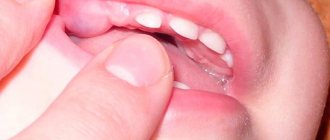
A baby at the age of four months is not yet able to communicate what is bothering him, where it hurts, what factors cause discomfort. Typically, the first baby teeth begin to emerge at six months, but it is not uncommon for the middle incisors to appear in four-month-old babies. It is very important to recognize the signs of teething in order to help your baby get through this period as easily as possible.
Signs of teething in a 4 month old baby
On a note! Early teething is not considered a pathology. The age of 4-7 months is considered the norm for the appearance of the first primary incisors.
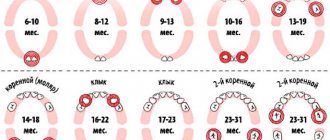
Teething Chart
Norm or pathology
Can teeth be cut at 3 months? The earliest age for the eruption of the first elements is considered to be three months of age. Dentists consider it normal for the first teeth to appear at 3 months of age. If the incisors appear earlier than the expected period, then the child should be shown to a therapist. The early appearance of elements on the surface of the gums may signal hormonal disruptions occurring in the body.
The appearance of baby teeth on the surface is accompanied by a number of distinctive symptoms:
- Pain in the gums. Because of this, the child puts fists and foreign objects into his mouth. At this moment, it is important for adults to ensure that there are no small toys or objects near the child that could get into the respiratory tract.
- Deterioration of the oral cavity. The gums swell and redden, becoming more sensitive to external irritants. In some cases, due to teething, the child may experience slight redness of the throat.
- Irritability and increased tearfulness of the baby. The symptom is associated with constant pain in the area of the eruption of the element. At this moment, children become more active and faster.
- Disorders of the digestive tract, manifested by loose stools, regurgitation, and rare bouts of vomiting.
- Temperature increase. The symptom is due to the fact that when teething, the newborn’s body is vulnerable to bacterial and viral pathogens.
How to help your baby when he is teething
Teeth are breaking through - it even sounds painful. Indeed, when a baby starts teething, it is often painful. Many children sleep poorly, often cry, and some even develop a fever. But there are other symptoms that indicate your baby is going through the baby teething period. The first signs of teething and, above all, what to do when teeth appear and how to reduce pain will be discussed in a conversation with first category pediatrician Ekaterina Borisovna Bulavina.
— Ekaterina Borisovna, please tell us when do babies usually start teething?
— The timing of teething varies quite widely. On average, the first teeth emerge at 5-7 months, but the process can begin earlier (at two or four months) or take up to a year. And some babies are born with teeth. Everything is very individual and depends on many factors, such as heredity, sufficient calcium intake in the body, the gender of the child, and the climate in the place of residence.
— How quickly will teeth be cut after the first one appears?
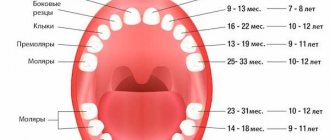
— In both boys and girls, the process of complete eruption of the primary dentition usually takes 2.5–3 years. The upper incisors appear 2-3 months after the appearance of the lower ones, then at the age of 9-13 months the upper and lower lateral incisors erupt. From one year to one and a half years, the upper and lower first molars alternately appear, then, by 20 months, the upper and lower canines, and by 2-2.5 years, the second molars. However, the order and timing when babies start teething are very arbitrary.
Table and chart by month: what time do children start teething?
How can you tell if your baby is teething?
— The appearance of teeth, although physiological, is a real test for the child and his mother and father. Only recently have we experienced colic, a feeding and sleeping schedule has been established, when suddenly the baby becomes restless again, is capricious, refuses to eat, or, on the contrary, often and greedily grabs the breast or bottle, sleeps poorly and puts everything in his mouth. These are sure signs that teething has begun.
