swell, speech becomes difficult.
- If the process is localized in the gastrointestinal tract, the child may complain of tingling of the tongue, followed by diarrhea and vomiting, and sharp pain in the intestinal area.
- Rarely, swelling of the meninges occurs. With it, the child cannot fully tilt his head forward, complains of a headache, and behaves inhibited. Convulsions and vomiting may occur.
- If only the skin is affected, joint pain, fever may appear, and the child may lose consciousness.
The pathological condition can last from an hour to several days.
How does angioedema begin in a child?
Immediately after contact with the allergen, the listed symptoms increase sharply. This happens in a matter of minutes. Source: G. I. Smirnova. Urticaria and Quincke's edema // Allergic diseases in children. Ed. M.Ya. Studenikina, I.I. Balabolkina. M.: Medicine, 1998: 279-287 If you press on the swollen area, the child will not experience pain, but you will feel a dense swelling, on which, after pressing, there will be no characteristic depression.
Signs of periostitis in a child:
• aching or nagging pain in a tooth or gum. Moreover, painful sensations intensify with any touch (including during meals);
• redness and swelling of the gums;
• when a lump appears above or below a tooth;
• o tech cheeks;
• enlargement of the lymph nodes (usually on the side where the source of inflammation is located);
• bad breath ;
• elevated temperature . It may not be present, but even if the temperature is normal and other symptoms are present, the child must be taken to the doctor;
• capriciousness and lethargy of the child.
The tooth does not hurt, but the cheek is swollen - the causes of the pathological condition
Very often, swelling is a consequence of an allergy to materials used for filling, prosthetics and treatment of dental units. In addition, the clinical situation may be associated with the body's reaction to food, pollen, dust or pet hair. In this case, the swelling does not have a clear localization and can spread to the area of the nose, lips and eyes. .
It should be understood that after the removal of a tooth, nerve or dissection of the gum, swelling and pain are considered normal and can persist for a week after the intervention. You should also exclude respiratory and viral pathologies accompanied by enlarged submandibular lymph nodes (mumps, pharyngitis), high body temperature, and chills.
Another reason is bruises and injuries to the face; in addition, the cheek may swell due to neurological disorders, for example, inflammation of the nerve. The problem is indicated by pain in the throat and parotid region, hearing impairment, facial expressions and diction.
The appointment includes consultation and drawing up a treatment plan with cost determination
sign up for a free consultation
Not ready for an in-person consultation with a doctor? Ask your question by phone
Causes of periostitis:
• of thorough oral care Small children do not yet know how to properly take care of their teeth, so plaque and food debris accumulate in the gum pockets, which can cause inflammation;
• injury to the gums . Children, especially toddlers, love to put almost everything in their mouths. Foreign objects can not only injure the gums, but also introduce harmful microbes into the wounds;
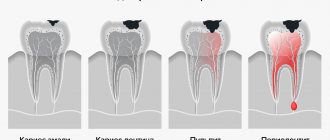
• to caries and its complications . Baby teeth are more vulnerable, so any defect can cause infection;
• angina , tonsillitis . _
What are the main treatments for cheek swelling?
The ATLANTIS DENTAL medical center has created ideal conditions for the diagnosis and treatment of dental diseases of any complexity. If you find that your cheek is swollen, you should urgently visit a doctor. Experienced therapists and surgeons will quickly and painlessly eliminate the problem, which will avoid unwanted complications.
- During the consultation, the doctor collects anamnesis, performs a dental examination, and prescribes diagnostic measures (x-rays, CT scans, blood tests, etc.).
- If necessary, the patient is referred for consultation to specialized specialists: neurologist, otolaryngologist, endocrinologist, etc.
- Based on the results of the examination, a treatment regimen is determined.
- When cystic neoplasms, pulpitis and inflammation of the periosteum are detected, surgical intervention is necessary.
- It may also be necessary to remove the tooth or refill the canals.
Good results are shown by treatment with antibacterial drugs, rinsing the mouth with antiseptics and applying dental gels to the affected areas.
Treatment of periostitis
The main thing to remember is that you cannot try to treat periostitis on your own . There are several actions that absolutely cannot be performed while waiting for a doctor’s appointment, so as not to aggravate the disease:
• apply hot compresses , rinse with soda or drink hot drinks and decoctions. Heat will only increase swelling;
• give painkillers , and even more so antibiotics;
• try to cut the abscess yourself .
Which doctor should I contact?
If you have a swelling of the cheek, you should first consult a dentist.
If the cause of the swelling is not dental, your doctor will refer you to other specialists:
- see a therapist for bacterial and viral infections;
- see a neurologist for neurological diseases;
- to an ENT specialist for inflammation of the ear and salivary gland;
- see a nephrologist for kidney pathologies;
- see a traumatologist or maxillofacial surgeon for trauma to the lower jaw.
Read also: Why does my ear hurt?
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with an allergist-immunologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1950 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT) - maintenance course (excluding the cost of the drug) | 8100 rub. |
What to do?
First of all, you need to make an appointment with a dentist and conduct an X-ray examination, as a result of which you can determine the true cause of the tumor, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe an individual treatment plan. Most patients are prescribed antibiotics or antiseptic drugs. Do not forget that treatment with traditional methods, which promise a quick recovery and supposedly relieve symptoms in a couple of hours, is not acceptable, since it can cause even more harm and lead to irreversible consequences. As a last resort, to relieve pain and reduce swelling, you can rinse your mouth with warm and clean water, but under no circumstances drink hot drinks or massage the sore spot.
