Publication date: 09/28/2020
How to remove bad breath? Effective, time-tested methods
- "Culprits" of bad breath
- What to do to eliminate unpleasant odor?
- Express methods
- Medicines
- Herbal breath fresheners
Bad breath is always an obstacle to communication with others. Therefore, the problem should be urgently eradicated so that it does not become the cause of psychological disorder and the appearance of complexes in a person. But first you need to find out what became the source of bad breath. Indeed, in most cases, halitosis indicates that serious disruptions are occurring in the body.
Bad breath: physiology or disease?
Bad breath
in medical language it is called
halitosis
. There are physiological and pathological halitosis. Bad breath often appears in the morning. During the night, bacteria and their metabolic products accumulate in the mouth, which causes a bad odor. This type of halitosis is physiological and can be eliminated by simply brushing your teeth. Physiological halitosis also includes odor caused by eating a number of foods, such as garlic, onions, cabbage. This smell will disappear on its own as soon as the substances that caused it are eliminated from the body. But it also happens that an unpleasant odor is not eliminated using hygiene procedures; in this case, most likely, it is of a pathological nature.
Diagnostics
To get rid of an unpleasant metallic taste and eliminate the iodine odor, it is very important to establish the root cause that provoked this phenomenon. If the symptoms appear constantly and are stable, it is necessary to undergo a full comprehensive examination at a medical center, based on the results of which effective and adequate treatment will be prescribed.
Consult with a therapist, endocrinologist, dentist, gastroenterologist. To make a diagnosis, the results of serological, microscopic, biochemical studies (tests for the hormone TSH), ultrasound diagnostics, and fluoroscopy are taken into account.
Bad breath: causes
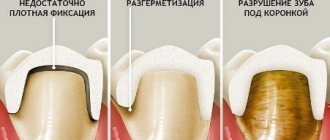
The most common cause of unpleasant odor is the active activity of pathological bacteria in the oral cavity. Diseases such as caries, periodontitis, pulpitis, periodontitis, gingivitis, stomatitis, as well as the formation of tartar can lead to persistent bad breath.
The second place among the causes of unpleasant odor is dry mouth (the medical term is xerostomia
). Mica, which moisturizes our mouth, has bactericidal properties. It kills bacteria, neutralizes their waste products, rinses and cleanses the oral cavity. If there is not enough saliva produced, bacteria are activated, resulting in an odor. Dry mouth can be a consequence of illness or taking a number of medications. It can also be caused by age: over time, the salivary glands begin to work less intensively, the composition of saliva changes, and its antibacterial properties are lost.
The smell can also be caused by ENT diseases: sore throat, chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis, runny nose.
Another cause of unpleasant odor is diseases of the internal organs. It can be:
- renal failure;
- liver failure;
- gastric diseases (gastritis, stomach ulcer);
- lung diseases.
Smoking is also a cause of persistent bad breath. The smell is caused by substances contained in tobacco smoke and deposited in the oral cavity. The only way to eliminate the unpleasant odor in this case is to quit smoking.
What causes excess iodine in the body?
Iodism is a pathological condition in which adverse reactions occur from exceeding the safe level of iodine in the human body. According to doctors, the dose of this substance should be 4-5 times higher than the daily norm. In addition, adverse reactions appear only from the absorption of iodine in a short period of time. For a healthy adult, the norm is 200–1000 mg. In children, it should not exceed 200 mg. It is important to consider the child’s age and health status. In the first years of a baby’s life, the immune system is weak and susceptible to any irritants. With the transition to artificial feeding, and then to solid food, the baby’s body receives a large number of different microelements in large and unusual volumes. Among them is iodine.
Iodomarin poisoning can occur if the dose does not correspond to the child’s weight
If a child has been eating solid food for a long time, one option for signs of iodism to appear is to eat fatty fish, oysters, shrimp and other foods rich in iodine. The causes of this pathological condition can also be caused by factors not related to the intake of a particular food.
These include:
- long stay on the sea coast (rest or simple walks);
- taking medications that contain iodine;
- disruptions of the gastrointestinal tract caused by Klebsiella bacteria.
Lots of seafood can cause iodine odor
What is bad breath like?
Peculiarities of odor can indirectly indicate the source of problems.
Hydrogen sulfide smell
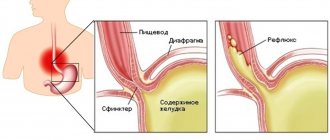
(the smell of rotten eggs) indicates rotting protein substances. This smell is typical for digestive problems. A persistent hydrogen sulfide odor may indicate gastritis with low acidity or a stomach ulcer.
Sourish smell
and a corresponding taste in the mouth is noted with gastritis with high acidity. This smell may appear at an early stage of the disease, when other symptoms are not yet present.
Bitter smell
and the taste in the mouth is typical of liver and gallbladder diseases. An additional symptom is the appearance of a yellow coating on the tongue.
Smell of acetone
and the accompanying sweet taste in the mouth is a characteristic symptom of diabetes.
Urine smell
from the mouth indicates a disease of the genitourinary system (primarily the kidneys or bladder).
Stool smell
from the mouth can occur due to intestinal diseases (dysbacteriosis, intestinal dyskinesia, intestinal obstruction).
Putrefactive
bad breath is typical for dental diseases (inflammatory processes of teeth and gums).
Consequences of poisoning and possible complications
Poisoning with iodine-containing substances can end in failure, even death, which occurs due to swelling of the larynx and lungs; a person simply cannot breathe. Possible consequences of poisoning include complications in the respiratory system: pneumonia, bronchitis; complications in the kidneys - nephritis.