Some lucky people endure the entire process completely painlessly, and only a casual tap on the gum with a spoon reveals the first tooth that has already erupted. But sometimes the moment of teething is so difficult for the baby that it is easy to confuse it with the onset of the disease.
Only a doctor can determine the real cause of the child’s anxiety, and you should definitely contact him if the temperature rises to febrile levels, severe lethargy, weakness or, conversely, severe excitability of the baby, as well as if signs of infection occur, such as a runny nose, cough, frustration digestion, vomiting, loose stools.
— Ekaterina Borisovna, parents are waiting for the appearance of the first incisors with caution. What symptoms characterize the process besides pain?
— When teeth are cut, the symptoms are very diverse, and everything is individual. In this case, the symptoms may differ depending on the location of the cutting teeth. Usually the most unpleasant sensations accompany the appearance of only the first teeth. All subsequent ones erupt more calmly, and the child practically stops paying attention to this process. When chewing teeth appear, pain may resume, but it is not as intense as at the very beginning of eruption. The appearance of the upper teeth is often accompanied by a runny nose: this is due to the proximity of the location and the single network of blood supply to the upper jaw and nasal cavity.
| First symptoms of teething | Features of the child’s condition and behavior |
| Swelling and redness of the gums |
|
| Excessive salivation |
|
| Decreased appetite or complete refusal to eat |
|
| Increased moodiness |
|
| Temperature |
|
| First symptoms of teething : Swelling and redness of the gums | Features of the child’s condition and behavior
|
| First symptoms of teething Excessive salivation | Features of the child’s condition and behavior
|
| First symptoms of teething Decreased appetite or complete refusal to eat | Features of the child’s condition and behavior
|
| First symptoms of teething Increased moodiness | Features of the child’s condition and behavior
|
| First symptoms of teething Temperature | Features of the child’s condition and behavior
|
— When is it better to lower the temperature during teething?
— Typically, antipyretic therapy is prescribed when the temperature rises above 38.5 degrees. Low-grade fever, up to 38 degrees, should always be brought down in children with organic damage to the central nervous system, with the threat of seizures, as well as with pronounced changes in the general condition of the child.
— Why do you need to carefully monitor your baby’s health during teething? Does teething affect the immune system?
— Teething is a rather complex process in which all systems of the child’s body are involved. The immune system is no exception. When the tooth moves, traumatic damage to the gums occurs and, as a result, inflammation occurs in the tissues. Immune cells rush to the inflammatory focus, trying to eliminate it, which somewhat weakens the local protective reaction. In addition, in abundantly secreted saliva, the content of the enzyme lysozyme is reduced, and it loses its protective properties. In addition, during this period the child puts everything into his mouth, trying to scratch the itchy gums, which increases the risk of infection and injury to the mucous membrane.
— How can parents distinguish teething from other problems, such as a cold?
— It is sometimes difficult even for a specialist to distinguish a viral infection from teething syndrome: very often the two conditions occur simultaneously. With eruption syndrome, the temperature rarely exceeds 38-38.5 degrees, the discharge from the nose is copious, mucous in nature, often transparent. The cough is superficial and occurs more often in a horizontal position. All symptoms are accompanied by profuse salivation. The child's general condition rarely deteriorates; the child is capricious, whiny, but not lethargic or apathetic.
Teething can also be accompanied by symptoms of dyspepsia, such as regurgitation, and sometimes even vomiting, and loose stools. Unlike an intestinal infection, regurgitation and vomiting are episodic and occur when there is an excessive accumulation of saliva.
Liquefied stools may be associated with increased motility due to an increase in temperature - swallowing large amounts of saliva and intense chewing movements. Stool 1-2 times a day, normal color and smell, without pathological impurities, but softer consistency.
If any symptoms appear that do not fit into the picture of teething, you should definitely consult a doctor.
— Does all children experience pain during teething?
— Each child has his own pain sensitivity threshold. The intensity of inflammatory reactions is also different for everyone, so each baby experiences teething differently. If one continuously cries all night, the other may behave in a completely normal way. It depends both on genetics and on the baby’s temperament.
