- Onychocryptosis
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Stages
- Treatment
- Surgical
- Non-surgical
- Correction bracket-plate
- Folk remedies
- Prevention
- Is it possible to remove an ingrown toenail at home?
- Complications
- Rehabilitation
- Make an appointment for treatment of ingrown toenails in our clinic
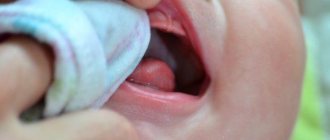
An ingrown toenail is a condition that causes the nail plate to grow into the nail fold. The reasons for this may be heredity and structural features of the fingers, wearing tight shoes, irregular and improper trimming of nails, flat feet and finger injury. To treat an ingrown toenail, you should consult a surgeon or podologist as soon as possible.
Onychocryptosis
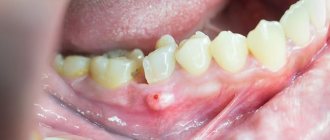
The disease of ingrown toenails is called onychocryptosis. Most often, the nail grows into the nail fold on the outside of the big toe. With onychocryptosis, the finger around the nail plate becomes red, swollen and begins to hurt. If such symptoms do not promptly consult a doctor, then a chronic inflammatory process may develop. Ingrown toenails are a common condition that anyone can experience. In addition, it is not recommended to self-medicate, since improper treatment may result in recurrence of the disease.
Both children and adults suffer from onychocryptosis, but ingrown toenails are more common in young people of working age. Onychocryptosis occurs in 10% of the working population.
Ptyalism
Ptyalism, or hypersalivation, is increased production of saliva due to overactivity of the salivary glands, which can occur in both adults and children. Pathology can be determined by frequent swallowing of saliva, its leakage from the corners of the mouth and the formation of wet marks on the pillow after sleep. In addition to ongoing psychological and physical discomfort, excess saliva can lead to irritation and damage to the skin around the mouth over time. If the necessary measures are not taken, the skin will first turn red and then a rash will appear on it.
Increased salivation is often observed in children aged 3-6 months, but this is not a pathology. It is in the first six months that the salivary glands begin to actively develop, and the child himself does not yet control the timely swallowing of saliva. Ptyalism under the age of 2 years can also be a consequence of objective reasons - in particular, teething. A short-term increase in saliva production is often observed in adults after consuming certain foods or drinks. However, if this is permanent, then ptyalism is already diagnosed.
For information about prices and treatment times, call:
+7
or fill out the feedback form:
What causes ptyalism?
A distinction is made between true and false hypersalivation: in the first case, the volume of saliva secreted is increased several times, and in the second, only the process of swallowing it during normal production is impaired. In addition, drooling can only be detected during sleep (nocturnal ptyalism), which becomes a consequence of malocclusion, diseases of the ENT organs, gastritis and other factors. Increased salivation often occurs in pregnant women in the early stages due to changes in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and hormonal changes.
Causes of constant drooling:
– Inflammation of the salivary glands and various pathologies of the oral cavity (for example, stomatitis).
– Worms and diseases of the digestive system: ulcers, gastritis with low acidity.
– Neurological disorders: strokes, cerebral palsy, Parkinson’s disease, neuroses.
– Poisoning with mercury, chlorine and other substances, as well as taking certain medications.
– Rabies and epidemic encephalitis.
Treatment of hypersalivation
If ptyalism is mild, you can use solutions based on chamomile, water pepper or viburnum fruits for rinsing. However, it is better not to self-medicate (especially since folk remedies do not solve the problem) and consult a doctor. After collecting anamnesis, checking the act of swallowing and the condition of the oral cavity, as well as calculating the amount of saliva secreted, a treatment regimen is determined.
The choice of therapeutic measures depends on the clinical picture and the underlying cause. Increased salivation is usually just a sign of another pathology, so other specialists may be involved in treatment, in particular a dentist, neurologist or gastroenterologist. For example, if ptyalism is caused by gastritis, then drugs that affect acidity are prescribed. For diseases of the oral cavity that provoke salivation, the existing pathology is also first eliminated. The most problematic is the treatment of hypersalivation that has developed against the background of mental disorders or neurological diseases.
Common methods include salivary suppressants, cold treatments, injections, and massage to strengthen the oral muscles. In particularly difficult cases, they resort to irradiation or removal of large salivary glands. Elimination of increased salivation in children has some special features, for whom speech therapy massage sessions are additionally recommended to normalize the act of swallowing. Prevention of ptyalism at any age means preventing the development or timely treatment of diseases that provoke it. Adults also need to choose the right diet and not abuse bad habits.
