The first reaction of parents who notice that their child is growing a second row of teeth is natural fear. In dentistry, it is generally accepted that there are two causes of pathology:
- abnormal growth of molars;
- polyodontia or supernumerary teeth.
Normally, permanent teeth replace baby teeth only after the latter fall out. The germ of the molar tooth stretches upward, thereby contributing to the destruction of the roots. With some features of jaw development, this does not happen, which is why the second row appears.
Reasons for the growth of the second dentition in a child
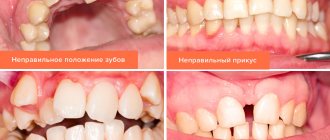
Double or “shark” teeth in children appear when the baby tooth and the rudiment of the molar are located at different points in the oral cavity. When a new set erupts, the baby tooth remains in place. A tooth grows above a tooth, which not only does not look aesthetically pleasing, but also interferes with the development of the rest of the row.
The most common reason why teeth do not change is improper breathing. A lot depends on how a child breathes. Breathing disorders lead to problems with bite, deterioration of posture and changes in facial shape.
A child’s jaw develops correctly only when he breathes correctly through his nose. The tongue in this position presses on the palate from the inside. A natural semicircular shape of the jaw is formed, in which there is enough space for all the molars. This is why it is so important to teach your child to breathe through his nose to prevent the growth of the second row of teeth.
Timing of baby teeth loss
The primary bite is formed during the period of active jaw growth. In this regard, already at the age of 3-4 years, three spaces should be formed - interdental spaces, which are necessary to ensure the physiological displacement of teeth during their replacement, the correct location of the erupting permanent teeth in the dentition.
By the age of five, children begin to experience, and then steadily progress, loosening of their teeth. This process is due to the gradual resorption of the roots of baby teeth, the place of which in the jaw is taken by the rudiments of permanent teeth moving towards the edge of the gum. When the time comes, the loose tooth falls out, and a permanent one should begin to emerge in its place within 2-3 weeks.
The entire period of mixed dentition requires increased attention from parents and specialists to the condition of the child’s oral cavity. Any pathological changes can lead to impaired teething, the formation of occlusion anomalies, crowding of teeth and other changes. Ideally, at the age of 5-6 years, you should visit the dentist every 2-3 months.
Supernumerary teeth in children
The appearance of additional tooth buds is rare, occurring in only 2% of cases. The anomaly is associated with a disorder of embryonic development. A tooth that appears above a child's tooth is usually removed. But this does not always happen: if the tooth does not disturb the shape and aesthetics of the dentition, the dentist can leave it.
Sometimes supernumerary teeth are located outside the dental arch. The appearance of a tooth on the palate of a child is rare, however, this is no exception. There is no need to be afraid of this: it does not affect your health in any way. The Natadent clinic has a pediatric orthodontist who will help solve this problem quickly and painlessly.
Diagnostics
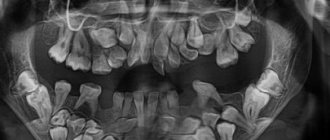
Examining supernumerary teeth during an x-ray is not as easy as it seems. They can be superimposed along the contour onto the permanent ones and remain invisible. In such cases, patients are recommended to undergo a computed tomography scan, which shows a more accurate picture of the disease.
If the extra dental elements have already erupted, the dentist can easily detect them. In practice, the patients themselves find the erupted supernumerary teeth and already at the initial appointment with the dentist they complain about the pathology.
What to do if the child’s teeth grow in the second row?
When a doctor sees a tooth above a patient’s tooth, he immediately understands what’s wrong. First, the orthodontist removes the baby tooth. After this, the permanent tooth will move into place on its own under the action of the tongue muscle, if there is enough space. But what to do if a child has a lack of space for molars?
The primary task of the dentist and parents will be to restore normal breathing. At this stage, it is necessary to “retrain” the muscles of the mouth to work differently. This is where trainers or mouthguards come to the aid of specialists.
Orthodontic appliances solve several important problems:
- train the muscles of the oral cavity, stimulating their natural development;
- correct the direction of development of the child’s jaws;
- correct the position of the tongue in the oral cavity;
- teach the child to breathe through the nose;
- get rid of bad habits.
Wearing trainers is most often considered as a preparatory stage. After this, more serious orthodontic treatment begins with the use of braces. However, here the first step is the most important, since the effectiveness of further work depends on it.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures for hyperdontia:
- relieving symptoms of eruption of supernumerary teeth, which are especially relevant for children;
- removal of supernumerary teeth;
- orthodontic treatment
Relief of teething symptoms
Relevant for young children, since in adults this period proceeds almost unnoticed.
Since supernumerary teeth give symptoms similar to the signs of the eruption of normal milk teeth, their therapy will be the same:
- When the temperature rises, it is recommended to take Ibuprofen or Paracetamol in the form of rectal suppositories or oral suspension. Such medications can both relieve pain and fever, and eliminate signs of inflammation of the soft tissues of the gums or palate.
