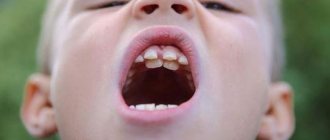
In 6-10 year old children, baby teeth often fall out - a harbinger of the appearance of permanent teeth in their place. This fact should not cause any particular concern. However, there are cases when real teeth begin to loosen on their own. This is a signal that you need to consult a doctor without wasting time before the child’s health condition becomes dangerous. Loosening of baby teeth is a sure sign of a malfunction in the immune system.
Loosening of permanent teeth is a sign of both emerging diseases in the oral cavity and sudden problems with internal organs. The most common manifestations are:
- Periodontitis;
- Inflammation of the gums;
- Caries;
- Generalized metabolic disorders;
- Injuries.
If you find that your child has one or more molars that are loose, contact your dentist immediately. In some cases, the tooth root may become loose due to not entirely successful heredity - the root of the new tooth does not grow well into the jaw. It is necessary to check whether the parents of this child had such cases.
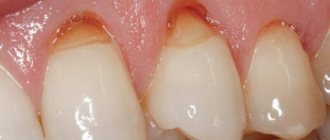
Periodontitis
This disease manifests itself at the age of 9 years - on average in 4% of children. When it occurs, the tissues surrounding the tooth become inflamed, and it begins to wobble. The basis of this process is the loss of properties. Inherent in tissues that have not yet fully matured. Here lies the main reason why teeth become loose and fall out.
To exclude such an unfavorable scenario, timely and proper teeth cleaning is needed. In childhood and adolescence, increased load on the same teeth (on the one hand), or the absence of products elastic enough for chewing, which allow, like a kind of simulator, to train growing teeth, is unacceptable. After all, what is trained during growth is what develops comprehensively.
What to do when a child’s molars are loose
Molars in a child’s bite are all the replaced units, as well as the outer chewing ones: “sixes”, “sevens”, “eights”. Due to the extensive root system, these teeth are firmly fixed in the dentoalveolar rows, but sometimes they begin to wobble.
Doctors distinguish between natural physiological mobility, which occurs when loads are redistributed by periodontal tissues, and pathological mobility, visible to the patient. The reasons for the loosening of radical units can be:
- Injuries – a strong blow to the jaw can easily cause dislocation or fracture of a tooth and damage adjacent soft tissues.
- Inflammation of the gums and periodontal tissues - due to changes in bite, poor hygiene and disruption of the microflora in the oral cavity. The development of gingivitis will worsen the situation, since if left untreated, young patients develop periodontitis - inflammation that leads to loosening and loss of teeth.
- Caries - developed from below at the neck of the root. It is especially common in remote units - “fives”, “sixes”.
- Incorrect bite – leads to uneven distribution of the load during chewing and loosening of individual teeth due to overload.
- Bruxism is a strong clenching of the jaws and grinding that often causes the incisors to wobble.
- Genetic diseases of the body - metabolic disorders and microcirculation in tissues harm periodontal health, which causes excessive mobility of healthy teeth.
Tottering root units often require complex solutions. The examination begins with a consultation with a pediatric dentist, who determines the main cause of molar mobility and draws up a treatment algorithm. Sometimes it is enough to cure caries or strengthen the enamel, but in other cases prosthetics, splinting or another solution may be required.
Dolotova Marina
“Young patients are very active, so injuries to permanent incisors or canines are not uncommon. Athletes especially often suffer from this problem. There is no need to be afraid of a moving tooth. Modern splinting techniques securely fix the tooth in place, restoring a rigid connection with the tissues. True, you will have to refrain from training and solid food. But this is temporary!
Any mobility of the dental crown, accompanied by pain, discomfort or poor health, is a reason to make an appointment at a children’s dental clinic. This will be either the first step towards peace of mind for parents and the child, or the beginning of professional treatment and saving the tooth.
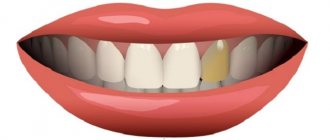
Caries
Caries in childhood and adolescence develops much more rapidly than in adults. With it, the enamel is rapidly affected first, then the carious cavity penetrates the dentin and reaches the pulp. The last stage can lead to pulpitis and the need for drilling of the dental canal. The tooth enamel itself in children is immature - it is the most vulnerable, that is, it does not resist caries damage as actively as it does in adults. The maturation of tooth enamel continues for up to several years; it is necessary to brush your teeth twice a day, as doctors advise, in order to prevent the parasitic process.
Caries also manifests itself from the inside or from below - it is not the enamel of the crown or even the neck of the tooth that is affected, but the root, or the underlying structures begin to collapse. You can guess this by the fact that the tooth suddenly began to loosen.
How does a baby tooth change to a permanent one?
Adults usually no longer remember their sensations when changing teeth when this process begins in their children. Hence the excitement. Parents feel that their child is in pain and uncomfortable when a baby tooth becomes loose. However, often the loss of baby teeth is completely painless.