Causes of ingrown toenails
An ingrown toenail can result from:
- Congenital or acquired structural features of the foot and fingers that contribute to the development of onychocryptosis, such as flat feet, deformation of the fingers and others.
- Wearing narrow shoes that press the periungual fold into the nail plate.
- Wearing high-heeled shoes, in which the feet are inclined and the main pressure is on the toes.
- Fungal diseases of nails.
- Wearing a cast or a very tight bandage for a long time.
- Foot injuries.
- Improper trimming of nails, cutting them too deep, cutting off the corners of the nails too much, or leaving a hangnail.
- Diabetes.
- Gout.
Other factors or a combination of them also lead to onychocryptosis. Excess weight, poor posture, untimely and improper foot hygiene, pregnancy, injuries and various diseases can affect the development of an ingrown toenail.
Diagnosis of onychocryptosis
Diagnosis of ingrown toenail disease may include the following steps:
- The doctor listens to the patient's complaints.
- The surgeon visually examines a finger with an ingrown nail, identifying the underlying disease and associated diseases, such as fungus.
- When the inflammatory process begins, the doctor prescribes tests:
- general analysis to determine the degree of the inflammatory process;
- blood glucose test to determine diabetes mellitus;
- culture of purulent discharge to determine the type of infection.
- The doctor prescribes an x-ray of the foot, which will determine the size and shape of the nail growth, damage to bone structures and the area of suppuration.
After diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment, which depends on the stage of the disease.
Xerostomia and hypofunction of the salivary glands: diagnosis and treatment
Hypofunction of the salivary glands, which is manifested by a lack of saliva, can be caused by the influence of a huge number of factors. Causes of xerostomia (a feeling of dry mouth), and therefore hypofunction of the salivary glands, include mouth breathing, smoking tobacco or marijuana, candidiasis, menopause, aging, dehydration, diabetes, radiation therapy and a number of other general somatic disorders (depression, stress, autoimmune neuropathy, CREST syndrome, eosinophilic myalgia syndrome, HIV/AIDS, Lyme disease, lymphoma, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, primary billiard cirrhosis, primary fibromyalgia, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren's syndrome, lupus, SOX syndrome, goiter, hyperlipidemia type 5). At the same time, completely unsubstantiated medications can often be used to stimulate salivation. Complaints of dry mouth are more common among older patients; approximately 80% of patients with xerostomia are people 80 years of age and older, who, in addition to dryness, experience signs of burning and taste disturbances, even when taking certain prescribed medications.
In order to determine the cause of hypofunction of the salivary glands, doctors have to resort to a laboratory blood test, and at times, to a biopsy of the salivary glands, the results of which can make a diagnosis of Sjögren's syndrome, amyloidosis, and sarcoidosis.
Clinical features associated with saliva
Hypofunction of glands
A patient with hypofunction of the salivary glands or with a feeling of dry mouth is characterized by the presence of a number of clinical signs and symptoms. The latter include impaired sensitivity and speech function, burning in the tongue and mucous membranes for no reason, as well as upon contact with certain foods, oral candidiasis, signs of biting the cheeks, cheilitis, caries, erosion and abrasion of dental tissues, dysphagia, food getting stuck between teeth, gingivitis and periodontitis, halitosis, GERD, general weight loss. Such clinical symptoms begin to develop when salivation decreases by at least 50%, and patients may experience both individual symptoms of the lesion and complexes of such symptoms.
When salivation is impaired, saliva parameters also change. It becomes white, foamy, thick, sticky and fibrous. Because of this, the patient may feel the presence of a kind of salivary film on the teeth and mucous membranes. Sometimes patients complain of an excessive amount of saliva in the mouth, which is caused by the fact that its density increases. Normally, the rate of salivation reaches 2-3 ml for 5 minutes; when it increases to more than 1 ml for a minute, sialorrhea is diagnosed. In patients with signs of dry mouth, the normal level of salivation is reduced by approximately one-fold.
With reduced salivation, the oral mucosa becomes dry and during diagnostics, gloves, rollers and even dental mirrors may stick to it. Filiform papillae and fissures may be visualized on the back of the tongue, the presence of which allows a diagnosis of a hairy tongue to be made (photo 1). In the cervical areas of the tooth, areas of carious lesions are often visualized (photo 2), small erythematous spots are diagnosed on the buccal mucosa, where bite marks from the teeth may also be present (photo 3). Patients may also have signs of gingivitis, recession, and periodontitis (Figure 4).