— When teeth are being cut, how can you help your baby? What medications are allowed to be given to relieve pain?
— Pain-relieving gels are widely used. However, you should remember the rules for their use. They have a short-term effect, about 20-30 minutes, but it is not recommended to use them more than five times a day. The gel is applied in a thin layer to avoid an overdose of the drug. And, as is the case with any medicine, do not forget about a possible allergic reaction in the baby.
You can quickly and permanently relieve pain only with anti-inflammatory drugs. And there are a lot of BUTs here. Any drug is unsafe, especially if given for the first time. Only a doctor can assess the child’s condition and prescribe anti-inflammatory therapy if necessary, taking into account the risk-benefit ratio.
Medicines from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be prescribed internally. The dosage is calculated by the doctor depending on the weight of the child. Gels with local anesthetic and antiseptic effects are used on the mucous membrane.
— Is it possible to relieve pain and other symptoms with folk remedies?
— Treatment with folk remedies is very popular in our country, although the global scientific community questions its effectiveness. Only exposure to cold has proven effectiveness, so it is recommended to give your child chilled pacifiers and teethers to chew on. Cold causes vasospasm, reduces swelling and inflammation in the gums, and, as a result, pain temporarily subsides. The effect is short-lived, but it still exists. Massaging the gums with a fingertip or soft brush is also helpful.
— Ekaterina Borisovna, tell us in more detail how pacifiers or toys that can be chewed help with toothache, and how to choose a pacifier and a special teether for a child.
— Gum massage helps the baby cope with unpleasant sensations. During the massage, itching decreases, gum tissue softens, and it is easier for the tooth to make its way. But constantly massaging a child’s gums is a very tedious task. He may well engage in self-massage, especially since during this period he himself happily puts everything into his mouth.
Special pacifiers or teethers will be excellent massage assistants. They differ from regular pacifiers in their greater rigidity and textured surface, and are made of latex or silicone. Many models of teethers are equipped with a cooling function - there is a liquid inside that can be cooled. Teethers are also made from plastic, wood or even textiles. But, in my opinion, they do not meet safety standards. It’s worth choosing brands that have been widely represented on the children’s goods market for a long time.
— What techniques can be used to distract a child from toothache?
- In this case, there is only one method - to surround the baby with care and attention as much as possible, pick him up more often, put him to the chest if the child asks. Next to the parents, the baby feels safe and calms down. Children react very sensitively to the behavior and emotions of adults, so it is important for parents to be calm and friendly, to distract the kids with a toy, song, or kind words. You can play finger games with older children. Relaxing massages and long walks are helpful.
Unfortunately, there are no absolutely effective methods. Parents can only help the child cope with the problem that has arisen. But there are some tips that will help you survive this difficult period.
— Please share them with our readers.
— The rudiments of teeth are formed long before birth. Therefore, during pregnancy, mothers should carefully monitor their diet. A sufficient supply of calcium is especially important for the formation of healthy teeth in a baby. But even after birth you shouldn’t forget about calcium. When breastfeeding, the mother's diet should include dairy products or calcium supplements in case the baby is intolerant to cow's milk proteins.
Hardening from birth is the key to good immunity. There is no need to wrap your child in a hundred clothes and be afraid to ventilate the rooms. Walk in any weather and for a long time, use a light contrast shower. And then the baby won’t be afraid of any cold.
Also, avoid public places, especially during the teething period. The baby is very vulnerable at this moment. Postpone visits from relatives, shopping trips and visits to closed playgrounds for a while - thereby you will reduce the risk of infection for your child.
It is also especially important to maintain optimal temperature conditions in the room during this period. Heat and dry air will only increase discomfort.