Every child has the rudiments of molars under the baby teeth at birth, and they continue to form in all subsequent years. When the time comes, the baby tooth must let the permanent one through, making its way up through the gums. The roots of baby teeth begin to dissolve several months before the tooth becomes loose. When it wobbles, it means that the roots are no longer there, only the gums hold it in place. And a new, permanent tooth is on the way.
What do we have to do
You don't need to do anything special. You can gently loosen the tooth little by little - the child can do this on his own, remembering to wash his hands first. You should not forcefully pull out a tooth with your fingers or deliberately bite hard objects - this can injure the gums and cause infection.
Be sure to warn your child about what is happening and make sure he doesn't accidentally swallow the tooth when it finally falls out. This is a good time to talk about the Tooth Fairy (Mouse, Squirrel). Then he himself will strive to say goodbye to the old milk tooth as quickly as possible.
When a visit to the doctor is necessary
If a baby tooth begins to loosen on time, but does not fall out for a long time, it needs to be removed. The problem is that a permanent one has probably already broken through underneath it. If you don't make room for it, it will begin to grow crookedly.
In addition, sometimes the child's temperature may rise. If it does not subside for more than three days, or is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, you should see a pediatrician.
There are also other situations when you should not wait for a loose baby tooth to fall out on its own and you need to remove it. Do not delay visiting the dentist if:
- The baby tooth has been loose for a long time and greatly interferes with chewing food;
- the tooth is broken and its sharp edges touch the oral mucosa or tongue;
- the tooth or its root is severely damaged by caries (this can lead to damage to the permanent tooth);
- the tooth is affected by pulpitis, gum inflammation or a cyst has occurred.
If the situation repeats itself - that is, the teeth begin to loosen, but do not fall out on their own, especially if the erupting permanent teeth are already clearly visible underneath them, you should undergo additional tests. Most likely, your child has excess calcium in the body. This is just as bad as its deficiency; nutritional adjustments are necessary.
If baby teeth begin to loosen too early - for example, at 2 or 3 years - you should contact a dentist immediately. This is not a sign of a natural, physiological process. This is a signal of a serious illness that requires urgent treatment. Teeth become loose due to pathologies such as:
- periodontal disease;
- hereditarily weak gums;
- rickets;
- vitamin deficiency or anemia;
- diabetes.
Today, all of them can be successfully treated, even in young children - but subject to timely diagnosis and compliance with all doctor’s instructions. The health and quality of your child's future life may depend on how quickly you react.
General diseases of the body
Children's teeth can also become loose due to systemic diseases. They are most often based on a violation of the blood flow of individual tissues adjacent to the teeth, or metabolic disorders. These include psoriasis, diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus, thyroid pathologies, congenital connective tissue disorders and several other diseases.
All these destabilizing factors lead to obstruction of blood flow through the capillaries in the body. The gums and pulp in the tooth are rich in microcapillaries, through which blood delivers oxygen and nutrients to the teeth, and removes waste products and excess carbon dioxide. If these processes are untimely, degenerative phenomena occur in which tissues starve, as a result, their growth and renewal stop, and their accelerated wear and degradation occurs. This causes the weakened tooth (or several teeth) to wobble and may fall out.
The permanent tooth is loose. What is the reason?
In most cases, excessively mobile teeth in children are a sign of injury, or a general poor condition of the body and a lack of microelements in the diet. It is important to show the child to a specialist in a timely manner and carry out treatment in order to stop the process at the very beginning.
What could cause the mobility?
- Bruises, unfortunate falls during games and sports. Newly erupted permanent teeth are very fragile. They have a thin layer of enamel and dentin, but a large nerve. Immature incisors, canines and molars are much easier to break than mature teeth. How to react and what to do if a child has a tooth injury, read here.
- Inflammation of oral tissues due to poor hygiene, chronic gingivitis, stomatitis, advanced caries and other diseases. Decreased immunity also serves as a factor in the appearance of infection of the mucous membrane and the gradual loosening of the dentition.
- Consequences of orthodontic treatment. Braces put pressure on your teeth and move them into new places. Therefore, immediately after removing the system, the dentition tends to return to its original position. To stop movement and prevent regression, the patient must wear retainers. If for various reasons the child refuses to do this, contact an orthodontist to undergo an examination and prescribe the correct treatment.
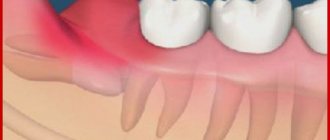
Injuries
Many children find it impossible to sit still. And some of them sometimes fall. If the injury occurs in the vicinity of the jaws, the teeth may also suffer. There are often cases where a child knocked out one or even two or three teeth during a fall. But tooth fractures are not always open - cracks and root fractures can also occur - the tooth tilts to the side, and accordingly, it immediately begins to wobble.
Dental injuries also appear when a child suffers from bruxism (grinding his teeth in his sleep), or tried to chew, for example, a candy that was too hard, or, for example, got a stone in the cereal from which the porridge was cooked.
