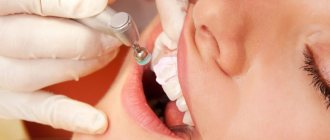
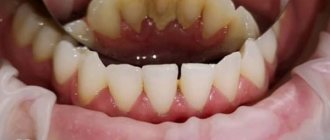
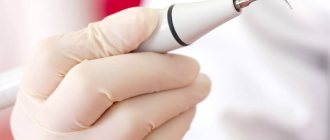
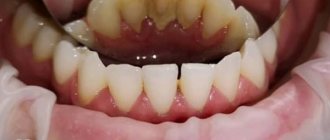
Dental deposits are plaque and tartar that form on the surfaces of teeth and accumulate in the supragingival and subgingival space. Dental plaque not only makes our teeth unsightly - dull and yellow, but they contribute to the development of a wide variety of dental diseases of the teeth and gums. It is for this reason that it is imperative to remove dental plaque and do it in the dentist’s office, using professional techniques and equipment.
How dental plaque is removed in dentistry, by what methods and what is the price for the service in Moscow - we will answer all these questions in detail in this article.
What are dental deposits?
Such formations on the teeth appear even in those who regularly and conscientiously brush their teeth and take care of their oral cavity. Deposits on teeth are formed under the influence of various factors. They affect not only the crown of the tooth, but also the surface of the gums. Dental deposits often cause the development of diseases of the gums and teeth. They are irritating to the gums and tooth enamel, as they contain a huge amount of bacteria and their metabolic products. Partially, soft plaque is removed when brushing your teeth. But this is only provided that the oral cavity is cleaned correctly and regularly. If personal hygiene rules are not followed, plaque remains on the teeth, between them and gradually leads to the formation of hard deposits.
1. Non-mineralized EOs
- pellicle
- tooth. Plaque
- soft tooth Raid
- food leftovers
2. Mineralized dental plaque
- supragingival tooth. Stone
- subgingival tooth. Stone
- cuticle - reduced enamel epithelium. After eruption it is lost. May persist on the lateral surfaces of the teeth.
Pellicle
- a thin acquired organic film that replaced the cuticle.
After teething, the tooth is exposed to saliva and microorganisms; as a result, the enamel surface undergoes dissolution of its proteins and demineralization. Microscopic tubules 1–3 µm deep are formed on its surface. These tubules are filled with an insoluble protein substance. To which salivary mucoproteins are precipitated. Microorganisms settle on them.
Pellicle
- a derivative of protein-carbohydrate complexes of saliva, has three layers. 2 on the surface of the enamel, 1 layer in the surface layer of the enamel itself. A characteristic feature of a pellicle is a jagged edge and niches in which microorganisms develop. The thickness of the daily pellicle is 2–4 µm. The pellicle contains a lot of glutamic acid, alanine, sialic acid, and amino sugars. Protects hard tooth tissues from acids, but promotes the fixation of microorganisms. Can be removed using strong abrasives. A toothbrush is not effective. Not visible visually. The pellicle becomes visible when stained with erythrosine. A light pink film is formed. If the film is removed, the tooth will not be stained. The pellicle is often stained in PR under the influence of chromogenic bacteria, tar, tar (from smoking), coloring food components, and medications. It recovers within 20-30 minutes after its complete removal.
Dental plaque.
The second layer of surface formations. It is located on the pellicle in the supra- and subgingival area. Microorganisms actively multiply and acid formation occurs. This is an amorphous granular deposit that accumulates on the surface of teeth, fillings and dentures. Colorless, not visible in small quantities. If it is not pigmented, staining is necessary to detect it. It is not washed off when rinsing, because the surface is covered with a mucous gel. It is not always removed when brushing your teeth, but is scraped off with a tool.
Compound:
microorganisms, epithelial cells, leukocytes, macrophages, organic and inorganic solid component 20% plaque, the rest water. Of the solid component, 70% are microorganisms, 30% are intercellular matrix. Matrix is a complex of polysaccharides and lipoproteins. Inorganic component – Ca, phosphate, K, mag, fluorine. The microbial composition changes as it grows. At first, it consists mainly of cocci (mutans, salivaris, etc.); as the plaque thickens, anaerobic conditions are created in it, and Gram cocci, fusobacteria, actinomycetes, and spirochetes appear. Food for microbes is easily digestible carbohydrates. During sleep, plaque formation increases due to decreased salivation. Accumulates 2 hours after brushing your teeth.
Stages of plaque formation
- 1. Fixation of bacteria to the pellicle - this is facilitated by epithelial cells, which attach to the pellicle within 1 hour after brushing the teeth and adsorb microorganisms on their surface (first salivaris, then mutans).