Photo 1. Whitish filiform papillae in a patient with xerostomia. There is also an odor from the mouth.
Photo 2. Carious and associated lesions in a patient with xerostomia.
Photo 3. Traces of biting the cheek.
Photo 4. Signs of gingivitis with severe hypofunction of the salivary glands.
The questionnaire for diagnosing xerostomia was designed specifically to assess existing disorders from a subjective point of view. It includes 11 statements (“I feel dry mouth”, “I have difficulty eating”, “I wake up at night to drink water”, “I feel dry mouth when I eat”, “I drink water to make it easier to swallow food”, “I have difficulty swallowing certain foods”, “The skin on my face seems too dry”, “My eyes feel dry”, “My lips feel dry”, “I have a feeling of dryness in the nasal cavity”), which patients rate using 5 possible options: (1) Never, (2) Hardly ever, (3) Sometimes (4) Quite often or (5) Very often . A score of 11 indicates the presence of moderate xerostomia, while a score of 55 indicates severe xerostomia. If the patient has already been diagnosed with xerostomia, the doctor may ask a few additional questions: Do you think the volume of saliva in the oral cavity is sufficient for you? Do you feel dry when eating? What complications do you experience when swallowing? Do you drink water to make it easier to swallow food? How often?
Objective diagnosis
Patients with mild xerostomia may not experience dry mouth at all, but they may also experience other symptoms of the disorder. As one of the tests to objectify the symptoms of xerostomia, it is recommended to evaluate the rate of salivation at least once a year. Moreover, such an assessment can be carried out both with stimulation of salivation and without any stimulation of the process. To diagnose the rate of salivation, the doctor uses a tube, a separatory funnel, strips for determining pH, and strips for conducting a Schirmer tensile test. The volume of salivary secretion after stimulation can be determined after the patient has chewed paraffin for 1 minute. These data can be compared with data obtained without stimulation, as well as data after administration of a specific drug that stimulates salivation.
Assessment of salivary flow can also be performed using Schirmer strips and pH strips before and after administration of 5 mg pilocarpine. Two hours before the test, the patient should not eat, drink, chew gum, or even brush his teeth. Diagnosis of unstimulated salivation is carried out in the dental chair with the patient in the coachman position, with his hands on the armrests. The patient holds the measuring funnel and tube on his lips, while his eyes should be open, but blinking is not prohibited. Within 5 minutes, saliva should simply flow into the flask and tube. After this, the collected volume of saliva is divided by 5, thus allowing you to set the rate of salivation per minute. Normal average values are 0.3-0.4 ml/minute.
Thus, hypofunction of the salivary glands is diagnosed when the saliva flow rate is less than 0.3 ml/min. When this indicator is less than 0.1 ml/min, then a severe form of hypofunction of the salivary glands is recorded. Normally, the pH of saliva is 7-7.5, that is, it is neutral or somewhat alkaline. A low rate of salivation provokes the development of dental erosion, irritation of the mucous membrane and a burning sensation. When the rate of salivation is normalized, pH values are usually normalized, and vice versa - with hypofunction of the salivary glands, the pH of saliva becomes more acidic.
Treatment
Saliva is a complex fluid consisting of enzymes, proteins, minerals and other components that help maintain a healthy oral cavity. Thus, normalization of salivation is an integral aspect of the complex treatment of dental patients. For patients who cannot control salivary stimulation, saliva substitutes or saliva analogues in the form of lubricants are used. The specific treatment for xerostomia depends on the underlying causative disease. The goal of such therapy is to relieve the symptoms of dry mouth, and to ensure the prevention of associated complications in the form of caries, candidiasis and other lesions. In addition, treatment of xerostomia also helps to slow down the complete loss of salivary gland function, and sometimes even promotes its restoration. At least in autoimmune diseases, with the help of salivary stimulants, it is possible to maintain a certain level of salivary gland function for as long as possible, and a drug such as rituximab even helps restore the structure of the salivary glands in Sjogren's syndrome. Taking dietary supplements such as coenzyme Q10 100 mg per day for 1 month also helps increase salivation and reduces the development of symptoms of dry mouth. Treatment of pharmacologically induced xerostomia is carried out in the same way as treatment of other forms of this disease. This form of pathology, as a rule, is reversible, but the dentist must take into account what kind of drug it was caused by, and what part he takes in the treatment of general somatic pathology. Control of the main symptom of dry mouth can be carried out with pilocarpine or cevimeline, as well as other drugs, depending on the current state of the pathology. The future in the treatment of xerostomia clearly involves genetic engineering, the use of stem cells and tissue engineering, but the principles of therapy remain the same: normalization, optimization of salivary flow, ensuring adequate hydration of the oral cavity and creating conditions for lubrication of all oral structures.
