Knowing the symptoms of teething and being able to provide assistance, loving parents will alleviate the baby’s condition and protect him from unpleasant complications. Often, teeth appear according to individual timing. Parents don't need to worry. A deviation from the norm of 1-2 months is not a pathology. If the schedule changes significantly, the help of a doctor is necessary. The examination begins with a pediatrician and dentist.
Signs that teeth are being cut
Many young parents do not immediately understand the reason for this child’s behavior and come up with terrible diagnoses before the doctor explains to them what the problem really is. But how not to confuse teething with illness or discomfort of the baby? At what age does the first tooth begin to cut? What to do to ease the baby's suffering? All this will be discussed below. Before the first teeth erupt, the baby feels discomfort, so he constantly tries to massage the gums with “improvised objects”
All babies experience the eruption of their first teeth differently: some go through this period steadily and relatively painlessly, while others suffer and suffer. It is difficult to explain what this difference depends on, but we can say with certainty that not a single newborn has had an absolutely comfortable teething process.
How can parents determine that their baby has started teething? There are several symptoms that are most common.
- The baby's salivation increases, he begins to move his jaws more often, as if he is trying to chew something or massage his gums.
- The child becomes more excitable, he may cry more often for no reason, be capricious, sleep poorly, and sometimes refuse to eat.
- An increase in body temperature also indicates the appearance of the first teeth.
- The baby may have diarrhea.
- The gums become swollen and red, and itching appears. If such symptoms are present, the baby more often touches his mouth with his hands, tries to stick his fingers into it, and rubs his cheeks.
- Teething is often accompanied by a weakened immune system. Against this background, the baby may develop a cough or runny nose.
The formation of teeth in humans begins several months before birth. For example, baby teeth are formed in a baby in the fourth month of the mother’s pregnancy, and then (the fifth and sixth months) the molars are formed.
Consequences of early destruction of primary teeth
After the early removal of a baby tooth, the gum in its place becomes overgrown, and the permanent one is deprived of its natural landmark. This leads to phenomena such as:
- dystopia - eruption of a permanent tooth outside the dental arch;
- retention - the occurrence of a formed tooth in the thickness of the jaw bone.
If the baby tooth does not receive treatment, and the inflammatory process spreads to its roots, then the permanent follicle located under them is damaged. In this case, the permanent one may die, and then its place in the dentition will remain empty. The absence of a tooth is confirmed by radiography.
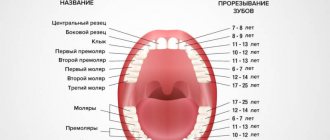
Scheme of baby teeth eruption
To make it easier for parents to navigate the teething system, they can print out a reminder for themselves with a picture of the jaws, an indication of the teeth, and a description of exactly when certain dental units are cut.
This is how a child’s teeth erupt according to the following pattern:
- 6-10 months - central incisor, lower jaw;
- 8-12 months - central incisor, upper jaw;
- 9-13 months - lateral incisors, upper jaw;
- 10-16 months - lateral incisors, lower jaw;
- 13-19 months - molar, upper jaw;
- 14-18 months - molar, lower jaw;
- 16-22 months - canines, upper jaw;
- 17-23 months - canines, lower jaw;
- 23-31 months - second molar, lower jaw;
- 21-31 months - second molar, upper jaw.
It turns out that at the age of two, the second molars of both jaws usually emerge. But it is difficult to say whether this is the most difficult teething for the baby. It is believed that fangs are more painful, which is due to their sharp edges. They literally tear the gums apart. The canines of the upper jaw are perhaps the most painful in their eruption. They are also called ophthalmic because they are connected to the facial nerve.
Table. Features of the eruption of baby teeth
| Category for evaluation | Description | Process Features |
| Age | Baby teeth erupt from six months to three years; if something doesn’t go according to plan, be sure to go to the doctor. | The average eruption rate may be shifted for some time |
| Duration | 2-7 days is the norm for the eruption of one tooth | It happens that this period is prolonged: if it lasts more than two weeks, consult a doctor |
| First tooth | Usually it takes longer to climb than others, i.e. more than a week | Depends on the individual characteristics of the body |
Many parents think that the first teeth are the most painful to cut, and the eruption of molars in two-year-old children is not accompanied by such pain. Therefore, parents may not understand what causes the capricious behavior of a two-year-old child, or what worries him.