- 2. Formation of extracellular matrix
- 3. The growth of bacteria and the formation of dental plaque, the more dental plaque, the higher the intensity of caries. Now many people consider dental plaque as a biofilm.
Basic properties of biofilm:
- In/acting community of different types of microorganisms
- Microorganisms are collected in microcollonies
- Microcollonies are surrounded by a protective matrix
- Different environment inside a microcolony
- Microorganisms have a noticeable communication system
- Microorganisms in biofilms are resistant to antibiotics, antimicrobial agents and host reactions
Ways to fight:
1. regulation of nutrition
a. admixture of nutrients forming bases (arginine)
b. reduction of circulation in the periodontal groove due to anti-inflammatory drugs
c. inhibition of key microbial enzymes
Regulating Biofilm pH
- sweeteners
- antimicrobial agents
- fluoride compounds
- stimulation of base production
Regulation of redox potential. Oxidizing and reducing agents are used
Soft plaque
– a white or yellow soft and sticky formation that adheres less tightly to the surface of the tooth than plaque. Visually clearly visible, fixed on the plaque, the surface of the teeth, fillings and dentures, gums. It can cause chronic hygiivitis and bad breath.
Plaque is washed off with water, but complete removal requires brushing your teeth.
Composition: microorganisms, desquamated epithelial cells, leukocytes, salivary proteins, lipids, food particles. Does not have a permanent internal structure from dental plaque.
Green plaque is more often observed in children and young people. It is located in a thin layer on the labial surface of mainly the anterior group of teeth. The color of plaque is determined by chromogenic microorganisms.
Brown plaque - more common in smokers who abuse coffee and tea, in people who work on the manufacture of brass and bronze products, in children it may indicate helminthic parasitic infestation or chronic enterocolitis.
Food leftovers
– located at retention points, easily removed by moving the lips, tongue and rinsing. Sticky components (candies) remain on the teeth for 1 hour.
Mineralized dental deposits.
Supragingival Z. stone
– located above the crest of the alve process, visually clearly visible, usually gray or yellow in color. Solid consistency. Most often it forms on teeth located opposite the ducts of the salivary glands. The type of stone is salivary (mineral components come from saliva).
The calcification time of dental plaque is 12 days. The formation of the ZK continues until it reaches the maximum size for a given individual.
Composition: 70 – 90% non-organic component, 10 – 30% organic component.
Inorganic component – Ca phosphate, Ca carbonate, magnesium phosphate. Total Ca - 39%, P - 19%, magnesium - 0.8%, carbonate - 1.9%, sodium, zinc, gold, iron, chromium.
Organic component - protein polysaccharide complex, desquamated epitheum, micro, leukocytes, carbohydrates (galactose, glycol, monosaccharide, glucuronic acid, predominantly gram + fibrous microorganisms.
Subgingival calculus
– located under the marginal gum and in periodontal pockets. Visible upon visual inspection, detected upon probing, has a hard consistency, dark brown or green-black color, tightly attached to the surface of the tooth. The type of stone is whey (mineral components come from gingival fluid). The composition is greater than Ca and P. There are no salivary proteins, gram+ and - microorganisms.
The intensity of deposition is affected by:
- Teeth position
- Condition of teeth and bite
- Salivation intensity
- Condition of periodontal tissues
- PR hygiene
- Nutritional nature
- General condition of the body
- Age
Due to its dense consistency, tartar exerts mechanical pressure, creates conditions for microtrauma of the gum epithelium, marginal periodontal fibers, and has a chemical effect due to the presence of toxic elements.
Elimination methods:
Individual oral hygiene
Types of dental plaque
- Dental plaque is a soft deposit that gradually accumulates on teeth, fillings, and dentures. It is formed from food residues and waste products of bacteria. This deposit is firmly fixed on the teeth and can only be removed by physical methods;
- soft clusters resemble a thick mass of white-yellow color. Also formed by bacteria, their waste products, saliva and food debris;
- leftover food.
Mineralized deposits. These include tartar. It can be supragingival and subgingival. It has a dense structure and dark color. There are several factors that contribute to the formation of dental plaque:
- content in the diet of too soft food;
- disruption of metabolic processes in the body;
- preference to chew on only one side;
- malocclusion.
Tartar is formed, as a rule, in places where there is bad impact during brushing and self-cleaning does not occur.
Why do deposits form?
There are a huge number of microorganisms in the oral cavity of every person. They are adsorbed on the surface of the teeth, which is covered with a thin film having a porous structure. Leftover food is a breeding ground for these bacteria and contributes to their active reproduction. The layer of bacteria rapidly increases and becomes denser due to their waste products. More than half of the volume of dental plaque is bacteria.