Normalization/optimization of salivary flow rate
Ideally, treatment of hypofunction of the salivary glands involves restoring their function and the physiological rate and volume of salivation. One treatment option is to stimulate saliva production by taking appropriate medications. The latter allow you to increase the initial level of salivation, thus also reducing the risk of developing subsequent complications (caries and candidiasis). Improvement in salivary flow rate can be achieved by taking pilocarpine 5 to 7.5 mg in tablet form three to four times daily or capsule 30 to 60 mg three times daily. Pilocarpine and cevimeline are salivary stimulants that the FDA prescribes for the treatment of dry mouth symptoms. By their nature they are muscarinic agonists. They increase saliva flow and reduce the feeling of dry mouth. The most common side effects with these medications are sweating, frequent urination, and gastrointestinal discomfort. These drugs should not be taken for uncontrolled asthma, narrow-angle glaucoma and acute iritis. They should also be prescribed with caution to patients with severe forms of cardiovascular disorders, Parkinson's disease, asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Polycarpine and cevimeline are cholinergic agonists that stimulate muscarinic-type receptors in the structure of the salivary glands and, to some extent, in the structure of other exocrine glands. Pilocarpine usually begins to work within 20 to 30 minutes, lasts 3 to 5 hours, and has no residual effect. Taking pilocarpine 20-30 minutes before meals with a glass of water allows you to achieve an optimal level of salivation already at the time of eating, facilitating the processes of chewing and swallowing. Taking the drug before bedtime will help relieve symptoms in those patients who are most bothered by dry mouth at night. Cevimeline begins to act in 30-90 minutes and provides an effect for 6-8 hours. This drug, unlike pilocarpine, has a residual effect, and over time, patients experience a higher salivary flow rate. Patients may also notice increased swallowing after starting to take the salivary stimulant. The fact is that the frequency of swallowing decreases with hypofunction of the salivary glands, and returns to normal during the treatment of xerostomia.
Normally, the patient swallows up to 2000 times a day. If the patient cannot restore the speed or required volume of salivation, he may be prescribed artificial saliva. Such drugs are Caphosol (EUSA Pharma), NeutraSal (OraPharma) and SalivaMAX (Forward Science); Aquoral (Mission Pharmacal). They help relieve dry mouth due to certain diseases, inflammation, medications, chemotherapy and radiotherapy, stress, and aging. Aquoral, in addition to relieving xerostomia, also helps solve difficulties with swallowing, speech and changes in taste.
Hydration
Dehydration of the oral cavity is associated with a reduced level of salivation, but the latter may be associated with general dehydration of the entire body. The loss of about 8% of the human body’s water, which is about 4 liters of fluid, provokes the development of an almost complete absence of salivation. Even after rehydration, the function of the salivary glands is restored only after 24 hours. During this period, saliva can be replaced by drinking 64-80 ounces of drinks that do not contain alcohol or coffee. The volume of fluid required can also be determined by dividing the patient's weight (in pounds) by two to obtain the number of ounces of fluid that should be drunk daily.
Oral lubrication
Since salivary stimulants do not restore the physiological function of saliva, sometimes patients find it necessary to use additional lubricants to relieve discomfort during speech or swallowing. These types of drugs include ACT Dry (Chattem Inc.), Allday Dry Mouth Spray (Elevate Oral Care), Biotene Oralblance (GlaxoSmithKline), Entertainer Secret Throat Relief (KLI Corp.), MedActive Oral Relief (MedActive Oral Pharmaceuticals, LLC), MighTeaFlow (Camellix), MI Paste (GC America), Moi-Stir Mouth Moistening Spray (Kingswood Labs, Inc.), Mouthe Kote (Parnell), Oasis (Gebauer Consumer Healthcare), Orajel (Church and Dwight, Inc.), Salese ( Nuvora Inc.), Salivart Synthetic Salica (Gebauer Consumer Healthcare), SalivaSure Saliva Substiture Tablets (Scandinavian Pure and Naturals), Spry Rain mouth spray (Xlear, Inc.), Stoppers4 Dry Mouth Spray (Woodridge Labs), Xerostom products (Practicon) . Patients may be encouraged to try new products to find the ones that work best for them. Rinsing the mouth with salt water or salt water (1/2 teaspoon) and sodium bicarbonate (1/2 teaspoon) diluted in 8 ounces of water helps cleanse the mouth, neutralize acids, and remove plaque. A drop of mineral oil or glycerin placed on the tongue can completely spread throughout the oral mucosa and improve the patient's comfort level. Oral care recommendations also include drinking plenty of water, brushing your teeth at least twice a day, chewing sugar-free gum, visiting your dentist regularly, and not smoking, caffeine, or alcohol.