The order of appearance of adult teeth
Almost all milk teeth that erupted in the first two and a half years, 10 on each half, are replaced by permanent ones. Compared to their predecessors, adult teeth form in a different order.
Table. The order of formation of permanent teeth
| Tooth name | Development timeframe | Peculiarities |
| Lower and then upper molars | This usually occurs in the seventh year of life | They make their way behind the second primary molars |
| Molar lateral | This can take three years – from 6 to 9 years old | They sprout when the central incisors are already formed |
| Permanent fangs | Normally, this occurs between the ages of 9 and 11 years. | By cutting the gum from the inside, they seem to displace milk precursors |
| First and second adult premolars | Appears at 10-13 years of age | They grow in place of central incisors, which become loose and fall out. |
| Third molars, better known as wisdom teeth | They may erupt at 18 years old, or at 25, or not at all. | Such cases are not considered a deviation from the norm. |
If a baby's individual teeth grow in a different order, this is not dangerous. Individual characteristics, deficiency of vitamins and minerals slow down the speed and sequence of formation of permanent teeth. It is important for parents to know that an adult tooth should not become loose; if there are similar symptoms, this should be a reason to visit the dentist.
- Teething in children: sequence up to one year
Teeth may fall out and grow in random order in different children
Permanent teeth should not be loose
Eruption of second molars
The first fundamental units of the primary occlusion are the molars. They have the largest chewing area. They are diamond-shaped from above and cube-shaped from below. Children have 8 molars - two on each side below and above. The first molar and the second molar are distinguished. In terms of ranking from the central incisors, they occupy 4th and 5th positions. Their cutting order is as follows:
- the first in the lower jaw – 13-18 months;
- the first in the upper jaw – 14-19 months;
- the latter in the lower and upper jaws erupt approximately equally - at 23-31 months.
After a year, parents should prepare to meet these “guests”: the first to climb will be the one in the top row. By the age of two, the second ones appear. The correct sequence of appearance ensures a beautiful and correct bite. Many parents like to look into their babies' mouths and check how their teeth are coming in. You shouldn’t do this and worry the baby once again. Genetics plays a large role in this process.
There is no need to interfere: nature will take care of everything itself. A photo of molars will help you find out what chewing units look like. To help the child and alleviate his condition, it is very important for parents to know what the symptoms of teething are. Since the process occurs after a year, many children can already point to the sore spot and even say what they feel.
How to help your baby?
The only troubles that can be explained by the appearance of teeth are mild “crankiness”, drooling and the formation of bad habits, for example, finger sucking. Appetite may decrease, the rhythm of sleep and wakefulness may be disrupted due to constant itching of the gums. Of course, these manifestations do not bother the baby for 2 years without stopping; as a rule, there are days when the child shows the greatest concern about teething. How can you make life easier for a child during this difficult period?
- Remedy No. 1
. Double the affection and care of parents. Don't be afraid to spoil your baby; Constant crying and whims spoil your character much more! - Remedy No. 2
. Using teethers. These are rubber or plastic toys that your baby can bite on. Chewing teething rings with liquid inside, which can be placed in the refrigerator and cooled, is especially soothing. A child aged 6 months and older will feel better even after chewing on a clean, cold cloth. - Remedy No. 3
. Gently massage the gums with a gauze pad. Wrap your index finger in a gauze pad soaked in cold water and gently massage your baby's gums. - Remedy No. 4
. A homeopathic medicine that must be prescribed by a pediatrician or homeopathic physician. - Remedy No. 5
. Medicinal. Pain-relieving gels containing a local anesthetic, such as lidocaine (available in pharmacies without a prescription). They cause numbness in the gums and thereby relieve pain.
Many mothers believe that while the child has few teeth and they are baby teeth, it is not necessary to brush them. However, this is not true at all! In young children, the protective properties of tooth enamel are reduced and in the presence of provoking factors (consumption of sugar-containing products, poor oral hygiene), this can lead to the development of caries.