If fresh dental plaque contains aerobic microorganisms that can neutralize acids coming from food, then mature deposits are dominated by anaerobes that do not perform this function. As a result, organic acids have a destructive effect on the enamel, causing caries. Soft deposits come into contact with saliva, which contains calcium salts in greater or lesser quantities. Mineralization leads to the formation of tartar.
The main reason for the formation of plaque is untimely removal of food debris, improper or irregular dental care. The predominance of carbohydrates in food and insufficient chewing activity are factors in the formation of soft deposits. Some diseases of the digestive system, individual characteristics of the composition of saliva, also provoke the formation of plaque in large quantities.
Closely spaced teeth, improperly made dentures, and braces can become an obstacle to thorough teeth cleaning. Such patients need to pay special attention to oral care.
Causes of deposits on teeth
When dental plaque forms, the reasons for this phenomenon can be identified as follows:
- Using toothpastes that do not meet all requirements.
- Brushing your teeth with a soft brush, which does not cope 100% with its task.
- Low content of vegetables, fruits and other solid foods in the diet.
- The diet is dominated by thermally processed food, which easily gets clogged between the teeth.
The most important reason for the appearance of deposits on teeth is poor oral hygiene or incorrect teeth cleaning technique. It is important to know that the teeth brushing procedure should last from 3 to 5 minutes, only then can you effectively get rid of all deposits.
Diagnosis of dental deposits
Detecting plaque on teeth is a fairly simple matter. Even if you run your tongue over their surface, you can feel it if there is a coating. The surface of the teeth does not seem so smooth. You can see it in the mirror; such deposits are best visible on the lower jaw from the inside.
Smokers can see the plaque without any problems, since it most often has a brownish color. At the pharmacy you can buy special pastes or tablets that color the plaque a different color, but the most effective way is to visit a dentist, who will determine how much your oral hygiene can be assessed.
Are there any disadvantages to ultrasonic tartar removal?
There are no downsides to the technology of removing tartar using ultrasound - it is the most modern and effective method of professional oral hygiene. However, before you go to the dentist’s office to remove tartar with ultrasound, you should find out the level of competence of the doctor, as well as the level of equipment of the clinic.
Why is it important? The fact is that if the removal of tartar and plaque from teeth is carried out by an inexperienced or illiterate specialist, or using outdated equipment, there is a high risk of damage to tooth enamel and poor quality of cleaning them from deposits.
Mechanical removal of deposits
Removal of dental plaque in this way is carried out manually or using special equipment. You can combine different cleaning methods to achieve the perfect result. At the end of the procedure, the dentist uses brushes and special pastes to polish the enamel, and the patient leaves the office with a snow-white smile.
- The manual method is carried out using special curettes. It is often combined with other methods. Personal manual cleaning is used only when the patient is contraindicated to use the devices. This happens in the presence of epilepsy, diabetes and some other pathologies.
- Ultrasound removal of dental plaque. This is an effective method of removal using a modern device. The method allows you to remove even large stones without damaging tooth enamel.
Chemical removal of tartar
If mechanical methods of removing deposits do not give the desired result or the case is particularly complex, then you will have to resort to the help of chemistry. If there is greater mobility of teeth or deposits are located in large clusters, then a gel is applied, which contains: alkalis, acids, iodine. It is capable of destroying plaque. The composition is applied for just one minute, and then removed, and the mouth is rinsed with water. If this method of combating dental plaque is used, the dentist must carefully protect the gums from the effects of the gel. Based on this, it can be argued that the root zone of the tooth remains poorly cleaned, so the method is considered insufficiently effective.
Who is contraindicated for dental cleaning?
Manual removal of tartar or soft plaque has practically no contraindications, which cannot be said about the use of devices. Such removal of deposits is contraindicated in the following conditions and pathologies:
- for heart diseases;
- if there are implants in the oral cavity;
- bronchial asthma and bronchitis;
- presence of hepatitis and tuberculosis;
- diabetes;
- if there is increased sensitivity, which can provoke a gag reflex;
- during pregnancy and while breastfeeding, it is better to refrain from such procedures;
- Such methods are also contraindicated for children and adolescents.
When visiting a dentist, you must inform him about the presence of chronic pathologies or existing acute diseases.
Is it possible to remove tartar at home?
On the Internet you can find countless recipes that claim to help remove tartar. Most of these recipes involve the use of caustic substances that must be applied to the surface of the teeth and, under the influence of these substances, the tartar should dissolve.
But we do not advise you to conduct such experiments on your health. Using caustic solutions will not help you remove tartar, but it will weaken and destroy tooth enamel and can lead to burns of the soft tissues of the mouth and other unpleasant consequences. In addition, no folk remedies will relieve you of subgingival tartar.