Stimulation of salivation - electrical stimulation
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) applied to the parotid gland for 5 minutes increased salivary flow in 68-81% of patients in the study. Various types of TENS machines are available for this purpose and have been approved by the FDA. They are portable analogues of the ballpoint pen shape that produce electrical impulses. These can already be purchased in Europe and Australia; in the USA they have not yet undergone final certification procedures.
Behavioral changes
The dentist's recommendations for treating xerostomia may require changes in certain aspects of the person's behavior. The latter include drinking water more often, using various fluoride-containing topical preparations, as well as various rinses, avoiding sugar-containing chewing gum, and using saliva-replacing gel-lubricants, sprays, and moisturizers. These products can be used as often as needed because they do not react with prescription medications and generally have no side effects unless the patient is sensitive to a particular ingredient. Studies have shown that patients prefer to use saliva stimulating drugs rather than salivary substitutes. In addition, dentists may recommend that patients with dry mouth rinse with salt water, eat ice chips, and swallow small amounts of liquid frequently.
In addition, chewing also stimulates the flow of saliva, so eating certain foods daily, such as raw carrots, can help treat xerostomia. You should avoid cigarettes, alcohol, caffeine and spicy, salty or acidic foods, as well as refined carbohydrates (sugar) in your diet if you have symptoms of dry mouth. Patients with xerostomia should take good oral care through frequent brushing, flossing, and fluoride-containing toothpastes and gels. For selected patients at increased risk of developing dental caries, mouth guards can be made for overnight fluoridation treatments. Moisturizing gels can also be used once or twice within an hour of bedtime to reduce the level of discomfort after the mouth guard.
conclusions
Patients with xerostomia or hypofunction of the salivary glands can be diagnosed based on the presence of certain clinical symptoms and the results obtained during an objective diagnosis of the level and condition of salivation. Current treatment options for xerostomia include taking certain medications to manage symptoms and prevent potential complications. Such medications include salivary stimulants, artificial saliva, lubricants, rinses, sprays and gels. Stimulation of salivation can also be achieved through electrical stimulation. Treatments such as gene therapy, stem cell therapy or tissue engineering may become the mainstay in the future for correcting salivary gland dysfunction.
Author: Susan L. Zunt, DDS, MS
Stages of an ingrown toenail
There are 3 main stages of the disease, which are characterized by the following symptoms:
- Stage 1
: Moderate pain, slight swelling and pressure in the finger. - Stage 2
: Severe swelling, suppuration, throbbing pain, the nail plate thickens and becomes dull, deformation and enlargement of the nail fold are observed. The wound becomes infected and an inflammatory process occurs. - Stage 3
: The disease enters a chronic stage in which proliferation of granulation tissue and deformation of the nail fold and plate are observed. In this case, even bone tissue can become inflamed.
The higher the stage of the disease, the more difficult and lengthy the treatment. Therefore, at the first symptoms you should immediately consult a doctor. Ingrown toenails are especially dangerous for people with diabetes.
Treatment of ingrown toenails
Treatment of onychocryptosis can be carried out by surgical and non-surgical methods, but more often the treatment consists of a combination of these two treatment methods.
Surgical treatment of onychocryptosis
The operation is performed under local anesthesia, in which pain relief is administered with a syringe into the finger. After 10 - 15 minutes, after the anesthetic has taken effect, the surgeon begins the operation.
The following tools and excision methods are used to remove an ingrown toenail:
- A scalpel
is a traditional tool for removing ingrown toenails. - Surgical laser
is the most preferred method of excision of ingrown toenails, allowing to minimize trauma, reduce recovery time and reduce the likelihood of relapses. The laser is very thin and at the same time additionally disinfects the excision area. - Radio wave method
- allows radio waves to evaporate the ingrown part of the nail. The method is preferable, as it causes little damage to areas of healthy skin and allows for faster recovery.