Teething is a difficult stage in a child’s life. If the process causes severe discomfort, is accompanied by the appearance of alarming symptoms, or high fever, then you should contact a specialist for help as soon as possible. Otherwise, surround your baby with care and attention, select pacifiers, teethers, toys that relieve itching, and use medications with the doctor’s permission. The main thing during this period is to be there and help the baby cope with the pain in every possible way.
Pediatrician Ekaterina Borisovna Bulavina
*The ideal food for an infant is mother's milk. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months. MAMAKO® supports this recommendation. Before introducing new foods into your baby’s diet, consult a specialist.
Scheme for cutting elements for children
Dentists have drawn up a specific scheme for the formation of primary occlusion in children. However, it is necessary to remember that each baby’s body is individual, and the teething dates established by doctors may deviate up or down by several months. Pathological signs of bite formation in babies include early eruption of incisors (up to 3 months of age) and the complete absence of elements in the oral cavity by 12 months.
The standard scheme for the formation of bite in children is as follows:
- 5–7 months – lower front incisors;
- 8–10 – upper incisors;
- 10–12 – upper lateral incisors;
- 11–13 – lower lateral incisors;
- 12–15 – upper and lower molars;
- 17–22 – canines (upper, then lower);
- 25–30 – upper and lower molars.
Pattern of tooth growth in infants
If a child is cutting teeth at 3 months, then these should be the front pair of incisors. If the side elements are shown first, then it is necessary to show the baby to the dentist. The symptoms corresponding to the process depend on the characteristics of the child himself. In some children, the elements appear completely unnoticed, in others they cause crying, fever, etc.
Alarming symptoms
Many signs of teething are harmless and go away on their own once the incisor comes to the surface. However, some signs may indicate the addition of bacterial or viral diseases against a background of weakened immunity.
Reviews of Dentokind for teething up to one year
Normal signs of the condition include:
- Profuse salivation. The symptom is observed in almost all children under three months. It does not require treatment for the child.
- Skin irritation near the chin. The symptom is caused by increased salivation during teething. It is enough to use an emollient cream every day at night to eliminate skin redness.
- The child's desire to breastfeed frequently. During feeding, the baby scratches its gums on the mother's nipple.
The list of alarming symptoms of teething includes:
- refusal to eat (more than 3-4 feedings);
- persistent diarrhea (may indicate an incipient intestinal infection);
- constant crying of the child.
Small bruises (hematomas) may appear in the eruption area. They dissolve quite quickly if you apply a compress to the problem area.
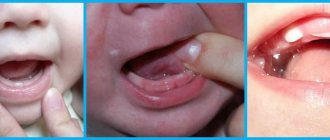
Signs of teething
You can understand that the first molar will soon come out by the following signs - the gums begin to swell and hurt greatly, which is accompanied by increased salivation. In this case, a similar picture can begin several months before the actual appearance of the teeth themselves. Sleep becomes restless, the child is capricious, due to severe discomfort, children refuse some meals, and an irresistible urge to put various objects in their mouth appears.
Once teething enters the active stage, you will notice a thin white line on the gum or a whitish protrusion. If you lightly tap the exposed teeth with a teaspoon, you will hear a slight clicking sound, some parents do this, but if you decide to do this test, do it very carefully.
How to correctly distinguish between symptoms
Some signs characteristic of the onset of the appearance of molars in children often overlap with the symptoms of infectious diseases. Therefore, if you have any doubts about this, it is better to seek advice from a specialist.
Pay attention to the temperature - it can rise to 38.5–39 degrees and stay for two days, this is normal. Paracetamol in small quantities is suitable for knocking it down, but if after this period the indicators do not decrease, you should not hesitate to go to the doctor.
Watery diarrhea also often occurs due to excessive salivation; normally, this repeats up to 2-3 times a day. If this period is exceeded and blood inclusions appear, there is already a reason to make an appointment with a specialist.
Regarding the runny nose, clear discharge that lasts 3-4 days does not cause concern; it is enough for parents to clear the sinuses of it in a timely manner.