In case of illness, with the manifestation of the smell of iodine when breathing, the life-supporting functions of the body are disrupted. Noted:
- Decreased vision;
- Retardation of consciousness;
- Weakening of the immune system;
- Liver problems, pain in the right hypochondrium.
Liver problems in humans
Bad breath: what to do?
The fight against bad breath begins with careful adherence to good oral hygiene. If the source of the odor is bacterial activity, proper brushing of your teeth will help. Teeth should be brushed not only from the outside, but also from the inside, and also treat the chewing surface of the teeth. The brush angle should be 45°. Using dental floss, hard-to-reach areas between teeth are treated. If your teeth are in poor condition, simply brushing your teeth will not solve the problem. You will need to visit a dentist and remove tartar, and if your teeth have caries, cure them. It is recommended to visit the dentist at least once or twice a year.
It is also necessary to combat dryness of the oral mucosa. If you feel dry mouth, take a few sips of water and rinse your mouth. However, it should be remembered that frequent dry mouth can be a symptom of serious diseases. However, like the unpleasant smell itself. Therefore, if you have persistent bad breath, you should definitely see a doctor and undergo an examination.
Treatment with folk remedies
It happens that the patient cannot be taken to the hospital, and a quick response is required. You should rinse your stomach at home. Then stock up on vegetable oil, milk, flour, starch to continue treatment. An adult patient should drink milk and water mixed with oil. Starch and flour are diluted to a paste and eaten. The sooner they enter the stomach, the less serious the consequences will be for the patient. Do not be alarmed if the water used to lavage the patient's stomach turns blue. If you have beets in the house, the juice of the vegetable can be used as an absorbent substance.
Herbal treatment
To relieve the effects of poisoning, take 20 g of elecampane, add 200 milliliters of boiling water, infuse under a closed lid for 20 minutes and take 1 tablespoon 4 times a day.
Take 2 tablespoons of the herb - knotweed, pour it into a thermos, pour half a liter of boiling water. Leave for an hour or two, drink the decoction three times a day, half a glass.
Pour boiling water over chamomile and its inflorescences and leave, cool and take half a glass orally during the day.
Diagnostic tests
A child's stale breath, which smells like iodine, can lead to a lot of questions from parents. Concerns about the reasons for the appearance of such signs and uncertainty about the risks to the baby’s health indicate the need to consult a specialist. Most often, worried parents go to the pediatrician. After listening to complaints, the doctor most often redirects the patient to an endocrinologist. The first thing this specialist will do is collect anamnesis from the words of the parents (or child). After receiving the information, the endocrinologist will proceed to an external examination of the patient. Based on its results, the specialist determines the need to conduct certain studies.
If there is a suspicion that the specific odor of iodine from the mouth is caused by one or another pathology, the child may be referred for an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland. A set of laboratory tests of blood, urine and stool may be required. A blood test is taken to determine the level of the pituitary hormone, and a urine test is taken to determine the amount of iodine in its composition.
In the last few years, the “aes-isap” method has been used to diagnose iodism.
Manifestations of iodism on nails
It involves testing the patient’s nail plate for iodine content. Its quantity is determined by the length of the light flux that the microelements emit. It can only be detected using special atomic emission spectrometry equipment.
Child's diet with elevated acetone
If a child’s high acetone level has already manifested itself, the child cannot be forced to eat, because in order to digest food, the body requires energy, the source of which is glucose. During an acute condition, the child must be fed in small portions. A diet with high acetone may include porridge with water, crackers, a baked apple, and cereal soup with vegetable broth. If a child has high acetone, the diet should not be a complete absence of food. This maintains acetone in the blood so the child does not have to go hungry. However, even after an acetonemic attack, a healthy diet is recommended for a week.
The high acetone diet is as follows:
- provide small and frequent meals (5-6 times a day);
- exclude fried, spicy and fatty foods from the menu as much as possible;
- Concentrated meat broths are not recommended; bone-based broths are strictly prohibited;
- increase the amount of consumed vegetables and fruits that have undergone heat treatment;
- introduce porridge into the diet;
- increase the amount of lactic acid low-fat products;
- ensure a stable drinking regime (at 1-2 years - about 1 liter of liquid per day, at 3-7 years - 1.2 liters, over 8 years - up to one and a half liters per day).
What can you feed
What to feed a child with high acetone? From the second day after the attack of high acetone, a child with high acetone can eat:
- porridge: rice, buckwheat, oatmeal, corn;
- vegetable broth soups;
- lean meats: rabbit, turkey, beef;
- lean fish;
- fresh vegetables: carrots, potatoes, cucumbers, cabbage, radishes, onions;
- berries and fruits: grapes, watermelon, apricot, peach, plum, pear, sweet apples;
- nuts;
- dried fruit compote, jelly;
- sugar, honey (in reasonable quantities);
- biscuits, crackers.
What not to eat
If acetone is high in children, it is recommended to exclude foods and dishes that increase the level of blood ketones:
- fatty meats: veal, pork;
- offal: liver, kidneys, heart, tongue;
- some types of fish: sardines, anchovies, sprats, cod;
- rich broths;
- mushrooms, cabbage, tomatoes, legumes;
- citrus fruits, kiwi;
- fat sour cream, cream;
- sausages, frankfurters, smoked meats;
- products containing cocoa;
- sauces: mayonnaise, ketchup, etc.;
- chips, sparkling water, fast food.