In our clinic, we mainly use the laser method of removing ingrown toenails as the most effective.
There are 4 main surgical operations used to remove an ingrown toenail:
- Complete removal of the nail plate
, which is used in very rare cases with advanced disease. After surgery, surgical stitches are placed on the finger. After such an operation, relapse is possible. - Marginal resection of the nail plate with resection of the periungual fold
. It is used at stages 2 and 3 of the disease. After surgery, sutures are placed on the periungual fold. - Marginal resection of the nail plate without resection of the periungual fold
. Used at an early stage of the disease. In this case, up to 2 millimeters of the nail plate is removed with the destruction of the germ layer. - Destruction of the nail growth zone with a laser
. Used in conjunction with other methods of removing ingrown toenails to reduce the likelihood of recurrence.
After removing the ingrown part of the nail, the doctor prescribes conservative treatment for successful recovery and reducing the likelihood of reoccurrence of onychocryptosis.
Non-surgical treatment of onychocryptosis
After surgery, to care for your finger, your doctor may prescribe:
- reducing or eliminating running, walking and working;
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs;
- timely dressing of the finger;
- compresses;
- disinfectant baths;
- use of ointments.
In order to prevent relapses, for a long time the surgeon may recommend:
- wearing loose shoes that do not put pressure on the toe;
- regular and correct trimming of nails, implying the absence of a hangnail on the nail and the formation of a nail plate of the desired size;
- losing weight to reduce the load on the finger;
- maintaining hygiene.
In addition, to treat an ingrown toenail, the doctor can use corrective staples-plates.
Using a corrective plate bracket on the nail
This is a method of conservative treatment of ingrown toenails using staples and plates that are inserted between the nail and the skin and correct the direction of growth of the nail plate. These devices allow you to straighten the nail and eliminate the occurrence of onychocryptosis.
The most common staples and plates are:
- Bracket 3-TO
. It consists of 2 hooks that are attached to the edges of the nail and a loop that tightens the hooks that guide the growth of the nail. It is used for ingrown or curled nails after injuries, calluses and relapses. Use with extreme caution in patients with diabetes. - Combiped bracket
. Attaches to the nail, straightening and straightening it. Can be used for unilateral ingrown nails. In this case, one of the staples is placed over the edge of the nail plate, and the other is combined with a plastic pad that is glued to the nail. Used for ingrown, deformed and curled nail plates. Use with extreme caution in patients with diabetes. May be contraindicated for patients who are allergic to the staple material. - Fraser bracket
. The hooks of the staple are inserted over the edges of the nail and the staple is tightened, and as the nail straightens, the tension force of the staple is reduced. It is used for ingrown and curled nails after injuries and relapses. May be contraindicated in case of fungus, discharge of blood and pus, as well as psoriasis. - Podofix plate
. It is installed with glue on the nail plate, and the tension force of the Podofix device is regulated by a special wire. used for ingrowth, curling and deformation of the nail against the background of core calluses and hypergranulation. Use with extreme caution in patients with diabetes. - B/S plate
. Installed on a pre-treated nail using glue. Used to correct ingrown toenails. Use with extreme caution in patients with diabetes.
Treatment of ingrown toenails with staples and plates is painless. This method allows you to achieve recovery with a high probability without relapse.
Treatment of onychocryptosis with folk remedies
Among those suffering from onychocryptosis, there is a high demand for treating ingrown toenails with folk remedies at home. But such treatment is ineffective and can only help as part of complex professional therapy. An ingrown toenail cannot be treated on your own, as there is a high risk of misassessing the situation, triggering and aggravating the disease.
If a symptom of onychocpriptosis appears, you should always consult a doctor - a surgeon or podiatrist. And if a medical specialist recommends something from folk remedies for a successful recovery, then in this case they can be used.
Folk remedies for treating ingrown toenails include:
- Lotion with a cotton pad on the wound with agents that have antiseptic and soothing properties:
- kombucha;
- aloe;
- essential oils (tea tree, fir, plantain, sea buckthorn).
- Ointments based on calendula or aloe.
- Baths with medicinal herbs, soda and salt, essential oils, iodine or potassium permanganate.
- Compresses, for example with laundry soap and fat or onions.
- Cotton swabs under the nail, soaked in sea salt, soda, lemon juice, essential oils or medicinal herbs.
And remember that folk remedies do not guarantee recovery, and in some cases, in the absence of timely treatment from a doctor, they can cause harm and worsen the course of the disease.