In especially severe and advanced cases, surgical intervention will be required: a dental surgeon in Minsk makes an incision in the gum, removes pus, and, if necessary, removes the diseased tooth. All operations are performed under anesthesia, but sedation will be more effective in this case, allowing treatment to be carried out while you sleep. While the patient sleeps peacefully, without feeling discomfort or pain, all procedures are carried out as accurately and quickly as possible. It is safe for the body and is often used even in pediatric dentistry.
undergo dental treatment under anesthesia using drug sedation at the Minsk Family Dentistry Center. High-level specialists, modern equipment that meets European quality standards, affordable prices and an individual approach to each patient - we guarantee high-quality treatment without pain and complications. But you can only maintain the beauty and health of your teeth through joint efforts, so don’t forget about prevention: regular teeth cleaning, dental checkups at least once every six months, as well as timely treatment of oral diseases - together we can create the perfect smile!
Swelling in the cheek area, causes
The most common dental causes of cheek swelling are:
- advanced caries;
- complication of pulpitis;
- complication of gingivitis;
- periostitis, periodontitis and other diseases of teeth and gums.
If you suspect flux, call: 8 (495) 558-88-77
Flux is inflammation of tissues of various origins, for example, periostitis, an inflammatory process in the periodontal gap - periodontium. Such inflammation can occur in acute and chronic forms; the chronic form can periodically enter an exacerbation phase and then subside again.
By origin, periostitis is as follows:
- infectious;
- non-infectious;
- spicy;
- chronic;
The main role in the development of flux of infectious origin belongs to microorganisms, as well as their toxins. Microbes penetrate into the periodontium through the root canal, periodontal pocket, as well as through the blood or lymph flow.
Most often, flux is caused by an infection that enters through the root canal and is a consequence of acute diffuse and chronic gangrenous pulpitis, as well as pulp necrosis.
Microorganisms and their toxins, penetrating into periodontal tissue, cause dangerous acute inflammation
Non-infectious periostitis/periodontitis (fluxes) can develop as a result of trauma (blow, bruise, periodontal trauma after pulp extirpation, sharp, uncomfortable biting on a tooth; cracking nuts, gnawing bones) or chronic microtrauma (smoking pipe, brass band instruments, biting threads, pressing on the tooth with a pencil, pen, etc.); also as a result of the influence of medications - the ingress of potent substances into the periodontium during the expansion of root canals (trilon B, aqua regia), their sterilization (formalin, silver nitrate, etc.) and in the ingestion of arsenic paste.
Causes and risk factors
The mucous membrane of the child's oral cavity is often injured. The appearance of ulcers can be caused by temperature effects (hot food and drinks), biting the inner surface of the cheeks or lips; damage by sharp edges of the filling, braces or the tooth’s own tissues in case of chipped enamel. Normally, the immune response allows the pathological process to be quickly eliminated, the mucous membrane heals, and bacteria do not have time to cause severe inflammation and ulceration.
Weakened children's immunity cannot cope with this task, which leads to the development of aphthous stomatitis. A small number of opportunistic bacteria that populate the oral cavity begin to actively multiply. Often the disease occurs against the background or as a result of a severe infection: influenza, ARVI, acute tonsillitis, infectious mononucleosis, etc.
Main risk factors:
- food allergies, allergic reactions to hygiene products, such as toothpaste;
- deficiency of vitamins and microelements due to a strict diet or impaired digestion of food;
- hereditary predisposition;
- foci of infection in the oral cavity: caries, chronic periodontitis, periodontitis, gingivitis;
- frequent respiratory diseases;
- severe systemic diseases: pathologies of the endocrine system, blood vessels, metabolic disorders, etc.
Ask a Question
First aid
call an ambulance immediately . Doctors may decide on emergency hospitalization if the patient has difficulty breathing, a swollen tongue, or symptoms indicating intestinal damage.
What to do before the doctors arrive?
First aid, which should be provided at the first symptoms of angioedema in children, involves clearing the airways, checking breathing intensity, heart rate, and blood pressure. Sometimes it is necessary to perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation, so after the first case, parents are recommended to take first aid courses. At the final stage, medications should be administered to the child.
First aid equipment includes:
- glucocorticosteroids (“Prednisolone”, “Dexamethasone”);
- antihistamines;
- adrenalin.
Sequence of administration: adrenaline, then glucocorticosteroid, then antihistamine. If the reaction is moderate, then adrenaline is excluded.
| Adrenalin | It is injected intramuscularly into the thigh (middle third outside) at the rate of 0.01 mg for each kg of the child’s weight. If there is no effect, then the injections are repeated every 15 minutes. |
| Glucocorticosteroids | Injected intramuscularly into the buttock or intravenously. You can pour the medicine from the ampoule under the tongue - this way the effect will come faster. The dosage of Prednisolone is from 60 to 150 mg, Dexamethasone is from 8 to 32 mg. |
| Antihistamine | Intramuscular injection is preferable. It is possible to take a pill, but the effect will come later. The dosage depends on the medicine. For example, “Loratadine” – 10 mg, “Cetrizine” – 20 mg. |
Important! In case of swelling of the larynx, a tracheostomy is performed urgently.
Complications of flux
Complications with these localizations of phlegmon can be much more severe than with superficially located purulent foci with clear local manifestations. It is especially important to emphasize the danger of developing phlegmon of the floor of the mouth, taking into account the probable anaerobic component of the microflora.
Therefore, if there are complaints about difficulty swallowing, an increase in the volume of the tongue, its pushing towards the hard palate, a forced position of the head, you should urgently seek help from a dentist in order to avoid the development of the most common complication with this localization of phlegmon - anterior mediastinitis.