Experts' opinion
The pleasant-tasting ASEPTA baby gel does not damage the milk enamel of teeth, has a beneficial effect on the gums, and plant extracts prevent the development of inflammation in the oral cavity. Thanks to the pleasant taste of “tutti-frutti”, toothpaste helps to develop the child’s daily oral hygiene skills. The paste does not contain fluoride or abrasives and is suitable for daily oral hygiene of a child.
An analysis of the clinical effectiveness of the use of various therapeutic and prophylactic agents of the Asepta series, carried out in Novosibirsk, at the State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education "Novosibirsk State University", confirmed that the line is different:
- Pronounced hygienic;
- Anti-inflammatory;
- Hemostatic property.
Sources:
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of the use of therapeutic and prophylactic agents of the ASEPTA series in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases in children and adolescents (I.V. Klimova) Irina Vladimirovna Klimova, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Novosibirsk State Medical University. Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Novosibirsk State Medical University.
- Prevention of recurrence of localized periodontitis in young A.K. YORDANISHVILI, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikov, Military Medical Academy named after. CM. Kirov, International Academy of Sciences of Ecology, Human Safety and Nature.
- Article “Treatment and hygiene features for mild and moderate periodontitis” by S.B. Ulitovsky head Department of PFS, Professor, Doctor of Medical Sciences, A.A. Leontyev Associate Professor of the Department of PFS, Ph.D. PSPbSMU named after. I.P. Pavlova
If your child has a fever
A temperature of 37 degrees is considered normal; up to 37.5 this will also not be considered a special or complicated situation. Children usually feel fine with such a slight increase in temperature. Naturally, there is no point in giving an antipyretic in this case.
If the temperature rises above 38 degrees, it is worth saying that inflammation or infection has joined the teething process. This situation requires seeing a doctor (he needs to be called to your home), and only his recommendations will be your tactics in future behavior.
During this period, children experience pain, malaise, and weakness that were not typical before, so their behavior changes, sleep disturbances and refusal to eat are noted, which only aggravates the temperature reaction. First of all, the child needs rest, calm and healthy sleep, because temperature, on the one hand, is a protective reaction, and on the other, a debilitating process, which, if unfavorable, can cause overstrain of all organs and systems with the development of pathological reactions: weakness, drowsiness, tachycardia and even febrile seizures.
And remember that the antipyretic should be strictly for children, ideally recommended by a doctor. These are usually paracetamol-based drugs. If they do not help, you can give the child Ibuprofen (but it is prescribed to children from one year old).
But under no circumstances should children be given medications of the aspirin and analgin group. These are toxic drugs that cause side effects.
An excellent tactic for high temperatures would be to humidify the air in the room, regularly ventilate (while the child is in another room), drink plenty of fluids and eat as desired. The child should drink a lot of warm drinks and eat only when he wants to. Avoid dry air, wrapping yourself up in three pajamas and two blankets. If a child wants to play at a high temperature, there is no need to force him to go to bed.
It is important to understand that if the temperature is elevated for more than three days, it is unlikely that the problem is teething. And when it still doesn’t go astray, urgently call a doctor and look for the real reason for this reaction of the body.
Teething is not a very long period. By the age of three, it is definitely completed, and then you will already wait for the loss of milk teeth and the growth of permanent ones. As a rule, the child tolerates these processes normally. To make sure everything is in order, visit your pediatric dentist every six months. You can take care of baby teeth from the moment they appear. Teach your child to brush his teeth twice a day, monitor the quality of brushing.
Help from folk remedies
If you do not want to give your baby medications, you can use natural formulations. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of an allergic reaction in the baby. Also follow safety precautions and remember that small objects can be swallowed or choked by the baby.
- Amber beads
. These products are made from Baltic products. They have a pronounced analgesic and regenerating effect. In addition, the product can relieve fever and fever. The beads are made in such a way that they can enhance the effect of other medications. - Plant herbs
. Herbs such as chamomile and phytolacca can help alleviate the teething condition of a child. They relieve inflammation and partially relieve gum pain. Remember that they must be used in accordance with the instructions. You should not give your baby prepared formulas to drink. Simply treat the inflamed areas of the mucous membrane with the decoction.