Pancreatic enzymes - types and functions
It's time to learn what enzymes are and how they affect digestion. Pancreatic enzymes are protein complexes or catalysts whose main task is to break down nutrients into simple, easily digestible compounds. Thus, the body easily absorbs all the necessary elements and vitamins.
With a lack of pancreatic enzymes, food is not digested fully, not all beneficial substances are absorbed, which affects the condition of the entire body1.
What enzymes does the pancreas produce and what are their functions?
The pancreas produces several types of enzymes, each of which does its own thing1,2.
- Proteases – break down proteins into amino acids;
- Lipases – decompose fats into fatty acids;
- Amylases - break down sugar (carbohydrates) and starch.
The amount of enzymes released is measured in units. The pancreas can produce up to 2 million units of enzymes per day. In this case, it is customary to take lipase units as a unit of measurement, since fats are the most difficult food components to digest8.
Now let’s look at the principle of how enzymes work, and to do this we’ll have to remember about the digestion process as a whole. The main task of digestion is to absorb all the nutrients that come with food. To do this, food must be disassembled into “bricks”. The process begins literally in the mouth, already during chewing, under the influence of saliva. Next, the food enters the stomach - the kingdom of gastric juice and the enzyme pepsin, where it acquires a mushy form and then, already prepared nutrients, enter the intestines in small portions.
It is in the intestines that the main stage of digestion occurs. Let us examine this stage in more detail, since it is directly related to pancreatic enzymes8.
After food enters the duodenum (the first section of the intestine after the stomach), it begins to be affected by the secretion (juice) of the pancreas, which contains digestive enzymes. At rest, the pancreas does not produce enzymes, but is in “standby mode.” But it is enough to catch the alluring smell of food or see a tasty dish, as the brain instantly gives the command to start working, and the pancreas begins to actively produce enzymes. This continues during meals and for some time after, because food does not reach the intestines instantly8.
It is especially interesting that the body can regulate the production of certain enzymes depending on the nature of the food consumed. That is, if you consume a lot of baked goods, then the emphasis in production will be on amylase, if you consume fatty foods, then the pancreas will send more lipase to the intestines.
It seems that the work is completely smooth and there can be no failures. But failures happen quite often: the operating mechanism is too delicate and easy to break. Even a large meal with a predominance of fats can break down the system, and the pancreas will not be able to provide the required amount of enzymes.
Prevention of ingrown toenails
To prevent the nail from growing in, it is necessary to take the following preventive measures:
- Wear loose and comfortable shoes that do not put pressure on your toes.
- Trim your nails correctly, avoiding the formation of a nail plate that is too short at the root or too long, as well as hangnails that can grow into the nail fold.
- Walk barefoot as much as possible.
- Maintain regular foot hygiene.
- Treat fungus and other foot diseases in a timely manner.
- Use orthopedic insoles for flat feet.
- Protect your feet from injury, be careful and follow safety precautions at work.
- If you are injured or experience symptoms, contact your doctor immediately to receive professional treatment.
- Reduce body weight and treat diabetes.
Preventive measures will help significantly reduce the likelihood of an ingrown toenail.
Main signs of pancreatic enzyme deficiency
Identifying enzyme deficiencies is quite simple. The key symptoms are heaviness after eating, a feeling of fullness in the abdomen and abdominal discomfort. Often these symptoms are accompanied by bloating, rumbling, flatulence, and diarrhea. Most often, such symptoms can occur in ordinary situations: when eating heavy, fatty foods or when overeating, when it was simply impossible to resist eating a lot of tasty dishes. In this case, you should not be afraid of problems with the pancreas or other gastrointestinal diseases. The pancreas simply cannot cope with much work and may need help.
Why does diarrhea occur? Fats are the most difficult components of food to digest. If there is a lack of enzymes in the body, it is with the processing of fats that difficulties arise. As a result, undigested fats that are not decomposed by enzymes contribute to a change in the nature of the stool and the rapid movement of contents along the intestines, which provokes diarrhea8.
If a lack of enzymes and digestive problems persist for a long time, then this does not go unnoticed by the body. Symptoms may worsen and become regular rather than episodic. Constant diarrhea gives rise to vitamin deficiency; protein-energy deficiency and dehydration throughout the body can develop. Significant weight loss may occur. In addition, in severe stages, the following symptoms of pancreatic enzyme deficiency may be observed8:
- nausea and vomiting;
- heartburn;
- a sharp decrease in appetite;
- general weakness.
Is it possible to remove an ingrown toenail at home?