If this period is exceeded, and the snot becomes whitish or greenish, do not hesitate to go to the doctor. The same applies to a cough, if it lasts more than two days and is accompanied by sputum, consultation is needed.
Factors affecting tooth growth
The speed of formation of a mixed bite depends on several circumstances:
- baby's genotype;
- performance of the thyroid gland;
- gender;
- severe infectious and viral diseases suffered in the past;
- duration of natural feeding;
- the presence of congenital diseases.
You also need to monitor the period of eruption of molars. They should come out to the surface of the gums only after the milk unit falls out. Otherwise, a mandatory visit to the dentist will be required. Early loss of milk elements is also undesirable, as this negatively affects the proportions of the baby’s jaw and his bite in the future.
Reasons for the atypical timing of the eruption of elements
Only a dentist can accurately determine the causes of abnormal teething in children. However, there are several common violations that lead to the problem:
- improper metabolism;
- lack of calcium in the body;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- gastrointestinal pathologies;
- incorrect direction of the tooth axis.
Anomalies of the dentition can be associated not only with the timing of the appearance of elements, but also with the color, location, and size of the units in the row. If a child is already born with teeth, they are usually removed. Such situations are diagnosed quite rarely, and they indicate intrauterine disorders in the baby.
Ways to alleviate the condition
The formation of a bite is often accompanied by an increase in temperature. Therefore, parents should always have antipyretic drugs in their medicine cabinet (Panadol, Nurofen, Ibuklin). They not only reduce the temperature, but also relieve pain associated with tooth growth.
The love and attention of parents will allow the child to cope with the problem. The baby should be put to the breast and picked up as often as possible. Special teethers with gel will help satisfy your baby’s desire to scratch his teeth.
You need to choose small devices so that the child can comfortably hold it in his hand.
Pediatricians advise cooling teethers with cold water before giving them to a child. Instead of toys, you can give your baby chilled pieces of apple or carrot. At the same time, parents should carefully monitor that the baby does not bite off the product and does not choke on it. In parallel with this, local anesthetics can be used.
On the pharmacological market there are many drugs in the form of a gel that relieve pain during the appearance of teeth - Kalgel, Kamistad, Cholisal. Additionally, the gels have an anti-inflammatory effect, which also alleviates the child’s condition. The analgesic effect occurs 2-3 minutes after using the drug.
How to make your baby feel better when teething
We have already dealt with the question of whether teeth can erupt at the age of three months. But when this process begins, parents are faced with another dilemma - what to do to alleviate the child’s condition. In such a stressful situation, he needs physical and psycho-emotional contact - carry the baby in your arms, rock him, talk to him gently. This will help relieve nervousness. To eliminate other unwanted symptoms, the following methods are used:
- Gum massage. Do it with the tip of your finger, after washing your hands. To avoid injuring the child, you should also trim your nails. There are also silicone finger pads with bristles or pimples on sale. To determine the intensity of the massaging movements, you need to monitor the baby's reaction.
- Cold. Since regular teethers are not suitable for a 3-month-old baby, other alternative methods are used - cool the pacifier or apply a gauze cloth soaked in cold boiled water.
- Pharmacy products. If you notice that your baby's incisors are starting to come out, you should consult with your pediatrician about which gel or ointment to choose. Not all drugs are suitable for the youngest, but there is still a choice. For example, "Kamistad" or "Kalgel" are safe for three-month-old children.
- Antipyretic. Preparations based on paracetamol and ibuprofen help. In addition to normalizing body temperature, they relieve pain. Babies are often given candles, for example, Efferalgan.
You need to be careful to notice which method best helps your baby. During the period when teeth erupt, it also needs careful care. To avoid infection of the gums, you need to keep his pacifier clean and monitor breast hygiene. Saliva should be wiped away with clean napkins, without making any effort, so as not to irritate delicate skin. After this, you can apply baby cream with light massaging movements. Walking in the fresh air in places where there are not large crowds of people will be useful for the baby.