Symptoms
The main symptom is one - when you press on a tooth, it moves left and right or back and forth. Associated symptoms depend on the cause of mobility and may include:
- bad breath;
- redness, bleeding, swelling, soreness of the gums;
- abundant dental plaque;
- itching, burning gums;
- the tooth is loose and hurts when pressed;
- gum recession (exposure of the neck of the tooth);
- pathological abrasion of enamel;
- muscle hypertonicity;
- symptoms of intoxication - headache, fever, nausea, etc.
All causes are accompanied by corresponding symptoms - the tooth became loose after a characteristic crunch was heard, most likely we are talking about a longitudinal or scaly fracture of the root. A healthy tooth is loose - more often than not, this indicates an occlusal, mechanical injury. Several teeth in a row loosen at once - this is a manifestation of periodontal pathologies (periodontal disease, periodontitis).
Treatment
When a child complains of looseness and pain in one or more molars, urgently visit the dentist with him. It is the dentist who will decide whether it is possible for a child not to lose a loose tooth. The doctor will take a number of measures to save the problematic tooth, which will avoid its loss and unpleasant consequences in the future. Of course, the tooth can later be replaced “from scratch” (along with a pin) - but it is better to try to preserve the original one.
When the cause of tooth loss is periodontitis or gingivitis, it is necessary to urgently clean the teeth of plaque, as well as prevent the development of inflammation that has already begun. It is possible that the teeth are splinted - this will stop their ongoing loosening.
In the event of a tooth injury, the question is raised about the possibility of saving it. When the damage is small, it is possible to preserve all intact dental tissues - they will help facilitate the process of prosthetics, becoming the “foundation” for a renewed tooth. If caries has developed, after a thorough examination, an attempt is made to save the molar. When the damage is too great, the tooth is simply removed to prevent it from rotting and damage to internal organs due to infection in the blood. If the carious cavity is small, the tooth is filled - nerves and blood vessels are removed from the pulp, disinfected with medications, and then dental cement is injected - an adhesive base that, after hardening, resembles hard dental tissue; In turn, a seal is installed on it.
If no visible damage to the teeth is found, the child undergoes a comprehensive medical examination. If any diseases are detected, he undergoes timely treatment.
Splinting teeth in children after injury
If your adventures result in dental injury, don’t be upset. Our doctors will carefully examine the damaged groups, carry out the necessary restoration of injured teeth, and also perform splinting and strengthening.
It is absolutely safe and aesthetically pleasing. A special orthodontic fiberglass or aramid thread is applied to the outer side of the teeth, which will unite several units into a stable chain.
In the early stages, this approach will completely eliminate mobility and will in no way prevent the little patient from leading a full life.
Splinting can be temporary or permanent, depending on the situation.
Pros:
- the ability to preserve loose teeth without the risk of premature atrophy of bone tissue;
- no need to grind crowns or remove pulp;
- an even distribution of the load between healthy and injured teeth is achieved;
- ease of care.
View prices for splinting teeth in children
Prevention
Taking care of your teeth is preserving the attractiveness of your smile, which is the calling card of both a child and, subsequently, an adult who sets important goals for himself. This means that taking care of your teeth should be timely, and it is better to get used to this right away in childhood. Parents will ensure that the child carries out high-quality sanitation of the oral cavity and teeth every day, and twice a year he needs to visit the dentist. Equally important is a balanced diet. If problems do affect at least one tooth, do not ignore them: you are responsible for the health of your child.
What to do
If your front tooth begins to loosen for no apparent reason, you should clearly understand that inaction can lead to its loss. Initially, it is necessary to identify the cause of the disease in order to take the necessary measures to eliminate it. But it is almost impossible to independently identify the cause and make a correct diagnosis, so it is extremely important to seek the help of a specialist. Quite often, loose teeth are a consequence of bad habits, such as drinking alcohol and smoking. There are also hereditary causes of this process. People with malocclusion often have loose front teeth. In such situations, treatment should be carried out by a qualified orthodontist.
Pregnancy
During pregnancy, hormonal changes occur in a woman's body, which significantly affect the deterioration of blood supply to the mucous membranes. The child takes away the mother's calcium supply, which significantly worsens the condition of the mother's teeth. Also, calcium leaching occurs during toxicosis. As a result of these processes, the gums begin to bleed and become inflamed, periodontal pockets form where food remains accumulate, and teeth can begin to wobble. In order to strengthen and restore the oral cavity, expectant mothers should visit a dental clinic. The specialist will prescribe a set of preventive and therapeutic measures that will strengthen loose teeth. Such events include:
- professional dental hygiene;
- recommendations for a proper diet, which includes the mandatory consumption of foods containing large amounts of calcium (fermented milk products, vegetables, fruits, fish and meat);
- prescribing additional intake of mineral and vitamin complexes;
- the use of additional oral care products, such as rinses, flosses, etc.