- Local agents with an anesthetic effect in the form of a gel or ointment (Dentinox, Kalgel, Solokoseryl). They have a rapid analgesic effect and a slight anti-inflammatory effect.
- For children over two years of age, treatment with folk remedies is possible: decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, calendula, lemon balm), bee products (honey and propolis). Rinsing your mouth with solutions prepared according to traditional recipes helps relieve pain and prevent the occurrence of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
Sometimes supernumerary baby teeth only partially erupt. In this case, part of the crown remains in the jaw tissues. In such cases, a special massage, electrical or vibration stimulation is prescribed to stimulate eruption.
Removal of supernumerary teeth
The fate of the supernumerary tooth depends on many factors:
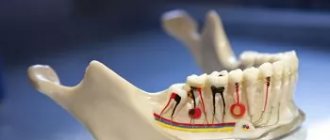
- In primary occlusion, all unnecessary elements are removed , as they negatively affect the growth and development of the maxillofacial system.
- All dystopic teeth (especially if they are loose), as well as impacted ones (even if at the time of their identification they do not cause any complications) are subject to mandatory removal
Typically, extraction surgery for well-formed supernumerary teeth is not particularly difficult.
A supernumerary tooth can be saved in the following cases:
- if it is located in the dental arch and does not cause malocclusion;
- has the shape of a regular tooth and does not cause a cosmetic defect;
- the root and crown are healthy and correctly formed, and the adjacent complete tooth is destroyed due to caries or injury.
Removal in a simple case
- Before any removal, an x-ray is required to determine the number of roots, their size and relationship with other teeth.
- After this, the doctor performs anesthesia and removes the dental element.
- If necessary, after surgery, sutures are placed on the soft tissues.
Removal of impacted supernumerary teeth
In order to carry out the operation accurately and without complications, the doctor needs to carefully examine the patient and plan the sequence of his actions.
- At the first stage, a survey radiography and computed tomography are performed to determine the exact topography of impacted dental elements.
- The tooth extraction operation is performed under local anesthesia, but in difficult cases the patient may be offered general anesthesia.
- Whenever possible, the supernumerary tooth is approached from the lingual side.
- After peeling off the mucous membrane, the bone tissue is opened and the crown and root parts of the tooth are extracted.
- If necessary, large bone defects are closed with osteoplastic materials, and the mucous membrane is sutured.
After the operation, the patient continues treatment at home, which includes taking antibiotics and rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions.
During the rehabilitation period, it is recommended to avoid eating too hard, hot or spicy foods, and to carefully brush your teeth on the operated side.
Sometimes, when a supernumerary tooth is located in the dental arch, has a developed crown of regular shape and a root with a normal structure, and the adjacent complete tooth is destroyed due to injury or caries, the defective dental element must be removed, followed by its replacement with a supernumerary one using orthodontic means.
Orthodontic treatment
After the removal of primary supernumerary teeth, the doctor decides what to do next. In the best case scenario, the baby does not need orthodontic treatment and simply visits the dentist for routine preventive examinations. In severe cases, the child will require the help of an orthodontist, including temporary prosthetics. This is necessary in order to:
- the child's jaw could grow and develop;
- after the age of six there were no problems with the eruption of permanent teeth;
- fully correct existing problems with the dentition.
After removal of excess permanent teeth, patients undergo bite correction. Modern orthodontics has at its disposal numerous options for braces or aligners, which allow you to quickly straighten your teeth and restore the beauty of your smile.
How to understand that a child is at risk of growing teeth in two rows?
Attentive parents should monitor the process of teeth growth and loss. The change of dentition begins at 6-8 years: the first to fall out are the central and lateral incisors. At 9-11 years old, the lower canines change. By the age of 10-12, the upper canines and small molars grow. The formation of the bite ends at the age of 13-14 years.
A child’s tooth grows above the tooth when the baby tooth does not leave its place in due time. In this case, parents should definitely consult a doctor. The earlier the pathology is detected, the easier it is to correct the child’s second dentition.
You don’t have to wait for your baby teeth to suddenly fall out on their own! If you notice that your child’s molars are cutting in, but his baby teeth aren’t even loose yet, take him to the dentist. With “shark” teeth, not only the appearance, but also the shape of the jaw is disrupted.
Reasons for appearance
Medicine does not give an exact answer why the program fails in the human body and supernumerary teeth appear.
Hypotheses explaining the etiology of the phenomenon:
- Atavism hypothesis . Supernumerary teeth are a return to the original number of dental elements, which was normal for human ancestors (it is believed that they had 6 incisors on the upper and lower jaws).
- Theory of splitting of the tooth germ . Hyperdontia is a consequence of impaired activity of the dental plate during embryonic development, as a result of which a significantly larger number of dental buds are formed from it. The hypothesis is supported by the increase in recent decades in the number of cases of the appearance of extra teeth as a result of the influence of unfavorable environmental conditions, thyroid diseases and other negative factors.