You need to remember that tartar removal should be carried out in a dental clinic, by a competent hygienist who uses safe materials and modern tools in his work! There is no need to be afraid of this procedure - it is painless, and in addition, before removing tartar, you can always apply local anesthesia, which completely removes all possible unpleasant sensations.
Getting rid of stones on teeth using improvised means
If there is tartar, how to get rid of it at home? We invite you to study some folk recipes:
- Use toothpastes with abrasive particles and a hard brush for cleaning, then you can get rid of soft plaque and even remove small stones.
- Prepare a decoction of 40 grams of walnut bark or shell and a glass of boiling water. You need to dip your brush in it and brush your teeth, adding a little toothpaste.
Removing dental plaque using folk remedies is a long process; you won’t be able to get rid of tartar in one use, so you will have to be patient and use the product regularly. If folk remedies do not help cope with plaque on the teeth, then you will have to visit a specialist who will quickly and safely return you have a beautiful smile and healthy teeth.
Choosing a method
Deposits on teeth can only be removed in a dental clinic using modern techniques, such as ultrasound, powder jet, instrumental, etc.
Ultrasound method
Ultrasonic cleaning uses a so-called scaler, the tip of which creates oscillatory movements with a frequency of 25-30 thousand Hz. Thanks to this, all deposits, both hard and soft, are removed.
Air-Flow method
With the Airflow powder blasting technique, soft deposits disappear instantly. The essence of this technique is to supply a strong aerosol jet through a special thin tube. It consists of air, water and a cleaning powder that knocks down all deposits from the most remote corners and gum pockets, up to 10mm deep.
Dry cleaning
Chemical treatment of deposits is based on the use of a special composition that easily softens deposits and allows them to be removed from teeth without difficulty. The procedure has many disadvantages (for example, the likelihood of damaging enamel or soft tissue, an unpleasant taste in the mouth, the inability to cope with hard deposits), which is why it is used less and less in practice.
Mechanical cleaning
The instrumental method - curettage, is used in cases of stone deposits in the gum pockets and under the gums, when other methods are ineffective. In this case, not only deposits are removed, but also pathologically altered gum tissue.
Laser Application
Laser technology in the treatment of dental plaque has proven itself to be effective and safe. In this case, the deposit is removed layer by layer, a painless method. The disadvantage is the high price, but the treatment is suitable even if children need help.
How to prevent the formation of dental plaque
If everything is so bad with personal hygiene that tartar has formed, how to get rid of it at home or with the help of a dentist is clear, but maybe it’s easier to prevent its formation? To do this, you don’t have to do anything complicated, you just need to follow the following recommendations:
- Regularly, morning and evening, thoroughly brush your teeth; the procedure should not last less than 3 minutes. Movements should be sweeping and circular.
- Use special pastes that remove plaque well.
- Reduce the amount of sweets and starchy foods in your diet; this environment is favorable for the accelerated proliferation of bacteria.
- Do not overuse strong tea or coffee, they can stain tooth enamel.
- Include fresh vegetables and fruits in your menu so that the oral cavity self-cleanses from plaque.
- Use dental floss to remove food debris between teeth.
- Rinse your mouth after eating.
- Even if nothing hurts, you need to make it a rule to visit the dentist every six months.
Modern hygiene products not only give freshness to your breath, but also help restore whiteness to your teeth, get rid of plaque and prevent the formation of tartar. The most important thing is to use them regularly, do not forget about personal hygiene, then no plaque is scary, it simply will not have a chance to appear. If you have questions about proper oral care, then you should visit a dentist, he will explain everything and help you choose teeth cleaning products, and if necessary, he will find ways to remove dental plaque.
Comprehensive teeth cleaning: service from our dentistry in Moscow “Aesthetica”
To ensure high-quality removal of tartar, we offer our patients a comprehensive teeth cleaning service, which includes:
- Ultrasonic cleaning;
- Air Flow cleaning;
- Grinding and polishing of enamel;
- Fluoridation.
An integrated approach to teeth cleaning guarantees a high quality procedure and is an excellent prevention of caries and gum inflammation. After the cleaning procedure, our hygienists will definitely give you recommendations on proper oral hygiene to help keep your teeth beautiful and healthy.
In our clinic, modern equipment is used to carry out comprehensive teeth cleaning, and all conditions have been created for comfortable treatment and procedures. We are proud that we can offer you the best dental technologies, high-quality materials from world-famous manufacturers and, of course, our professionalism, knowledge and experience.
Dental clinic “Aesthetica” - with us your teeth will be healthy and your smile will be dazzling! Come to us: we have opened two branches for you in Moscow - in Barvikha and in Podsosensky Lane!