If the nail has already grown into the periungual fold, then removing the part of the nail plate that has grown into the skin yourself at home will be difficult and dangerous.
Cutting off an ingrown toenail yourself will be very painful. In addition, a person without medical education can do something wrong with the nail, which will aggravate the situation or lead to a relapse in the future. In addition to surgical skills, during removal, sanitary and hygienic requirements must be observed, which are not always available at home.
It is very important to consult a podiatrist or surgeon at the first symptoms of an ingrown toenail so that the operation takes place correctly in a medical clinic. Correctly performed surgery and treatment will most likely allow you to quickly recover and avoid the recurrence of onychocryptosis.
Complications
With an advanced stage of an ingrown toenail and improper treatment, the following complications may occur:
- Gangrene of the finger is a serious complication in which tissue necrosis occurs. The only way out is complete removal of dead tissue - amputation of the finger.
- Inflammation of the soft tissues of the entire finger with the development of a purulent process, which requires immediate clinical treatment.
- The appearance of tumors requiring surgical removal.
- Purulent inflammation of the bones of the finger, requiring immediate conservative and surgical treatment.
- Other complications delaying the recovery process.
All complications of an ingrown toenail can lead to even more serious consequences if you do not consult a doctor in time. At the first symptoms of onychocryptosis, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible in order to avoid complications and longer treatment. The sooner you start treating an ingrown toenail, the faster and easier this process will be.
The appearance of digestive problems
We have found that digestive problems can occur due to a lack of enzymes. There are two main mechanisms by which the body lacks pancreatic enzymes. In the first option, the problem with the production of enzymes lies in the pancreas itself, i.e. the organ itself is not functioning properly.
Impairment of the pancreas can be a congenital problem or acquired, for example, after surgical interventions. As a rule, such a mechanism underlies serious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), the symptoms of which will sooner or later lead to an appointment with a doctor8.
In the second option, the conditions under which enzymes can work correctly are violated. This is possible as a result of changes in the acidity of the intestinal environment, for example, due to inflammation or a change in the standard ambient temperature (36-37 ° C). The inflammatory process in the intestines can occur under various conditions: intestinal infections, allergic reactions (food allergies, atopic dermatitis).
Rehabilitation after removal of an ingrown toenail
The recovery period after excision of an ingrown nail is on average 1 month. During the rehabilitation period it is recommended:
- Ensure the patient remains calm.
- Regular treatment of the nail with antiseptic agents and bandaging.
- Applying medications prescribed by a doctor to the wound.
- Taking painkillers for pain.
- Wearing loose shoes that do not put pressure on the toe.
- Other procedures indicated by the surgeon.
During the recovery period, you must strictly adhere to the doctor's instructions for a successful recovery.
Maintaining digestion and treating enzyme deficiencies
If you have problems with digestion, enzyme preparations (more often called drugs to improve digestion) can help, the main task of which is to compensate for the lack of the body’s own enzymes. It’s not for nothing that this therapy is called “enzyme replacement”. It is critical that the enzyme preparation “mimics” the physiological process as closely as possible.
Today, there are various drugs to improve digestion. How to navigate the variety of means and make the right choice?
An effective enzyme preparation must meet the following criteria5,6:
- have an optimal particle size
- do not break down in the stomach
- quickly activate in the intestines
The drug Creon® meets all these requirements.
To learn more
1) Today, pancreatin minimicrospheres, which are contained only in the drug Creon®5,7, are recognized as the optimal particles. The invention of minimicrospheres was the result of many years of work to improve the effectiveness of enzyme preparations, which left far behind drugs in the form of tablets and capsules with other types of particles inside: pellets, mini-tablets, etc. In addition, Creon® minimicrospheres are produced using patented technology, which prevents other manufacturers from reproducing the same release form.
2) Creon® minimicrospheres are enclosed in a capsule that protects them from the destructive effects of the stomach. But that is not all. Each particle is covered with an acid-resistant coating in order to “reach” the intestines, where its work is necessary, completely intact. At the same time, some other encapsulated drugs can lose up to 30% of their activity6.
3) Creon® begins to work within 15 minutes after entering the intestines, improving digestion and thereby eliminating heaviness and discomfort after eating6.
Creon® has several dosages, including 10,000 IU of lipase - the minimum required dose of lipase to improve digestion in case of dietary errors, eating heavy foods and overeating. To obtain the effect, Creon®10000, like any enzyme preparation, must be taken with every meal - during breakfast, lunch and dinner.