Mouthguard as a preventive measure for the second dentition
In dental practice, mouth guards are worn by children over four years of age. At this age, the child is already consciously approaching wearing a trainer and can wear it for a long time. The device is made according to individual casts, taking into account the characteristics of jaw development. The material from which the mouthguard is made is soft and does not injure the mucous membrane.
From the age of two, children can wear removable plates to correct bad habits. If a child often sucks a pacifier or fingers, his bite does not develop properly. These children are more likely to have teeth growing in two rows. A soft plate will help avoid this.
In our clinic, parents trust doctors with their most valuable asset – their children. You can rely on our specialists in any situation. To confirm these words, we publish reviews from our grateful clients.
Natadent specialists know how to win over the youngest patients. Most guys leave the dentist's office without the same fears. True professionals in their field not only master their tools flawlessly, but also make every trip to them as comfortable as possible.
How much does treatment cost?
The cost of treating hyperdontia is determined by the complexity of the case. The price for a simple removal of an additional tooth is, on average, 1,500 rubles . In cases with impacted or dystopic teeth, it will be slightly higher - for its removal you need to pay from 4,000 to 15,000 rubles .
Depending on the clinic, the cost of treatment may include preoperative examination, the operation itself and postoperative management. You can accurately calculate the final price only in the dentist's chair, since it is impossible to know in advance how the operation will go, whether complications will arise, or how the recovery period will go.
Why is it dangerous
Taking into account the number, location, size of the jaw and the age of the patient, the negative consequences are:
- delayed eruption of primary teeth;
- the formation of a diastema - a gap between the front incisors;
- damage to the mucous membrane leading to inflammation;
- inability to comply with hygiene measures;
- violation of the chewing process and digestive problems;
- the impossibility of proper oral hygiene and, as a consequence, the spread of carious bacteria.
Let's consider a clinical example of transposition correction using orthodontics
Patient N., 14 years old, came with her mother to the dental clinic. Complaints were made about the incorrect location of the canine on the upper jaw on the right. We already had a panoramic radiograph in hand, which complemented the analysis of the clinical situation in the oral cavity. To clarify the diagnosis and determine the optimal treatment plan, the patient was referred for a computed tomography scan of the jaws
After analyzing the diagnostic data, it was found that the root of the first premolar 1.4 is inclined towards the persistent primary canine 5.3, and the root of the permanent canine 1.3 is projected into the area between the roots of the premolars. Consequently, the situation was complicated by the fact that it was necessary not only to move the crowns, but also to “separate” the roots of the canine and premolar in their places.
When discussing the treatment plan with the patient and parents, a clear decision was made: to put the teeth in their places, despite the duration and complexity of the correction. The treatment method involved fixing a metal brace system initially only on the upper jaw, and after moving the crowns and roots, installing a brace system on the lower jaw for final correction and detailing the position of the teeth.
After removal of a recumbent wisdom tooth
While the anesthesia is in effect, the patient does not feel pain. But when the effect of the drug wears off, sensitivity gradually returns, and the person begins to feel pain. This pain is physiological, because the doctor cut the tissue, touched the bone, and the nerve endings were damaged. After a few days, the sensations finally subside. The following symptoms are possible:
- Mild hyperthermia;
- General malaise, weakness;
- Development of edema;
- Bleeding in the socket area.
Sometimes bleeding from the site of tooth extraction frightens a person; this is a natural reaction. The patient always thinks that he has lost more blood than actually happened. Sometimes the phenomenon continues for hours and usually stops completely by the evening. But if the nature of the bleeding remains unchanged throughout the day, the pain increases, and purulent spots appear in the socket, then the discomfort cannot be tolerated. This requires quick response measures to stop the developed inflammatory process.
The final stage of transposition treatment - making teeth beautiful
This was followed by the long-awaited getting rid of the braces system, cleaning and polishing of the teeth and the manufacture of fastening devices - retainers. A removable transparent night guard (aligner) was made for the upper jaw, and a non-removable wire retainer from canine to canine was made for the teeth of the lower jaw. Control examinations are recommended every six months for several years.
Conclusions of orthodontist Alexey Trezubov:
- Orthodontic treatment of tooth transposition should be considered as the preferred method of treatment.
- When planning treatment, it is important to take into account the patient’s age, degree of transposition, location of the roots, thickness of the bone tissue in the area of displacement and gum biotype.
- If the orthodontic method of correction is considered inappropriate, then other methods of correction are used.
- During such a rather complex movement of teeth, the orthodontist must be very careful and attentive, monitor the situation at each visit and make the necessary changes.
- The prognosis for treatment of such patients is in most cases favorable, but do not forget about the retention period.
The second stage of transposition treatment is moving the teeth into place.
Next, it was necessary to move the crown of the first premolar 1.4 from the palatal position and the reverse overlap to its rightful place. This required the separation of the bite with onlays. And, of course, the long and labor-intensive stage of normalizing the position of the tooth roots began. It is at this stage of treatment that the canine root is partially located outside the alveolar process of the upper jaw and, accordingly, the risk of gum recession is high. After a year and a half (!) of treatment, we managed to move the crowns and roots of the teeth to the correct position. And the third stage of treatment began